Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
KSSM Form 2: by Tutor Syahirah 2018
Caricato da
Tanisa SaminTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
KSSM Form 2: by Tutor Syahirah 2018
Caricato da
Tanisa SaminCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CHAPTER 2
Ecosystem
KSSM
FORM 2
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
Energy Flow in
Ecosystem
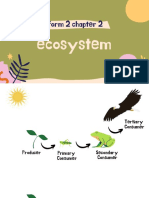
Food chains and food webs
Food chain - nutrition and energy transfer from producer to
consumer.
Primary User Secondary User
Producer Herbivor or omnivor
(using light to produce Carnivorous who
who ate the
green plants producers eat primary
users
Tertiary Users
Larger carnivorous
who eat
secondary users
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
Decomposers - bacteria and fungi decompose
dead plants and animals
The combination of several food chains form a food web.
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
o How does the energy flow into the food chain?
The primary consumers
Green plants (producers) eat the producers, the
Sunlight as a source of convert sunlight into chemical energy from
energy in the food chain chemical energy (food) the producers is
through photosynthesis transferred to primary
users.
The tertiary consumers
Secondary users eat
eat secondary users, the
primary users, the
chemical energy from
chemical energy from
the secondary is
the primary is transferred
transferred to tertiary
to secondary users
users
Not all energy is transferred because part of it is lost as heat energy through respiration,
excretion and decomposition.
Total energy decreases when transferred from one user to another.
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
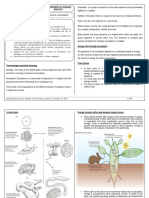
Nutrient Cycle in Ecosystem
Carbon Cycle cycle.
The plant absorbs carbon dioxide to
produce glucose through the
photosynthesis process.
Glucose - carbon compounds
oxidized by plant cells and animal
cells during respiration to release
energy and carbon dioxide.
Carbon dioxide is reabsorbed by
plants during photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide is also released
during burning of fossil fuels and
decay of dead organisms.
Thus, carbon is continuously cycled
in an ecosystem known as carbon
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
Oxygen Cycle
Photosynthesis releases the oxygen
used by the organism during
respiration.
Oxygen is also used during
combustion of fossil fuels, corrosion
and decay. This cycle is known as
the oxygen cycle.
Photosynthesis releases oxygen and
absorbs carbon dioxide from the
atmosphere while animal and plant
respiration utilizes oxygen and
releases carbon dioxide.
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
Water cycle
Animals and plants release carbon dioxide and water vapor during
respiration.
Water vapor rises to the atmosphere and partly into a water cycle.
Animals also contribute to the water cycle through sweating, urination and
decomposition.
Plants absorb water in the soil transported to the leaves through
photosynthesis.
Excessive water then disappears from plants through transpiration.
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
Carbon dioxide is
increasing
Oxygen is getting
reduced
Excessive use of The rate of
water photosynthesis
The logging of decreases
trees is
uncontrollable Transpiration rate
decreases
The amount of
rain water
decreases
Burning of fossil Water resources
fuels are reduced in
Human activities the earth
that disturb the
natural cycle
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
Dependency and mutual interaction
between organisms and between organisms
and the natural environment
Species - organisms of the same species
and breed.
Population - a group of organisms of the species
same species living in a habitat.
Communities - several populations of
different species of organisms interact to
form a community. population
Ecosystems - communities of organisms
that interact with one another with their
environment.
community
ecosystem
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
Penyesuaian Haiwan Dan Tumbuhan
Terhadap Iklim Habitat Di Gurun,
Tundra Dan Tropika
Desert
- Camel stores fat in the humps as energy
supplies.
- The cactus has a watery stem to store water.
Tropical
- light intensity and high humidity promotes
the growth of various plants.
- Mammals have short fur so they keep less
heat
Reptiles become inactive during hot times.
Tundra
- Arctic foxes have small ears and thick fur to
reduce heat loss.
- Plants in this area is only moss and grass for
a prolonged cold climate and little rainfall.
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
Interaction Between Living
Organisms
Interaction Between
Living Organisms
Prey-predator symbiosis competition
Interactions that make use of The interaction that Interactions that make use
one side, while the other one makes use of both of one side while another
does not benefit.. parties one loses.
commensalism Mutualism Parasitism
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
Prey-predator - prey benefited while the
victim was eaten by predators.
Competition - animals and plants
compete for the same living conditions as
homes, water, food and couples to
breed.
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
Symbiosis
Commensalism - only one organism that
benefits. Remora fish, which is
commensal attached to shark fish, gets
protection, transportation and food
waste. Shark, which is the host did not
suffer any impact from this relationship.
Mutualism - both organisms benefit. For
example, algae make food for fungi
while fungi supply water, minerals and
protection to the fight.
Parasitism - tapeworms (parasites) gain
protection and nutrients in the human
intestine (housekeeper). Humans suffer
losses due to loss of nutrients to
tapeworms.
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
Kawalan Biologi
Biological control - the use of natural
predators to control pests.
Pre-predator interactions are used in
biological control. For example:
Owls and snakes are used to reduce the
number of mice (pests) in oil palm
estates.
Fish is kept in the pond to eat mosquito
larvae.
The disadvantages of biological Disadvantages of the use of
The benefits of biological control
control chemicals
Does not pollute the Slower effects of chemical
Pollute the environment
environment. controls
Predators eat the prey (pests) Causes imbalance in food
Harmful to human health
only chains in ecosystems
Cheaper than pesticides.
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
Factors Affecting Population Size
Disease -
reducing the
size of plant
and animal
population.
Migration - an
Food sources - organism into
reduce an ecosystem
population changes the
size. Factors balance of the
population.
Affecting
Population
Size
Victimization -
Drought -
reduce the size
many plants
of the
die due to lack
population of
of water.
organisms
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
The role of human in maintaining the
balance of nature
Recycling of
Educate people waste
about awareness Planned logging
of conservation and planting
and new trees
conservation
Legal action
against anyone Animal
who pollutes and conservation
destroys the center
ecosystem
Steps to
conserve Marine Park to
Reserved forest and conserve coral
reefs.
preserve the
environment
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
QUIZ
1) Construct a food web based on the figure below.
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
2) A farmer sprayed his field with a kind of pesticide to kill mangosteen insects. In the next
mango planting season, the mango tree produces only a small amount of fruit. Create an
analysis of the following situations and explain one of the reasons why the results are very
little.
By Tutor Syahirah 2018
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chapter 2 Ecosystem: Learning OutcomesDocumento10 pagineChapter 2 Ecosystem: Learning OutcomesREKSHENA A/P PERKAS MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Exploring Ecosystems with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceDa EverandExploring Ecosystems with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNessuna valutazione finora
- EcosystemDocumento14 pagineEcosystemNuraz Zafreen100% (1)
- Chapter 2 EcosystemDocumento60 pagineChapter 2 EcosystemJu WenNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Slide IchiDocumento23 pagineBiology Slide IchiShiro ArcadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Level Biogeography NotesDocumento35 pagineA Level Biogeography NotesBlessmore Chitanha100% (1)
- 02 Energy and Mass Transfers in Ecosystems - Rev02Documento21 pagine02 Energy and Mass Transfers in Ecosystems - Rev02GRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecology II Part B - Ecological Interactions - Food Chains Food Webs 2017Documento38 pagineEcology II Part B - Ecological Interactions - Food Chains Food Webs 2017Shahriar HaqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 35Documento3 pagineLecture 35Tzuyu TchaikovskyNessuna valutazione finora
- Exploring Ecosystems A Journey Into Natures MarvelsDocumento10 pagineExploring Ecosystems A Journey Into Natures Marvelstejaswaniverma289Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sec 4 Ecology NotesDocumento21 pagineSec 4 Ecology Notesanya de silvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sains SPM Chapter 3 Form 5Documento10 pagineSains SPM Chapter 3 Form 5Sensei J-dai89% (18)
- Ecosystem (Full)Documento58 pagineEcosystem (Full)meerafiqah07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Organisms and Their EnvironmentDocumento5 pagineOrganisms and Their EnvironmentkiswariazbuttNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecosystem Notes PDFDocumento17 pagineEcosystem Notes PDFNEHA BANSALNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecosystem (Part-I) : Mr. Tarun ChauhanDocumento17 pagineEcosystem (Part-I) : Mr. Tarun ChauhanNEHA BANSALNessuna valutazione finora
- BiosphereDocumento29 pagineBiosphereJaicel ClaudetteNessuna valutazione finora
- 10th Science Our EnvironmentDocumento10 pagine10th Science Our EnvironmentLe TensaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Presented by Musheer Khan Payal Dhanvijaya Parag BhuddheDocumento44 paginePresented by Musheer Khan Payal Dhanvijaya Parag BhuddheparagbuddheNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis, Food Chains and CyclesDocumento6 paginePhotosynthesis, Food Chains and CyclesOsmany MadrigalNessuna valutazione finora
- CHP 2 EcologyDocumento73 pagineCHP 2 EcologySIMBA The Lion KingNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecology Notes!!Documento10 pagineEcology Notes!!Raudha Athif100% (3)
- Chapter 2Documento32 pagineChapter 2Nurul AqilahNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Flow 1Documento7 pagineEnergy Flow 1Kaycin Duzon Soriano0% (1)
- Chapter 2 - EcosystemDocumento48 pagineChapter 2 - Ecosystemsyuhada zakariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nature Course PresentationDocumento9 pagineNature Course Presentationashith8095382766Nessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Flow of Energy in Ecosystems Text-MergedDocumento14 pagine02 Flow of Energy in Ecosystems Text-Mergedsurya narayanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Flow in EcosystemsDocumento36 pagineEnergy Flow in EcosystemsCllyan ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Flow in EcosystemsDocumento35 pagineEnergy Flow in EcosystemsIRFAN ZAIN ULABIDEENNessuna valutazione finora
- ECOLOGYDocumento4 pagineECOLOGYMellisa SimonNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 PDFDocumento22 pagineUnit 3 PDFआई सी एस इंस्टीट्यूटNessuna valutazione finora
- EnSci Reviewer #1 - Ecosystem ReviewerDocumento2 pagineEnSci Reviewer #1 - Ecosystem ReviewerJohn PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- ECOSYSTEMSDocumento42 pagineECOSYSTEMSJohn michael Del rosarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Ecosystem Form 2Documento44 pagineChapter 2 Ecosystem Form 2Nurul Faten AdeliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Ii Ecosysten and BiodiversityDocumento21 pagineUnit Ii Ecosysten and BiodiversityRajinithanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1B EcosystemDocumento11 pagineUnit 1B EcosystemAkshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Our Environment-Handout 2Documento8 pagineOur Environment-Handout 2ANSHIKA RAJNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecosystem and BiodiversityDocumento54 pagineEcosystem and BiodiversityVinoth KannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Notes Q4Documento17 pagineScience Notes Q4Nyx hshshshNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamics of EcosystemDocumento36 pagineDynamics of EcosystemPORAKH MONE GOHAINNessuna valutazione finora
- 20171110151139topic 2 Biotic FactorsDocumento54 pagine20171110151139topic 2 Biotic FactorsMizsarah Siti SarahNessuna valutazione finora
- EcosystemDocumento43 pagineEcosystemPhantom DeluxNessuna valutazione finora
- Organism and Their EnvironmentDocumento2 pagineOrganism and Their EnvironmentkNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 EcosystemsDocumento77 pagineLecture 2 EcosystemsFaisal NYC dilshad AwesomNessuna valutazione finora
- How Ecosystems WorkDocumento8 pagineHow Ecosystems WorkyjnhtgrfNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes - Evs Unit - 3Documento20 pagineLecture Notes - Evs Unit - 3Nambi RajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit I Chapter 2-EcosystemsDocumento49 pagineUnit I Chapter 2-EcosystemsSATISHNessuna valutazione finora
- Communities and EcosystemsDocumento37 pagineCommunities and Ecosystemsalmaz.ismayilova0808Nessuna valutazione finora
- 16 Flow of EnergyDocumento2 pagine16 Flow of Energyramloghun veerNessuna valutazione finora
- The EcosystemDocumento5 pagineThe EcosystemPrincess Lourdes CarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Proper For Week 2 GEE1Documento3 pagineLesson Proper For Week 2 GEE1Russel Kent PaduaNessuna valutazione finora
- WINSEM2021-22 CHY1002 TH VL2021220504796 Reference Material I 14-02-2022 KGS-EVSc-Module1Documento164 pagineWINSEM2021-22 CHY1002 TH VL2021220504796 Reference Material I 14-02-2022 KGS-EVSc-Module1Captain ThejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Art Integration ActivityDocumento22 pagineArt Integration ActivityHarishkumaran VNessuna valutazione finora
- Illustrative Notebook Exploring The Circle of Life - Food Chain Lesson For ElementaryDocumento20 pagineIllustrative Notebook Exploring The Circle of Life - Food Chain Lesson For Elementarymarinixo122Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ecosystems: Concept of An EcosystemDocumento9 pagineEcosystems: Concept of An EcosystemCristel CaraigNessuna valutazione finora
- Group II: - Ecosystem - Ecological ChainDocumento33 pagineGroup II: - Ecosystem - Ecological ChainSariah MirandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecology NotesDocumento6 pagineEcology NotesFatma Zorlu100% (1)
- Unit 1-EcosystemsDocumento60 pagineUnit 1-EcosystemsRidhi GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Eco Midterm ReviewerDocumento18 pagineEco Midterm ReviewerbfhdsjNessuna valutazione finora
- KSSM f1c5Documento52 pagineKSSM f1c5Tanisa SaminNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Energy and PowerDocumento2 paginePractice Energy and PowerTanisa SaminNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Tutorial 1Documento4 pagineChapter 2 Tutorial 1Tanisa SaminNessuna valutazione finora
- KSSM F1 C6Documento74 pagineKSSM F1 C6Tanisa SaminNessuna valutazione finora
- KSSM F1 C9Documento61 pagineKSSM F1 C9Tanisa SaminNessuna valutazione finora
- KSSMF 1 C 6Documento74 pagineKSSMF 1 C 6Tanisa Samin100% (1)
- Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeDocumento67 pagineCell As The Basic Unit of LifeTANNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectricityDocumento25 pagineElectricityTanisa SaminNessuna valutazione finora
- PollinationDocumento5 paginePollinationTanisa SaminNessuna valutazione finora
- MagnetismDocumento20 pagineMagnetismTanisa SaminNessuna valutazione finora
- Science NotesDocumento376 pagineScience NotesRohit YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam+ KeyDocumento3 pagineExam+ Keymaiche amarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pashan Lake Report FORSUBMISSION2Documento64 paginePashan Lake Report FORSUBMISSION2Suman SaurabhNessuna valutazione finora
- Adaptation in Plants Worksheet PDFDocumento7 pagineAdaptation in Plants Worksheet PDFSamit Kumar Saha100% (2)
- Living Things in Their EnvironmentDocumento50 pagineLiving Things in Their EnvironmentSolocal100% (2)
- Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocumento5 pagineBiodiversity and Its ConservationEenadu paperNessuna valutazione finora
- CRP Mid Contract Management - 2007Documento62 pagineCRP Mid Contract Management - 2007NEGameandParksNessuna valutazione finora
- Aaradhy Sharma 2210110100 CCC 704 Aravali Field ReportDocumento21 pagineAaradhy Sharma 2210110100 CCC 704 Aravali Field ReportKrishnav SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ì (SK$M) BDHDGH + - Ä-U-Ä-U Ì (SK$M) BDHDGH + - Ä-U-Ä-U: Life Science Life ScienceDocumento10 pagineÌ (SK$M) BDHDGH + - Ä-U-Ä-U Ì (SK$M) BDHDGH + - Ä-U-Ä-U: Life Science Life ScienceTECOTEC GROUPNessuna valutazione finora
- Checked-Forest Protection and ConservationDocumento49 pagineChecked-Forest Protection and ConservationAhammed Jobair ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Community EcologyDocumento4 pagineCommunity EcologyBiju ThomasNessuna valutazione finora
- Advisory List Environmental Weeds VICDocumento170 pagineAdvisory List Environmental Weeds VICKarthick PalaniappanNessuna valutazione finora
- Medicinal PlantsDocumento18 pagineMedicinal PlantsbharatNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 8Documento52 pagineForm 4 Biology Chapter 8Gaya GayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Ecological Concept and PrinciplesDocumento3 pagineBasic Ecological Concept and PrinciplesJoanah Fernandez100% (1)
- Oxford Discover 5 TestDocumento9 pagineOxford Discover 5 TestreeceinhueNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 - Shrestha BB - Invasive Alien Plant Species in NepalDocumento15 pagine2016 - Shrestha BB - Invasive Alien Plant Species in NepalShrawan GiriNessuna valutazione finora
- Temperature and Precipitation Influences On Freshwater Fish CompositionDocumento22 pagineTemperature and Precipitation Influences On Freshwater Fish CompositionEmiley JenkinsNessuna valutazione finora
- BiodiversityDocumento2 pagineBiodiversityAshok MathireddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Trees Plantation by - : Terra Walker Drilling Pvt. LTDDocumento10 pagineTrees Plantation by - : Terra Walker Drilling Pvt. LTDDeepak SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Forest Types (FHU3219) : Razak TerhemDocumento21 pagineForest Types (FHU3219) : Razak TerhemPrasna NairNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.3 Threats To BiodiversityDocumento10 pagine3.3 Threats To BiodiversitysnehaNessuna valutazione finora
- Langenberger 2004 Review of Research On Philippine Forest VegetationDocumento15 pagineLangenberger 2004 Review of Research On Philippine Forest VegetationJeny Rose S PolicarpioNessuna valutazione finora
- Forest ResourcesDocumento23 pagineForest ResourcesLevi LeviNessuna valutazione finora
- Let The Wetlands StandDocumento4 pagineLet The Wetlands StandAdhila SuphanNessuna valutazione finora
- Timber Extraction and MiningDocumento4 pagineTimber Extraction and MiningFirst name Last nameNessuna valutazione finora
- Wildlife Conservation Efforts in IndiaDocumento6 pagineWildlife Conservation Efforts in IndiaAmanda Price67% (9)
- Biology Form 4 by CHONG JIA PINGDocumento12 pagineBiology Form 4 by CHONG JIA PINGJia Ping Jia Ping100% (7)
- Natres Finals ReviewerDocumento32 pagineNatres Finals ReviewerAavhNessuna valutazione finora
- Stanford - Shifting Habitat MosaicDocumento14 pagineStanford - Shifting Habitat Mosaiccarlos castellanosNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutDa EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (142)
- Lessons for Survival: Mothering Against “the Apocalypse”Da EverandLessons for Survival: Mothering Against “the Apocalypse”Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Water: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationDa EverandWater: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (37)
- Chesapeake Requiem: A Year with the Watermen of Vanishing Tangier IslandDa EverandChesapeake Requiem: A Year with the Watermen of Vanishing Tangier IslandValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (38)
- Climate Uncertainty and Risk: Rethinking Our ResponseDa EverandClimate Uncertainty and Risk: Rethinking Our ResponseNessuna valutazione finora
- Grandma Gatewood's Walk: The Inspiring Story of the Woman Who Saved the Appalachian TrailDa EverandGrandma Gatewood's Walk: The Inspiring Story of the Woman Who Saved the Appalachian TrailValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (308)
- The Great Displacement: Climate Change and the Next American MigrationDa EverandThe Great Displacement: Climate Change and the Next American MigrationValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (32)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastDa EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (31)
- On Fire: The Case for the Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The Case for the Green New DealValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (109)
- How to Be Alive: A Guide to the Kind of Happiness That Helps the WorldDa EverandHow to Be Alive: A Guide to the Kind of Happiness That Helps the WorldValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Braiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsDa EverandBraiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (1424)
- When the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeDa EverandWhen the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- The Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanDa EverandThe Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil: The Story of a Black Mother's GardenDa EverandSoil: The Story of a Black Mother's GardenValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (16)
- The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateDa EverandThe Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1003)
- Under a White Sky: The Nature of the FutureDa EverandUnder a White Sky: The Nature of the FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (159)
- Badluck Way: A Year on the Ragged Edge of the WestDa EverandBadluck Way: A Year on the Ragged Edge of the WestValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (8)
- The Exploration of the Colorado river and its CanyonsDa EverandThe Exploration of the Colorado river and its CanyonsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Braiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsDa EverandBraiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (177)
- 438 Days: An Extraordinary True Story of Survival at SeaDa Everand438 Days: An Extraordinary True Story of Survival at SeaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (188)
- Fen, Bog and Swamp: A Short History of Peatland Destruction and Its Role in the Climate CrisisDa EverandFen, Bog and Swamp: A Short History of Peatland Destruction and Its Role in the Climate CrisisValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (24)