Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Grade 2 Unit 4 Parentletter
Caricato da
api-294044622Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Grade 2 Unit 4 Parentletter
Caricato da
api-294044622Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Grade 2 Unit 4
Applying Base Ten Understanding
Volume 1 Issue 4
References Dear Parents,
During this unit your child will be exploring addition and subtraction of two and three-digit
Helpful Links:
numbers and will get to try many different strategies based on place value and understanding.
Math Magician (Fact Practice) Please keep in mind that while these strategies may be different from the way you are familiar
http://oswego.org/ocsd- with adding and subtracting, the purpose of these strategies is to build a strong foundation of
web/games/mathmagician/mat place value when computing so students will understand why the traditional methods of
hs1.html
addition and subtraction work but will have a variety of strategies than can use for flexibility and
ABCYa (Counting Money) efficiency. Students will also be working with money and they use their place value
http://www.abcya.com/countin understanding to solve simple word problems involving money.
g_money.htm
Learning Box (Place Value)
http://www.learningbox.com/Ba Concepts Students will Use and Understand
se10/BaseTen.html • Continue to represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction.
• Add up to 4 two-digit numbers.
Johnnie’s Math Page (Facts &
Operations Practice) • Understand and apply properties of operations and the relationship between addition
http://jmathpage.com/topics/jm and subtraction (inverse operations).
p2ndgradeoperations.html • Become fluent with mentally adding or subtracting 10 or 100 to a given three-digit
number.
Johnnie’s Math Page
(Developing Number Sense) • Know the multiple meanings for addition (combine, join, and count on) and subtraction
http://jmathpage.com/topics/jm (take away, remove, count back, and compare)
p2ndgradenumbersense.html • Recognize and use place value to manipulate numbers.
• Count with pennies, nickels, dimes, and dollar bills.
• Solve problems using mental math strategies.
Math Grade 2
Textbook Connection:
Ch. 6, Lessons 6.1-6.3, 6.8 Vocabulary
Ch. 7, Lessons 7.1-7.3 • expanded form: A multi-digit number is expressed in expanded form when it is written as a sum of
Ch. 8, Lessons 8.1-8.3
single-digit multiples of powers of ten. For example, 643 = 600 + 40 + 3.
Textbook Online: base ten blocks: A manipulative used to build numbers and to help with addition and subtraction at
the conceptual level.
http://connected.mcgraw- place value: The value of a digit based on its place in a number.
hill.com/connected/login.do symbols: +, -, =,
join: to put together (add)
Student User ID:
ccsd(student ID)
separate: to take apart (subtract)
Password: cobbmath1 total: The number when sets are combined.
sum: The total when numbers are added.
inverse operations: the inverse operations for addition is subtraction; the inverse operation for
subtraction is addition.
difference The result when one number is subtracted from another.
equation A mathematical expression where one part is equal to the other part. Example: 50 + 26 = 70
+ 6.
• Fluently is accurately and efficiently.
Grade 2 Unit 4 2015-2016
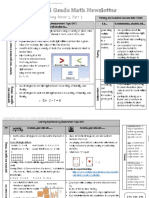
Symbols Example 1
+ addition
Students are going to use their understanding of place value and expanded form from unit 1 to
help them add and subtract within 100 fluently and within 1000 using strategies based on place
- subtraction value. The following is a common way students might add 2 or 3-digt numbers.
= equal
2nd grade students need to understand that they can group hundreds, tens and ones and the
order does not matter. Drawing Base Ten blocks to help them solve this problem is also
common.
Keep in mind that “naked” numbers are abstract and given a context can help students
conceptualize the numbers more easily. Instead of using numbers such as 248 and 345, say 248
pencils and 345 pencils.
Example 2
An open number line allows students to add or subtract in chunks and serves as a visual recording
method to keep track of the computation. Students are encouraged to use this strategy in a way
that makes sense to them – numbers may be broken apart in many different ways. This is one
example of using an open number line to model addition. Students become more efficient in
their models as their knowledge solidifies.
Example 3
Students can also use an open number line to model adding up to find the difference between
236 and 79.
Example 4
Students start to work with two-step word problems using simple numbers. Promote students
reading, thinking about and visualizing 1 sentence at a time:
Jose had 24 tickets after playing ski ball. He used 7 of tickets to buy a rubber ball and some more
to buy an eraser. Jose has 9 tickets left. How many tickets did the eraser cost?
Grade 2 Unit 4 2015-2016
Activities at Home
• Let your child count the change from your pockets or purse.
• Encourage your child to practice skip counting by 5’s, 10’s, and 100’s starting at numbers other than 0. For
example, skip count by 5’s from 35 to 50 or skip count by 10’s from 78 to 128.
• Have students mentally add up to four 2-digit numbers. For example, add 20 + 30 + 10. Progress to adding more
difficult 2-digit numbers such as 27 + 15 + 10 + 12. Students
• Check out the websites from page 1.
Grade 2 Unit 4 2015-2016
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 1stgrade Math UnitDocumento54 pagine1stgrade Math UnitRivka Share100% (1)
- Stress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9Da EverandStress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson PlansDocumento8 pagineLesson Plansapi-416444696Nessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching & Learning Plans: Decimals and Place ValueDocumento35 pagineTeaching & Learning Plans: Decimals and Place ValueSmartBugamNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom-Ready Number Talks for Kindergarten, First and Second Grade Teachers: 1,000 Interactive Activities and Strategies that Teach Number Sense and Math FactsDa EverandClassroom-Ready Number Talks for Kindergarten, First and Second Grade Teachers: 1,000 Interactive Activities and Strategies that Teach Number Sense and Math FactsNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Multiplication and Division Conceptually Grades 3-5Documento39 pagineTeaching Multiplication and Division Conceptually Grades 3-5Atomen KambinkNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeDa EverandMath Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- CFC Kids For Christ Kids Ambassadors ProgramDocumento10 pagineCFC Kids For Christ Kids Ambassadors ProgramRonnel LlaveNessuna valutazione finora
- RUBRICS For Research Paper Defense, Peer, EtcDocumento3 pagineRUBRICS For Research Paper Defense, Peer, EtcAnny YanongNessuna valutazione finora
- How to be Brilliant at Mental Arithmetic: How to be Brilliant at Mental ArithmeticDa EverandHow to be Brilliant at Mental Arithmetic: How to be Brilliant at Mental ArithmeticValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- QuestionnaireDocumento3 pagineQuestionnaireAyah Paasa0% (1)
- Grade 4 (Science) RubricDocumento1 paginaGrade 4 (Science) RubricMa. Christian Dayon100% (1)
- 2ndgrade Math Unit - FinalDocumento133 pagine2ndgrade Math Unit - FinalRivka ShareNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Digest Basic Legal Ethics Subject DONNA MARIE S. AGUIRRE, Complainant, vs. EDWIN L. RANA, Respondent (B.M. No. 1036, 10 June 2003)Documento2 pagineCase Digest Basic Legal Ethics Subject DONNA MARIE S. AGUIRRE, Complainant, vs. EDWIN L. RANA, Respondent (B.M. No. 1036, 10 June 2003)Grandeur P. G. GuerreroNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL MAPEH 6 Q3 Week 5Documento5 pagineDLL MAPEH 6 Q3 Week 5Bea DeLuis de TomasNessuna valutazione finora
- Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 1 Parent Tip SheetDocumento2 pagineEureka Math Grade 2 Module 1 Parent Tip Sheetapi-522113163Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sema Aydin-Lesson Plan 1Documento3 pagineSema Aydin-Lesson Plan 1api-256269043Nessuna valutazione finora
- Student A: Mia Grade: 2 Date Interviewed: 27/03/2013: Domain Assigned Growth PointDocumento9 pagineStudent A: Mia Grade: 2 Date Interviewed: 27/03/2013: Domain Assigned Growth Pointapi-285941433Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit OverviewDocumento4 pagineUnit Overviewapi-242316638Nessuna valutazione finora
- Multiplication Facts UnitDocumento9 pagineMultiplication Facts UnitMaria NasoneNessuna valutazione finora
- Math LP Feb 16-20, 2015Documento9 pagineMath LP Feb 16-20, 2015Tasia Starling ScruggsNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Math JsDocumento4 pagineLesson Plan Math Jsapi-709224173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Key Stage 1 Maths Workshop: Mrs Wright and Miss RingDocumento43 pagineKey Stage 1 Maths Workshop: Mrs Wright and Miss RingWalid SassiNessuna valutazione finora
- LessonplanmathDocumento5 pagineLessonplanmathapi-698817165Nessuna valutazione finora
- New LP TemplateDocumento10 pagineNew LP TemplateTasia Starling ScruggsNessuna valutazione finora
- IMB Lesson Plan: Activity Description of Activities and Setting TimeDocumento6 pagineIMB Lesson Plan: Activity Description of Activities and Setting Timeapi-453481434Nessuna valutazione finora
- Math LP Feb 23-27, 2015Documento9 pagineMath LP Feb 23-27, 2015Tasia Starling ScruggsNessuna valutazione finora
- Year 5 Week 2 Lesson 1 Main Focus Prior Knowledge Key Vocabulary Curriculum ObjectivesDocumento16 pagineYear 5 Week 2 Lesson 1 Main Focus Prior Knowledge Key Vocabulary Curriculum Objectiveslenson kinyuaNessuna valutazione finora
- First Form Mathematics Module 6Documento34 pagineFirst Form Mathematics Module 6Chet AckNessuna valutazione finora
- Thinking RelationallyDocumento4 pagineThinking Relationallyapi-321743492Nessuna valutazione finora
- Math LP Feb 2-6, 2015Documento10 pagineMath LP Feb 2-6, 2015Tasia Starling ScruggsNessuna valutazione finora
- Year 6 Week 6 Lesson 1 Main Focus Prior Knowledge Key Vocabulary Curriculum ObjectivesDocumento17 pagineYear 6 Week 6 Lesson 1 Main Focus Prior Knowledge Key Vocabulary Curriculum Objectiveslenson kinyuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathunitplan 20170426 CgushikumaDocumento28 pagineMathunitplan 20170426 Cgushikumaapi-357523738Nessuna valutazione finora
- Math LP Feb 9-13, 2015Documento10 pagineMath LP Feb 9-13, 2015Tasia Starling ScruggsNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5 Multiplication and DivisionDocumento13 pagineUnit 5 Multiplication and DivisionRicha jaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- 440 CapstoneDocumento3 pagine440 Capstoneapi-529122496Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson PlanDocumento10 pagineLesson PlanMahad RasoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Plan Psiii - MathDocumento32 pagineUnit Plan Psiii - Mathapi-438892784Nessuna valutazione finora
- Miaa 360 Intervention PBLDocumento5 pagineMiaa 360 Intervention PBLapi-268936515Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 3, Unit Two: Place Value Structures & Multi-Digit ComputationDocumento2 pagineGrade 3, Unit Two: Place Value Structures & Multi-Digit ComputationMeganMaynardNessuna valutazione finora
- SMTH Grade 6 AAC Public OverviewDocumento14 pagineSMTH Grade 6 AAC Public OverviewAshleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Condensed Term 2Documento9 pagineCondensed Term 2api-250619894Nessuna valutazione finora
- Year 6 Week 2 Lesson 1 Main Focus Prior Knowledge Key Vocabulary Curriculum ObjectivesDocumento19 pagineYear 6 Week 2 Lesson 1 Main Focus Prior Knowledge Key Vocabulary Curriculum Objectiveslenson kinyuaNessuna valutazione finora
- FRIT 7739 - Technology Enhanced Unit - WeeksDocumento15 pagineFRIT 7739 - Technology Enhanced Unit - WeeksdianambertNessuna valutazione finora
- mp1 Parent Newsletter BDocumento8 paginemp1 Parent Newsletter Bapi-326552742Nessuna valutazione finora
- Year 6 Week 3 Lesson 1 Main Focus Prior Knowledge Key Vocabulary Curriculum ObjectivesDocumento23 pagineYear 6 Week 3 Lesson 1 Main Focus Prior Knowledge Key Vocabulary Curriculum Objectiveslenson kinyuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 6 CompleteDocumento377 pagineGrade 6 CompleteAlecia RahmingNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Lab Grade 3 Module 1a pdf1Documento18 pagineMath Lab Grade 3 Module 1a pdf1api-276903925Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit StandardsDocumento7 pagineUnit Standardsapi-284886534Nessuna valutazione finora
- Math UnitplanDocumento5 pagineMath Unitplanapi-252035669Nessuna valutazione finora
- 00 2015 2016 6th Number System Unit 1 PlanDocumento20 pagine00 2015 2016 6th Number System Unit 1 Planapi-305603483Nessuna valutazione finora
- Educ 255, Sandlin, Kiss Lesson PlanDocumento8 pagineEduc 255, Sandlin, Kiss Lesson Planapi-216183591Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Power of Routines - Rename The NumberDocumento5 pagineThe Power of Routines - Rename The Numberanan.mohamed1308Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 Family LetterDocumento2 pagineUnit 2 Family Letterapi-626096357Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5 E Lesson Plan - Getting To Know Unknown VariablesDocumento4 pagine5 E Lesson Plan - Getting To Know Unknown VariablesRUEL CERVANTESNessuna valutazione finora
- g4 m1 Full ModuleDocumento256 pagineg4 m1 Full ModuleKe HebeNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Lesson Plan 1Documento5 pagineMath Lesson Plan 1api-372799212Nessuna valutazione finora
- Graduated Difficulty Lesson - BosseDocumento3 pagineGraduated Difficulty Lesson - Bosseapi-252935769Nessuna valutazione finora
- Te 801 Project 2Documento13 pagineTe 801 Project 2api-404347657Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 1: Unit 1.OA.B.3-4 Properties of Operations & The Relationship Between Addition & SubtractionDocumento25 pagineGrade 1: Unit 1.OA.B.3-4 Properties of Operations & The Relationship Between Addition & SubtractionTasia Starling ScruggsNessuna valutazione finora
- Edma262 - Assignment TwoDocumento9 pagineEdma262 - Assignment Twoapi-358330682Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2016NJSLS-M Grade1Documento16 pagine2016NJSLS-M Grade1Gene HermanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson7 Ed315Documento4 pagineLesson7 Ed315api-218300742Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tech Trends Lesson PlanDocumento5 pagineTech Trends Lesson PlantonyagrantNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade Level: 4th Grade Curriculum Resource(s)Documento5 pagineGrade Level: 4th Grade Curriculum Resource(s)api-351601386Nessuna valutazione finora
- Usr Local SRC Education - Com Files Static Lesson Plans Lets Jump To Add Two Digit Numbers Lets Jump To Add Two Digit NumbersDocumento10 pagineUsr Local SRC Education - Com Files Static Lesson Plans Lets Jump To Add Two Digit Numbers Lets Jump To Add Two Digit NumbersClarrise ToyokenNessuna valutazione finora
- Ea and Gsa Interview QuestionsDocumento4 pagineEa and Gsa Interview Questionsmaisie RameetseNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan: Teacher: Date: Time: School: ClassDocumento2 pagineLesson Plan: Teacher: Date: Time: School: ClassDragana MilosevicNessuna valutazione finora
- Elementary Greek II SyllabusDocumento4 pagineElementary Greek II Syllabusapi-232538409Nessuna valutazione finora
- Al Farah Izzatie Al Buhari (Resume)Documento7 pagineAl Farah Izzatie Al Buhari (Resume)Khairul IshakNessuna valutazione finora
- Technology in Special EducationDocumento7 pagineTechnology in Special Educationapi-491565788Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Change Management Life CycleDocumento16 pagineThe Change Management Life CycleAli IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- RPH Lesson StudyDocumento4 pagineRPH Lesson Studyjkj1370Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pice Students DirDocumento45 paginePice Students DirBrian Paul100% (1)
- Amazon Education in FocusDocumento7 pagineAmazon Education in FocusanacachinhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ped 121Documento171 paginePed 121Selenai SelenaiNessuna valutazione finora
- My Career PresentationDocumento11 pagineMy Career Presentationapi-490022795Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics & Physics of Emerging Biomedical ImagingDocumento261 pagineMathematics & Physics of Emerging Biomedical ImagingDewi LestariNessuna valutazione finora
- English in Canada: Toronto & Vancouver - Ilac Viewbook 2020Documento37 pagineEnglish in Canada: Toronto & Vancouver - Ilac Viewbook 2020Roger CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Task 2Documento9 pagineTask 2AishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Keili B Harrison ResumeDocumento1 paginaKeili B Harrison ResumeKeili HarrisonNessuna valutazione finora
- 5083Documento25 pagine5083neo.foe100% (1)
- Johnston The Gongsun Longzi A Translation and An Analysis of Its Relationship To Later Mohist WritingsDocumento25 pagineJohnston The Gongsun Longzi A Translation and An Analysis of Its Relationship To Later Mohist WritingsHaeook JeongNessuna valutazione finora
- The Anti-ought-To Self and Language Learning MotivationDocumento12 pagineThe Anti-ought-To Self and Language Learning MotivationJenn BarreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Curriluim Vitae: Civil StatusDocumento2 pagineCurriluim Vitae: Civil StatusFolegwe FolegweNessuna valutazione finora
- A Learning Process Model To Achieve Continuous Improvement and InnovationDocumento9 pagineA Learning Process Model To Achieve Continuous Improvement and Innovationkaushikb3100% (1)
- Applicationform Checklist 2014 15Documento8 pagineApplicationform Checklist 2014 15Oshilojo IsraelNessuna valutazione finora
- National Government AgenciesDocumento7 pagineNational Government Agencieslois8596Nessuna valutazione finora
- Statement of ResultDocumento1 paginaStatement of ResultisissantanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Record: IV Learners' Names Written Works Performance TasksDocumento29 pagineClass Record: IV Learners' Names Written Works Performance TasksLance Aldrin AdionNessuna valutazione finora