Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
BIOL1364 Tutorial 4 Linkage Analysis 2018
Caricato da
Ibrahim AliDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
BIOL1364 Tutorial 4 Linkage Analysis 2018
Caricato da
Ibrahim AliCopyright:
Formati disponibili
BIOL1364- INTRODUCTORY GENETICS TUTORIAL NO-4
LINKAGE ANALYSIS
1. Why is genetic linkage not considered a modifying factor? Indicate two other phenomena
that you have learned that are also not considered modifying factors? (3 marks)
2. If the recombination percentage between two genes linked in the coupling phase is ‘r’. What
will be the recombination percentage if they were linked in the repulsion phase? (1 mark)
3. If linked genes violate Mendel's second principle, which gametes will be predominant if the
two genes (A and B) were linked in the repulsion phase? (2 marks)
4. Which genotypes will be predominant in a testcross involving two genes linked in the
coupling phase? (4 marks)
5. If chiasma frequency is ‘r’, what is the recombination frequency and the frequency of one
of the parental gametes? (4 marks)
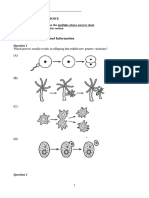
6. Look at the diagram below: Genes X and Y are found on chromosome-5 of okra.
X Y
x y
a. What is the product of a single crossover between X and Y? (1 mark)
b. What is the product of a double crossover between X and Y? (1 mark)
c. What is the major disadvantage of using a two-point linkage analysis? (3 marks)
d. Which linkage analysis addresses the deficiency of two-point linkage? (1 mark)
7. If a good character is linked to an undesirable character in a crop plant, what strategy do you
suggest for removing the bad character? (1 mark)
8. Two-point linkage analysis (testcross data)
Two genes control pod length and colour in Species Q. Gene A- codes for purple colour, aa
for green colour; B- codes for long pod and bb for short pod. A true breeding pure purple, long
pod variety was crossed with a true breeding green, short pod variety. When the F1 plants
were testcrossed with a true breeding green, short pod variety, clones with the following
phenotypes were obtained: AaBb = 100; Aabb = 21; aaBb =30; aabb = 84
a. What is the recombination %? (2 marks)
b. What is the genotype of the F1 parent? (1 mark)
c. What is the linkage relationship? (1 mark)
d. What is the distance between the two genes? (1 mark)
9. Two-point linkage analysis (F2 data)
GgHh x GgHh yields the following progenies:
G-H- = 165; G-hh =40; ggH- =47; gghh = 4
a. What is the recombination percentage between genes G and H? (8 marks)
b. What is the distance between genes G and H? (1 mark)
c. What is the linkage relationship between the genes? (1 mark)
d. Find the genotype of the original parents? (2 marks)
Three point linkage analysis
10. Genetic analysis has shown that the recessive genes an (Anther ear), br (brachytic) and f (fine
stripe) are all found on chromosome #1 of maize. When a plant that is heterozygous for each of
these markers is testcrossed with a homozygous recessive plant, the following results are
obtained:
Testcross Progeny Numbers:
wild type- 3 (+++)
fine- 48 (++f)
brachytic- 400 (+br+)
brachytic fine – 42 (+brf) Total Offsprings = 1000
anther -45 (an++)
anther fine -402 (an+f)
anther brachytic -56 (anbr+)
anther brachytic fine- 4 (anbrf)
a. Calculate recombination frequencies between each of these three pairs of genes. (14
marks)
b. Draw a genetic map for the location of these 3 genes on chromosome #1 of maize. Be sure
to show the map distances between each loci. (4 marks)
c. Calculate the interference. (4 marks)
we/WE
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsDa EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsNessuna valutazione finora
- Assig III Fall 17.fimDocumento3 pagineAssig III Fall 17.fimedomin00Nessuna valutazione finora
- Morphological Variation in a Population of the Snake, Tantilla gracilis Baird and GirardDa EverandMorphological Variation in a Population of the Snake, Tantilla gracilis Baird and GirardNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 03Documento9 pagineCH 03SpringjesJiesiNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 03Documento10 pagineCH 03Maiah Phylicia LatoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics Exam 3 - KeyDocumento6 pagineGenetics Exam 3 - KeyGestinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics Ch04 Test Bank PDFDocumento10 pagineGenetics Ch04 Test Bank PDFejanlindsay50% (2)
- Genetics ExamDocumento6 pagineGenetics ExamanewflorescaNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics HW 1Documento3 pagineGenetics HW 1edomin00Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology MCQDocumento5 pagineBiology MCQSungdeok MinNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Analysis An Integrated Approach 2nd Edition Sanders Test BankDocumento15 pagineGenetic Analysis An Integrated Approach 2nd Edition Sanders Test Bankjenniferedwardsmpnidwyjkb100% (49)
- Principles of Genetics Chapter 3 ProblemsDocumento9 paginePrinciples of Genetics Chapter 3 Problemskoolgirl212Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gene Mapping PracticeDocumento4 pagineGene Mapping PracticeBobbyWhite100% (1)
- Genetic Analysis An Integrated Approach 2nd Edition Sanders Test BankDocumento14 pagineGenetic Analysis An Integrated Approach 2nd Edition Sanders Test BankRichard Champney100% (32)
- Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11Th Edition Griffiths Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 pagineIntroduction To Genetic Analysis 11Th Edition Griffiths Test Bank Full Chapter PDFarthur.hendricks257100% (13)
- Revision Exer.1Documento4 pagineRevision Exer.1ravintheran kalimuthu0% (1)
- Test Bank For Principles of Genetics 6th Edition D Peter Snustad Michael J SimmonsDocumento15 pagineTest Bank For Principles of Genetics 6th Edition D Peter Snustad Michael J Simmonsshawncookcoqgardemf100% (28)
- Part A: Multiple Choice: Answer With The Best Choice. Make Sure That You Clearly Circle TheDocumento8 paginePart A: Multiple Choice: Answer With The Best Choice. Make Sure That You Clearly Circle TheQueng ElediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Inheritance & Variation-Neet Pyqs-6290457667-SampleDocumento95 paginePrinciples of Inheritance & Variation-Neet Pyqs-6290457667-Sampleseetharaman8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dihybrid Cross Problems 2013Documento1 paginaDihybrid Cross Problems 2013kirancanada1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic ProblemsDocumento20 pagineGenetic Problemsatik0% (2)
- Homework 3 AnswersDocumento5 pagineHomework 3 AnswersButterlesstoastNessuna valutazione finora
- Dihybrid Cross Problems 2015Documento1 paginaDihybrid Cross Problems 2015api-233757247Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lingkages ProblemsDocumento7 pagineLingkages ProblemsAnthony HugillNessuna valutazione finora
- Levels of QuestionsDocumento20 pagineLevels of QuestionsprasannamentelNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions and Problems 3Documento8 pagineQuestions and Problems 3Arnytha VebrianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam 1 Review QuestionsDocumento10 pagineExam 1 Review Questionsprincess26390Nessuna valutazione finora
- Which Response Describes The Behaviour of Chromosomes in Metaphase I and Anaphase II of Meiosis?Documento6 pagineWhich Response Describes The Behaviour of Chromosomes in Metaphase I and Anaphase II of Meiosis?Alicia San JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Prelim 3Documento9 paginePractice Prelim 3EricaNessuna valutazione finora
- 10th Biology Assignment Module 4 - HEREDITYDocumento9 pagine10th Biology Assignment Module 4 - HEREDITYanshikaas240Nessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocumento25 paginePrinciples of Inheritance and VariationAshwani PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Genetics 6Th Edition Snustad Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 paginePrinciples of Genetics 6Th Edition Snustad Test Bank Full Chapter PDFBrettClinewdjc100% (11)
- Principles of Genetics 6th Edition Snustad Test BankDocumento15 paginePrinciples of Genetics 6th Edition Snustad Test Bankmarthajessegvt100% (30)
- Genetics ReviewerDocumento3 pagineGenetics ReviewerAlyzza Victoria TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics 2nd Week Dihybrid and Trihybrid CrossesDocumento25 pagineGenetics 2nd Week Dihybrid and Trihybrid CrossesAna RosyidahNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics.... Questions 2001 - 2012Documento3 pagineGenetics.... Questions 2001 - 2012peacevictorjNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics A Conceptual Approach 6Th Edition Pierce Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento37 pagineGenetics A Conceptual Approach 6Th Edition Pierce Test Bank Full Chapter PDFsoojeebeautied9gz3h100% (10)
- LS4 Lec2 Final Exam 3/21/2002: Last Name First Name Student ID Disc. SectionDocumento13 pagineLS4 Lec2 Final Exam 3/21/2002: Last Name First Name Student ID Disc. SectionLe DuongNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics A Conceptual Approach 6th Edition Pierce Test Bank DownloadDocumento27 pagineGenetics A Conceptual Approach 6th Edition Pierce Test Bank DownloadMax Martinez100% (21)
- 12-Principles of Inher & variation-MCQDocumento103 pagine12-Principles of Inher & variation-MCQDheekshith KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapt 05Documento23 pagineChapt 05vaishali shuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework 3Documento3 pagineHomework 3ButterlesstoastNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11Th Edition Griffiths Wessler Carroll Doebley 1464109486 9781464109485 Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 pagineTest Bank For Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11Th Edition Griffiths Wessler Carroll Doebley 1464109486 9781464109485 Full Chapter PDFjane.boyles334100% (15)
- Bio3TC17 Chi Square Test NotesDocumento9 pagineBio3TC17 Chi Square Test NotesFounder ChaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 MidtermI Form1Documento12 pagine2009 MidtermI Form1svNessuna valutazione finora
- A Discussion About A Scientific Paper (Fisherman Et Al)Documento4 pagineA Discussion About A Scientific Paper (Fisherman Et Al)Levi NeelyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 9 ProtocolDocumento7 pagineLab 9 ProtocolKareem HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 5 - Homework - Answer Key Due Feb. 23, 2013Documento6 pagineWeek 5 - Homework - Answer Key Due Feb. 23, 2013Ricardo Afonso SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- TBDocumento403 pagineTBT.Son50% (2)
- GENETICSDocumento5 pagineGENETICSkundhanathanNessuna valutazione finora
- RecombinationDocumento3 pagineRecombinationJon HosmerNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 NotesDocumento7 pagineChapter 5 NotesNandiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics Practice ProbsDocumento4 pagineGenetics Practice Probsajaysharma19686191Nessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics Canadian 2nd Edition Hartwell Test BankDocumento45 pagineGenetics Canadian 2nd Edition Hartwell Test BankHeatherAllencejrx100% (9)
- Problem Set 1Documento3 pagineProblem Set 1Serene SheikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Paper 2023 Task 1Documento18 paginePractice Paper 2023 Task 1Elissa ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Concepts of Genetics 10th Edition Klug Test BankDocumento12 pagineConcepts of Genetics 10th Edition Klug Test Bankhutaq100% (1)
- Test Bank For Biological Science Freeman 5th EditionDocumento19 pagineTest Bank For Biological Science Freeman 5th Editionunbloodystrakeow2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Task: Genetic Engineering: Pros & ConsDocumento13 pagineAssessment Task: Genetic Engineering: Pros & ConsAlvin PaboresNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics WorkbookDocumento57 pagineGenetics WorkbookLauren WinnettNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM 1067 Lec 5 - 2019 - 5 PDFDocumento14 pagineCHEM 1067 Lec 5 - 2019 - 5 PDFIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermochemistry: Enthalpy of Reactions: Pre-Lab ExercisesDocumento12 pagineThermochemistry: Enthalpy of Reactions: Pre-Lab ExercisesIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Determination of The Concentration of Atmospheric Carbon DioxideDocumento7 pagineDetermination of The Concentration of Atmospheric Carbon DioxideIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM 1067 Lec 5 - 2019 - 5Documento5 pagineCHEM 1067 Lec 5 - 2019 - 5Ibrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- First Law Thermo PDFDocumento45 pagineFirst Law Thermo PDFIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM 1067 Lec 3 - 2019 - NJ - 4 PDFDocumento21 pagineCHEM 1067 Lec 3 - 2019 - NJ - 4 PDFIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Intra-Allelic InteractionsDocumento20 pagineIntra-Allelic InteractionsIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Maternal EffectsDocumento10 pagineGenetic Maternal EffectsIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Difference Between Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento18 pagineDifference Between Mitosis and MeiosisIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Allelism and Polygenic TraitsDocumento18 pagineMultiple Allelism and Polygenic TraitsIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Difference Between Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento3 pagineDifference Between Mitosis and MeiosisFabiola GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow Chart For Lab 2Documento3 pagineFlow Chart For Lab 2Ibrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Mendels Basic Principles of InheritanceDocumento33 pagineMendels Basic Principles of InheritanceIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Goodness of Fit TestDocumento16 pagineGoodness of Fit TestIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- TutorialKinetics1 (2019) PDFDocumento1 paginaTutorialKinetics1 (2019) PDFIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics: Cell Division and Reproduction MitosisDocumento17 pagineGenetics: Cell Division and Reproduction Mitosiserica williamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics-I: Cell Division and Reproduction MeiosisDocumento19 pagineGenetics-I: Cell Division and Reproduction MeiosisIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- BIODocumento14 pagineBIOIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- The Genetic MaterialDocumento16 pagineThe Genetic MaterialIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- KaryotypingDocumento18 pagineKaryotypingIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics TutorialDocumento2 pagineThermodynamics TutorialIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- CEAC 104 Son 3 DeneyDocumento28 pagineCEAC 104 Son 3 DeneyIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Exp # 1Documento3 pagineLab Exp # 1Ibrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Release in A Neutralization Reaction and Acid Strength - CleanedDocumento8 pagineHeat Release in A Neutralization Reaction and Acid Strength - CleanedIbrahim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Experiments in BiochemistryDocumento5 pagine5 Experiments in BiochemistrySCIENCE Benjie AvecillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Diagram of Meiosis: UNIT 4 - Mendellian Genetics Name - HRDocumento3 pagineSimple Diagram of Meiosis: UNIT 4 - Mendellian Genetics Name - HRKholifaturRosidahNessuna valutazione finora
- Polytene Chromosomes in The Salivary Glands of DrosophilaDocumento3 paginePolytene Chromosomes in The Salivary Glands of DrosophilaRica Marquez100% (4)
- Abraham 2008Documento13 pagineAbraham 2008Andrés Pereyra RabanalNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Biology?Documento3 pagineWhat Is Biology?Aljonian PaeteNessuna valutazione finora
- History Scope and Development of Biotechnology 1Documento58 pagineHistory Scope and Development of Biotechnology 1Jarryd Galve LeonorNessuna valutazione finora
- Estadística. Serie SchaumDocumento18 pagineEstadística. Serie SchaumÁngel AranaNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications of BioinformaticsDocumento34 pagineApplications of BioinformaticsAntonMauntNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Defense WorksheetDocumento3 pagineCell Defense WorksheetAdriana UrquiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Genome Analysis 1Documento5 pagineGenome Analysis 1Jhilik PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- Tentative Datesheet UG Programme & Integrated Courses 1st Semester (NEP W.E.F. 2023-24)Documento6 pagineTentative Datesheet UG Programme & Integrated Courses 1st Semester (NEP W.E.F. 2023-24)sahilsahil92986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Free Radical Biology & Medicine: Justin L. Rains, Sushil K. JainDocumento9 pagineFree Radical Biology & Medicine: Justin L. Rains, Sushil K. JainAlmas TNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotechnology A Problem ApproachDocumento223 pagineBiotechnology A Problem ApproachPathifnder Publication93% (46)
- BIO213-Introduction To Quantitative BiologyDocumento14 pagineBIO213-Introduction To Quantitative BiologyMansi SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gene WikiDocumento4 pagineGene Wikinoah676Nessuna valutazione finora
- ScriptDocumento22 pagineScriptJed GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- CVDocumento2 pagineCVviveksingh_singh35Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Plant Transformation MethodsDocumento31 pagine3 Plant Transformation MethodsVenkateswarlu Yadavalli100% (2)
- Immunoassay TheoryDocumento22 pagineImmunoassay TheoryFAWKESKNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis Complete PowerpointDocumento48 pagineProtein Synthesis Complete PowerpointJohn Osborne100% (1)
- Enzyme InhibitionDocumento8 pagineEnzyme InhibitionfayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Muhammad Wildan Alfian - 20106040023 - Tahapan-Tahapan Metode Site-Directed Mutagenesis - Id.en PDFDocumento3 pagineMuhammad Wildan Alfian - 20106040023 - Tahapan-Tahapan Metode Site-Directed Mutagenesis - Id.en PDFWildan AlfianNessuna valutazione finora
- Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Lab 3 (Virtual Lab and Worksheet)Documento2 pagineProkaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Lab 3 (Virtual Lab and Worksheet)Enzo MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ancestry DnaDocumento11.339 pagineAncestry DnaTsvetanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure and Functions PDFDocumento43 pagineCell Structure and Functions PDFFíre B DimayugaNessuna valutazione finora
- BibliographyDocumento6 pagineBibliographyPoNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Chap 2 (Biological Molecules) F.SC 1st Year Biology Helping Notes PDFDocumento10 pagine12 Chap 2 (Biological Molecules) F.SC 1st Year Biology Helping Notes PDFZainab fatimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Karnataka 2nd Puc Biology Board Exam Question Paper Eng Version-March 2019Documento4 pagineKarnataka 2nd Puc Biology Board Exam Question Paper Eng Version-March 2019Vinod MN0% (1)
- Perineural Invasion of Cancer A Complex Crosstalk Between Cells and Molecules in The Perineural NicheDocumento21 paginePerineural Invasion of Cancer A Complex Crosstalk Between Cells and Molecules in The Perineural NichegangligonNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure and Function Part 3Documento14 pagineCell Structure and Function Part 3Suli FlamencoNessuna valutazione finora
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessDa EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNessuna valutazione finora
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceDa EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (18)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDa EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (392)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceDa EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (516)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDa EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (137)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Da EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (378)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsDa EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (223)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeDa EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDa EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (69)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedDa EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouDa EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (62)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDa EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperDa EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (15)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainDa EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (65)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionDa EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (811)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessDa Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (33)
- Water: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationDa EverandWater: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (37)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsDa EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorDa EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNessuna valutazione finora
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveDa EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (66)