Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
٣٢٥ Molecular biology Sabah Linjawi ١
Caricato da
Zainab Raik0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
44 visualizzazioni13 pagineTitolo originale
Lecture+1 (2).pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
44 visualizzazioni13 pagine٣٢٥ Molecular biology Sabah Linjawi ١
Caricato da
Zainab RaikCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 13
Lecture 1
Molecular biology ٣٢٥ Sabah Linjawi ١
Proteins
Proteins are polymers of
amino acids covalently linked
through peptide bonds into a
chain.
Within and outside of cells,
proteins serve a myriad of
functions, including structural
roles (cytoskeleton), as
catalysts (enzymes),
transporter to ferry ions and
molecules across membranes,
and hormones.
Molecular biology ٣٢٥ Sabah Linjawi ٢
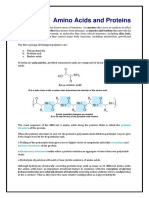
Amino Acids
Proteins are polymers of amino acids joined together by
peptide bonds.
There are 20 different amino acids that make up essentially all
proteins on earth
Each of these amino acids has a fundamental design composed
of a central carbon (also called the alpha carbon) bonded to:
a hydrogen
a carboxyl group
an amino group
a unique side chain or R-group
Molecular biology ٣٢٥ Sabah Linjawi ٣
Amino Acids
Molecular biology ٣٢٥ Sabah Linjawi ٤
Amino Acids
The characteristic that distinguishes one amino acid from
another is its unique side chain, and it is the side chain that
dictates an amino acids chemical properties .
The amino acids are shown with the amino and carboxyl
groups ionized, as they are at physiologic pH.
Molecular biology ٣٢٥ Sabah Linjawi ٥
Amino Acids
Except for glycine, which has a hydrogen as its R-
group, there is asymmetry about the alpha carbon in
all amino acids.
Because of this, all amino acids except glycine can
exist in either of two mirror-image forms.
The two forms - called stereoisomers - are referred to
as D and L amino acids.
With rare exceptions, all of the amino acids in
proteins are L amino acids.
Molecular biology ٣٢٥ Sabah Linjawi ٦
Peptides and Proteins
Amino acids are covalently bonded together in chains by
peptide bonds.
If the chain length is short (say less than 30 amino acids) it is
called a peptide
longer chains are called polypeptides or proteins.
Peptide bonds are formed between the carboxyl group of one
amino acid and the amino group of the next amino acid.
Peptide bond formation occurs in a condensation reaction
involving loss of a molecule of water.
Molecular biology ٣٢٥ Sabah Linjawi ٧
Types of Proteins
Based upon chemical composition, proteins are divided into
two major classes:
1- simple proteins, which are composed of only amino acids
2- conjugated proteins, which are composed of amino acids
and additional organic and inorganic groupings, which are
called prosthetic groups.
Conjugated proteins include:
glycoproteins, which contain carbohydrates
lipoproteins, which contain lipids
nucleoproteins, which contain nucleic acids
Molecular biology ٣٢٥ Sabah Linjawi ٨
Classified by biological function
proteins include the enzymes, which are responsible for
catalyzing the thousands of chemical reactions of the living
cell
keratin, elastin, and collagen, which are important types of
structural, or support, proteins
hemoglobin and other gas transport proteins; ovalbumin,
casein, and other nutrient molecules
antibodies, which are molecules of the immune system
protein hormones, which regulate metabolism
proteins that perform mechanical work, such as actin and
myosin, the contractile muscle proteins.
Molecular biology ٣٢٥ Sabah Linjawi ٩
Conjugated proteins
These proteins consist from protein and other compounds,
which are called according to the group associated with it,
such as:
1- Nucleoproteins: protein and nucleic acid which are found in
the nucleus
2- Chromoproteins: Proteins and colored compounds such as
hemoglobin in the blood is associated with an iron (Fe +2), as
well as chlorophyll, the green protein is associated with the
element magnesium (Mg +2) and may not contain an element
of the group such as proteins associated with melanin in hair
Molecular biology ٣٢٥ Sabah Linjawi ١٠
Conjugated proteins
Molecular biology ٣٢٥ Sabah Linjawi ١١
Conjugated proteins
3- Phosphoproteins: Proteins and the phosphate group such as
Casein in milk and Vitellin in the egg yolk
4- Glycoproteins :Protein and sugars,the carbohydrates part
consists of short-chain branching, and plays an important role
in the cell, such as some enzymes, hormones and antibodies
5- Lipoproteins : Protein and fat which are found in cell
membranes and blood plasma and egg yolk
Molecular biology ٣٢٥ Sabah Linjawi ١٢
References
www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/genetics/.../prostruct.html
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein_structure
www.chemguide.co.uk/organicprops/.../proteinstruct.html
www.rothamsted.ac.uk/notebook/courses/guide/prot.htm
www.friedli.com/herbs/phytochem/proteins.html
themedicalbiochemistrypage.org/protein-structure.html
Molecular Biology. P.C. Turner, A.G. Mclennan, A.D. Bates &
M.R.H. White.School of Biological Sciences, University of Liverpool,
Liverpool, UK. Second edition. BIOS Scientific Publishers, 2000.
Molecular biology ٣٢٥ Sabah Linjawi ١٣
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Clinical Chemistry - ProteinsDocumento6 pagineClinical Chemistry - Proteinsrosellae.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Myoglobin Alpha Helices X-Ray Crystallography Max Perutz Sir John Cowdery Kendrew 1958 Nobel Prize in ChemistryDocumento11 pagineMyoglobin Alpha Helices X-Ray Crystallography Max Perutz Sir John Cowdery Kendrew 1958 Nobel Prize in Chemistryashu548836Nessuna valutazione finora
- ProteinsDocumento38 pagineProteinseugieniogienioNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 ProteinsDocumento42 pagine3 ProteinsTeam BEENessuna valutazione finora
- ZO 503 Physiological Chemistry by Dr.S.S.KunjwalDocumento22 pagineZO 503 Physiological Chemistry by Dr.S.S.KunjwalAbhishek Singh ChandelNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological Molecules 2 2013Documento32 pagineBiological Molecules 2 2013Eugenia Migranova100% (1)
- ProteinDocumento23 pagineProteinsamantha garciaNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesDocumento5 pagineCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesSIDHARTH SBNessuna valutazione finora
- Proteins Structure and FunctionsDocumento48 pagineProteins Structure and FunctionsKouta SanNessuna valutazione finora
- 3-Bch303 Chapter3 Protein Structure and FunctionDocumento105 pagine3-Bch303 Chapter3 Protein Structure and Functionsandaramae04Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biomedical Analysis Techniques and MethodsDocumento25 pagineBiomedical Analysis Techniques and MethodsKrisan Mallion LuisNessuna valutazione finora
- Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary Structures of A ProteinDocumento21 paginePrimary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary Structures of A ProteinDALITSO CHIKOYA100% (1)
- Lecture 3-ProteinsDocumento9 pagineLecture 3-ProteinsOminousCroakNessuna valutazione finora
- PROTEINDocumento90 paginePROTEINYo1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chem InvestigatoryDocumento22 pagineChem InvestigatoryDevendra Yadav78% (40)
- Vizcarra, Alyssa Marie D. APSY 1-3Documento5 pagineVizcarra, Alyssa Marie D. APSY 1-3ALYSSA MARIE VIZCARRANessuna valutazione finora
- Macromolecule - ProteinDocumento50 pagineMacromolecule - Proteinadinda tyasprabandariNessuna valutazione finora
- Proteins: A Protein Is A Naturally Occurring, Unbranched Polymer in Which The Monomer Units Are Amino AcidsDocumento45 pagineProteins: A Protein Is A Naturally Occurring, Unbranched Polymer in Which The Monomer Units Are Amino Acidsdarleen joy dimaanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Industrial Chemistry: Bahir Dar UniversityDocumento25 pagineDepartment of Industrial Chemistry: Bahir Dar UniversityFikere'ab HabtamuNessuna valutazione finora
- Proteins: Proteins Are Large Biomolecules, or Macromolecules, Consisting of One orDocumento15 pagineProteins: Proteins Are Large Biomolecules, or Macromolecules, Consisting of One orKaleem KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOCHEM LarozaDocumento9 pagineBIOCHEM LarozaDianne LarozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein N.2023Documento35 pagineProtein N.2023ea4184386Nessuna valutazione finora
- BiochemistryDocumento130 pagineBiochemistryshiyntumNessuna valutazione finora
- Proteins: Nature's WorkhorsesDocumento4 pagineProteins: Nature's WorkhorsesSatheesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- ProteinDocumento251 pagineProteinJohn BrandonNessuna valutazione finora
- This Week's Lecture Topics: - Cell Chemistry and BioenergeticsDocumento27 pagineThis Week's Lecture Topics: - Cell Chemistry and BioenergeticsHirad SalehnezhadNessuna valutazione finora
- 2Documento5 pagine2Nunee AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- ProteinsDocumento10 pagineProteinsRishikesh BhintadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acids and Proteins: Bs I Biochemistry by Ms Nimra MaqsoodDocumento14 pagineAmino Acids and Proteins: Bs I Biochemistry by Ms Nimra MaqsoodSufyan MaharNessuna valutazione finora
- Living OrganizationDocumento10 pagineLiving OrganizationAbbas TalibNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology: (Guidelines For The Preparation of The Entrance Exam To MSC Program in Biotechnology)Documento304 pagineBiology: (Guidelines For The Preparation of The Entrance Exam To MSC Program in Biotechnology)Hà Anh Minh LêNessuna valutazione finora
- Proteins: Submitted To: Mam Saima Khubaib Submitted By: Muhammad HannanDocumento13 pagineProteins: Submitted To: Mam Saima Khubaib Submitted By: Muhammad HannanMuhammad HannanNessuna valutazione finora
- AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND PROTEINS STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONSDocumento43 pagineAMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND PROTEINS STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONSAlemayehu MelkamuuNessuna valutazione finora
- 04b AP Bio The Structure and Function of Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDocumento51 pagine04b AP Bio The Structure and Function of Proteins and Nucleic Acidsrahul singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Class1, Macromolecular AnalysisDocumento34 pagineClass1, Macromolecular AnalysisArup SheeNessuna valutazione finora
- BiomoleculesDocumento117 pagineBiomoleculesBhaski MadhappanNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acids and Proteins ExplainedDocumento17 pagineAmino Acids and Proteins ExplainedAbhijat Jha100% (1)
- Unit 14:-Biomoulecules: ProjectDocumento4 pagineUnit 14:-Biomoulecules: ProjectAnkit KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry - Module 4Documento18 pagineBiochemistry - Module 4ricky fecaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry of Cell-1Documento101 pagineChemistry of Cell-12022mcb1267Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2.4. PolysaccharidesDocumento12 pagine2.4. PolysaccharidesCH Rajan GujjarNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein PDFDocumento27 pagineProtein PDFSumaiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- BiomoleculesDocumento4 pagineBiomoleculesiyahh5.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 7 ProteinsDocumento140 pagineUnit 7 ProteinsJan Ariel AficialNessuna valutazione finora
- Proteins Structure & Composition: DR Mohamed AbumareeDocumento24 pagineProteins Structure & Composition: DR Mohamed Abumareeapi-19824406Nessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Proteins from Primary to Quaternary StructureDocumento10 pagineUnderstanding Proteins from Primary to Quaternary StructureDarshan RNessuna valutazione finora
- Karakteristik Protein Dalam Upaya Menentukan Metode Uji Yang TepatDocumento12 pagineKarakteristik Protein Dalam Upaya Menentukan Metode Uji Yang Tepataxl___Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class 11 Biology NotesDocumento147 pagineClass 11 Biology NotesreilyshawnNessuna valutazione finora
- ADVANCED BIOCHEMISTRYDocumento70 pagineADVANCED BIOCHEMISTRYCik Syin100% (1)
- 1E Activity No. 4.3 Essay - 1EDocumento4 pagine1E Activity No. 4.3 Essay - 1EZeal Alexis MontellorNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein PDFDocumento15 pagineProtein PDFmradu1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Chemistry Chapter # 3 ProteinsDocumento11 pagineBio Chemistry Chapter # 3 ProteinsEmo tionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Proteins Structure, Classification and Biological Functions: DR - AchyuthaDocumento33 pagineProteins Structure, Classification and Biological Functions: DR - AchyuthaMohammad AadilNessuna valutazione finora
- Local Media5209454088282345Documento19 pagineLocal Media5209454088282345Michaela Lyn Parilla MianaNessuna valutazione finora
- 252-Article Text-1458-2-10-20230225dididikdjejejejdjdjdDocumento9 pagine252-Article Text-1458-2-10-20230225dididikdjejejejdjdjdJuan SitinjakNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomolecules: MacromoleculesDocumento5 pagineBiomolecules: MacromoleculesPaulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 7 Biological MoleculesDocumento38 pagineModule 7 Biological MoleculesJoana CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDa EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- A-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDa EverandA-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- Ralph's Healthy Choice: L-Glutathione - Science, Production & BenefitsDa EverandRalph's Healthy Choice: L-Glutathione - Science, Production & BenefitsNessuna valutazione finora
- ٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Documento16 pagine٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Zainab RaikNessuna valutazione finora
- ٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Documento16 pagine٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Zainab RaikNessuna valutazione finora
- ٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Documento15 pagine٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Zainab RaikNessuna valutazione finora
- ٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Documento19 pagine٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Zainab RaikNessuna valutazione finora
- ٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Documento15 pagine٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Zainab RaikNessuna valutazione finora
- ٣٢٥ Molecular Biology ١ Sabah LinjawiDocumento15 pagine٣٢٥ Molecular Biology ١ Sabah LinjawiZainab RaikNessuna valutazione finora
- ٣٢٥ Molecular biology Sabah Linjawi ١Documento13 pagine٣٢٥ Molecular biology Sabah Linjawi ١Zainab RaikNessuna valutazione finora
- ٣٢٥ Molecular biology Sabah Linjawi ١Documento13 pagine٣٢٥ Molecular biology Sabah Linjawi ١Zainab RaikNessuna valutazione finora
- 6441 Topper 21 129 510 2 8550 Amines and Aromatic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Up201612091904 1481290486 9301 PDFDocumento45 pagine6441 Topper 21 129 510 2 8550 Amines and Aromatic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Up201612091904 1481290486 9301 PDFSakethNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Cleaner Production: Sabzoi Nizamuddin, Muhammad Jamal, Rebecca Gravina, Filippo GiustozziDocumento12 pagineJournal of Cleaner Production: Sabzoi Nizamuddin, Muhammad Jamal, Rebecca Gravina, Filippo GiustozziHiba GhandourNessuna valutazione finora
- Aas 2022Documento42 pagineAas 2022ANDREA QUIROZ ARCILANessuna valutazione finora
- Studies of Helicteres Isoras Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Activity ReviewDocumento6 pagineStudies of Helicteres Isoras Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Activity ReviewEditor IJTSRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Geosciences 09 00431 v2Documento17 pagineGeosciences 09 00431 v2omkarindulkar21Nessuna valutazione finora
- NDT Lecture - CarbohydratesDocumento7 pagineNDT Lecture - Carbohydratesgelean payodNessuna valutazione finora
- F. Moreno, Rachel Anne Melc 4 Activity 3 Calvin CycleDocumento3 pagineF. Moreno, Rachel Anne Melc 4 Activity 3 Calvin CycleF. Moreno, Rachel AnneNessuna valutazione finora
- Rubber Properties Chart PDFDocumento1 paginaRubber Properties Chart PDFArasarethina KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 0715 MCG (6) - 1 PDFDocumento7 pagineChemistry 0715 MCG (6) - 1 PDFTalatouremi FruNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Oils ExtractionDocumento17 pagineEssential Oils ExtractionAmaan RizviNessuna valutazione finora
- Regulations on Managing Chemicals and Hazardous WastesDocumento47 pagineRegulations on Managing Chemicals and Hazardous WastesLilvic Galera-SabladNessuna valutazione finora
- Panjab University Syllabus BSC III Zoology B Option II (Economic Entomology and Pest Management)Documento2 paginePanjab University Syllabus BSC III Zoology B Option II (Economic Entomology and Pest Management)Dr Arvinder Pal Singh (A P Singh)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Noble 2014Documento13 pagineNoble 2014Restu DanikaNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 Acid Base and Buffer MS 2021Documento25 pagine05 Acid Base and Buffer MS 2021VayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Obtain Natural Hydroxytyrosol Concentrate from Olive WasteDocumento13 pagineObtain Natural Hydroxytyrosol Concentrate from Olive Wastesalvatore raffaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case StudyDocumento46 pagineCase StudyKRISCHELLE MAGRACIANessuna valutazione finora
- Bio-Based Composites Made From Agrowaste: Lucas Whale & Suviti ChariDocumento38 pagineBio-Based Composites Made From Agrowaste: Lucas Whale & Suviti CharisuvicNessuna valutazione finora
- EMULSIONSDocumento39 pagineEMULSIONSDanielNessuna valutazione finora
- Genamin BTLF (Version 2010) - NewDocumento3 pagineGenamin BTLF (Version 2010) - NewMaximiliano Mackevicius100% (1)
- Effect of Packaging On Mopane Worm QualityDocumento20 pagineEffect of Packaging On Mopane Worm Qualityondiek_ja_rawaloNessuna valutazione finora
- First Periodic Test in Science 5 19 20Documento7 pagineFirst Periodic Test in Science 5 19 20Florence Lizardo Liwanag100% (1)
- l10 Structure, Classification Biosynthesis of ProstaglandinsDocumento22 paginel10 Structure, Classification Biosynthesis of Prostaglandinsbilawal khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Kayonga Louis 1996Documento92 pagineKayonga Louis 1996eman mamdohNessuna valutazione finora
- Dicyclopentadiene Material Safety Data SheetDocumento6 pagineDicyclopentadiene Material Safety Data SheetOmar Eduardo Davalillo MarínNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization of Natural Dye Extraction From Basella Alba Linn. (Alugbate) FRUITSDocumento35 pagineOptimization of Natural Dye Extraction From Basella Alba Linn. (Alugbate) FRUITSDante Jr. BitoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Food Chemistry RevisionDocumento3 pagineFood Chemistry RevisionHigh HopesNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 7 Lesson1 - General Biology IDocumento32 pagineMODULE 7 Lesson1 - General Biology IAlvin PaboresNessuna valutazione finora
- Table 1-Typical Rubber Properties Used in The Oil WellDocumento8 pagineTable 1-Typical Rubber Properties Used in The Oil WellabodolkuhaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Personal Care & Cosmetics: Olorol 95Documento1 paginaPersonal Care & Cosmetics: Olorol 95Mohamed AdelNessuna valutazione finora
- The Future of Sustainable Cleaning Products to 2026: Key Drivers and TrendsDocumento1 paginaThe Future of Sustainable Cleaning Products to 2026: Key Drivers and TrendsLEIDY YULIANANessuna valutazione finora