Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Rangkuman GI
Caricato da
Boby FelixTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Rangkuman GI
Caricato da
Boby FelixCopyright:
Formati disponibili
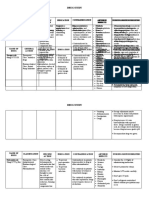
Manifestasi Penyakit Sistemik pada Rongga Mulut
Harrison’s GEH chapter 2
Atresia Esofagus
Epidemiologi Kelainan kongenital esophagus paling banyak,
prevalensi 1,7 per 10000 kelahiran, >90% TEF
Etiologi Defek pemisahan mesenkima antara esofaus dan
trachea, bukan kelainan genetik
Patogenesis & Patofisiologi The tracheoesophageal septum deviates too far
dorsally, causing the esophagus to end as a closed
tube.
Manifestasi klinis VACTERL (Vertebral anomalies, Anal atresia, Cardiac
anomalies, TEF, Renal anomalies, Limb anomalies)
Diagnosis Anamnesis Mengalami polyhydramnios
Pemeriksaan Mengalami respiratory distress, tachypnea, coughing,
Fisik choking, drooling, mucous and saliva bubbling from
nose and mouth
Pemeriksaan Gagalnya pemasangan pipa nasogastric atau
Penunjang orogastrik
CT scan diperoleh gambaran coiled feeding tube in
esophageal pouch dan/atau air-distended stomach
Tatalaksana Farmakologi Pemberian antibiotic untuk mencegah pneumonia
Non farmakologi Surgical ligation of the TEF and primary end-to-end
anastomosis of the esophagus via right-sided
thoracotomy
Pencegahan & Prognosis The surgically reconstructed esophagus is not normal
and is prone to poor motility, GER, anastomotic
stricture, recurrent fistula, and leakage. The trachea
also is malformed; tracheomalacia and wheezing are
common.
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (Bochdalek)
Epidemiologi Insidensi antara 1/2000 dan 1/5000; 90% pada kasus
hernia masa newborn; female = 2x male; Defek pada
sebelah kiri 85% bilateral <5%; sporadic
Etiologi Largely unknown, but associated malformation.
Patogenesis & Patofisiologi Defek diafragma posterolateral mengakibatkan
viscera abdomen memasuki rongga toraks. The orifice
in diaphragm is caused by delayed or disturbed
separation of thoracic and abdominal compartments
of the body by closure of embryonic pleuroperitoneal
canals effected by growth of the post-hepatic
mesenchymal plate and of the pleuroperitoneal folds.
Manifestasi klinis Hipoplasia paru, mediastinal shift, respiratory distress
Diagnosis Anamnesis Mengalami polyhydramnios
Pemeriksaan Tachypnea, cyanosis, scaphoid abdomen, peningkatan
Fisik diameter toraks
Pemeriksaan Findings on ultrasonography may include polyhy-
dramnios, chest mass, mediastinal shift, gastric bubble or
Penunjang
a liver in the thoracic cavity, and fetal hydrops
Tatalaksana Farmakologi
Non farmakologi Conventional mechanical ventilation, HFOV, and ECMO
are the 3 main strategies to support respiratory failure in
the newborn with CDH, prolonged mask ventilation must
be avoided.
The ideal time to repair the diaphragmatic defect is under
debate
Pencegahan & Prognosis Penderita yang survive mengalami gangguan
pernapasan, GERD, delayed growth, defek
neurokognitif
Hiatal Hernia (Sliding and Paraesophageal Hernia)
Epidemiologi Insidensi bertambah seiring bertambahnya usia
Etiologi Hiatal hernia terjadi adanya peningkatan tekanan
intra abdomen seperti obesitas, kehamilan
Patogenesis & Patofisiologi Herniation of the stomach through the esophageal
hiatus can occur as a common sliding hernia (type 1),
in which the gastroesophageal junc- tion slides into
the thorax, or it can be paraesophageal (type 2), in
which a portion of the stomach (usually the fundus) is
insinuated next to the esophagus inside the
gastroesophageal junction in the hiatus
Manifestasi klinis Sliding: GERD, acid reflux, regurgitation, epigastric
pain, dysphagia, odynophagia, nausea, bloating,
belching
Paraesophageal: gastric volvulus, regurgitation,
heartburn, dysphagia, chest pain, pulmonary problem,
nausea, hematemesis, iron-deficiency anemia
Diagnosis Anamnesis Fullness after eating and upper abdominal pain
Pemeriksaan
Fisik
Pemeriksaan Classic 24-hour pH test, impedance test, Bravo
Penunjang technique
CT: air-fluidd behind the heart
Tatalaksana Farmakologi Sliding: PPI
Paraesophageal: H2 blocker + PPI
Non farmakologi Surgical, laparoscopy
Pencegahan & Prognosis
Pyloric Stenosis
Epidemiologi 20% male and 10% female dengan ibu yang
mengalami pyloric stenosis
Etiologi Unknown; adanya korelasi penggunaan eritromisin
pada kehamilan usia 2 minggu pertama; kemungkinan
defisiensi NO sintetase
Patogenesis & Patofisiologi
Manifestasi klinis Anak: vomiting, dehidrasi, penurunan berat badan,
asidosis metabolik
Dewasa: nausea, vomiting, satiety, espigastric pain
after eating, lose weight
Diagnosis Anamnesis
Pemeriksaan Large, dilated stomach
Fisik Anak: classing ‘olive’ might be felt in pyloric area,
strong peristaltic movements observed on inspection
Pemeriksaan Barium: narrowed pylorus
Penunjang USG: classic-e-mm sonolucent “doughnout”
Tatalaksana Farmakologi Anticholinergic therapy + very soft food
Non farmakologi IV fluid and electrolite resuscitation, followed by
Ramstedt pyloromyotomy
Pencegahan & Prognosis Prognosis excellent
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Internal Medicine Qs For GP Saudi PrometricDocumento140 pagineInternal Medicine Qs For GP Saudi PrometricM A100% (4)
- Test Bank For Medical Terminology Simplified A Programmed Learning Approach by Body System 6th Edition Barbara A Gylys Regina M Masters DownloadDocumento15 pagineTest Bank For Medical Terminology Simplified A Programmed Learning Approach by Body System 6th Edition Barbara A Gylys Regina M Masters Downloadchristinemays21121993bgw100% (22)
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation in Paediatrics: Revathi Rajagopal, Jecko Thachil, Paul MonagleDocumento8 pagineDisseminated Intravascular Coagulation in Paediatrics: Revathi Rajagopal, Jecko Thachil, Paul MonagleRizky LumalessilNessuna valutazione finora
- By: Francis James Rigodon, RNDocumento21 pagineBy: Francis James Rigodon, RNKathreen TamayoNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQs IN MEDICINEDocumento150 pagineMCQs IN MEDICINERITESH SINGH100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Hospital Pharmacy Notes Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Documento25 pagineChapter 3 Hospital Pharmacy Notes Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Shamant TNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQS ANS 03 Sol PDFDocumento4 pagineMCQS ANS 03 Sol PDFSamir Rekha Mukund Joshi100% (1)
- Neonatal Sepsis: Prof DR Saima BatoolDocumento31 pagineNeonatal Sepsis: Prof DR Saima BatoolSAIMA BATOOLNessuna valutazione finora
- Moore Et Al-2018-Clinical Liver DiseaseDocumento4 pagineMoore Et Al-2018-Clinical Liver DiseaseCarlos Francisco Enciso MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenal CrisisDocumento4 pagineAdrenal CrisisRichie Marie BajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Charles Maytum, Rochester, MinnDocumento6 pagineCharles Maytum, Rochester, Minngopal08Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 5Documento28 pagineQuiz 5YNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathognomonic Imaging Signs in Abdominal RadiologyDocumento11 paginePathognomonic Imaging Signs in Abdominal RadiologyifzarNessuna valutazione finora
- A Novel Technique For Pudendal Nerve BlockDocumento4 pagineA Novel Technique For Pudendal Nerve Blockmohs2007100% (1)
- N. Family Planning - With LoDocumento123 pagineN. Family Planning - With LoRadha ChiombonNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory System QuestionsDocumento8 pagineRespiratory System Questionschristine_8995Nessuna valutazione finora
- GENTAMICINDocumento3 pagineGENTAMICINjacquejackieNessuna valutazione finora
- From Rare Diseases, Genetic Disorders To Orphan DrugsDocumento192 pagineFrom Rare Diseases, Genetic Disorders To Orphan DrugsShing Ming TangNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiomyopathy and Myocarditis HarrisonsDocumento62 pagineCardiomyopathy and Myocarditis HarrisonsGrace CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug of ChoiceDocumento2 pagineDrug of ChoiceRia Tiglao Fortugaliza100% (1)
- Lung ExaminationDocumento14 pagineLung Examinationსალომე მუმლაძე “Slay” TMANessuna valutazione finora
- ICD For OncologyDocumento337 pagineICD For OncologytphivuongNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study: Classification Contraindication Classification ContraindicationDocumento6 pagineDrug Study: Classification Contraindication Classification ContraindicationMel Izhra N. MargateNessuna valutazione finora
- Alfuzosin Hydrochloride PDFDocumento1 paginaAlfuzosin Hydrochloride PDFbachvbNessuna valutazione finora
- Macrocytosis - Macrocytic Anemia - UpToDateDocumento36 pagineMacrocytosis - Macrocytic Anemia - UpToDateMarvin VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Manipal Manual of Surgery 4th Edition PDFDocumento1.196 pagineManipal Manual of Surgery 4th Edition PDFYuga Dhuri63% (8)
- Special Pathology Viva Questions by AMS 46Documento32 pagineSpecial Pathology Viva Questions by AMS 46Mohan Dass100% (1)
- A Sinister Cause For Recurrent Syncope: Metastatic Parapharyngeal Space TumorDocumento4 pagineA Sinister Cause For Recurrent Syncope: Metastatic Parapharyngeal Space TumorasclepiuspdfsNessuna valutazione finora
- Mymaxicare Revised Brochure 2023Documento15 pagineMymaxicare Revised Brochure 2023Engilbert MaqueraNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Abdul Kalam - President of India Speech at Medical ConferenceDocumento7 pagineDR Abdul Kalam - President of India Speech at Medical ConferenceSibia SukhbindarNessuna valutazione finora