Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Liplesion 13
Caricato da
megahedhazeem0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
32 visualizzazioni13 pagine1
Titolo originale
liplesion-13
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documento1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
32 visualizzazioni13 pagineLiplesion 13
Caricato da
megahedhazeem1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 13
Wasan Magdy khmais
LIP LESION 5212333
Renad Magdy khamis
5212147
OUTLINE
- Introduction
- Cheilitis Glandularis
- Cheilitis Granulomatosa
- Exfoliative Cheilitis
- Contact Cheilitis
- Actinic Cheilitis
- Angular Cheilitis
- Lip-Licking Dermatitis
- Median Lip Fissure
- Angioneurotic Edema
INTRODUCTION
Disorders that exclusively affect the lips, systemic diseases that
produce characteristic lip lesions, and some other entities are
included in this group. In some of them, the diagnosis should be
made on the basis of clinical criteria, but histopathological
confirmation of the diagnosis is always necessary.
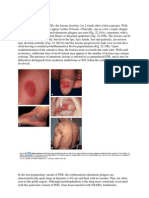
CHEILITIS GLANDULARIS
Cause : Unknown
Clinical features : It presents as a swelling
of the lower lip due to hyperplasia and inflammation
of the glands Characteristically, the orifices
of the salivary glands are dilated ,
and pressure on the lip may produce mucous
or mucopustular fluid from the ductal openings ,
Crusting and erosions may also occur.
CHEILITIS GRANULOMATOSA
Cause : Unknown
Clinical features :It presents as a painless , persistent ,
and diffuse swelling of one or both lips Small vesicles,
erosions, and scaling may occur.
It is thought that cheilitis granulomatosa is
a monosymptomatic form of
Melkersson–Rosenthal syndrome.
EXFOLIATIVE CHEILITIS
Cause : Unknown
Clinical features : It is characterized by
scaling, crusting, and erythema
of the vermilion border of the lips.
This pattern is repetitive, resulting in yellowish,
hyperkeratotic thickening, crusting, and fissuring .
The lesions are more common in young women,
usually persist with variable severity for months
or years , and may cause cosmetic problems. The diagnosis is based
on the clinical findings.
CONTACT CHEILITIS
Cause : Topical contact with various chemical agents.
Clinical features : It is characterized by
mild edema and erythema,
followed by irritation and thick scaling .
It is usually confined to the vermilion border
of both lips.
The diagnosis is based on clinical criteria and a skin patch test.
ACTINIC CHEILITIS
Cause : Long-term exposure to sunlight.
Clinical features : In the early stage, mild erythema
and edema followed by dryness and
fine scaling of the lower lip vermilion border
are the presenting signs. As the lesion progresses,
the epithelium becomes thin and smooth,
with small whitish-gray areas intermingled
with red regions and scaly formations .
Erosions and tiny nodules may develop. The lesion is premalignant,
and usually occurs in men over 50 years of age
ANGULAR CHEILITIS
Cause : Reduced vertical dimension, mechanical trauma, Candida
albicans, staphylococci, streptococci, iron-deficiency anemia,
riboflavin deficiency.
Clinical features : The condition is characterized by erythema,
maceration, fissuring, erosions, and crusting at the commissures .
Classically, the lesions do not extend beyond the mucocutaneous
border. A burning sensation and a feeling of dryness may occur.
Remissions and exacerbations are common. The diagnosis is based on
the clinical findings.
LIP-LICKING DERMATITIS
Cause : Chronic licking.
Clinical features : The lips and the perioral skin are erythematous,
associated with scaling, crusting,
and fissuring of variable severity .
A burning sensation is a common symptom.
The diagnosis is based on the clinical findings.
MEDIAN LIP FISSURE
Cause : Unclear.
Clinical features : It presents as a deep, inflammatory,
persistent vertical fissure at the middle of the lip,
usually infected by Candida albicans and bacteria.
Spontaneous bleeding, discomfort, and pain are common.
The diagnosis is based on the clinical findings.
ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA
Cause : Inherited or acquired (food allergy, chemicals, infections,
stress).
Clinical features : It characteristically has a sudden onset,
and lasts for 24–48 hours.
The lesion presents as a painless,
smooth swelling of the lips .
Other intraoral regions
and the glottis may also be involved.
The diagnosis is usually based on the clinical findings.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Dermatology NotesDocumento37 pagineDermatology NotesTamilmani n.mNessuna valutazione finora
- A Beginners Guide To Pre-Hospital Emergency Medicine PDFDocumento20 pagineA Beginners Guide To Pre-Hospital Emergency Medicine PDFmegahedhazeem100% (1)
- Dermatology Made EasyDocumento46 pagineDermatology Made EasyHeather Marie Mathis100% (1)
- Derma Notes 22pages. DR - Vishwa Medical CoachingDocumento23 pagineDerma Notes 22pages. DR - Vishwa Medical CoachingΝίκος ΣυρίγοςNessuna valutazione finora
- Melanocytic TumorsDocumento170 pagineMelanocytic TumorsOlteanu Dragos-Nicolae100% (1)
- Geographic TongueDocumento5 pagineGeographic Tonguebhawna_aroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatitis DR Citra 260907Documento56 pagineDermatitis DR Citra 260907Adam AriwibawaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Report ChickenpoxDocumento6 pagineCase Report ChickenpoxNofilia Citra CandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatoscopy The Basics With ExercisesDocumento130 pagineDermatoscopy The Basics With Exerciseslaszlo_mihalyimre2100% (3)
- Bite Splints 14 PDFDocumento14 pagineBite Splints 14 PDFmegahedhazeemNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology and Principles Of-18Documento49 pagineBiology and Principles Of-18megahedhazeemNessuna valutazione finora
- Sur Mucosal Lesions-207Documento207 pagineSur Mucosal Lesions-207megahedhazeemNessuna valutazione finora
- pl07025 PDFDocumento10 paginepl07025 PDFmegahedhazeemNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 HomeworkDocumento6 pagineModule 3 HomeworkCj LinceNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurodermatitis (Lichen Simplex Chronic)Documento26 pagineNeurodermatitis (Lichen Simplex Chronic)Yusran Ady FitrahNessuna valutazione finora
- Fixed Drug Eruption, Bolognia DermatologyDocumento2 pagineFixed Drug Eruption, Bolognia Dermatologyjacob89Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pricelist Poliklinik Kecantikan Klinik Dahayu MedikaDocumento9 paginePricelist Poliklinik Kecantikan Klinik Dahayu MedikaAini AjizahNessuna valutazione finora
- EpsDocumento24 pagineEpsRosaldy MuhamadNessuna valutazione finora
- Blisters Read Only RVDocumento75 pagineBlisters Read Only RVFrederica MutiaraNessuna valutazione finora
- DERMA Common DX TX 1Documento2 pagineDERMA Common DX TX 1Ger Maine ApalisokNessuna valutazione finora
- Syphilis - The Great ImitatorDocumento4 pagineSyphilis - The Great ImitatorIJAERS JOURNALNessuna valutazione finora
- Lip LesionsDocumento4 pagineLip LesionsGhada AlqrnawiNessuna valutazione finora
- Fever With Rash Atlas PDFDocumento14 pagineFever With Rash Atlas PDFK C Goutham ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 iMAGE BASED MCQSDocumento9 pagine15 iMAGE BASED MCQSonline mbbsNessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer: Basal & Squamous CellDocumento14 pagineNon-Melanoma Skin Cancer: Basal & Squamous Cellrafak2medNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Report: Journal of Chitwan Medical College 2020 10 (31) :91-93Documento3 pagineCase Report: Journal of Chitwan Medical College 2020 10 (31) :91-93Yeni PuspitasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Homeostatic Imbalances: in The Integumentary SystemDocumento27 pagineHomeostatic Imbalances: in The Integumentary SystemMarilou Dacles IINessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnosis Dan DD Lesi Ulserative VesikoBulosaDocumento21 pagineDiagnosis Dan DD Lesi Ulserative VesikoBulosaAbd RaqibNessuna valutazione finora
- Han Book of Signs in Clinical DermatologyDocumento180 pagineHan Book of Signs in Clinical DermatologyLumière Cosmetología integralNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuliah Pengantar Kuku Rambut: DR Silvi Suhardi SPKK FK Univ. Tarumanagara 2016Documento33 pagineKuliah Pengantar Kuku Rambut: DR Silvi Suhardi SPKK FK Univ. Tarumanagara 2016Dio PattersonNessuna valutazione finora
- Palmoplantar PustulosisDocumento6 paginePalmoplantar PustulosisputraimanullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Rainbow Pattern-EADV2016 PosterDocumento1 paginaRainbow Pattern-EADV2016 PosterlpozohNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebook Nonneoplastic Dermatopathology PDF Full Chapter PDFDocumento77 pagineEbook Nonneoplastic Dermatopathology PDF Full Chapter PDFmichael.doctor466100% (26)
- HGDocumento7 pagineHGRuchi HumaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Eczema and DermatitisDocumento47 pagineEczema and DermatitisDeborah ChemutaiNessuna valutazione finora