Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
BK7 Jawapan Kertas 2
Caricato da
Iza MohdSabriDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
BK7 Jawapan Kertas 2
Caricato da
Iza MohdSabriCopyright:
Formati disponibili
SULIT 1 4541/2
BK7 – Peperiksaan Percubaan 2016
SIJIL PELAJARAN MALAYSIA
4541/2 KIMIA
Kertas 2
Section A
1 (a) (i) Contact Process 1
(ii) H2SO4 1
(b) (i) SO2 1
(ii) SO2 react with rain water 1
Produced acid rain 1 ...2
(c) (i) NH3 1
(ii)
Urea, (NH2)2CO = 2 × 14 × 100
2(14+2)+12+16
= 46.67 % 1
Compound Y /ammonium
sulphate, (NH4)2SO4 = 2 × 14 × 100
2(14+4) + 32 + 4(16)
= 21.21 % 1
Better Fertilizer : Urea 1 ...3
TOTAL 9
2 (a) Base to ascending order of proton number 1
(b) C and E 1
(c) Group 2 and Period 3 1
Have 2 valence electron and 3 shells occupied with electron 1 ...2
(d) C more reactive than E. 1
Nuclei attraction toward electrons in C is stronger than E. 1
It is easier for atom C to attract/gain electron. 1 …3
(e) D, E, A, B, C 1
(f) D 1
TOTAL 9
BK7 - TRIAL SPM 2016 MARKING SCHEME
SULIT 2 4541/2
3 (a) Carbon 1
(b) Formula that show the simplest ratio of atom of each element 1
in a compound.
(c) (i) C4H8O2 1
C2H4O 1 ...2
(ii) Similarity : Type of element // C, H, O 1
Difference : Number of atom of each element 1 ...2
(d) (i) 2C4H8O2 + Mg → (C3H7COO)2Mg + H2 1+1 ...2
(ii) Mol Mg = 0.5 1
Mass Mg = 0.5 × 24 // 12 g 1 ...2
TOTAL 10
4 (a) Change of volume of gas released per time taken 1
(b) Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2 1+1 ...2
(c) Size of reactant / Total surface area 1
(d) (i) Experiment I :
50 = 10 cm3 min-1 // 0.167 cm3 s-1
5
Experiment II :
50 = 16.667 cm3 min-1 // 0.278 cm3 s-1
3
1. Correct value for both experiment 1
2. Correct unit for both value 1 ...2
(ii) 1. Size of magnesium in Experiment II is smaller than
Experiment I // Total surface area of magnesium in
Experiment II is greater than Experiment I. 1
2. Frequency of collision between magnesium atoms and
hydrogen ions, H+ in Experiment II is higher than
Experiment I. 1
3. Frequency of effective collision between magnesium
atoms and hydrogen ions, H+ in Experiment II is higher
than Experiment I. 1 ...3
(e) The mass of magnesium in both experiments are the same. 1
TOTAL 10
BK7 - TRIAL SPM 2016 MARKING SCHEME
SULIT 3 4541/2
5 (a) Chemical substance that ionises in water to produce hydroxide 1
ion / OH- ion.
(b) (i) Strong alkali : R 1
(ii) Weak acid :Q 1 ...2
(c) Dissolve the malic acid in water. 1
Add zinc/zinc carbonate* into the malic acid solution. 1
Bubbles of gas released. 1 ...3
(d) (i) Number of mole of NaOH = 2.0 × 500
1000
= 1 mol 1
Mass of NaOH = 1 × 40
= 40 g 1 ...2
(ii) 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O 1
Ma × 25.0 = 1
2.0 × 50.0 2 1
Ma = 2.0 mol dm-3 1 ...3
TOTAL 11
6 (a) (i) Copper 1
(ii) The concentration / number of copper ion decrease 1
(iii) The oxidation number of magnesium change from 0 to +2 //
The oxidation number of copper change from +2 to 0. 1
[Change in oxidation number] 1 ...2
(iv) Mg + CuSO4 → MgSO4 + Cu 1
(v) No reaction. 1
Copper is less electropositive than magnesium. 1 ...2
(b) (i) Presence of oxygen and water. 1
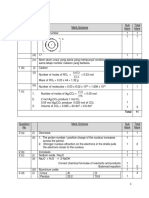
(ii)
Fe Fe2+ +2e
Water droplet O2
e
Iron
1. Label for iron, water and oxygen 1
2. Ionization of iron in the water droplet (at anode) 1
3. Flow of electron in the iron to the edge of water droplet 1 ...3
TOTAL 11
BK7 - TRIAL SPM 2016 MARKING SCHEME
SULIT 4 4541/2
Section B
7 (a) Electrode P : Concentration of electrolyte 1
Electrode Q : Position of the ions in the electrochemical series 1 2
(b) Electrode P Electrode Q
Ions attracted to Cl- and OH- Na+ and H+ 1+ 1
Names the ions
selectively Cl- H+
discharged 1+1
+
Reason why the Concentration of H ion is placed
ions are Cl- is higher than lower than Na+ in
selectively OH- the 1+1
discharged electrochemical
series
Observation Greenish yellow Colourless gas is
gas is released released 1+1 ...8
(c) Cell X Cell Y
Type of cell Electrolytic cell Voltaic cell 1
The energy Electrical energy Chemical energy to
change to chemical electrical energy 1
energy
The terminal of Positive terminal / Positive terminal / 1
the cell anode: Copper cathode: copper
Negative terminal Negative terminal / 1
/ cathode: copper anode: aluminium
Ions present in Cu 2+, H+
the electrolyte SO42- , OH- 1
Observation Anode: Negative
Thinner terminal/Aluminium
plate: thinner 1
Cathode: Positive
brown terminal/Copper
deposit//brown plate: brown 1
solid is deposit//brown solid
deposited//thicker is deposited//thicker
Half equation for Anode: Al plate/- terminal:
both electrodes Cu Cu2+ + 2e Al Al3+ + 3e
Cathode: Cu plate//+ 1
Cu 2+ +2e Cu terminal:
Cu 2+ +2e Cu
1
Name of the Anode/Al plate: Oxidation
process occurred Cathode/Copper plate//negative
at both terminal: Reduction 1
electrodes/ ..10
terminal
TOTAL 20
BK7 - TRIAL SPM 2016 MARKING SCHEME
SULIT 5 4541/2
8 (a) (i) Temperature increase //
Zinc dissolve //
Brown solid formed //
Blue solution turn colourless
[any two] 1+1 ...2
(ii) Exothermic reaction / Heat released //
When 1 mol of copper is displaced, 240 kJ heat released //
Energy content of reactant is higher than product.
[Any two] 1+1 ...2
(iii) Mg + CuSO4 → MgSO4 + Cu
[Correct chemical formula] 1
[Balanced equation] 1
Mole of CuSO4 // Cu2+ = 0.2 × 200/1000 = 0.04 mol 1
Heat change = 200 × 4.2 × 15.5 1
= 13020 J 1
13020 × 1/0.04 // 325500 // 325.5 1
Heat of displacement = - 325.5 kJ mol-1 1 ...7
(b) (i) P = HCl // HNO3 1
Q = CH3COOH 1
R = NH3 solution 1
HCl // HNO3 is a strong acid // ionised completely in water 1
CH3COOH is a weak acid 1
ionised partially in water 1
some of heat release during the reaction is absorb to ionise
completely 1 ...7
(ii) Heat of neutralisation is heat released when 1 mol of water
formed. 1
In the reaction, 2 mol of water is formed;
Heat of neutralisation = 114/2 // 57 kJ mol-1 1 ...2
TOTAL 20
BK7 - TRIAL SPM 2016 MARKING SCHEME
SULIT 6 4541/2
Section C
9 (a)
2-methylpropene 1
But-2-ene 1 ...4
(b) (i) Reaction I : Oxidation 1
Reaction II : Dehydration 1
Reaction III : Esterification 1
Ethanol 1
Alcohol 1
C2H5OH // C2H6O 1 ...6
(c) 1. Alcohol : Ethanol 1
2. Carboxylic acid : ethanoic acid 1
Procedure :
3. Pour [2 – 10] cm3 of glacial ethanoic acid into boiling tube. 1
4. Add [2 – 10] cm3 of absolute ethanol into the acid. 1
5. Add [1 – 2] cm3 / a few drops of concentrated sulphuric
acid to the mixture. 1
6. Heat the mixture. 1
7. Equation :
CH3COOH + C2H5OH → CH3COOC2H5 + H2O 1
8. [Functional diagram] 1
9. [Labelled] 1
10. Pour /add bromine water /acidified potassium
manganate(VII) solution into test tube containing the gas. 1
11. The brown / purple of bromine water / acidified potassium
manganate(VII) solution is decolourised. 1 Max
10
TOTAL 20
BK7 - TRIAL SPM 2016 MARKING SCHEME
SULIT 7 4541/2
10 (a) (i) Lead(II) nitrate :
Acid reacts with base/ metal oxide/ metal hydroxide/ metal
carbonate/ metal 1
Lead(II) sulphate :
Double decomposition // Precipitation reaction 1 ...2
(ii) Lead(II) nitrate solution and 1
sodium sulphate* 1 ...2
*[any suitable solution which contains sulphate ion, SO42-]
(b) 1. Pour [20 -100] cm3 nitric acid [0.1 – 2.0] mol dm-3 to a 1
beaker.
2. Add PbO/PbCO3. 1
3. Stir the mixture. 1
4. Until some solid remains unreacted / excess. 1
5. Filter off the excess solid. 1
6. Evaporate until a 1/3 of volume of solution / saturated. 1
7. Leave to cool until crystal formed. 1
8. Filter and dried between filter paper. 1
9. PbO + 2HNO3 Pb(NO3)2 + H2O //
PbCO3 + 2HNO3 Pb(NO3)2 + CO2 + H2O 1+1 ..10
(c) Sample Answer : 1
1. Pour the solutions into two different test tubes.
2. Add barium nitrate* solution into the test tubes. 1
3. White precipitate formed.
4. Sulphate ion, SO42- present; the solution is sodium 1
sulphate. 1
5. No precipitate formed. 1
6. No sulphate ion, SO42-; the solution is sodium chloride. 1 ...6
*[Accept other methods that can be used to detect chloride ion]
TOTAL 20
END OF MARKING SCHEME
BK7 - TRIAL SPM 2016 MARKING SCHEME
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- KIMIA K2 SkimaDocumento7 pagineKIMIA K2 SkimaTay Poh Leng0% (1)
- SPM Chemistry Skema Set 9 Paper 2Documento8 pagineSPM Chemistry Skema Set 9 Paper 2Miesya87Nessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Skema Kimia K1 & K2 Trial SPM Terengganu MPP3 2019Documento14 pagine7 Skema Kimia K1 & K2 Trial SPM Terengganu MPP3 2019Ain MiorNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Upk1 Kimia 2019Documento8 pagineSkema Upk1 Kimia 2019Fadyana GhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Upk1 Kimia 2019Documento8 pagineSkema Upk1 Kimia 2019donutNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Answers PDFDocumento126 pagineChemistry Answers PDFNurafiqah FarhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Skima Kimia Tingkatan 4 Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2019Documento8 pagineSkima Kimia Tingkatan 4 Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2019ahbingNessuna valutazione finora
- MS Chem F5Documento4 pagineMS Chem F5Muhamad Aizuddin Abd RazakNessuna valutazione finora
- SKEMA GERAK GEMPUR KIMIA 2 JPN PERAK SET 2 NewDocumento8 pagineSKEMA GERAK GEMPUR KIMIA 2 JPN PERAK SET 2 NewZulkefliNessuna valutazione finora
- Kimia Trial TRG Bk3 k2 Skema 2017Documento14 pagineKimia Trial TRG Bk3 k2 Skema 2017shintasamtoNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Skema Kimia K1 & K2 Trial SPM Terengganu MPP3 2019Documento13 pagine7 Skema Kimia K1 & K2 Trial SPM Terengganu MPP3 2019SaravananNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema K2 Trial Kedah Chemistry 2018Documento9 pagineSkema K2 Trial Kedah Chemistry 2018Harreesh Krisna ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Trial Kedah 2014 SPM Kimia K1 K2 K3 Dan Skema (SCAN)Documento78 pagineTrial Kedah 2014 SPM Kimia K1 K2 K3 Dan Skema (SCAN)Cikgu Faizal67% (3)
- Po Leung Kuk No.1 W.H.Cheung College Yearly Examination (2021-2022) FORM 6 CHEMISTRY PAPER 2 Suggested AnswersDocumento4 paginePo Leung Kuk No.1 W.H.Cheung College Yearly Examination (2021-2022) FORM 6 CHEMISTRY PAPER 2 Suggested AnswersChun Kit LauNessuna valutazione finora
- Test No-3 Basics of Chem + Basics of Org Chem - Key PDFDocumento3 pagineTest No-3 Basics of Chem + Basics of Org Chem - Key PDFNaveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 - MPP3 - Paper2 MScheme Kimia TerengganuDocumento16 pagine3 - MPP3 - Paper2 MScheme Kimia TerengganuNurul FarhanahNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathongo Jee Main 2015Documento28 pagineMathongo Jee Main 2015rishithhr rajeevNessuna valutazione finora
- HKDSE Chemistry: Suggested Answer For Mock Examination 4 (Paper 2)Documento5 pagineHKDSE Chemistry: Suggested Answer For Mock Examination 4 (Paper 2)Vinaigrette HeNessuna valutazione finora
- D Strucutred Question AnswersDocumento27 pagineD Strucutred Question Answerskaziem68% (19)
- Unofficial Mark SchemeDocumento6 pagineUnofficial Mark SchemeRodolph SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- KimiaDocumento4 pagineKimiaijah rosmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Jawapan Paper 2 Kimia PDFDocumento9 pagineSkema Jawapan Paper 2 Kimia PDFAMIRA EZZATIE BINTI MOHD HATTA -Nessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Kertas 2 PPT 2016Documento8 pagineSkema Kertas 2 PPT 2016indianaNessuna valutazione finora
- June 2017 (v1) MS - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry IGCSEDocumento7 pagineJune 2017 (v1) MS - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry IGCSEJazzzNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Skema Pemarkahan Rate of ReactionDocumento47 pagine4 Skema Pemarkahan Rate of ReactionJun QiangNessuna valutazione finora
- CT 1 CheDocumento8 pagineCT 1 Chekiruthikpranav147Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kiangsu-Chekiang College (Shatin) MID-YEAR EXAMINATION (2013-2014) Form 5 Chemistry Marking Scheme: Section A: (30%)Documento5 pagineKiangsu-Chekiang College (Shatin) MID-YEAR EXAMINATION (2013-2014) Form 5 Chemistry Marking Scheme: Section A: (30%)wslNessuna valutazione finora
- Kimia Modul Peace Cemerlang (Answer) 2018: Bab 6: ElektrokimiaDocumento8 pagineKimia Modul Peace Cemerlang (Answer) 2018: Bab 6: ElektrokimiaKamala MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- MHT-CET 2021 Question Paper: 25 September 2021Documento3 pagineMHT-CET 2021 Question Paper: 25 September 2021Sank DamNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 Pahang - MPSM Chemistry K1 - K2 JawapanDocumento14 pagine2022 Pahang - MPSM Chemistry K1 - K2 JawapanCrystal GohNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Answer Scheme For Form 4 Paper 2 Seri Temasik SchoolsDocumento9 pagineChemistry Answer Scheme For Form 4 Paper 2 Seri Temasik SchoolsBenjamin TeeNessuna valutazione finora
- KBSM t4 Skema Kimia k2Documento9 pagineKBSM t4 Skema Kimia k2kancil416670Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Marking SchemeDocumento12 pagineChemistry Marking Schemeasamoahxolali390Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge International Examinations: Chemistry 0620/41 May/June 2017Documento7 pagineCambridge International Examinations: Chemistry 0620/41 May/June 2017elezabethNessuna valutazione finora
- QC - 2019-20 - Mock - S6 - Chem 1 - AnsDocumento7 pagineQC - 2019-20 - Mock - S6 - Chem 1 - AnsOof GucciNessuna valutazione finora
- SKEMA Chemi KERTAS 2Documento11 pagineSKEMA Chemi KERTAS 2uranium97Nessuna valutazione finora
- SKEMA TEST 1 Form 5Documento3 pagineSKEMA TEST 1 Form 5Floreo BlossomNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 2 November 2000Documento6 paginePaper 2 November 2000MSHNessuna valutazione finora
- S6 Test 5Documento7 pagineS6 Test 5XD XDNessuna valutazione finora
- PLKVKTCSFC - F6 - 2019-2020 - Chem Ans - Kuok KellyDocumento8 paginePLKVKTCSFC - F6 - 2019-2020 - Chem Ans - Kuok KellyOof GucciNessuna valutazione finora
- Sch4uc PTMGDocumento11 pagineSch4uc PTMGMarwan MohamudNessuna valutazione finora
- SHCC - 2023 - Chem Paper2 - AnnaDocumento8 pagineSHCC - 2023 - Chem Paper2 - AnnaOof GucciNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Test 2 300920Documento11 pagineUnit 1 Test 2 300920ibrahim ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Chms3y20e2 AnsDocumento3 pagineChms3y20e2 Ansno nameNessuna valutazione finora
- GG07 P2 Marking SchemeDocumento12 pagineGG07 P2 Marking Schemeazirawati nurNessuna valutazione finora
- Act Thrissur +1 Chem KeyDocumento6 pagineAct Thrissur +1 Chem KeyYADUKRISHNAN K NAIRNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 AMS and Redox Tutorial Partial Upload of Worked SolutionDocumento15 pagine2022 AMS and Redox Tutorial Partial Upload of Worked SolutionBooNessuna valutazione finora
- Marking Scheme Paper ChemistryDocumento20 pagineMarking Scheme Paper ChemistryArvin DiNozzoNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Chemistry Class 11 (Mid Term Exam Model Paper)Documento3 pagineCBSE Chemistry Class 11 (Mid Term Exam Model Paper)RounakNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Kertas 2 KimiaDocumento9 pagineSkema Kertas 2 KimiaariesNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Table 5 MSDocumento5 paginePeriodic Table 5 MSYabhijit DuttaNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Penilaian 1 Kimia T5Documento10 pagineSkema Penilaian 1 Kimia T5NIK NORASHRAH BT CHE MAT MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- XII Chemistry EveningDocumento15 pagineXII Chemistry EveningAyush Kumar singhNessuna valutazione finora
- International Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid State: Propylene (Propene)Da EverandInternational Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid State: Propylene (Propene)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Graphene Oxide: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDa EverandGraphene Oxide: Fundamentals and ApplicationsAyrat M. DimievNessuna valutazione finora
- International Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid State Helium-4Da EverandInternational Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid State Helium-4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bentonite Functionalised with 2-(3-(2-aminoethylthio)propylthio)ethanamine (AEPE) for the Removal of Hg(II) from Wastewaters: Synthesis, Characterisation and Hg(II) Adsorption PropertiesDa EverandBentonite Functionalised with 2-(3-(2-aminoethylthio)propylthio)ethanamine (AEPE) for the Removal of Hg(II) from Wastewaters: Synthesis, Characterisation and Hg(II) Adsorption PropertiesNessuna valutazione finora
- Progress in Reaction Kinetics: Volume 6Da EverandProgress in Reaction Kinetics: Volume 6K. R. JenningsNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Halus Persamaan Kimia - PDFDocumento9 pagineSkema Halus Persamaan Kimia - PDFIza MohdSabri33% (3)
- Soalan Halus Persamaan KimiaDocumento23 pagineSoalan Halus Persamaan KimiaIza MohdSabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Halus Persamaan Kimia - PDFDocumento9 pagineSkema Halus Persamaan Kimia - PDFIza MohdSabri33% (3)
- Chapter 2: Carbon Compounds: A Understanding Carbon CompoundDocumento28 pagineChapter 2: Carbon Compounds: A Understanding Carbon CompoundIza MohdSabriNessuna valutazione finora
- SM - Teknik - Johor - Trial2016 Kertas 123 DGN JWPN PDFDocumento86 pagineSM - Teknik - Johor - Trial2016 Kertas 123 DGN JWPN PDFIza MohdSabriNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Periodic Table of ElementsDocumento17 pagine4 Periodic Table of ElementsIza MohdSabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Rubber ExerciseDocumento3 pagineNatural Rubber ExerciseIza MohdSabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Catalyst On The Rate of ReactionDocumento9 pagineEffect of Catalyst On The Rate of ReactionIza MohdSabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Sampel Soalan PisaDocumento318 pagineSampel Soalan PisaIza MohdSabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Naskah Murid Modul 1-Rate of ReactionDocumento14 pagineNaskah Murid Modul 1-Rate of ReactionIza MohdSabriNessuna valutazione finora
- CAA CatalogueDocumento68 pagineCAA CataloguearnettoNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxidation of Alkenes With Potassium Manganate - Chemistry LibreTextsDocumento5 pagineOxidation of Alkenes With Potassium Manganate - Chemistry LibreTextsDannyelle BaileyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chromcarb N6006: WeldingDocumento2 pagineChromcarb N6006: WeldingCasa de Adoración ConcepciónNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 19-Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsDocumento22 pagineChapter 19-Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsNada MeselhyNessuna valutazione finora
- United States Patent Office: Patented Nov. 26, 1963Documento2 pagineUnited States Patent Office: Patented Nov. 26, 1963Bharata BadranayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Inorganic Reaction Mechanisms: January 2020Documento225 pagineInorganic Reaction Mechanisms: January 2020AdistaNessuna valutazione finora
- EN24 and EN24T Steel: BS970: 1955 EN24, BS970/PD970: 1970 OnwardsDocumento2 pagineEN24 and EN24T Steel: BS970: 1955 EN24, BS970/PD970: 1970 OnwardsParesh Patel100% (1)
- GB T 700-2006-Carbon Structural Steels-En&CNDocumento22 pagineGB T 700-2006-Carbon Structural Steels-En&CNNespak P&M100% (1)
- Calculation ChemistryDocumento13 pagineCalculation ChemistryRemi EyonganyohNessuna valutazione finora
- Redox ReactionsDocumento4 pagineRedox ReactionsFayzanAbdulWasay100% (1)
- Def ReplyDocumento23 pagineDef ReplySanjeev SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Tigfil 70S-2: Aws A/sfa 5.18 en Iso 636-ADocumento1 paginaTigfil 70S-2: Aws A/sfa 5.18 en Iso 636-AsatnamNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of HaloalkaneDocumento10 pagineSummary of HaloalkaneTai PanNessuna valutazione finora
- SCH4U - Unit 4 - Version CDocumento45 pagineSCH4U - Unit 4 - Version CMr. SharpnNessuna valutazione finora
- Aluminia Hydrate Technical SpecificationDocumento1 paginaAluminia Hydrate Technical SpecificationAffy SydNessuna valutazione finora
- Stainless Steel GradesDocumento1 paginaStainless Steel GradesRm1262Nessuna valutazione finora
- Iodometric Determination of Copper and Iron in One SolutionDocumento3 pagineIodometric Determination of Copper and Iron in One SolutionSianiiChavezMoránNessuna valutazione finora
- Stoichiometric Calculations Worksheet KEYDocumento4 pagineStoichiometric Calculations Worksheet KEYGabby Lisowicz100% (1)
- Proteksi Katodik Dengan Menggunakan Anoda Korban Pada Struktur Baja Karbon Untuk Mengendalikan Laju KorosiDocumento5 pagineProteksi Katodik Dengan Menggunakan Anoda Korban Pada Struktur Baja Karbon Untuk Mengendalikan Laju KorosiIhlasul AmalNessuna valutazione finora
- Acids, Bases and Chemical Bonding Challenging QuestionsDocumento6 pagineAcids, Bases and Chemical Bonding Challenging Questionschong5650% (2)
- 13MET KIN A Gas Purging System For Metallurgic 152995Documento15 pagine13MET KIN A Gas Purging System For Metallurgic 152995Carlos Ortega JonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Guide Path To Periodic Table PDFDocumento2 pagineStudent Guide Path To Periodic Table PDFAlmiah AlfaroukNessuna valutazione finora
- 123Documento2 pagine123AbdelmoumenAbdelmoumenNessuna valutazione finora
- Bioinorganic Introduction - 11Documento28 pagineBioinorganic Introduction - 11harjitkaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Investigatory Project On Consistuents of AlloysDocumento11 pagineChemistry Investigatory Project On Consistuents of AlloysKrishna Singh Panwar XI BNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic TableDocumento8 paginePeriodic TableKhairiyah AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- SGS Test Report For SNCC Nylon Ink PDFDocumento11 pagineSGS Test Report For SNCC Nylon Ink PDFKamruzzaman Sheikh100% (1)
- Ch4 Watertreatment DisinfectionDocumento30 pagineCh4 Watertreatment DisinfectionSUBHAM KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009-04-CEN-TC121 N1574 Working Programme CEN TC 121Documento28 pagine2009-04-CEN-TC121 N1574 Working Programme CEN TC 121Manuel ValenteNessuna valutazione finora
- Leaching of Nickel (Group B) 2Documento16 pagineLeaching of Nickel (Group B) 2Thato MaamoeNessuna valutazione finora