Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Tense of The Verb
Caricato da
JJ RiveraDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Tense of The Verb
Caricato da
JJ RiveraCopyright:
Formati disponibili
TENSE OF THE VERB
Tense is the term used to show relationship between time and other
conditions in the form of the verb. Not all changes in the verb form are directly
related to time. The way the action is understood to take place also affects verb
forms. In addition to showing time, different forms show conditions.
You don’t have to learn all the grammatical terms to express yourself
clearly, but you must learn the exact verb forms to use to express your ideas if
you want your readers to understand your writing.
THE PRESENT TENSE
Remember to add s in the present tense (singular) is very important in
academic and technical writing since a large part of it is done in the
present tense. (Ex: The professor denies participation to the petition.)
1. Use the present tense to show present state or conditions
particularly with stative verbs. They are verbs that show a state or
condition rather than an activity or event. These are verbs having a
meaning of: knowledge or of sense of perception.
Knowledge or mental activity, often followed by that
Examples: Mr. Hanson believes that his diagnosis is correct.
Paula imagines she will be a great actress someday.
John wants a cup of coffee.
Sometimes, Dan forgets his appointments.
Martha understands my problems.
Ed knows tennis.
Sense Perception or verbs of the senses. They are not usually used in
the continuous/progressive forms except for special emphasis on the
duration of the activity.
Examples: Tom is deaf; he does not hear well.
An eagle sees small animals from far above the ground.
The rotten meat smells bad.
Your plans sound interesting.
My music teacher notices every mistake.
2. Use the present tense to show an eternal truth or natural law.
Examples: The moon affects the tides.
Man proposes but God disposes.
Parallel lines never meet.
Hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water.
Subjects and verb agree in number.
Hot air rises.
3. Use the present tense to show habitual action – repetition or non-
repetition of the same act.
Examples: Beverly drinks coffee every morning.
We always celebrate my birthday with a party.
The neighbors do not wash their windows every week.
The kids plant tomatoes every year.
Sometimes we go to a soccer game on Sunday afternoon.
4. Use the present tense to show the historical present in criticism to
discuss writing, drama, music, and art, and in research that quotes
or paraphrases what other people have said or written in the past.
Examples: In the short story “The Lottery,” Shirley Jackson writes an
allegory of the injustices of life.
Darwin presents evidence for the development of life from
lower to higher forms.
Looking at all the evidence, one agrees with the critic who
calls the play a success.
5. Use the present tense for definitions and explanations.
Examples:
Gross National Product means the total value of all goods produced and
services performed in one country in one year.
The screw is inserted in the lower-right hand corner of the frame.
Plate B replaces Plate A in the old model, as shown in Diagram 2.
6. Use the present tense to show future possibility in conditional and
time clauses.
Examples:
Uncle Bunny will give you one thousand pesos, if he likes your work.
(condition)
Uncle Bunny will give you one thousand pesos when he sees you. (time)
7. Use present tense to show future events that are considered certain
to happen.
Examples:
The plane leaves at 9:25 tonight.
The term is over on December 16
THE PRESENT PERFECT TENSE
[Has-have + past participle (ed form) of the main verb]
The present tense usually shows an action that began in the past and
goes on to the present or to an indefinite time closely related to the
present.
1. Use the present perfect tense to show an action that began in the
past and is still going on.
Examples:
She has lived in the United States for six years now. (still living in Chicago)
They have waited since ten o’clock. (still waiting)
During the last century, many people have moved from rural to urban areas.
(the movement continues)
I have not finished that problem yet (still unfinished).
2. Use the present perfect tense to show an action that began in the
past and was finished at an indefinite time but is closely related to
the present and/or future.
Examples:
I have already finished those exercises.
You have been absent a great deal lately.
The players have come early.
The players have just arrived.
Paul has rebuilt the engine of his car.
They have recently announced their engagement.
THE PRESENT CONTINUOUS/PROGRESSIVE TENSE
Make the present continuous from the present tense of TO BE and the –ING form
of the main verb (present participle)
The present continuous/progressive tense shows action as a process that
is incomplete but now will end. With an adverb of frequency, the
continuous can show habitual action and in certain situations it can show
future action.
1. Use the present continuous/progressive tense to show action as a
process that is going on now.
Examples:
Our dog is chasing your cat.
The children are playing outside.
2. Use the present continuous/progressive tense to show habitual
action, often with the idea of showing dislike or disapproval.
Examples:
The dog is usually chasing the cat.
They are always asking for special favors.
That little girl is always biting her fingernails
3. Use the present continuous/progressive tense to show future actions
that you are looking forward to now.
Examples:
My mother and father are arriving from New York.
A storm is coming tonight.
We are going to a concert tomorrow night.
THE PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
Present tense of has-have + been + ing
The present perfect continuous tense shows incompleteness or indefiniteness
very close to the present time, often contrasted with now. Just shows that the
activity is very recent.
Examples:
He has been washing the car, but he isn’t now.
She has been feeling ill, but she feels better now.
She has been asking about you.
THE PAST TENSE
Add ed to the simple present
Use the past tense for events that happened at a specific time in the
past. Use the past for a single event or for events that took place over a
period of time if that period is finished.
Examples:
Gerald was in Australia two years ago.
Winifred came here yesterday.
We worked for the same office two years back.
THE PAST PERFECT TENSE
HAD + PAST PARTICIPLE
The past perfect tense shows action in the past that happened before
another past action.
Examples:
Before Karen came here, she had studied in Paris.
After Philip had failed twice, he finally passed his test for his license.
If meaning is clear as to which past came first, past tense is often used for
both verbs.
Ex. Before Karen came here, she studied in Paris.
THE PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE
(WAS/WERE + ING FORM OF THE VERB)
1. Use the past tense to show duration, with emphasis on the length of
time of an act that is no longer going on.
Betsy was training her horse for two years.
They were waiting to buy a house for three years.
2. Use the past continuous tense for an action in the past that was not
completed in the time period mentioned.
I was trying to clean house yesterday. (I did not complete the cleaning)
They were looking for an apartment yesterday.
3. Use the past continuous tense for an action that was going on at a time in
the past when something else happened.
James and I were watching television when lightning struck the house.
THE PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
Use the past perfect continuous tense to show that an action in the remote
past was temporary or that an action was going on when something else
happened.
No one knew that Mr. Allen had a wig because he had been wearing it secretly.
Women had been demanding the right to vote for many years before they finally
got it.
THE FUTURE TENSE
WILL OR SHALL + the infinitive (simple present)
American English uses will for all forms. I will ask you to comply with the
requirements.
British English uses shall with I and we; but reversed for emphasis.
Going to as future. Ex: I am going to walk two miles everyday.
Present of BE + infinitive as future (to show obligation/regulation). Ex:
New students are to register at 2pm.
Present tense as future. Ex: the sun sets at 6:02 this evening.
Present Continuous as future: Ex: We are having dinner at seven this
evening.
THE FUTURE PERFECT TENSE
WILL + HAVE + PAST PARTICIPLE (ED FORM)
To show an action that will be completed in the future.
Examples:
This school will have trained fifty teachers by the end of the year.
I will have finished the revision before noon tomorrow.
By the end of the winter season, more tourist will have visited the place.
THE FUTURE CONTINUOUS TENSE
WILL + BE + ING FORM
To show duration, intention, or a temporary condition in the future.
Ex: I will mail that package for you since I will be walking by the post office
tomorrow.
As long as we live next to you, our dog will be chasing your cat.
Sometimes, I think I will be studying English for the rest of my life.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- WordsDocumento1 paginaWordsJJ RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Vocabulary Development: Jo I. Bartolata, BucalDocumento13 pagineVocabulary Development: Jo I. Bartolata, BucalJJ RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is 'Bitcoin': Digital Currency White PaperDocumento11 pagineWhat Is 'Bitcoin': Digital Currency White PaperJJ RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial ContDocumento25 pagineTutorial ContJJ Rivera75% (4)
- A Group of Eukaryotic, Non-Phototrophic Organisms With Rigid Cell Walls, That Includes Mushrooms, Molds and YeastsDocumento10 pagineA Group of Eukaryotic, Non-Phototrophic Organisms With Rigid Cell Walls, That Includes Mushrooms, Molds and YeastsJJ RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- SolutiontoDocumento25 pagineSolutiontoJJ RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- This Is A File Created by JJDocumento1 paginaThis Is A File Created by JJJJ RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- This Is A File Created by JJDocumento1 paginaThis Is A File Created by JJJJ RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- This Is A File Created by JJDocumento1 paginaThis Is A File Created by JJJJ RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
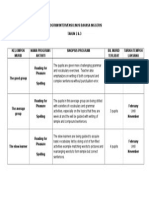
- 10 Grade "B" Daily Routine Ii Bimester Unit 3: Languages: Brain Power Boosters Evaluation Criteria: Needs To Improve 1 Fair 2 Good 3 Excellent 4Documento8 pagine10 Grade "B" Daily Routine Ii Bimester Unit 3: Languages: Brain Power Boosters Evaluation Criteria: Needs To Improve 1 Fair 2 Good 3 Excellent 4Juan T.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental Body MovementsDocumento17 pagineFundamental Body MovementsLavenia Sarcena100% (1)
- Otl545 Module 6 CT TemplateDocumento5 pagineOtl545 Module 6 CT Templateapi-446537912Nessuna valutazione finora
- AI - Data LiteracyDocumento239 pagineAI - Data LiteracyAry AntoniettoNessuna valutazione finora
- 08 - Forward and Backward ChainingDocumento12 pagine08 - Forward and Backward ChainingAndrea DreaminNessuna valutazione finora
- Y6 Literature Lesson PlanDocumento7 pagineY6 Literature Lesson PlanShanty TeoNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is TrustworthinessDocumento12 pagineWhat Is Trustworthinesswwccff100% (1)
- Program Intervensi BIDocumento1 paginaProgram Intervensi BILotus Mines0% (1)
- Comprehension Strategies For Reading Historical FictionDocumento10 pagineComprehension Strategies For Reading Historical Fictionapi-251249268Nessuna valutazione finora
- Your Ipersonic TypeDocumento4 pagineYour Ipersonic TypeJade Clarke-MackintoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Transactional Analysis in Contemporary Psychotherapy (Edited - Richard - G - Erskine)Documento347 pagineTransactional Analysis in Contemporary Psychotherapy (Edited - Richard - G - Erskine)Josiah Hudson100% (1)
- G95 FilipinoDocumento18 pagineG95 FilipinoMelody KillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fs Futsal Coaching Workshops: The Full Stop in Everything Related ToDocumento3 pagineFs Futsal Coaching Workshops: The Full Stop in Everything Related Toasdffdsa32Nessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of A WellDocumento1 paginaProperties of A WellKristine Grace Guillermo100% (2)
- Guias # 2 Segundo Periodo Genitive CaseDocumento7 pagineGuias # 2 Segundo Periodo Genitive Caseferney cordobaNessuna valutazione finora
- Skill Related FitnessDocumento14 pagineSkill Related FitnessTrisha Mae ArmamentoNessuna valutazione finora
- Q3 Tos English 8Documento1 paginaQ3 Tos English 8gayle badorayaNessuna valutazione finora
- MG305 Tutorial - Week 7 - March - 25Documento2 pagineMG305 Tutorial - Week 7 - March - 25s11187304Nessuna valutazione finora
- Symbolism and Environmental DesignDocumento7 pagineSymbolism and Environmental Designshivashz2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Note 7 - The Writing ProcessDocumento55 pagineNote 7 - The Writing ProcessHamza ArainNessuna valutazione finora
- EVALUATIONDocumento11 pagineEVALUATIONiqrrehman0Nessuna valutazione finora
- Silabus EFTDocumento10 pagineSilabus EFTbatulayarNessuna valutazione finora
- HOUSEKEEPING - WEEK 1 UpdatedDocumento5 pagineHOUSEKEEPING - WEEK 1 UpdatedMaria Rizza IlaganNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultimate List of EmotionsDocumento6 pagineUltimate List of Emotions1719008uNessuna valutazione finora
- Automod Key FeaturesDocumento5 pagineAutomod Key Featuresfullkule0% (1)
- B Tech DTDP PDFDocumento2 pagineB Tech DTDP PDF18011BC031 charanNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychoanalytic Process Research StrategiesDocumento378 paginePsychoanalytic Process Research StrategiesbrthstNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes PDFDocumento296 pagineLecture Notes PDFHarish KattaNessuna valutazione finora
- Research AssignDocumento2 pagineResearch AssignKit ViescaNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Management - Course OutlineDocumento3 paginePrinciples of Management - Course OutlineMuhammad Salman Rasheed100% (2)