Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
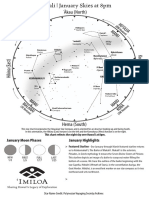
February 2019 Sky Chart
Caricato da
Honolulu Star-AdvertiserCopyright
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
February 2019 Sky Chart
Caricato da
Honolulu Star-AdvertiserCopyright:
HO
ori AU (NW'O
) Ho LU
zon
H L
MA rizon A
'O
KO
NU
U
)
(NE
N
MA
MA
M NU
U
(SE ALA
N
A zon)
MA
Ho N N
riz AI
o KO Hori
n)
(SW
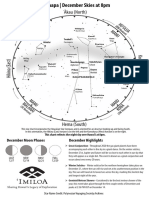
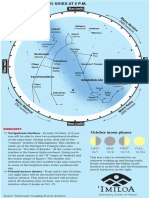
This star chart incorporates the Hawaiian Star Compass and is oriented for an observer looking up and facing South.
In this orientation, the Hikina (East) horizon is on the left and the Komohana (West) horizon is on the right.
This chart reflects the night sky over Hawai'i at 8pm.
February Moon Phases February Highlights
> Orion Nebula - Amongst the starline of Kekaomakli’i, a multitude of
famous astronomical objects are easily spotted. Beneath the famous three
stars of Kaheiheionākeiki, Orion we can see a few stars that are often
considered to be Orion’s sword. Behind these stars, we can sight faint
NEW FIRST FULL LAST fuzziness that is the glow from the Orion Nebula (M42), a larger stellar
2/4 2/12 2/19 2/26
nursery and the closest region of massive star formation to Earth.
> Supermoon - In February, the full moon will fall on the day when the
moon is at its closest physical position to the Earth. The moon does not
orbit around Earth in a perfect circle; it orbits in an ellipse or oval shape,
which means that the moon’s distance from Earth changes as it orbits. The
moon’s closest physical position to Earth is called perigee; the moon
passes through its perigee point every month and is often thought to look
bigger in the sky when it is at this point. A supermoon occurs when the
moon is full and at its perigee.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- October 2021 Sky ChartDocumento1 paginaOctober 2021 Sky ChartHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- January 2021 Sky ChartDocumento1 paginaJanuary 2021 Sky ChartHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- November 2020 Sky ChartDocumento1 paginaNovember 2020 Sky ChartHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- February 2022 Sky ChartDocumento1 paginaFebruary 2022 Sky ChartHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- November 2021 SkywatchDocumento1 paginaNovember 2021 SkywatchHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- January 2022 SkywatchDocumento1 paginaJanuary 2022 SkywatchHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- December 2021 Sky ChartDocumento1 paginaDecember 2021 Sky ChartHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- May 2021 Sky ChartDocumento1 paginaMay 2021 Sky ChartHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- August 2020 Sky ChartDocumento1 paginaAugust 2020 Sky ChartHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- August 2021 Sky ChartDocumento1 paginaAugust 2021 Sky ChartHonolulu Star-Advertiser100% (1)
- December 2020 Sky ChartDocumento1 paginaDecember 2020 Sky ChartHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- September SkywatchDocumento1 paginaSeptember SkywatchHonolulu Star-Advertiser100% (1)
- Skywatch May 2022Documento1 paginaSkywatch May 2022Honolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Star Chart June 2022Documento1 paginaStar Chart June 2022Honolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Malaki (March) Skies at 8 P.M.: Manu Ho OluaDocumento1 paginaMalaki (March) Skies at 8 P.M.: Manu Ho OluaHonolulu Star-Advertiser100% (1)
- May 2023 Sky WatchDocumento1 paginaMay 2023 Sky WatchHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- January 2023 Sky WatchDocumento1 paginaJanuary 2023 Sky WatchHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Scy5 Unit 9 Phases of The MoonDocumento23 pagineScy5 Unit 9 Phases of The MoonMARIAYEE A/P PERUMAL MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- April 2022 Sky ChartDocumento1 paginaApril 2022 Sky ChartHonolulu Star-Advertiser100% (1)
- Celestial SpehereDocumento27 pagineCelestial Spehererishithhr rajeevNessuna valutazione finora
- Lun Nar Pha Ase: From Wik Kipedia, The F Ree Encyclope EdiaDocumento10 pagineLun Nar Pha Ase: From Wik Kipedia, The F Ree Encyclope EdiaFranko MilovanNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 The Phases of The MoonDocumento5 pagine1 The Phases of The Mooncharles blairNessuna valutazione finora
- Coordinate System With Longi and LatiDocumento24 pagineCoordinate System With Longi and LatiBaby Hazel RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lunar Map Will TirionDocumento7 pagineLunar Map Will TirionFellipy SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- The MoonsDocumento5 pagineThe MoonsChristine Loise T. MarianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar For ScienceDocumento24 pagineSeminar For ScienceSankar PNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 en FinalDocumento19 pagineChapter 3 en FinalLidijaSpaseskaNessuna valutazione finora
- MOONDocumento43 pagineMOONArthur SerdeñaNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 - Lecture Constellations Nov 2009Documento21 pagine02 - Lecture Constellations Nov 2009api-240330821Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6B15PHY Astronomy & AstrophysicsDocumento62 pagine6B15PHY Astronomy & AstrophysicsDeepu JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- LESSON 3 4th QUarter Eclipses PSDocumento3 pagineLESSON 3 4th QUarter Eclipses PSKhate G. PrestozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jyotisha Hindu Astrology - Ei PDFDocumento9 pagineJyotisha Hindu Astrology - Ei PDFGgffghNessuna valutazione finora
- Celestial Sphere PPT.NDocumento44 pagineCelestial Sphere PPT.NMary MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Constellation Grade 9 IMDocumento24 pagineConstellation Grade 9 IMCeleste BawagNessuna valutazione finora
- Fases de La LunaDocumento5 pagineFases de La LunaLUIS DIEGO UREÑA SEGURANessuna valutazione finora
- Stars, Constellations & Celestial CordinatesDocumento29 pagineStars, Constellations & Celestial CordinatesvrihadNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 8 CELESTIAL NAVIGATIONDocumento26 pagineCH 8 CELESTIAL NAVIGATIONJeet Singh100% (1)
- Apelila (April) Skies at 8 P.M.Documento1 paginaApelila (April) Skies at 8 P.M.Honolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Exploring The Cosmos - An Introduction To AstronomyDa EverandExploring The Cosmos - An Introduction To AstronomyNessuna valutazione finora
- Discovering The Essential UniverseDocumento24 pagineDiscovering The Essential UniverseShanelle OwensNessuna valutazione finora
- Constellations Hand OutDocumento2 pagineConstellations Hand OutMckenrie AnasNessuna valutazione finora
- Penumbra LDocumento1 paginaPenumbra LHartford CourantNessuna valutazione finora
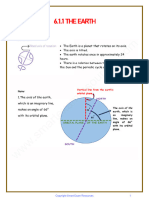
- 6 1 1-The-EarthDocumento5 pagine6 1 1-The-EarthCK LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Moon Phases and EclipsesDocumento12 pagineMoon Phases and EclipsesDaisyNessuna valutazione finora
- Compás Estelar Hawaiano - Hawaiian Star Compass and Unit CircleDocumento4 pagineCompás Estelar Hawaiano - Hawaiian Star Compass and Unit Circleanzaeduardo1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Astronomy LessonDocumento432 pagineAstronomy LessonMaryam Ali100% (1)
- Precession of The Equinoxes and Its Importance in Calendar MakingDocumento13 paginePrecession of The Equinoxes and Its Importance in Calendar MakingJayesh NehareNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Phases of The MoonDocumento4 pagine8 Phases of The MoonBhel D. GuevarraNessuna valutazione finora
- How We Come To Realize That The Earth Is Not The Center of The Universe ReadDocumento94 pagineHow We Come To Realize That The Earth Is Not The Center of The Universe ReadreiNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Ess All The WordsDocumento2 pagineActivity Ess All The WordsAdriana HurtadoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cycles of The MoonDocumento31 pagineThe Cycles of The MoonPrasad ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Moon PhasesDocumento7 pagineMoon PhasesResearchingPub100% (4)
- Engineering AstronomyDocumento13 pagineEngineering AstronomyFayaz S NabilNessuna valutazione finora
- Moon PhasesDocumento1 paginaMoon PhasesSonny Boy SajoniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp SC 3 - Chapter 12Documento8 pagineExp SC 3 - Chapter 12megamind publicationNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 - Positional AstronomyDocumento19 pagine04 - Positional AstronomySiddharth BhattNessuna valutazione finora
- 2023 Legislative Report Release To LegislatureDocumento22 pagine2023 Legislative Report Release To LegislatureHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- DOT OST 2023 0186 0010 - Attachment - 1Documento8 pagineDOT OST 2023 0186 0010 - Attachment - 1Honolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Report From Special Counsel Robert K Hur February 2024Documento388 pagineReport From Special Counsel Robert K Hur February 2024New York Post100% (7)
- Indictments Against Sebastian Mahkwan and Paul CameronDocumento11 pagineIndictments Against Sebastian Mahkwan and Paul CameronHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Report From Special Counsel Robert K Hur February 2024Documento388 pagineReport From Special Counsel Robert K Hur February 2024New York Post100% (7)
- DOT OST 2023 0186 0009 - Attachment - 1Documento14 pagineDOT OST 2023 0186 0009 - Attachment - 1Honolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- CSA PRC State Sponsored Cyber Living Off The LandDocumento24 pagineCSA PRC State Sponsored Cyber Living Off The LandHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Ready For Kindergarten AssessmentDocumento1 paginaReady For Kindergarten AssessmentHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Meet The 2024 Hawaii State LegislatureDocumento1 paginaMeet The 2024 Hawaii State LegislatureHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Letter To ParentsDocumento1 paginaLetter To ParentsHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- EPA Drinking Water Complaints Investigation ReportDocumento9 pagineEPA Drinking Water Complaints Investigation ReportHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Hawaii Department of Health MemoDocumento18 pagineHawaii Department of Health MemoHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- The Honolulu Star-Advertiser All-State Football Team 2023Documento1 paginaThe Honolulu Star-Advertiser All-State Football Team 2023Honolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Attempted Murder Suspect Sidney Tafokitau WantedDocumento1 paginaAttempted Murder Suspect Sidney Tafokitau WantedHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- HSTA 2023 2027 Member Settlement SummaryDocumento6 pagineHSTA 2023 2027 Member Settlement SummaryHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- FINAL 20230810 CWRM W Maui Fire LTR From WMLCDocumento3 pagineFINAL 20230810 CWRM W Maui Fire LTR From WMLCHonolulu Star-Advertiser100% (1)
- GOP House Committee Letter To Hawaiian Electric, Hawaii Public Utilities Commission and Hawai'i State Energy OfficeDocumento4 pagineGOP House Committee Letter To Hawaiian Electric, Hawaii Public Utilities Commission and Hawai'i State Energy OfficeHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Dallas Pearce, Redacted Investigation Report FinalDocumento53 pagineDallas Pearce, Redacted Investigation Report FinalHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Top HMSA Officers' CompensationDocumento1 paginaTop HMSA Officers' CompensationHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- All-State Softball TeamDocumento1 paginaAll-State Softball TeamHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- BOR Settlements RPRT Roh8-12 FY22Documento10 pagineBOR Settlements RPRT Roh8-12 FY22Honolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- All-State Boys Soccer TeamDocumento1 paginaAll-State Boys Soccer TeamHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- All-State Girls Soccer TeamDocumento1 paginaAll-State Girls Soccer TeamHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Hawaii Baseball Report - July 16, 2023Documento1 paginaHawaii Baseball Report - July 16, 2023Honolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- May 2023 Sky WatchDocumento1 paginaMay 2023 Sky WatchHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- CSS Hawaii Final Report For Redaction Redacted FinalDocumento570 pagineCSS Hawaii Final Report For Redaction Redacted FinalHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- CSS Hawaii Final Report For Redaction Redacted FinalDocumento570 pagineCSS Hawaii Final Report For Redaction Redacted FinalHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Police Statement From Principal Murphy To HPDDocumento6 paginePolice Statement From Principal Murphy To HPDHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Text of Mayor Rick Blangiardi's State of City SpeechDocumento16 pagineFull Text of Mayor Rick Blangiardi's State of City SpeechHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- All-State Boys Basketball TeamDocumento1 paginaAll-State Boys Basketball TeamHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Atg Boardgame Future PerfectDocumento1 paginaAtg Boardgame Future PerfectLorena MancillaNessuna valutazione finora
- LKG English Activity Book FinalDocumento94 pagineLKG English Activity Book FinalManoj SNessuna valutazione finora
- No Sanskrit, Hindi, Marathi, Telugu, Gujarati Malayalam TamilDocumento4 pagineNo Sanskrit, Hindi, Marathi, Telugu, Gujarati Malayalam TamilSup_Rao100% (1)
- Week 7-Comets, Asteroids and MeteoroidsDocumento49 pagineWeek 7-Comets, Asteroids and MeteoroidsArnold Ballen FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Scarborough Shoal, Also Known As Scarborough Reef, Reef (MasinlocDocumento5 pagineScarborough Shoal, Also Known As Scarborough Reef, Reef (MasinlocGrace Angelie C. Asio-SalihNessuna valutazione finora
- Nitya Yoga (Panchanga)Documento7 pagineNitya Yoga (Panchanga)K P SiinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure PDFDocumento34 pagineAtomic Structure PDFDHR GAMINGNessuna valutazione finora
- Equator Passes Through 13 Countries These AreDocumento11 pagineEquator Passes Through 13 Countries These AreVinod yadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Prono Peru EngDocumento15 pagineProno Peru EngSantiago GuttiNessuna valutazione finora
- Jataka ChandrikaDocumento14 pagineJataka ChandrikalovershivaNessuna valutazione finora
- Forces W.B-NewDocumento11 pagineForces W.B-NewAnanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Appsc Static Quiz - 2023Documento115 pagineAppsc Static Quiz - 2023tejeswararaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Gochara PDFDocumento2 pagineGochara PDFnp091083100% (1)
- Mars and SaturnDocumento37 pagineMars and SaturnAdriana RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 Follow The Drinking Gourd (PDF Library)Documento3 pagine04 Follow The Drinking Gourd (PDF Library)Julia Villaluenga AbenojarNessuna valutazione finora
- Katalog MikroskopDocumento14 pagineKatalog MikroskopDewi Endar YatunNessuna valutazione finora
- Silicon Solar Cell Enhancement by Using Au NanoparticlesDocumento8 pagineSilicon Solar Cell Enhancement by Using Au NanoparticlesInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- Dawn of The JediDocumento224 pagineDawn of The JediPablo Edo Castro0% (2)
- Didactical Proposal JustificationDocumento5 pagineDidactical Proposal JustificationLuz Astrid ariza hernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chaotic Dynamics An Introduction Based On Classical MechanicDocumento427 pagineChaotic Dynamics An Introduction Based On Classical MechanicMichael Andres Gonzalez Henao100% (1)
- On Solar System (Prithviraj Singh Class 9th E)Documento18 pagineOn Solar System (Prithviraj Singh Class 9th E)JAIRAJ SINGH100% (3)
- 2018 Photopiller of The YearDocumento385 pagine2018 Photopiller of The YearFerran Amelibia100% (1)
- Free Space Optical Communication Tip-Tilt-Mirror BrochureDocumento15 pagineFree Space Optical Communication Tip-Tilt-Mirror Brochuresandeep kumar100% (1)
- Astronomy and Mathematics in Ancient IndiaDocumento11 pagineAstronomy and Mathematics in Ancient IndiaAvvaru Srinivasa RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding The Universe Term PaperDocumento24 pagineUnderstanding The Universe Term PaperChooniTayNessuna valutazione finora
- Delayed MarriageDocumento4 pagineDelayed MarriageAcharya RamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Summative in Physical Science 4th QDocumento4 pagineSummative in Physical Science 4th QJoelynBitosNessuna valutazione finora
- CH#5 F.SC I Physics Total Marks 40: Q#1 Encircle The Best OptionDocumento1 paginaCH#5 F.SC I Physics Total Marks 40: Q#1 Encircle The Best OptionQaisar RiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Grace DocumentatioDocumento62 pagineGrace Documentationajill10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tamil Calender in TamilDocumento7 pagineTamil Calender in TamilMohan RajNessuna valutazione finora