Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Numerical Optimization With Mathematica
Caricato da
Dennis La CoteraTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Numerical Optimization With Mathematica
Caricato da
Dennis La CoteraCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Printed from the Complete Wolfram Language Documentation 1
TUTORIAL Related Tutorials Functions URL
Numerical Optimization
FindMinimum f , x,x0 search for a local minimum of f , starting at x x0
FindMinimum f ,x search for a local minimum of f
FindMinimum f , x,x0 , y,y0 ,
search for a local minimum in several variables
FindMinimum f ,cons , x,x0 , y,y0 ,
search for a local minimum subject to the constraints
cons starting at x x0 , y y0 ,
FindMinimum f ,cons , x,y, search for a local minimum subject to the constraints
cons
FindMaximum f ,x , etc. search for a local maximum
Searching for local minima and maxima.
This finds the value of x which minimizes x , starting at x 2.
In[1]:= FindMinimum Gamma x , x, 2
encuentra mín gamma de Euler
Out[1]= 0.885603, x 1.46163
The last element of the list gives the value at which the minimum is achieved.
In[2]:= Gamma x . Last
gamma de Eu último
Out[2]= 0.885603
Like FindRoot , FindMinimum and FindMaximum work by starting from a point, then progressively searching for a minimum or maximum. But
since they return a result as soon as they find anything, they may give only a local minimum or maximum of your function, not a global one.
This curve has two local minima.
In[3]:= Plot x ^ 4 3 x^2 x, x, 3, 2
representación gráfica
Out[3]=
1988–2018 Wolfram Research, Inc. All rights reserved. http://reference.wolfram.com/language
Printed from the Complete Wolfram Language Documentation 2
Starting at x 1, you get the local minimum on the right.
In[4]:= FindMinimum x ^ 4 3 x^2 x, x, 1
encuentra mínimo
Out[4]= 1.07023, x 1.1309
This gives the local minimum on the left, which in this case is also the global minimum.
In[5]:= FindMinimum x ^ 4 3 x^2 x, x, 1
encuentra mínimo
Out[5]= 3.51391, x 1.30084
You can specify variables without initial values.
In[6]:= FindMinimum x ^ 4 3 x^2 x, x
encuentra mínimo
Out[6]= 1.07023, x 1.1309
You can specify a constraint.
In[7]:= FindMinimum x^4 3 x^2 x, x 0 ,x
encuentra mínimo
Out[7]= 3.51391, x 1.30084
NMinimize f ,x try to find the global minimum of f
NMinimize f , x,y, try to find the global minimum over several variables
NMaximize f ,x try to find the global maximum of f
NMaximize f , x,y, try to find the global maximum over several variables
Finding global minima and maxima.
This immediately finds the global minimum.
In[8]:= NMinimize x ^ 4 3 x^2 x, x
minimiza aproximadamente
Out[8]= 3.51391, x 1.30084
NMinimize and NMaximize are numerical analogs of Minimize and Maximize . But unlike Minimize and Maximize they usually cannot guarantee
to find absolute global minima and maxima. Nevertheless, they typically work well when the function f is fairly smooth, and has a limited
number of local minima and maxima.
NMinimize f ,cons , x,y, try to find the global minimum of f subject to
constraints cons
NMaximize f ,cons , x,y, try to find the global maximum of f subject to
constraints cons
Finding global minima and maxima subject to constraints.
1988–2018 Wolfram Research, Inc. All rights reserved. http://reference.wolfram.com/language
Printed from the Complete Wolfram Language Documentation 3
With the constraint x 0, NMinimize will give the local minimum on the right.
In[9]:= NMinimize x^4 3 x^2 x, x 0 ,x
minimiza aproximadamente
Out[9]= 1.07023, x 1.1309
This finds the minimum of x 2 y within the unit circle.
In[10]:= NMinimize x 2 y, x ^ 2 y^2 1 , x, y
minimiza aproximadamente
Out[10]= 2.23607, x 0.447214, y 0.894427
In this case Minimize can give an exact result.
In[11]:= Minimize x 2 y, x ^ 2 y^2 1 , x, y
minimiza
4 2
Out[11]= 5 , x 5 ,y
5 5
But in this case it cannot.
In[12]:= Minimize Cos x 2 y , x^2 y^2 1 , x, y
minimiza coseno
Out[12]= MinimizeCos x 2 y , x2 y2 1, x, y
This gives a numerical approximation, effectively using NMinimize .
In[13]:= N
valor numérico
Out[13]= 0.617273, x 0.447214, y 0.894427
If both the objective function f and the constraints cons are linear in all variables, then minimization and maximization correspond to a linear
programming problem. Sometimes it is convenient to state such problems not in terms of explicit equations, but instead in terms of matrices
and vectors.
LinearProgramming c,m,b find the vector x which minimizes c.x subject to the
constraints m.x b and x 0
LinearProgramming c,m,b,l use the constraints m.x b and x l
Linear programming in matrix form.
Here is a linear programming problem in equation form.
In[14]:= Minimize 2x 3 y, x 5y 10, x y 2, x 1 , x, y
minimiza
32 10 4
Out[14]= , x ,y
3 3 3
Here is the corresponding problem in matrix form.
In[15]:= LinearProgramming 2, 3 , 1, 5 , 1, 1 , 1, 0 , 10, 2, 1
programación lineal
10 4
Out[15]= ,
3 3
You can specify a mixture of equality and inequality constraints by making the list b be a sequence of pairs bi , si . If si is 1, then the ith constraint
is mi .x bi . If si is 0 then it is mi .x bi , and if si is 1 then it is mi .x bi .
1988–2018 Wolfram Research, Inc. All rights reserved. http://reference.wolfram.com/language
Printed from the Complete Wolfram Language Documentation 4
This makes the first inequality use .
In[16]:= LinearProgramming 2, 3 , 1, 5 , 1, 1 , 1, 0 , 10, 1 , 2, 1 , 1, 1
programación lineal
Out[16]= 2, 0
In LinearProgramming c, m, b, l , you can make l be a list of pairs l1 , u1 , l2 , u2 , representing lower and upper bounds on the xi .
In doing large linear programming problems, it is often convenient to give the matrix m as a SparseArray object.
Related Tutorials
Numerical Operations on Functions
1988–2018 Wolfram Research, Inc. All rights reserved. http://reference.wolfram.com/language
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Lecture 9 - SVMDocumento42 pagineLecture 9 - SVMHusein YusufNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization: ES 204 Numerical Methods in EngineeringDocumento15 pagineOptimization: ES 204 Numerical Methods in EngineeringkennethmsorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Max MinDocumento3 pagineMax MinShobuj Hossen NeilNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3: Lagrangian Duality and Algorithms For The Lagrangian Dual ProblemDocumento47 pagineLecture 3: Lagrangian Duality and Algorithms For The Lagrangian Dual ProblemAnabelNessuna valutazione finora
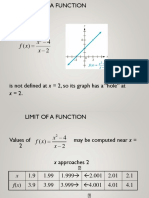
- 1 Limits & Continuity NotesDocumento82 pagine1 Limits & Continuity Notesmseconroy84Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Function: X FX XDocumento47 pagineThe Function: X FX XvanillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Matlab Session 5Documento23 pagineMatlab Session 5apurva.tudekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Finding The Roots of F (X) 0Documento56 pagineFinding The Roots of F (X) 0rk87Nessuna valutazione finora
- ECE5550-Notes04 - KopyaDocumento50 pagineECE5550-Notes04 - KopyaZeynep Vildan IşıkNessuna valutazione finora
- Limit at InfinityDocumento9 pagineLimit at Infinityloreign sinocruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization Using Calculus: Stationary Points: Functions of Single and Two VariablesDocumento28 pagineOptimization Using Calculus: Stationary Points: Functions of Single and Two Variablestejas mNessuna valutazione finora
- Maximun and Minimun Values: Wbeimar VeraDocumento13 pagineMaximun and Minimun Values: Wbeimar VeraValeria Marrugo MoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Computational Lab in Physics: Finding Roots of Nonlinear FunctionsDocumento12 pagineComputational Lab in Physics: Finding Roots of Nonlinear Functionsbenefit187Nessuna valutazione finora
- Math Calculus Coursenotes m231 2018 SDocumento408 pagineMath Calculus Coursenotes m231 2018 SEuro VillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Max and MinDocumento16 pagineMax and MinJeff GicharuNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 2-4: Limits Properties: Lim Lim Lim LimDocumento7 pagineSection 2-4: Limits Properties: Lim Lim Lim LimortizNessuna valutazione finora
- MTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 8 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 4.1 To 4.4Documento11 pagineMTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 8 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 4.1 To 4.4Roy VeseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Fin500J ConstrainedOptimization 2011Documento31 pagineFin500J ConstrainedOptimization 2011PeterNessuna valutazione finora
- LIMITSDocumento59 pagineLIMITSxyz abcNessuna valutazione finora
- What Do Limits Have To Do With Calculus?: An Unlimited Review of LimitsDocumento18 pagineWhat Do Limits Have To Do With Calculus?: An Unlimited Review of LimitsBretana joanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unconstrained and Constrained OptimizationDocumento31 pagineUnconstrained and Constrained OptimizationPhilip PCNessuna valutazione finora
- Convex FunctionsDocumento13 pagineConvex Functionswesley maxmilianoNessuna valutazione finora
- LimitFunction PDFDocumento4 pagineLimitFunction PDFNajmul IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 5 Optimum Design Concept 2Documento70 pagineWeek 5 Optimum Design Concept 2fzubairisaabNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4Documento58 pagineLecture 4Hoàng HàNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization 2Documento29 pagineOptimization 2SakethBharadwajNessuna valutazione finora
- CALENG1 Lesson 01b Introduction To Calculus and Limits Edited by LFRDocumento63 pagineCALENG1 Lesson 01b Introduction To Calculus and Limits Edited by LFRcareyNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization 111Documento29 pagineOptimization 111mohammed aliNessuna valutazione finora
- DiffrentiationDocumento16 pagineDiffrentiationfathalla tarekNessuna valutazione finora
- Limits and ContinuityDocumento33 pagineLimits and Continuitydomm prozNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus - Lecture 4Documento13 pagineCalculus - Lecture 4paramingirlNessuna valutazione finora
- L-5 - AodDocumento38 pagineL-5 - AodanuraghNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.2 Algebraic Limits and ContinuityDocumento6 pagine1.2 Algebraic Limits and ContinuityVhigherlearning100% (1)
- B For I 1,, M: N J J JDocumento19 pagineB For I 1,, M: N J J Jضيٍَِِ الكُمرNessuna valutazione finora
- PPT8-Curve SketchingDocumento18 paginePPT8-Curve SketchingIndri Ria WinnyNessuna valutazione finora
- Limit at InfinityDocumento9 pagineLimit at Infinityloreign sinocruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Cal - 5. App. - of - DerivativesDocumento28 pagineCal - 5. App. - of - DerivativesNat NaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes On DifferentiationDocumento12 pagineLecture Notes On DifferentiationMd Arif Ul Islam-KowshikNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction, Function and Limits With Derivatives: Module OutlineDocumento10 pagineIntroduction, Function and Limits With Derivatives: Module OutlineErn NievaNessuna valutazione finora
- L8 Polynomial FunctionsDocumento23 pagineL8 Polynomial FunctionsFlorence FlorendoNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 5A. DifferentiationDocumento52 pagineTopic 5A. DifferentiationZEEL PATELNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 5A. DifferentiationDocumento52 pagineTopic 5A. DifferentiationZEEL PATELNessuna valutazione finora
- Constrained OptimizationDocumento9 pagineConstrained OptimizationananyaajatasatruNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Chapter 2 Part4Documento15 pagineCalculus Chapter 2 Part4ياسر ابو عليانNessuna valutazione finora
- Limits of FunctionsDocumento10 pagineLimits of FunctionsLourençoNessuna valutazione finora
- L2 DomainsDocumento18 pagineL2 DomainsFrednixenGapoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 3 The Limit LawsDocumento13 pagineWeek 3 The Limit LawsCynthia PlazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Finding Extreme Values. Extreme Values Maximum Minimum: Untitled-1Documento6 pagineFinding Extreme Values. Extreme Values Maximum Minimum: Untitled-1Syed Arsalan AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Aod (Day-6)Documento4 pagineAod (Day-6)Faizan AnsariNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Calculus: Engr. Roan N. MambaDocumento48 pagineDifferential Calculus: Engr. Roan N. MambaWilliam CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Rules of Derivative PDFDocumento28 pagineRules of Derivative PDFAriel Clopino PiolNessuna valutazione finora
- ch03 Ma1300Documento13 paginech03 Ma1300rimskysNessuna valutazione finora
- Limit of A FunctionDocumento30 pagineLimit of A FunctionhamZaNessuna valutazione finora
- Limits and Continuity PDFDocumento107 pagineLimits and Continuity PDFAnonymous 0MTQ0BNessuna valutazione finora
- Concavity and Curve SketchingDocumento14 pagineConcavity and Curve SketchingFahrettin CakirNessuna valutazione finora
- LimitsDocumento42 pagineLimitsbernardNessuna valutazione finora
- Global (Absolute) Extrema Point: Report TitleDocumento14 pagineGlobal (Absolute) Extrema Point: Report TitleDaneal SofiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec - 3 Bisection MethodDocumento31 pagineLec - 3 Bisection MethodNadia ImranNessuna valutazione finora
- Why GPUs Are More Suited For Deep Learning?Documento9 pagineWhy GPUs Are More Suited For Deep Learning?Dennis La CoteraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematica 12. Insetting Objects in GraphicsDocumento3 pagineMathematica 12. Insetting Objects in GraphicsDennis La CoteraNessuna valutazione finora
- Symbolic Tensors With Mathematica 12Documento6 pagineSymbolic Tensors With Mathematica 12Dennis La CoteraNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of New Features in 12.0Documento19 pagineSummary of New Features in 12.0Dennis La CoteraNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Automata With MathematicaDocumento9 pagineCellular Automata With MathematicaDennis La CoteraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tensors in MathematicaDocumento6 pagineTensors in MathematicaDennis La Cotera0% (1)
- Complete List of Data Science ResourcesDocumento2 pagineComplete List of Data Science ResourcesDennis La CoteraNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Exam Gor Grade 11Documento2 pagineMidterm Exam Gor Grade 11Algelle AbrantesNessuna valutazione finora
- Logic NotesDocumento19 pagineLogic NotesCielo PulmaNessuna valutazione finora
- S TR GEN ID (Component Marking) (Rev 3 2009) - AN Marked UpDocumento6 pagineS TR GEN ID (Component Marking) (Rev 3 2009) - AN Marked UpsnclgsraoNessuna valutazione finora
- WPBSA Official Rules of The Games of Snooker and Billiards 2020 PDFDocumento88 pagineWPBSA Official Rules of The Games of Snooker and Billiards 2020 PDFbabuzducNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2 Unit 20 Fully Completed - ReviewedDocumento5 pagineAssignment 2 Unit 20 Fully Completed - Reviewedchris.orisawayiNessuna valutazione finora
- DudjDocumento4 pagineDudjsyaiful rinantoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Broadband ForumDocumento21 pagineThe Broadband ForumAnouar AleyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Updated G10 Class Routine Effective From 12 January 2023Documento1 paginaUpdated G10 Class Routine Effective From 12 January 2023NiloyNessuna valutazione finora
- Anxiety Disorders - Causes, Types, Symptoms, & TreatmentsDocumento5 pagineAnxiety Disorders - Causes, Types, Symptoms, & Treatmentsrehaan662Nessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Artificial Intelligence For Industry 4.0-Based Manufacturing SystemsDocumento5 pagineIndustrial Artificial Intelligence For Industry 4.0-Based Manufacturing SystemsMuhammad HaziqNessuna valutazione finora
- PIX4D Simply PowerfulDocumento43 paginePIX4D Simply PowerfulJUAN BAQUERONessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet Series 5: Answer Any 3 Questions From 1 To 6. (2 Score Each)Documento6 pagineWorksheet Series 5: Answer Any 3 Questions From 1 To 6. (2 Score Each)AswithNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3Documento12 pagineUnit 3Erik PurnandoNessuna valutazione finora
- 41z S4hana2021 Set-Up en XXDocumento46 pagine41z S4hana2021 Set-Up en XXHussain MulthazimNessuna valutazione finora
- 07ercoskun 05 01 PDFDocumento23 pagine07ercoskun 05 01 PDFjagmadridNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Pain Medicine: Jianguo Cheng Richard W. RosenquistDocumento346 pagineFundamentals of Pain Medicine: Jianguo Cheng Richard W. RosenquistMayNessuna valutazione finora
- Mean Variance Portfolio TheoryDocumento85 pagineMean Variance Portfolio TheoryEbenezerNessuna valutazione finora
- User'S Guide: Tm4C Series Tm4C129E Crypto Connected Launchpad Evaluation KitDocumento36 pagineUser'S Guide: Tm4C Series Tm4C129E Crypto Connected Launchpad Evaluation KitLương Văn HưởngNessuna valutazione finora
- L27/38S Project Guide - Power Plant: Four-Stroke GensetDocumento392 pagineL27/38S Project Guide - Power Plant: Four-Stroke GensetAaron Chan100% (1)
- Eng DS Epp-2314 1410Documento2 pagineEng DS Epp-2314 1410MarkusAldoMaquNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Diabetic Foot Ulcers ReadingDocumento21 pagineManaging Diabetic Foot Ulcers Readinghimanshugupta811997Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To LCCDocumento32 pagineIntroduction To LCCGonzalo LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Amnaya Sutra (English)Documento458 pagineAmnaya Sutra (English)Assam Bhakti SagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Analysis and Design of Pressure Hulls - The State of The Art and Future TrendsDocumento118 pagineStructural Analysis and Design of Pressure Hulls - The State of The Art and Future TrendsRISHABH JAMBHULKARNessuna valutazione finora
- Ad149 Manual RDocumento69 pagineAd149 Manual RCharityNessuna valutazione finora
- H107en 201906 r4 Elcor Elcorplus 20200903 Red1Documento228 pagineH107en 201906 r4 Elcor Elcorplus 20200903 Red1mokbelNessuna valutazione finora
- Digging Deeper: Can Hot Air Provide Sustainable Source of Electricity?Documento2 pagineDigging Deeper: Can Hot Air Provide Sustainable Source of Electricity?Рустам ХаджаевNessuna valutazione finora
- Therapeutic Nutrition: Khien S. Sasi, RN, ManDocumento33 pagineTherapeutic Nutrition: Khien S. Sasi, RN, ManKhien Sasi100% (4)
- Semi Finals in Tle 2015Documento3 pagineSemi Finals in Tle 2015LoraineTenorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Dawn of Solar PV CookingDocumento5 pagineDawn of Solar PV CookingAbhinav AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora