Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Computers Are Electronic Machines Which Can Accept Data in A Certain Form
Caricato da
dzenitaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Computers Are Electronic Machines Which Can Accept Data in A Certain Form
Caricato da
dzenitaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Computers are electronic machines which can accept data in a certain form, process the data and
give results of the processing in a specified format as information.
Information in the form of data and programs is known as software.
Electronic and mechanical parts that make up a computer system are called hardware.
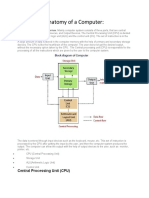
Perhaps the most influential component is the central processing unit. Its function is to execute
program instructions and coordinate the activities of all other unit. The main memory holds the
instructions and data which are currently being processed by the CPU.
Storage devices (hard or optical disks) provide a permanent storage of both data and programs.
Input devices enable data to go into computer’s memory.
The most common input devices are the mouse and the keyboard.
Output devices enable us to extract the finished product from the system.
For example, the computer shows the output on the monitor or prints the results onto paper by
means of a printer.
The control unit, which examines the instructions in the user’s program, interprets each instruction
and causes the circuits and the rest of the components – disk drives, monitor, etc. – to be activated
to execute the functions specified;
The arithmetic logic unit (ALU) which performs mathematical calculations (+,-, etc.) and logical
operations (and, or, etc.)
The registers, which are high-speed units of memory used to store and control information. One of
these registers is the program counter (PC) which keeps track of the next instruction to be
performed in the main memory. Another is the instruction register (IR) which holds the instruction
that is currently being executed.
What are the main parts of the CPU?
2. What is RAM?
3. What memory section is permanent and contains instructions needed by the CPU?
4. What information is lost when the computer is switched off?
5. What is the typical unit used to measure RAM memory and storage memory?
6. What is the meaning of the acronym SIMM?
7. What is a megahertz?
8. What is ALU? What does it do?
9. What is the abbreviation for 'binary digit'?
10. How can we store data and programs permanently
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Components of A ComputerDocumento5 pagineComponents of A ComputersoujanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 1:-Introduction of Computer HardwareDocumento13 paginePractical 1:-Introduction of Computer HardwareKaveesh NykNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1Documento15 pagineUnit 1Aryan AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 - Computer Organization and Architecture - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocumento33 pagineUnit 1 - Computer Organization and Architecture - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inRanjana DalwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Workshop - I Lab ManualDocumento36 pagineWorkshop - I Lab Manualatulya singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1Documento18 pagineUnit 1Harshvardhan MohiteNessuna valutazione finora
- File 1674110529 5000677 1.1FunctionalblocksofacomputerCPUmemoryinput-outputsubsystemscontrolunitDocumento3 pagineFile 1674110529 5000677 1.1FunctionalblocksofacomputerCPUmemoryinput-outputsubsystemscontrolunitManaswi GargNessuna valutazione finora
- In The Heart of Computers-Trabalho de TraduçãoDocumento2 pagineIn The Heart of Computers-Trabalho de TraduçãoMaiPereiraSilva100% (1)
- Computer Anatomy ExplainedDocumento9 pagineComputer Anatomy ExplainedAnjuman AraaNessuna valutazione finora
- 11computer Science-Computer System Overview-NotesDocumento12 pagine11computer Science-Computer System Overview-NotesDeepanshu GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 11 - Central Processing UnitDocumento4 pagineLecture 11 - Central Processing UnitPragya SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On Computer PDFDocumento19 pagineNotes On Computer PDFGolam Rasul KibriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Block Diagram of A ComputerDocumento4 pagineBlock Diagram of A Computerwoyaf61625Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pps NotesDocumento193 paginePps Notesatulya singhNessuna valutazione finora
- IT-Unit 1Documento11 pagineIT-Unit 1anithareddygpcetNessuna valutazione finora
- Hardware Components and FunctionsDocumento8 pagineHardware Components and Functionsigwe nnabuikeNessuna valutazione finora
- Qno1: Draw Block Diagram of Computer. and Also Define Major Parts in Own LanguageDocumento6 pagineQno1: Draw Block Diagram of Computer. and Also Define Major Parts in Own LanguageMohsin IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Pps Notes (4 Files Merged)Documento175 paginePps Notes (4 Files Merged)atulya singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer System Computer ArchitectureDocumento7 pagineComputer System Computer ArchitectureSuman Samal MagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Components of Computer SystemDocumento4 pagineBasic Components of Computer SystemAnonymous u64nn35tHCNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are The 5 Basic Operations of A ComputerDocumento3 pagineWhat Are The 5 Basic Operations of A ComputerShin NeulNessuna valutazione finora
- Programming For Problem Solving-NotesDocumento52 pagineProgramming For Problem Solving-NotesVeeramaniNessuna valutazione finora
- COMPUTER APPLICATION IN HRMDocumento10 pagineCOMPUTER APPLICATION IN HRMshazzymutukuNessuna valutazione finora
- IT Basics & ComponentsDocumento12 pagineIT Basics & ComponentsAamin singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer COMPONENTDocumento6 pagineComputer COMPONENTwowafer745Nessuna valutazione finora
- Comfuter Fundamentals Networking IdT1xQZfsDocumento199 pagineComfuter Fundamentals Networking IdT1xQZfsRhdheh BdhehenNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 Block Diagram of ComputerDocumento9 pagineLecture 1 Block Diagram of ComputerGaurav BishtNessuna valutazione finora
- HardwareDocumento22 pagineHardwarealexNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental of Computer ProgrammingDocumento93 pagineFundamental of Computer ProgrammingSarmi HarshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Xi Ip 2013-14Documento136 pagineXi Ip 2013-14Ravi JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- CSC 111 - (3) Computer HardwareDocumento39 pagineCSC 111 - (3) Computer Hardwarevictoriaiyanuoluwa40Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Computer TerminologiesDocumento2 pagineBasic Computer TerminologiesBeverly CentinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3 PDFDocumento3 pagineLesson 3 PDFcharimaine hernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- CO - OS Unit-1 (Part1)Documento40 pagineCO - OS Unit-1 (Part1)ffjsNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2Documento28 pagineLesson 2Princess Rose MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Notes Hardware ConceptsDocumento11 pagine01 Notes Hardware ConceptsAbhinav AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- CSDocumento292 pagineCSSantanu Kumar SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of a Digital Computer: Key Components and FunctionsDocumento24 pagineAnatomy of a Digital Computer: Key Components and FunctionsanilkumarosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- A Computer Is An Electronic DeviceDocumento10 pagineA Computer Is An Electronic Devicearvinder kaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Block Diagram of Computer SystemDocumento7 pagineBlock Diagram of Computer Systemnsmk malerkotlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of ComputerDocumento6 pagineStructure of ComputerMADONZA, CHERRILOU M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Computers: Data, Processing, and SystemsDocumento60 pagineIntroduction to Computers: Data, Processing, and SystemsaveegoNessuna valutazione finora
- IT Fundamentals of Hardware and SoftwareDocumento2 pagineIT Fundamentals of Hardware and SoftwareKenya LevyNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Basic Operations Performed by Computer SystemDocumento5 pagine5 Basic Operations Performed by Computer SystemNuj Wehtam Inairam100% (7)
- Computer System: Prepared By: Suresh KhatiwadaDocumento18 pagineComputer System: Prepared By: Suresh KhatiwadakamalshrishNessuna valutazione finora
- Cite1004 Activity 1 MidtermDocumento3 pagineCite1004 Activity 1 MidtermJoshua LimbagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Components of A ComputerDocumento11 pagineFunctional Components of A Computerypk10072003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Components of A Computer SystemDocumento26 pagineComponents of A Computer SystemheheheheNessuna valutazione finora
- Distinguish computer architecture and organizationDocumento36 pagineDistinguish computer architecture and organizationsunnybaggaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 of Computer OrganizationDocumento27 pagineModule 1 of Computer OrganizationNimmymolManuelNessuna valutazione finora
- The Essential Guide to Computer Hardware and SoftwareDocumento6 pagineThe Essential Guide to Computer Hardware and SoftwareAjit JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Notes - Computer HardwareDocumento6 pagineClass Notes - Computer Hardwaregerrad cortezNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional units and buses in digital systemsDocumento20 pagineFunctional units and buses in digital systemsDivyaanshu AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Leeson 5 Comp 101Documento6 pagineLeeson 5 Comp 101Patricia Mae D. RamboangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter No.1 Basics of Information TechnologyDocumento17 pagineChapter No.1 Basics of Information TechnologyAmruta DhengaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Material 2012-13 CLASS XI INFORMATION PRACTICIESDocumento136 pagineStudy Material 2012-13 CLASS XI INFORMATION PRACTICIESKrishna Gurjar0% (1)
- Block Diagram-Wps OfficeDocumento35 pagineBlock Diagram-Wps OfficeArmando Delos SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Direction Ni NanatDocumento2 pagineDirection Ni NanatKeni KennNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2. Hardware ComponentsDocumento10 pagineUnit 2. Hardware ComponentsRaju KumaarNessuna valutazione finora
- IB HL Chemistry Lab Report Format: Name: Date: TitleDocumento2 pagineIB HL Chemistry Lab Report Format: Name: Date: TitledzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Studies On Egyptian Honey and Royal Jelly: Samir Yousef Abdelsaid YousefDocumento251 pagineStudies On Egyptian Honey and Royal Jelly: Samir Yousef Abdelsaid YousefdzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Konsultacije 1Documento4 pagineKonsultacije 1dzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Computers Are Electronic Machines Which Can Accept Data in A Certain FormDocumento2 pagineComputers Are Electronic Machines Which Can Accept Data in A Certain Formdzenita0% (1)
- En 22047 PDFDocumento5 pagineEn 22047 PDFdzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Air PollutionDocumento57 pagineFundamentals of Air PollutiondzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diazo CompaundsDocumento13 pagineDiazo CompaundsdzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Urn NBN Si Doc 4jfwbmyhDocumento5 pagineBody Urn NBN Si Doc 4jfwbmyhdzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 1 1 605 1167Documento9 pagine10 1 1 605 1167dzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Discovery and Structure of Aromatic CompoundsDocumento108 pagineDiscovery and Structure of Aromatic Compoundsdzenita100% (1)
- Steve Jobs: The Innovative Mind Behind Apple's SuccessDocumento4 pagineSteve Jobs: The Innovative Mind Behind Apple's SuccessAlena JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- Manyi-Loh Et AlDocumento9 pagineManyi-Loh Et AldzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Steven Paul JobsDocumento2 pagineSteven Paul JobsdzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Steve Jobs: The Innovative Mind Behind Apple's SuccessDocumento4 pagineSteve Jobs: The Innovative Mind Behind Apple's SuccessAlena JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- DopingDocumento46 pagineDopingdzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- ROS White Paper - 2015Documento21 pagineROS White Paper - 2015dzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Honey CodexDocumento8 pagineHoney CodexcosminubNessuna valutazione finora
- En 22047 PDFDocumento5 pagineEn 22047 PDFdzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atmospheric Chemistry Is A Branch ofDocumento1 paginaAtmospheric Chemistry Is A Branch ofdzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Air PollutionDocumento57 pagineFundamentals of Air PollutiondzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Food Chemistry: Geetha Samak, Revathi P. Shenoy, S.M. Manjunatha, K.S. VinayakDocumento4 pagineFood Chemistry: Geetha Samak, Revathi P. Shenoy, S.M. Manjunatha, K.S. VinayakdzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemisty of AirDocumento1 paginaChemisty of AirdzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bees and Honey Against Tuberculosis 2329 8731.1000e103 PDFDocumento2 pagineBees and Honey Against Tuberculosis 2329 8731.1000e103 PDFdzenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Knjiga MeddDocumento25 pagineKnjiga MedddzenitaNessuna valutazione finora