Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Geothermal Energy Crust Eruption Planets Earth Satellites Effusive Eruption Igneous Rock Viscous Thixotropic Shear Thinning
Caricato da
Saad AhsanDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Geothermal Energy Crust Eruption Planets Earth Satellites Effusive Eruption Igneous Rock Viscous Thixotropic Shear Thinning
Caricato da
Saad AhsanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
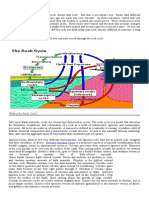
Lava is molten rock generated by geothermal energy and expelled through fractures in
planetary crust or in an eruption, usually at temperatures from 700 to 1,200 °C (1,292 to 2,192 °F).
The structures resulting from subsequent solidification and cooling are also sometimes described
as lava. The molten rock is formed in the interior of some planets, including Earth, and some of
their satellites, though such material located below the crust is referred to by other terms.
A lava flow is a moving outpouring of lava created during a non-explosive effusive eruption. When it
has stopped moving, lava solidifies to form igneous rock. The term lava flow is commonly shortened
to lava. Although lava can be up to 100,000 times more viscous than water, lava can flow great
distances before cooling and solidifying because of its thixotropic and shear thinning properties.[1][2]
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- What Are Igneous Rocks?Documento3 pagineWhat Are Igneous Rocks?christine puraNessuna valutazione finora
- Volcanoes: by Jacaranda Lopez Submitted To Instructor Hutchinson GE101 Fall 2000Documento4 pagineVolcanoes: by Jacaranda Lopez Submitted To Instructor Hutchinson GE101 Fall 2000sjshoresNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth Science HandoutsDocumento17 pagineEarth Science HandoutsCatherine DiscorsonNessuna valutazione finora
- What Happens Before and After Volcanoes Erupt? Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksDa EverandWhat Happens Before and After Volcanoes Erupt? Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNessuna valutazione finora
- What Happens After Magma Is FormedDocumento15 pagineWhat Happens After Magma Is Formedjohncarlocanete7Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Rock CycleDocumento3 pagineThe Rock CycleRODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLANessuna valutazione finora
- Hotspot of Volcano LavaDocumento3 pagineHotspot of Volcano LavaLT ExtraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Sheet 1 - Layers of Earth and Its CoreDocumento23 pagineLecture Sheet 1 - Layers of Earth and Its CoreNafin AfnanNessuna valutazione finora
- VolcanoesDocumento3 pagineVolcanoesapi-403791467Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 - Week 5Documento26 pagineModule 5 - Week 5Alice ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch12 Study GuideDocumento6 pagineCh12 Study GuideEdjie LluparNessuna valutazione finora
- Rocks And: The Rock CycleDocumento49 pagineRocks And: The Rock CycleKamruz zamanNessuna valutazione finora
- LavaDocumento3 pagineLavaella retizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lava FlowDocumento10 pagineLava Flowducusincrissa42Nessuna valutazione finora
- Volcanoes-How It Is FormedDocumento55 pagineVolcanoes-How It Is FormedHenry JacobNessuna valutazione finora
- By Vuyo PeterDocumento7 pagineBy Vuyo Petertoriya80Nessuna valutazione finora
- Report About RocksDocumento112 pagineReport About Rocksallen2912100% (1)
- TuffDocumento14 pagineTuffdjdjfnNessuna valutazione finora
- A Rock Is LivelyDocumento7 pagineA Rock Is LivelyChronicleBooks100% (1)
- 4b - Igneous Activity - BDocumento37 pagine4b - Igneous Activity - BBektur AbdillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Volcanic HazardsDocumento9 pagineVolcanic HazardsClaire MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth ScienceDocumento4 pagineEarth ScienceTae BearNessuna valutazione finora
- Easrthsci NotesDocumento15 pagineEasrthsci NotesMary Rhose VidalloNessuna valutazione finora
- Weathering Erosion Dep 12Documento47 pagineWeathering Erosion Dep 12Mhona ChriseNessuna valutazione finora
- Weathering Fossils EarthDocumento2 pagineWeathering Fossils EarthZaynab BelouhNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.3 Earth's ProcessesDocumento4 pagine1.3 Earth's ProcessesRufo FelixNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes (Midterm)Documento5 pagineNotes (Midterm)Rachel Hanh AbaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Weathering. Form 1-4 Notes Compiled by MR K. Romo 0772858765Documento16 pagineWeathering. Form 1-4 Notes Compiled by MR K. Romo 0772858765Sharon MasikiNessuna valutazione finora
- Composition Types of DepositsDocumento106 pagineComposition Types of DepositsmichelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Social ScienceDocumento1 paginaSocial Scienceshaswatmishra007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of A VolcanoDocumento7 pagineParts of A VolcanoReynielclydeEscoberNessuna valutazione finora
- Volcanoes and EarthquakesDocumento17 pagineVolcanoes and Earthquakesruv.asn17Nessuna valutazione finora
- ROCKSDocumento12 pagineROCKSAce ManicaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Weathering Erosion and DepositionDocumento33 pagineWeathering Erosion and DepositionFrank DescartesNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment No 3Documento19 pagineAssignment No 3ALI ZUBAIRNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment No 3Documento19 pagineAssignment No 3Ali ZubairNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Mechanical WeatheringDocumento2 pagineTypes of Mechanical WeatheringPerly PeterNessuna valutazione finora
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksDa EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNessuna valutazione finora
- Trivias About EarthDocumento3 pagineTrivias About EarthJiblerNessuna valutazione finora
- Corelower MantleDocumento2 pagineCorelower MantleJeremiah ConalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Group 1 ReportDocumento92 pagineChapter 5 Group 1 ReportAxel ElisonNessuna valutazione finora
- ROCKS: The Building Blocks of LithosphereDocumento17 pagineROCKS: The Building Blocks of LithosphereMalik Sheraz Ahmed Sherazi100% (1)
- Earth Materials and Processes CMDocumento28 pagineEarth Materials and Processes CMJaicelyn JarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter3 (ELS)Documento23 pagineChapter3 (ELS)chloe cresendoNessuna valutazione finora
- Erupted Material: Volcanic GasesDocumento3 pagineErupted Material: Volcanic GasesNaditaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 - VolcanoesDocumento45 pagineLesson 1 - VolcanoesTeacher DennisNessuna valutazione finora
- Magmatism Group 3Documento29 pagineMagmatism Group 3MARY JOSEPH OCONessuna valutazione finora
- Es 2ND Week1Documento12 pagineEs 2ND Week1Isaiah Timothy RabangNessuna valutazione finora
- For NTBK Q2 EarthSciDocumento11 pagineFor NTBK Q2 EarthSciTrishia Lane GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Interior of The EarthDocumento44 pagineInterior of The EarthdrishtiNessuna valutazione finora
- Compilation of ReportsDocumento18 pagineCompilation of Reportsyoow.youthNessuna valutazione finora
- Describe What Happened If Magma Is FormedDocumento7 pagineDescribe What Happened If Magma Is FormedMadeline SuratNessuna valutazione finora
- Science-Reviewer-Q2 g11Documento9 pagineScience-Reviewer-Q2 g11Joshua PiamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- GLY-Chapter 4 PDFDocumento15 pagineGLY-Chapter 4 PDFBrendon GovaNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Standard Geograpy: Chapter 2 Inside Our EarthDocumento3 pagine7 Standard Geograpy: Chapter 2 Inside Our EarthSumit YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Volcanoes and TypeDocumento4 pagineIntroduction To Volcanoes and TypeMonaoray BalowaNessuna valutazione finora
- Magma and Volcanism Reviewer GROUP 4Documento7 pagineMagma and Volcanism Reviewer GROUP 4muhamsumandresNessuna valutazione finora
- 15Documento2 pagine15Eden Leysam PulmonNessuna valutazione finora
- The Rock Cycle Groupwork - Davina MegsonDocumento5 pagineThe Rock Cycle Groupwork - Davina MegsondavvNessuna valutazione finora
- Notification: Government of Pakistan Cabinet Secretariat Establishment Division Federal Public Service CommissionDocumento5 pagineNotification: Government of Pakistan Cabinet Secretariat Establishment Division Federal Public Service CommissionSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mars Is The FourthDocumento1 paginaMars Is The FourthSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- HRM MCQsDocumento10 pagineHRM MCQsSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth AtmosphereDocumento1 paginaEarth AtmosphereSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- hν, where E is the energy per ν is the frequency of the photon, and h isDocumento1 paginahν, where E is the energy per ν is the frequency of the photon, and h isSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- LiquidDocumento1 paginaLiquidSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tethered Heavier-Than-Air Wing Box KitesDocumento1 paginaTethered Heavier-Than-Air Wing Box KitesSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Goat Caprinae: Chinese Pinyin Chinese Zodiac Chinese Calendar Chinese Taxonomic SubfamilyDocumento1 paginaGoat Caprinae: Chinese Pinyin Chinese Zodiac Chinese Calendar Chinese Taxonomic SubfamilySaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Comp of SmokeDocumento2 pagineChemical Comp of SmokeSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- BoatDocumento1 paginaBoatSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- New Zealand Australia Britain: Dessert Gelatine Set Jello Pectin Savoury Meat DessertDocumento1 paginaNew Zealand Australia Britain: Dessert Gelatine Set Jello Pectin Savoury Meat DessertSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rugby Union, Commonly Known in Most of The World Simply As RugbyDocumento1 paginaRugby Union, Commonly Known in Most of The World Simply As RugbySaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Spherical Ovoid Ball Games Juggling Engineering Ball Bearings Black-Powder Projectiles Rubber Columbus Mesoamerican BallgameDocumento1 paginaSpherical Ovoid Ball Games Juggling Engineering Ball Bearings Black-Powder Projectiles Rubber Columbus Mesoamerican BallgameSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- CreamDocumento1 paginaCreamSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pages Papyrus Parchment Vellum Paper Bound Cover: CodexDocumento1 paginaPages Papyrus Parchment Vellum Paper Bound Cover: CodexSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Is A Transparent, Tasteless, Odorless, and Nearly ColorlessDocumento1 paginaWater Is A Transparent, Tasteless, Odorless, and Nearly ColorlessSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Correspondence MCQ COEDocumento21 pagineBusiness Correspondence MCQ COESaad Ahsan79% (14)
- Gustave Ponton D'amécourt: Rotorcraft Lift Thrust Rotors Hover Fixed-Wing Aircraft VtolDocumento1 paginaGustave Ponton D'amécourt: Rotorcraft Lift Thrust Rotors Hover Fixed-Wing Aircraft VtolSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Car MovieDocumento1 paginaCar Moviehijaps123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tomb Raider PlotDocumento1 paginaTomb Raider PlotSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- AD ATC SyllabusDocumento1 paginaAD ATC SyllabusSaad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tomb Raider Is A 2018Documento1 paginaTomb Raider Is A 2018Saad AhsanNessuna valutazione finora