Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
2019 Wmd-Foldout en
Caricato da
panDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
2019 Wmd-Foldout en
Caricato da
panCopyright:
Formati disponibili
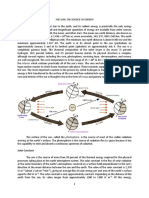
W O R L D M E T E O R O L O G I C A L D AY
THE SUN
The Sun delivers the energy that powers all life on Earth. animals, humans – needs liquid water to survive. The Sun
It drives the weather, ocean currents and the hydrological powers the hydrological cycle, constantly evaporating
cycle. It shapes our mood and our daily activities. It is water into the atmosphere, which then falls back to Earth.
the inspiration for music, photography and art.
Over the span of 11 years, the Sun’s activity waxes and
The Sun is a star, just like the ones we can see in the wanes as magnetic field lines that are wound and tangled
night sky, but much, much closer. Located nearly inside the Sun periodically break through to the surface,
150 million kilometres from the Earth, it is the heart of producing sunspots that travel across the face of the
our solar system and keeps our planet warm enough Sun. The heightened magnetic activity associated with
for living things to thrive. For over 4.5 billion years, this sunspots can lead to solar flares, coronal mass ejections,
hot ball of glowing plasma has been the driving force and other far-reaching electromagnetic phenomena. The
behind weather, climate and life on Earth. Aurora Borealis (Northern Lights) and Aurora Australis
(Southern Lights) are visible manifestations of space
weather.
The Sun’s diameter is about 1.39 million kilometres
(864 000 miles), or 109 times that of the Earth. National Meteorological and Hydrological Services
At its core, its temperature is about 15 million °C provide expertise and services both to harness the power
(27 million °F). The surface of the Sun – the part we of the Sun and to protect us from it. These include 24/7
can see – is about 5 500 °C (10 000 °F). weather observations and forecasts, as well as monitoring
of atmospheric greenhouse gases, ultraviolet radiation,
aerosols and ozone and their consequent effects on
Without the steady light and heat of the Sun, life on Earth people, climate, air and water quality and marine and
would cease to exist. The Sun’s heat makes liquid water on terrestrial life.
our planet possible. And all life – bacteria, plants, insects,
THE SUN’S IMPACT ON THE EARTH
Throughout Earth’s history, the amount of energy small fraction is reflected back into space. In total,
received from the Sun has varied, with major conse- approximately 70% of incoming radiation is absorbed
quences for the climate and all living things. Since by either Earth’s atmosphere or its surface, while
the end of the last Ice Age nearly 12 000 years ago, around 30% is reflected back into space and does not
the climate has been relatively stable, although it has heat the planet.
regularly been affected by small changes in the amount
of solar radiation reaching the Earth’s surface. These Without this natural greenhouse effect, the Earth’s
minor variations are often caused by long-term cycles average surface temperature would be an inhospitable
affecting the Earth’s orbit around the Sun, changes -18 °C (0 °F) instead of the 14 °C (59 °F) we experience
in cloud cover and other fluctuations here on Earth. today. This natural greenhouse effect is enhanced by
Even relatively small climate fluctuations have had ever increasing greenhouse gas concentrations in the
drastic regional effects on human civilizations and atmosphere due to emissions by human activities
caused empires like the Mayans or the Old Kingdom such as the burning of fossil fuels.
of Egypt to rise and fall.
The amount of sunlight received on Earth’s surface
depends on the output of the Sun, its overhead angle
and the cyclical variations of Earth’s orbit around the
Sun, as well as how much sunlight is absorbed or
reflected back into space by the atmosphere.
Solar radiation that is not absorbed or reflected by the
atmosphere (for example by clouds) reaches Earth’s
surface. Earth absorbs most of this energy, and a
THE SUN AND
CLIMATE CHANGE
Climate fluctuations induced by the Earth’s orbit around the Sun
are on a time scale of millennia, whereas climate change linked to
human activities has occurred since the start of the industrial era. The
unprecedented speed at which climate change is presently occurring
makes it hard for ecosystems as well as humankind to adapt.
The burning of fossil fuels and other industrial and agricultural
activities release carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into
the atmosphere. These gases trap the Sun’s heat and disrupt the
Earth’s energy balance.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations reached 405.5 parts per million
(ppm) in 2017 and continue to rise. Since 1990, there has been a 41%
increase in total radiative forcing – the warming effect on the climate
– by long-lived greenhouse gases. CO2 accounts for about 82% of the
increase in radiative forcing over the past decade.
Since the start of the industrial era in the second part of the 19th
century, average global temperatures have risen by about 1 °C. As a
result, ice is melting at the poles, oceans are warming and sea levels
are rising, which in turn all fuel more extreme weather.
Satellite measurements taken over the past 30 years show that the
Sun’s energy output has not increased and that the recent warming
observed on Earth cannot be attributed to changes in Sun activity.
THE SUN, OUR WELL-BEING AND HEALTH
Sunlight plays a pivotal role in human health and well- information and alerts on UV levels and work with health
being. It triggers an increased production of serotonin, authorities to disseminate safety tips to the public.
which influences how we feel. Limited exposure to
sunlight, in addition to increasing the risk of Vitamin D The stratospheric ozone layer protects humans from
deficiency, negatively impacts our mood. This is seen in dangerous ultraviolet and other solar radiation. Ozone
seasonal variations of psychiatric phenomena related to concentrations in the atmosphere vary naturally according
exposure to longer and shorter sunlight hours, especially to the season, latitude and presence of sunspots. However,
mood and anxiety symptoms, as well as suicide. in the mid-1980s, it was discovered that the ozone shield
was being depleted well beyond natural processes as a
result of chlorine and bromine atoms coming into contact
Overexposure to sunlight causes harmful effects to with ozone and destroying ozone molecules. This led to
the skin, eyes and immune system. Experts believe international action to phase out the production of the
that four out of five cases of skin cancer could be most damaging chemicals. Thanks to measures taken
prevented, as the damage caused by sunburn- under the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete
producing ultraviolet (UV) radiation is mostly the Ozone Layer, the destruction of the stratospheric
avoidable. ozone layer has been halted.
The UV Index is an international standard measurement
of the strength of ultraviolet radiation at a particular place
and time. Many national meteorological services provide
THE SUN AND
MEASURING SUNLIGHT
RENEWABLE ENERGY
Scientists use solar radiation measurements to study The sun provides us with a valuable tool for climate
climate variability and change and to forecast the change mitigation in the form of solar energy, which
weather. is becoming cheaper and more widely available and
has the potential to replace fossil fuels like coal or
Measuring sunlight, however, is not as easy as it may oil as a major source of electricity.
sound. Long-term measurements that are comparable
from place to place, from time to time, and from Energy can be harnessed directly from the sun, even in
instrument to instrument are essential. This requires cloudy weather. Solar energy is increasingly popular
a special effort to finely calibrate thousands of ground- for generating electricity and heating and desalinating
based instruments all around the world. water. Renewable energy, including solar energy,
has become the technology of choice, making up
almost two-thirds of global capacity additions to 2040
Radiation measurements are essential for decision- thanks to falling costs and supportive government
makers in the solar energy industry. To calculate how policies. This is transforming the global power mix,
much electricity a proposed solar energy installation with the share of renewables in generation rising
will produce, decision-makers need to know how from 25% today to over 40% by 2040, according to
much sunlight will be available on sunny days and the International Energy Agency.
cloudy days, or on short winter days versus long
summer days.
SOLAR POWER IS GENERATED
The Physikalisch-Meteorologisches Observatorium IN TWO MAIN WAYS:
Davos (PMOD) institute in Davos, Switzerland, has
been studying how to measure sunlight for over one Photovoltaics (PV), also called solar cells, are electronic
hundred years. Serving as the WMO World Radiation devices that convert sunlight directly into electricity.
Centre since 1971, it maintains the primary standard for These solar cells can be seen everywhere – on roofs
measuring the Sun’s irradiance, the World Radiometric and windows of houses and office buildings, battery
Reference. This ensures that these highly sensitive chargers and computers, new cars and airplanes,
instruments, known as pyrheliometers, are accurate solar farms – the list is endless. Today, PV is one of
and their data are comparable. the fastest-growing renewable energy technologies
and is ready to play a major role in the future global
Without this WMO-led international collaboration, electricity generation mix.
scientists would have a much weaker understanding
of the climate system, and the solar energy industry Concentrated solar power (CSP) uses mirrors to
would be less efficient. concentrate solar rays. These rays heat fluid, which
creates steam to drive a turbine and generate
electricity. CSP is used to generate electricity in
large-scale power plants.
Power generation from photovoltaics is strongly
dependent on the weather. Therefore, reliable
meteorological forecasts are indispensable for
balancing the power grid and will gain even more
importance as the renewable energy sector expands.
For this reason, weather forecasts optimized for
energy applications are required.
For more information, please contact:
The requirements from the energy sector pose
World Meteorological Organization a new challenge and opportunities for national
7 bis, avenue de la Paix meteorological services. The Global Framework for
Climate Services (GFCS) is leading international efforts
P.O. Box 2300 – CH 1211
to enhance the quality, quantity and application of
Geneva 2 – Switzerland
climate information and predictions in support of
Communications and Public Affairs Office decision-making by renewable energy producers.
Tel: +41 (0) 22 730 83 14
Email: cpa@wmo.int
public.wmo.int
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Global Climate SystemDocumento4 pagineGlobal Climate SystemAnne WabanNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Change: Group 6Documento31 pagineClimate Change: Group 6Owen VelascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Disadvantages of Using Coal To Produce ElectricityDocumento20 pagineDisadvantages of Using Coal To Produce Electricitykofi99Nessuna valutazione finora
- IB Geography SL NotesDocumento30 pagineIB Geography SL NotesFN6012021 RAVICHANDRAN GOKULNessuna valutazione finora
- 30-Second Meteorology: The 50 most significant events and phenomena, each explained in half a minuteDa Everand30-Second Meteorology: The 50 most significant events and phenomena, each explained in half a minuteNessuna valutazione finora
- (Routledge Perspectives On Development 7) Jennifer Elliott - An Introduction To Sustainable Development-Routledge (2012) PDFDocumento384 pagine(Routledge Perspectives On Development 7) Jennifer Elliott - An Introduction To Sustainable Development-Routledge (2012) PDFArjita SaxenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Participate in Environmentally Sustainable Work Practices BSBSUS201 - PowerpointDocumento57 pagineParticipate in Environmentally Sustainable Work Practices BSBSUS201 - PowerpointJuan Diego Pulgarín HenaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines For Climate Resilient Coastal Protection and Management in India PDFDocumento441 pagineGuidelines For Climate Resilient Coastal Protection and Management in India PDFTusar ArifNessuna valutazione finora
- Module For Climate Change Chapter 2 - Physical Processes On EarthDocumento23 pagineModule For Climate Change Chapter 2 - Physical Processes On EarthAngelo CabrerosNessuna valutazione finora
- Agro-Meteorology For BSC Agriculture StudentsDocumento54 pagineAgro-Meteorology For BSC Agriculture StudentsMadan ThapaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Climate ChangeDocumento45 pagineThe Climate ChangeEnitsuj Eam EugarbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Core 3 Environmental SustainabilityDocumento15 pagineCore 3 Environmental Sustainabilitydell yangNessuna valutazione finora
- CONSTELLATIONSDocumento5 pagineCONSTELLATIONSJo-Ann Oliva - DyNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Cooker and Water HeaterDocumento59 pagineSolar Cooker and Water HeaterDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE100% (5)
- Energy Engineering (15ME71) Module-3: Solar EnergyDocumento4 pagineEnergy Engineering (15ME71) Module-3: Solar EnergyChirayu JanamattiNessuna valutazione finora
- Abiotic FactorsDocumento37 pagineAbiotic FactorsTudor CiolanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pollution and Its Negative EffectsDocumento4 paginePollution and Its Negative EffectsERIKA JOHANA MAYA CORTESNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Radiation: Sunlight and More: Non Conventional Sources OF EnergyDocumento15 pagineSolar Radiation: Sunlight and More: Non Conventional Sources OF EnergyAnutosh BhaskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-III Solar EnergyDocumento27 pagineUnit-III Solar Energyabhishekbachchan626Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-2-Solar Thermal EnergyDocumento15 pagineUnit-2-Solar Thermal EnergyDr. Navneet Kumar PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Change, Environmental Awareness, and Alternative Energy ResourcesDocumento11 pagineClimate Change, Environmental Awareness, and Alternative Energy ResourcesMichael TimbolNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Change MANUELDocumento3 pagineClimate Change MANUELYOSIMAR DEL C. GUTIERREZ NUÑEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Seven Theories of Climate ChangeDocumento16 pagineSeven Theories of Climate ChangeMd. Abrar Mahir, 170021028Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - Physical Processes On EarthDocumento65 pagineChapter 2 - Physical Processes On EarthClydeNessuna valutazione finora
- Geo 1 Biophysical Interaction PDFDocumento6 pagineGeo 1 Biophysical Interaction PDFquinlanNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Properties: Scattering:When Light Passes Through Our Atmosphere, Photons InteractDocumento7 pagineOptical Properties: Scattering:When Light Passes Through Our Atmosphere, Photons InteractmilabelmilabelNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 2 - Natural Causes of Climate ChangeDocumento8 pagineUNIT 2 - Natural Causes of Climate ChangeRegved PandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Enhancing The Greenhouse Effect: Naturally Occurring Greenhouse Gases, AsDocumento2 pagineEnhancing The Greenhouse Effect: Naturally Occurring Greenhouse Gases, AsAnsari SufiyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Week #3: Causes of Climate ChangeDocumento67 pagineWeek #3: Causes of Climate ChangeHaha GeNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 10Documento31 pagineCH 10scribd.b012bdNessuna valutazione finora
- Rhoko Quilban 9 - St. AlbertDocumento4 pagineRhoko Quilban 9 - St. AlbertJohn Eridog Xcx-World MatelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Factors in Formation of Global ClimateDocumento6 pagineFactors in Formation of Global Climateshahid rasoolNessuna valutazione finora
- AtmosRadCh1 3 PDFDocumento73 pagineAtmosRadCh1 3 PDFmohsinusufNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2: Micro EnvironmentDocumento8 pagineUnit 2: Micro EnvironmentHasini KadaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar and Solar Radiation - Air Temperature-Atmospheric PressureDocumento21 pagineSolar and Solar Radiation - Air Temperature-Atmospheric PressureMarjorie TacordaNessuna valutazione finora
- Explosion of Sun: Alexander Bolonkin, Joseph FriedlanderDocumento14 pagineExplosion of Sun: Alexander Bolonkin, Joseph FriedlanderRamón Elías Cerrada MontoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Project About Global WarmingDocumento8 pagineA Project About Global Warmingraju1271990100% (2)
- Climate Change Scientific Basis and Impacts Lecture Part 1Documento21 pagineClimate Change Scientific Basis and Impacts Lecture Part 1Muhammad AsifNessuna valutazione finora
- The Missing SunspotsDocumento2 pagineThe Missing SunspotsRedzaNessuna valutazione finora
- GeafewfwefDocumento2 pagineGeafewfwefMega ShowsNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture #3 - Causes of Climate ChangeDocumento67 pagineLecture #3 - Causes of Climate ChangeEarlnieNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Balance and The Greenhouse EffectDocumento6 pagineEnergy Balance and The Greenhouse Effectsteph wallNessuna valutazione finora
- Glory Understanding Earth's Energy BudgetDocumento20 pagineGlory Understanding Earth's Energy BudgetBob AndrepontNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Sources: Figure 1: Current Energy Mix. The Total Energy Consumption Is Roughly 15 TW. SourceDocumento39 pagineEnergy Sources: Figure 1: Current Energy Mix. The Total Energy Consumption Is Roughly 15 TW. SourceAli KarakyNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiation SolarDocumento5 pagineRadiation SolarMuluken Temesgen100% (1)
- Environmental Awareness and Climate Change 1Documento10 pagineEnvironmental Awareness and Climate Change 1graceconogana1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 13 Climate Change ReportDocumento17 pagine13 Climate Change ReportNorwellah MacmodNessuna valutazione finora
- Agaton Cep324 Reactionpaper#1Documento1 paginaAgaton Cep324 Reactionpaper#1Marco AgatobNessuna valutazione finora
- ME 301 Notes2Documento51 pagineME 301 Notes2Lloyd MunthaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Weather and HydrologyDocumento20 pagineWeather and HydrologyIamKish Tipono ValenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Change ReviewerDocumento11 pagineClimate Change ReviewerFlorie Mae ViernesNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Change ReviewerDocumento5 pagineClimate Change ReviewerFlorie Mae ViernesNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Envio SummerDocumento8 pagineMidterm Envio SummerIlhan KlisuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Energy - NCS, Mumbai UniversityDocumento28 pagineSolar Energy - NCS, Mumbai UniversityVaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Warmin1Documento14 pagineGlobal Warmin1Kankan ChakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate ChangeDocumento6 pagineClimate ChangeEdgardo Ylanan UrsalNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2Documento42 pagineModule 2Renuka KutteNessuna valutazione finora
- Environment ManagementDocumento11 pagineEnvironment ManagementbillatonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Note 1 B - 2B - Radiation and Temperature-1Documento23 pagineClass Note 1 B - 2B - Radiation and Temperature-1Mangal MurmuNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Note 1 B - 2B - Radiation and Temperature-1Documento23 pagineClass Note 1 B - 2B - Radiation and Temperature-1Mangal MurmuNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Climate SystemDocumento3 pagineGlobal Climate SystemAnne WabanNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Change and Energy CrisisDocumento11 pagineClimate Change and Energy CrisisAsher GeronimoNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 7.1. Natural Processes of Variations in Climate Dot Point 1Documento16 pagineModule 7.1. Natural Processes of Variations in Climate Dot Point 1Kaira JogNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Geography 12: Unit II - The Planet EarthDocumento40 pagineGlobal Geography 12: Unit II - The Planet Earthapi-240746852Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ianos - A Hurricane in The Mediterranean: Corresponding Author: Dr. Kostas Lagouvardos, Lagouvar@Documento31 pagineIanos - A Hurricane in The Mediterranean: Corresponding Author: Dr. Kostas Lagouvardos, Lagouvar@panNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 WMD Poster Crops enDocumento1 pagina2019 WMD Poster Crops enpanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cap1430 Uk Atm Vocabulary 5jan2017Documento60 pagineCap1430 Uk Atm Vocabulary 5jan2017panNessuna valutazione finora
- Meteoworld: Science Takes Centre-Stage at COP24Documento4 pagineMeteoworld: Science Takes Centre-Stage at COP24panNessuna valutazione finora
- WMO Gcos 195 en PDFDocumento373 pagineWMO Gcos 195 en PDFpanNessuna valutazione finora
- Wmobulletin 65-1 en PDFDocumento64 pagineWmobulletin 65-1 en PDFpanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bulletin 64-2 en PDFDocumento60 pagineBulletin 64-2 en PDFpanNessuna valutazione finora
- OMAE2008-57082: A New Wind and Wave Atlas of The Hellenic SeasDocumento9 pagineOMAE2008-57082: A New Wind and Wave Atlas of The Hellenic SeaspanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bulletin: (Un) Natural Disasters: Communicating Linkages Between Extreme Events and Climate ChangeDocumento60 pagineBulletin: (Un) Natural Disasters: Communicating Linkages Between Extreme Events and Climate ChangepanNessuna valutazione finora
- WMO66 (1) enDocumento68 pagineWMO66 (1) enpanNessuna valutazione finora
- WMObulletin 67-2 enDocumento80 pagineWMObulletin 67-2 enpanNessuna valutazione finora
- Newsletter: Relax With Theweather ClubDocumento16 pagineNewsletter: Relax With Theweather ClubpanNessuna valutazione finora
- Competencies For Meteorologists & Meteorological TechniciansDocumento47 pagineCompetencies For Meteorologists & Meteorological TechnicianspanNessuna valutazione finora
- Euroforecaster 2017 NewsletterDocumento46 pagineEuroforecaster 2017 NewsletterpanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hot Flat and Crowded by FriedmanDocumento5 pagineHot Flat and Crowded by FriedmanDheera KalotaNessuna valutazione finora
- GO Envi IssueDocumento1 paginaGO Envi IssueMohd Nazrul AkmalNessuna valutazione finora
- The Break Up of AnswersDocumento3 pagineThe Break Up of AnswersMuhammad MudassirNessuna valutazione finora
- 2012 M. Zinzi , S. Agnoli Cool. and green roofs. An energy and comfort comparison between passive cooling and mitigation urban heat island techniques for residential buildings in the Mediterranean region.pdfDocumento11 pagine2012 M. Zinzi , S. Agnoli Cool. and green roofs. An energy and comfort comparison between passive cooling and mitigation urban heat island techniques for residential buildings in the Mediterranean region.pdfHeidys YohanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate ChangeDocumento84 pagineClimate ChangeKyla Ellen CalelaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Global WarmingDocumento28 pagineGlobal WarmingRahul Murlidhar BhatiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 011Documento10 pagineChap 011Thao TrungNessuna valutazione finora
- BCA 1st Year Possible Environmental StudiesDocumento20 pagineBCA 1st Year Possible Environmental StudiesPabitra NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Bali Action Plan 2007 PDFDocumento4 pagineBali Action Plan 2007 PDFJustz LimNessuna valutazione finora
- An Introduction To Global Warming For Students in Grades 6-8Documento12 pagineAn Introduction To Global Warming For Students in Grades 6-8Dian Permata AdmNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.3 Listening Multiple ChoiceDocumento6 pagine5.3 Listening Multiple ChoiceNatasa MitricNessuna valutazione finora
- Marine Gas Hydrates: Their Economic and Environmental ImportanceDocumento2 pagineMarine Gas Hydrates: Their Economic and Environmental ImportanceBiswarup DuttaNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Toolkit A Resource Manual For Science and Action 1593663303 PDFDocumento180 pagineClimate Toolkit A Resource Manual For Science and Action 1593663303 PDFJhinsher TagleNessuna valutazione finora
- NUMBER For Each Answer. Write Your Answers in The Correspondent Numbered Boxes. (10 Points)Documento12 pagineNUMBER For Each Answer. Write Your Answers in The Correspondent Numbered Boxes. (10 Points)Nhật Bình0% (3)
- tlm4all@DCEB Guntur Social-EM-Paper-IDocumento70 paginetlm4all@DCEB Guntur Social-EM-Paper-ICherukupally KrishnaiahNessuna valutazione finora
- Visualising Density Chapter 1Documento28 pagineVisualising Density Chapter 1Liviu IancuNessuna valutazione finora
- Short ParagraphDocumento2 pagineShort ParagraphSuvro Avro75% (8)
- Environmental Change and Security Program Report 1Documento105 pagineEnvironmental Change and Security Program Report 1The Wilson CenterNessuna valutazione finora
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2011: GCE Geography (6GE01) Paper 1Documento15 pagineMark Scheme (Results) January 2011: GCE Geography (6GE01) Paper 1karuneshnNessuna valutazione finora
- A Summary of The Special Issue On Remote Sensing of Land Change Science With Google Earth Engine-2020Documento9 pagineA Summary of The Special Issue On Remote Sensing of Land Change Science With Google Earth Engine-2020Antonio Arroyo PazNessuna valutazione finora
- Article On Weather Index InsuranceDocumento3 pagineArticle On Weather Index InsuranceOmkar PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Air PollutionDocumento21 pagineAir PollutionstephanievogelNessuna valutazione finora
- Cultural Values and Indigenous Knowledge of Climate Change and Disaster Prediction in Rajasthan, IndiaDocumento7 pagineCultural Values and Indigenous Knowledge of Climate Change and Disaster Prediction in Rajasthan, IndiaPrasanna KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Politics, Money, Obliviousness, and The AnthropoceneDocumento4 paginePolitics, Money, Obliviousness, and The AnthropoceneArsalaan GhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Change and Water ResourcesDocumento42 pagineClimate Change and Water ResourcesMateo Gomez BajoNessuna valutazione finora
- Capitalism Good - A2 Cap K'sDocumento44 pagineCapitalism Good - A2 Cap K'sTj RiggsNessuna valutazione finora