Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
Caricato da
MomPreneeCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
Caricato da
MomPreneeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Artificial Vegetative reproduction / Sciene Grade 7/ gcamus 10.23.
2018
Artificial vegetative reproduction/ propagation is a type of plant reproduction that is
accomplished through artificial means involving human intervention. The most common types
of artificial vegetative reproductive techniques involve cutting, layering, grafting, suckering,
and tissue culture. These methods are employed by many farmers and horticulturists to produce
healthier crops with more desirable qualities.
Types of Artificial vegetative reproduction/ propagation :
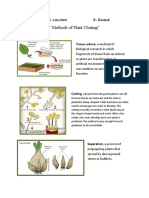
Cutting - A part of a plant, typically a stem or leaf, is cut off and planted. Adventitious
roots develop from the cuttings and a new plant eventually forms. Cuttings are
sometimes treated with hormones before being planted to induce root development.
Example: Magnolia
Grafting - In grafting, a desired cutting or scion is attached to the stem of another plant
that remains rooted in the ground. Eventually, the tissue systems of the cutting become
grafted into or integrated with the tissue systems of the base plant.
Example: Apple plant/tree, citrus, cedar
Layering - This method involves bending plant branches or stems so that they touch the
ground. The portions of branches or stems in contact with the ground are then covered
with soil. Adventitious roots develop in the parts covered by soil and the attached shoot
(branch or stem) with new roots is known as a layer. This type of layering also occurs
naturally. In another technique called air layering, branches are scraped and covered
with plastic to reduce moisture loss. Adventitious roots develop where the branches were
scrapped and the branches are removed from the tree and planted. The branches
develop into new plants over time.
Example: forsythia, boxwood
Suckering - Suckers are allowed to grow to form a dense compact mat that is attached
to the parent plant. Since too many suckers can lead to a smaller crop size, excess
numbers are pruned. Mature suckers are cut away from the parent plant and
transplanted to a new area where they grow into new plants.
Example: lilacs, hedge bushes, maki
Tissue Culture - This technique involves the culturing of plant cells that may be taken from
different parts of a parent plant. The tissue is placed in a sterilized container and nurtured
in a special medium until a mass of cells known as a callus is formed. The callus is then
cultured in a hormone-ladened medium and eventually develops into plantlets. Plantlets
can then be planted and develop into fully grown plants.
Example: orchids, female papaya, or any plant that can be cloned
Artificial Vegetative reproduction / Sciene Grade 7/ gcamus 10.23.2018
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Methods of Plant Propagation: Sexually and Asexually Propagating PlantsDocumento30 pagineMethods of Plant Propagation: Sexually and Asexually Propagating PlantsCarrylle Janne NovalNessuna valutazione finora
- Propagating OrchidsDocumento4 paginePropagating OrchidsHelenChung100% (1)
- Plant PropDocumento63 paginePlant PropVeronica NiemNessuna valutazione finora
- Seed Propagation Techniques For The Home OwnerDocumento16 pagineSeed Propagation Techniques For The Home OwnerVinny100% (4)
- Lesson 6 LO5 - Lesson Information 5.1Documento13 pagineLesson 6 LO5 - Lesson Information 5.1It's me zafra blogsNessuna valutazione finora
- Obligation and Contracts Art 1156 To 1178 Civil Code of The Philippines - Republic Act No 386Documento3 pagineObligation and Contracts Art 1156 To 1178 Civil Code of The Philippines - Republic Act No 386Mom Gie100% (7)
- Artificial Vegetative Propagation For Fruit Tree NurseryDocumento27 pagineArtificial Vegetative Propagation For Fruit Tree NurseryDerrick Yson (Mangga Han)Nessuna valutazione finora
- GraftingDocumento8 pagineGraftingCecilia Baculio100% (1)
- AgroforestryDocumento5 pagineAgroforestryNasira KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil ClassificationDocumento14 pagineSoil Classificationanimesh100% (1)
- Asexual Reproduction in Plants SEREDDYDocumento34 pagineAsexual Reproduction in Plants SEREDDYDr.Eswara Reddy SiddareddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Vegetative PropagationDocumento5 paginePrinciples of Vegetative PropagationJensenNessuna valutazione finora
- Propagation and Nursery ManagementDocumento22 paginePropagation and Nursery ManagementVutchili Utchili100% (1)
- Land Preparation Key Check 2 Well-Leveled FieldDocumento21 pagineLand Preparation Key Check 2 Well-Leveled FieldThe Municipal AgriculturistNessuna valutazione finora
- Grafting and Budding: A Practical Guide for Fruit and Nut Plants and OrnamentalsDa EverandGrafting and Budding: A Practical Guide for Fruit and Nut Plants and OrnamentalsNessuna valutazione finora
- Unified Soil Classification (Astm D-2487-98)Documento1 paginaUnified Soil Classification (Astm D-2487-98)carmaxteodrzNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.02 Plant PropagationDocumento38 pagine4.02 Plant PropagationJessel Argente Basadre100% (1)
- Five Simple Grafting Techniques Best Suited for Most Exotic Fruit PlantsDa EverandFive Simple Grafting Techniques Best Suited for Most Exotic Fruit PlantsNessuna valutazione finora
- Resistance To Airflow of Grains, Seeds, Other Agricultural Products, and Perforated Metal SheetsDocumento7 pagineResistance To Airflow of Grains, Seeds, Other Agricultural Products, and Perforated Metal SheetsDaniela DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Artificial Vegetative PropagationDocumento4 pagineArtificial Vegetative PropagationRainZZaK100% (1)
- Natalie Cole ScienceDocumento25 pagineNatalie Cole ScienceD JNessuna valutazione finora
- Pink Lined Illustration Communication Training Talking PresentationDocumento14 paginePink Lined Illustration Communication Training Talking PresentationJimmy Q MadroneroNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson: Propagating Plants AsexuallyDocumento39 pagineLesson: Propagating Plants AsexuallyKayNessuna valutazione finora
- LAS GenBio2 MELC 1 Week 1Documento14 pagineLAS GenBio2 MELC 1 Week 1Roland Jacques AlconisNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant PropagationDocumento4 paginePlant PropagationChryselleNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction in Plants G7 SDocumento37 pagineReproduction in Plants G7 Sgeorgy shibuNessuna valutazione finora
- Umesh Thappa Plant PropagationDocumento11 pagineUmesh Thappa Plant PropagationLoma somNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Quarter Lessons 2.0Documento97 pagine2nd Quarter Lessons 2.0Jean Zyrelle AuronNessuna valutazione finora
- CropSci ReviewerDocumento5 pagineCropSci ReviewerVENTURA, ANNIE M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Planting MethodsDocumento5 paginePlanting Methodsryan angelo de guzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- BA 3884 Propagation in Fruit CropsDocumento12 pagineBA 3884 Propagation in Fruit CropsKevin SaúlNessuna valutazione finora
- Vegetative ReproductionDocumento5 pagineVegetative ReproductionaerollennoxNessuna valutazione finora
- Vegetative PropagationDocumento3 pagineVegetative PropagationShubham SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Cadsvzfdbgxfnhcgjvkbklnl M'Documento21 pagineCadsvzfdbgxfnhcgjvkbklnl M'Bharat PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Layering in PlantsDocumento3 pagineLayering in PlantsS.K. AkhtarzaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Eli Whenonah Q040 Exercise5Documento6 pagineEli Whenonah Q040 Exercise5WhenonahNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant PropagationDocumento6 paginePlant PropagationAminalhaya UsmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods of Plant Propagation Sexual and VegetativeDocumento8 pagineMethods of Plant Propagation Sexual and VegetativeEditor IJTSRDNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 TVL 11 Pasay Els q2 w3Documento20 pagine04 TVL 11 Pasay Els q2 w3Ana Kristelle Grace SyNessuna valutazione finora
- AgricultureDocumento2 pagineAgriculturevim09480Nessuna valutazione finora
- G11 LAS in ACP Q2Wk1 Care For Germinating SeedlingsDocumento11 pagineG11 LAS in ACP Q2Wk1 Care For Germinating SeedlingsEleanor CabungcagNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Artificial Propagation Essay Agung 9Documento3 pagineScience Artificial Propagation Essay Agung 9api-197385195Nessuna valutazione finora
- Agri 11 - QTR 2 - LAS - Week 6Documento15 pagineAgri 11 - QTR 2 - LAS - Week 6Raquel B. GarridoNessuna valutazione finora
- Asexual Propagation by Miming Momaming PDFDocumento6 pagineAsexual Propagation by Miming Momaming PDFLebron DoggiNessuna valutazione finora
- Propagating Plants Asexually: Unit. Plant Science Problem Area. Plant PropagationDocumento37 paginePropagating Plants Asexually: Unit. Plant Science Problem Area. Plant PropagationRanjan SarmahNessuna valutazione finora
- Crop Science 140Documento4 pagineCrop Science 140steven.jc664Nessuna valutazione finora
- Scientific Classification For BananaDocumento16 pagineScientific Classification For Bananakour jaspreetNessuna valutazione finora
- Historical of TleDocumento22 pagineHistorical of TleEdgar Jr MagalonaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Grafting?Documento6 pagineWhat Is Grafting?Ace MielNessuna valutazione finora
- Commercial Production of Grafting Method of Plantation - A New InnovationDocumento34 pagineCommercial Production of Grafting Method of Plantation - A New InnovationMaster PrintersNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento22 pagineChapter 2Orlan AmbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Propagating HouseplantsDocumento3 paginePropagating HouseplantsKirk's Lawn CareNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen Bio 2Documento33 pagineGen Bio 2Rick RhomanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fruit and Seed DispersalDocumento6 pagineFruit and Seed DispersalLenovoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mode of ReproductionDocumento21 pagineMode of ReproductionGian CabayaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Propagation. in Nature, Clonal Propagation Occurs by Apomixis (Seed Development WithoutDocumento12 paginePropagation. in Nature, Clonal Propagation Occurs by Apomixis (Seed Development WithoutAmalia ZaidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grafting Procedure: For Sweet TamarindDocumento41 pagineGrafting Procedure: For Sweet TamarindHermie LicuanNessuna valutazione finora
- EPP Reviewer2ndDocumento2 pagineEPP Reviewer2ndMariejo DumalagNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmd 2Y 2.3 Pharmacognosy & PhytopharmaceuticalsDocumento12 paginePharmd 2Y 2.3 Pharmacognosy & PhytopharmaceuticalsMeghali ChoudhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.02 Plant PropagationDocumento38 pagine4.02 Plant Propagationjayson sorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- 'Methods of Plant Cloning": Lourinne Marie S. Lolong 8 - EagleDocumento2 pagine'Methods of Plant Cloning": Lourinne Marie S. Lolong 8 - EagleMarieNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods of Propagating TreesDocumento11 pagineMethods of Propagating TreesYvonne DolorosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Angels Project PlantsDocumento6 pagineAngels Project Plantsmarycris gonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Mahogani PlantationDocumento21 pagineMahogani Plantationfox mNessuna valutazione finora
- How - Do - Organisms - Reproduce - Full NotesDocumento6 pagineHow - Do - Organisms - Reproduce - Full Noteskfjg47zq26Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4.02 Plant PropagationDocumento38 pagine4.02 Plant PropagationJessel Argente BasadreNessuna valutazione finora
- Quadratic ExercisesDocumento1 paginaQuadratic ExercisesMomPreneeNessuna valutazione finora
- Figures of SpeechDocumento2 pagineFigures of SpeechMomPreneeNessuna valutazione finora
- Home Reading Report - Romeo and JulietDocumento1 paginaHome Reading Report - Romeo and JulietMomPreneeNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Behavior - ReviewerDocumento2 pagineGas Behavior - ReviewerMomPreneeNessuna valutazione finora
- HELE Grade 6-Reveiwer - 1st Periodical TestDocumento7 pagineHELE Grade 6-Reveiwer - 1st Periodical TestMomPreneeNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Journal of Horticulture, in Vitro Pollen Germination Studies in BrinjalDocumento196 pagineIndian Journal of Horticulture, in Vitro Pollen Germination Studies in BrinjalsabavaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Pomegranate Bonsai Care From BonsaiOutletDocumento3 paginePomegranate Bonsai Care From BonsaiOutletMatthew StebbinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Coconut HuskDocumento4 pagineCoconut HuskErik WeeksNessuna valutazione finora
- PP-202 Plant VirologyDocumento43 paginePP-202 Plant VirologyMahnoorIshtiaqNessuna valutazione finora
- BOTANY Chapter 7Documento8 pagineBOTANY Chapter 7Mikee AbrahamNessuna valutazione finora
- Kiwi Fruit FarmingDocumento4 pagineKiwi Fruit Farmingaryan jainNessuna valutazione finora
- Constt. of 01 No Watch Towers: Add SICOP Service Charges@6% Total RsDocumento6 pagineConstt. of 01 No Watch Towers: Add SICOP Service Charges@6% Total Rshakim imtiyazNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION Background of TheDocumento50 pagineCHAPTER I INTRODUCTION Background of TheAdrian VillafloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Stabilisasi Tanah Ekspansif Dengan Campuran Abu Batu Bara Dan AbuDocumento16 pagineStabilisasi Tanah Ekspansif Dengan Campuran Abu Batu Bara Dan AbuLydia DarmiyantiNessuna valutazione finora
- FAO Veggie Production GuidelinesDocumento13 pagineFAO Veggie Production GuidelinesBendzGeronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Using Saturated Lime Water in The Production of Concrete Using Pozzolanic Cement Cem II B-PDocumento18 pagineEffect of Using Saturated Lime Water in The Production of Concrete Using Pozzolanic Cement Cem II B-PKellymax olakitarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lazzeri 9.4 PDFDocumento1 paginaLazzeri 9.4 PDFmauriciomathiasNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber Reinforced ConcreteDocumento16 pagineFiber Reinforced ConcreteNaviya K NaviyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alien Invasive Species of South Africa A3 PosterDocumento1 paginaAlien Invasive Species of South Africa A3 PosterMichaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Halfen HBT Rebend Connection: - Dibt Approval Z-21.8-2035 - Type Tested Acc. To ApprovalDocumento24 pagineHalfen HBT Rebend Connection: - Dibt Approval Z-21.8-2035 - Type Tested Acc. To ApprovalFarisTresnjoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydro Plant 1 Botanical NameDocumento23 pagineHydro Plant 1 Botanical NamePriya BalajiNessuna valutazione finora
- LabDocumento7 pagineLabMohammad FitriNessuna valutazione finora
- Envis Dec08 March09Documento8 pagineEnvis Dec08 March09Pramba Kumar AhujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Civil Work QuantitiesDocumento6 pagineCivil Work QuantitiesRenvil PedernalNessuna valutazione finora
- Aggrand Agriculture ProductsDocumento4 pagineAggrand Agriculture ProductsBruce WappmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pizza OvenDocumento8 paginePizza OvenNebojsa GolubovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture - 14Documento4 pagineLecture - 14MuktikiranNessuna valutazione finora
- Cabbage Fertigation - PDF'Documento7 pagineCabbage Fertigation - PDF'Bhushan Gosavi100% (1)
- Info About Teff PDFDocumento52 pagineInfo About Teff PDFGirma Kassa DubaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 1 PresentationDocumento26 pagineGroup 1 PresentationNomanNessuna valutazione finora