Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
DRRM Module 4 Triage
Caricato da
Anmer Layaog BatiancilaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
DRRM Module 4 Triage
Caricato da
Anmer Layaog BatiancilaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
DRRM MODULE 4 LEGAL REFERENCES:
Section 9, Powers and Functions of
OCD under R.A. 10121 (Philippine
Concepts on Incident Command Disaster Risk Reduction and
System Management Act of 2010)
“Establish standard operating
procedures on the communications
What is an Incident Command System? system among provincial, city, municipal
and barangay disaster risk reduction and
ICS is a standardized approach to management councils, for purposes of
command, control, and coordination of warning and alerting them and for
emergency response providing a common gathering information on disaster areas
hierarchy within which responders from before, during and after disasters”.
multiple agencies can be effective.
RATIONALE:
OBJECTIVE: Communication equipment,
Provision of an emergency voice,
procedures, and systems must operate
data, video, and information systems
across jurisdictions.
for response clusters;
Establishment of communications
framework for the Emergency
Why is there a need for ICS?
Operations Center (EOC) and
Incident Command Posts (ICP’s) in
The lessons of the past events such as the
disaster areas; and
Wowowee Stampede (February 2006),
Tropical Storm Ondoy (September 2009), Fostering of communications
and Tourist Bus Hostage-Taking (August interoperability and commonality for
2010), have manifested the inadequacy or all levels.
lack of an on - scene management of
emergency operations
ICS is now the common international
There is a big gap! It is confirmed that language for crisis, disaster and
there is an absence of Incident Command emergency response! ASEAN members
System at the inception of the incident, no gearing towards ICS Communication.
Incident Command Post, poor crowd control,
poor media management and failure of IN TRANSITION FULLY
communications. TO ICS: IMPLEMENTED
ISSUES & CONCERNS IN Indonesia USA
COMMUNICATION: Philippines Canada
Lack of clarity of who’s in - charge Thailand Australia
Who’s directing the ground Brunei New Zealand
operation? Mexico
Confusion and miscommunication!
Lack of coordination and planning
Political Intervention
Concepts on Principles of
Triage
Weakness in Incident Management was
often due to failure in Communications – What is a TRIAGE?
the inefficient use of available systems!
Triage is a medical decision-making
process of prioritizing and sorting of patients
What is RETT (Rapid Emergency based on the severity of their condition so as to
Telecommunications Team)? treat as many as possible when resources are
insufficient for all to be treated immediately.
RETT is a rapid deployment team
equipped with ICT resources that are organized This is typically used in emergency
to address the communications, electronics, rooms, battlefields, and disaster sites when
and information needs of the Emergency limited resources must be allocated.
Operations Center (EOC) and/or Incident
Command Posts (ICP’s) in a disaster area. GUIDING PRINCIPLES:
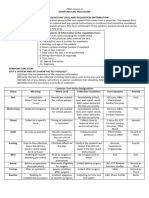
75-85% of fatalities occur within the Procedure for S.T.A.R.T.
first 20 minutes of an incident
The triage personnel DOES NOT Use this particular sequence “RPM”!
DECIDE WHO LIVES OR DIES!
THE NEED FOR SPEED! – Triage 1st – assess Respiration (assess for
should be complete in 60 seconds respiratory rate)
The four colors of triage are as
follows: RR > 30/min – tag RED
o Green (minor) RR < 30/min – DO NOT
Minor injuries TAG and proceed to
Status unlikely to Perfusion
deteriorate
Can assist in own care 2nd – assess Perfusion (assess
“walking wounded” capillary refill)
o Yellow (delayed)
Requires urgent care CR > 2 secs – tag RED
but may be delayed up CR < 2 secs – DO NOT
to one hour TAG and proceed to
Includes serious and Mental Status
life-threatening injuries
but status is not 3rd – assess Mental Status (ask
expected to deteriorate simple questions or commands)
over several hours
o Red (immediate) cannot answer / follow –
Requires immediate tag RED
intervention and care to can answer / follow – TAG
ensure survival YELLOW
Requires immediate
transport If all of the RPM is absent – TAG
o Black (dead) BLACK (deceased)
Deceased or unlikely to If one of the RPM is not normal –
survive TAG RED (immediate)
Requires palliative care If all of the RPM is normal but
or pain relief cannot walk – TAG YELLOW
(delayed)
If all of the RPM is normal but can
walk – TAG GREEN (minor)
What is a S.T.A.R.T.?
The START (Simple Triage and Rapid Who can perform Triage?
Treatment) is the widely-used type of triage. It
is a type of triage that aims at correcting the The Triage Officer – may be
main threats to life-blocked airways and severe emergency physician or a member of the first
bleeding. emergency medical crew to arrive at the scene
who is experienced in paramedics and in
S.T.A.R.T has three components which making decisions with medical control on the
sorting is based: scene.
Respiration (the action of
breathing);
Perfusion (passage of fluid
through the circulatory system);
and
Mental status
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Saint Joseph Academy Inc.: Bugasong, Antique, PhilippinesDocumento18 pagineSaint Joseph Academy Inc.: Bugasong, Antique, PhilippinesDwight CondezNessuna valutazione finora
- Prevalence of Child Abuse in Davao City: Preventive MeasuresDocumento83 paginePrevalence of Child Abuse in Davao City: Preventive MeasuresJoy CalceñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Research 1: Prelim ExaminationDocumento6 paginePractical Research 1: Prelim ExaminationJac PolidoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Three Schools of SystematicsDocumento3 pagineThe Three Schools of SystematicsLOUISE ANDRHEA D. DOLOTALLASNessuna valutazione finora
- CWTS 2 Module 2 Bandaging Rescue...Documento9 pagineCWTS 2 Module 2 Bandaging Rescue...Jozel ValenzuelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Javier Et Al. Final ..Documento19 pagineChapter 4 Javier Et Al. Final ..Jose BernelNessuna valutazione finora
- YolandaDocumento2 pagineYolandalapNessuna valutazione finora
- Humss 12a Group 2 ManuscriptDocumento16 pagineHumss 12a Group 2 Manuscriptevangeline angayenNessuna valutazione finora
- Research PanelistDocumento2 pagineResearch PanelistStephanie Marhen AbuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Disaster PreparednessDocumento13 pagineDisaster PreparednessLeodoro LabragueNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1.1-DRRRDocumento3 pagineAssignment 1.1-DRRRJhoana Jhane VillegasNessuna valutazione finora
- Iii-Q2 Module 7Documento6 pagineIii-Q2 Module 7Lielanie NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Midterm ReviewerDocumento9 pagineResearch Midterm ReviewerrebekahNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant and Animal Chemical and Nervous ControlDocumento27 paginePlant and Animal Chemical and Nervous ControlAlnedKirby Carijutan Mendiola100% (1)
- Level of Awarenss of Hypertension Among Grade 12 Science Technology Engineering and Mathematics Students of Systems Plus College FoundationDocumento35 pagineLevel of Awarenss of Hypertension Among Grade 12 Science Technology Engineering and Mathematics Students of Systems Plus College FoundationMary Grace MendeNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is SHS?Documento23 pagineWhat Is SHS?Aubreyleen Vasquez CarpioNessuna valutazione finora
- DRRR Reviewer 2NDDocumento25 pagineDRRR Reviewer 2NDMaria Elaine S. QuinalayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Research 2Documento3 paginePractical Research 2Marielyn CacheroNessuna valutazione finora
- Funda 1 30 1Documento52 pagineFunda 1 30 1Neil GuntingNessuna valutazione finora
- Scope of Theories and AnalysisDocumento10 pagineScope of Theories and AnalysismesdejenNessuna valutazione finora
- Pracres Module 9 - 14Documento15 paginePracres Module 9 - 14Prince SanjiNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Project Summary - 10%Documento5 pagineI. Project Summary - 10%ChristianAvelinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant ReproductionDocumento25 paginePlant ReproductionAngel Cipriano LiliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Study (Narra)Documento16 pagineSample Study (Narra)mariellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Research 1 ModuleDocumento23 pagineResearch 1 ModuleNina Anne ParacadNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer For Formative Assessment Gen Bio 2Documento1 paginaReviewer For Formative Assessment Gen Bio 2Melanie ArangelNessuna valutazione finora
- Gb2 Las q3 w1 GeneticsDocumento14 pagineGb2 Las q3 w1 GeneticsAnn Clarisse OndianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Poverty ResearchDocumento9 paginePoverty ResearchBravo,Jessy Anne G.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Population and SampleDocumento6 paginePopulation and SampleMaam ArenavlasNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein StructuresDocumento6 pagineProtein StructuresNugget DivineNessuna valutazione finora
- PDRRM ActDocumento21 paginePDRRM Actgene boy pitosNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen Bio 2 Summative Test Q4 Week 1 and 2Documento3 pagineGen Bio 2 Summative Test Q4 Week 1 and 2Daniel Angelo Esquejo ArangoNessuna valutazione finora
- Narrative Report Group 2Documento6 pagineNarrative Report Group 2Wendell Flores100% (1)
- 2013 Bohol EarthquakeDocumento11 pagine2013 Bohol EarthquakeMonday VerdejoNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Qualitative ResearchDocumento19 pagineIntroduction To Qualitative ResearchAnonymous LToOBqDNessuna valutazione finora
- DRRM Module 5 Activities PDFDocumento10 pagineDRRM Module 5 Activities PDF2MOLINORemelene Joyce AceresNessuna valutazione finora
- IS Hay InfusionDocumento3 pagineIS Hay InfusionRedstone SalazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Commercial Fertilizer and Natural Fertilizer To The Height of Pechay PlantDocumento27 pagineEffect of Commercial Fertilizer and Natural Fertilizer To The Height of Pechay PlantCatherine Ventura100% (1)
- Introduction To Disasters and Disaster RisksDocumento22 pagineIntroduction To Disasters and Disaster RisksREYNON GREGORIONessuna valutazione finora
- Causes of Absenteeism of Grade 9 StudentsDocumento6 pagineCauses of Absenteeism of Grade 9 StudentsRosendo Bernabe0% (1)
- Script DRRRDocumento1 paginaScript DRRReraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Lived Experience of Filipino Nurses' Work in COVID-19 Quarantine Facilities: A Descriptive Phenomenological StudyDocumento11 pagineThe Lived Experience of Filipino Nurses' Work in COVID-19 Quarantine Facilities: A Descriptive Phenomenological StudyAldrin Zolina100% (1)
- Philippine Normal University - Center For Teaching and LearningDocumento41 paginePhilippine Normal University - Center For Teaching and LearningFritz Ren KeifferNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Nursing Practice-Rle A. Environmental CleaningDocumento5 pagineFundamentals of Nursing Practice-Rle A. Environmental CleaningViea Pacaco SivaNessuna valutazione finora
- Scope and LimitationsDocumento1 paginaScope and LimitationsRachy 레이첼 FadriquelaNessuna valutazione finora
- UTS Plato ReportDocumento10 pagineUTS Plato ReportMaeq LolaNessuna valutazione finora
- G12 Makabansa (Stem) 2 Semester Q2: Written and Performance ActivityDocumento13 pagineG12 Makabansa (Stem) 2 Semester Q2: Written and Performance ActivityFritzie Corpuz0% (1)
- Checklist For Thesis Chapter 3Documento3 pagineChecklist For Thesis Chapter 3Richmon SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- DRRR Q1 Midterm ExamDocumento2 pagineDRRR Q1 Midterm ExamJeffrey OralizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Patient Positioning: Complete Guide For Nurses: Marjo S. Malabanan, R.N.,M.NDocumento43 paginePatient Positioning: Complete Guide For Nurses: Marjo S. Malabanan, R.N.,M.NMercy Anne EcatNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphy 100 Lab Practice Review Sheet 1 and 2Documento6 pagineAnaphy 100 Lab Practice Review Sheet 1 and 2Mariam GamosNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Directions: Explain Your Understanding About The Text by Answering The Following QuestionsDocumento2 pagineI. Directions: Explain Your Understanding About The Text by Answering The Following QuestionsKyle Frian HuertoNessuna valutazione finora
- Disaster RiskDocumento20 pagineDisaster RiskMariane Orola CaduyacNessuna valutazione finora
- BATANG INA Lived Experiences of StudentDocumento63 pagineBATANG INA Lived Experiences of StudentSam OxfordNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Concept of DRRRDocumento39 pagineBasic Concept of DRRRJim CandiiNessuna valutazione finora
- University Research Ethics CommitteeDocumento2 pagineUniversity Research Ethics CommitteeKyle Alexander OzoaNessuna valutazione finora
- Snowball SamplingDocumento19 pagineSnowball SamplingAnam khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Disaster Nursing PrefinalsDocumento6 pagineDisaster Nursing PrefinalsZarida ArabainNessuna valutazione finora
- Susan Quiambao - CNDR Summit PPT Edited As of 14 JulyDocumento28 pagineSusan Quiambao - CNDR Summit PPT Edited As of 14 JulyRemer JalbunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Triage: Code Tags and Triage TerminologyDocumento5 pagineMedical Triage: Code Tags and Triage TerminologyAnna Mae SuminguitNessuna valutazione finora
- Chariot of The Sun GodDocumento6 pagineChariot of The Sun GodAnmer Layaog BatiancilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Handouts CapacityDocumento4 pagineHandouts CapacityAnmer Layaog BatiancilaNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Cebu-Main Campus Entrepreneurship 100 Chapter 11 QuizDocumento3 pagineUniversity of Cebu-Main Campus Entrepreneurship 100 Chapter 11 QuizAnmer Layaog BatiancilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Leadership ModuleDocumento3 pagineLeadership ModuleAnmer Layaog BatiancilaNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Cebu-Main Campus Entrepreneurship 100 Chapter 11 QuizDocumento3 pagineUniversity of Cebu-Main Campus Entrepreneurship 100 Chapter 11 QuizAnmer Layaog BatiancilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome To WPS OfficeDocumento7 pagineWelcome To WPS OfficenlubawiNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome To WPS OfficeDocumento7 pagineWelcome To WPS OfficenlubawiNessuna valutazione finora
- Rose-Marie Vill PDFDocumento4 pagineRose-Marie Vill PDFAnmer Layaog BatiancilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rose-Marie Vill PDFDocumento4 pagineRose-Marie Vill PDFAnmer Layaog BatiancilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Varisara Kriya PDFDocumento14 pagineVarisara Kriya PDFGottimukkala Muralikrishna100% (1)
- Resume Jurnal ADocumento11 pagineResume Jurnal AannisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Psyc Essay Final 010420Documento2 paginePsyc Essay Final 010420Ali HajassdolahNessuna valutazione finora
- Portable Toilet For Disaster Relief KinstedtDocumento3 paginePortable Toilet For Disaster Relief KinstedtMustafa HyaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Epo Rsud 2020Documento45 pagineEpo Rsud 2020vera arimbiNessuna valutazione finora
- PychologyDocumento3 paginePychologynoman nomiNessuna valutazione finora
- Kidney TransplantationDocumento5 pagineKidney TransplantationDeadly ChillerNessuna valutazione finora
- Art Therapy and Dialectical Behavioral Therapy - A WorkbookDocumento35 pagineArt Therapy and Dialectical Behavioral Therapy - A WorkbookZainab BorjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Hematology CasesDocumento27 pagineHematology Casessamkad214100% (2)
- DHN 374 News BriefDocumento2 pagineDHN 374 News Briefapi-340516995Nessuna valutazione finora
- Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocumento53 paginePeripheral Vascular DiseaseShenbagam Mahalingam100% (1)
- Vertigo Vertigoheel 2001Documento7 pagineVertigo Vertigoheel 2001Dr. Nancy Malik100% (1)
- NSAID Safety Audit Jan2019 Vs6Documento10 pagineNSAID Safety Audit Jan2019 Vs6Shokooh MansouriNessuna valutazione finora
- Heavy HandsDocumento8 pagineHeavy HandsPicklehead McSpazatronNessuna valutazione finora
- Acceptance and Mindfulness Treatments For Children and Adolescents. A Practitioner's Guide - Greco, L. y Hayes, S.Documento249 pagineAcceptance and Mindfulness Treatments For Children and Adolescents. A Practitioner's Guide - Greco, L. y Hayes, S.Antonella María De Jesús Napán Carbajal100% (4)
- PMLS Lesson 4Documento3 paginePMLS Lesson 4Void MelromarcNessuna valutazione finora
- 2ton Steel 56.8gDocumento4 pagine2ton Steel 56.8gYasir AzmatNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.1 - Common Nutritional Problems in ToddlersDocumento6 pagine4.1 - Common Nutritional Problems in ToddlersDrSajid BuzdarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pyromania-The Urge To Set Fires For Pleasure, Gratification, or Release of Tension Ezhae SymptomsDocumento2 paginePyromania-The Urge To Set Fires For Pleasure, Gratification, or Release of Tension Ezhae SymptomsptbarnabicNessuna valutazione finora
- Part A. Reading Comprehension: Attitude Therapy Misleading Recognize Refuse EstablishmentDocumento2 paginePart A. Reading Comprehension: Attitude Therapy Misleading Recognize Refuse EstablishmentCarol80% (5)
- PEG Information With AzithromycinDocumento9 paginePEG Information With AzithromycinTrần Lê Tuyết ChâuNessuna valutazione finora
- Gastrocnemius SoleusDocumento8 pagineGastrocnemius SoleusgoldfishxNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Limb Ischemia: Clinical PracticeDocumento9 pagineAcute Limb Ischemia: Clinical PracticeKezia TambunanNessuna valutazione finora
- Guinea Pigs PDFDocumento1 paginaGuinea Pigs PDFYaserAbbasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Postpartum Care: Emergency SignsDocumento13 paginePostpartum Care: Emergency SignsJohnnette BedoniaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCD Guidelines 2012Documento12 pagineNCD Guidelines 2012Nari BurathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Advisor Vol 14Documento8 pagineAdvisor Vol 14ninh2dNessuna valutazione finora
- Parasitology Lec 3.01a Intestinal NematodesDocumento16 pagineParasitology Lec 3.01a Intestinal NematodesEnaWahahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clasificare Carii Dentare Otr Cariologie An IIIDocumento79 pagineClasificare Carii Dentare Otr Cariologie An IIIStefana NanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Mind Control Forums - Complete Book ListDocumento11 pagineMind Control Forums - Complete Book ListSimon Benjamin100% (2)