Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Jaata
Caricato da
Mohammad ChharchhodawalaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Jaata
Caricato da
Mohammad ChharchhodawalaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Digital/Automated contracts using permissioned
blockchain
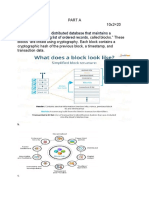
“Blockchain technology” means distributed ledger technology that uses a distributed, decentralized, shared
and replicated ledger, which may be public or private, permissioned or permissionless, or driven by tokenized
crypto economics or tokenless. The data on the ledger is protected with cryptography, is immutable and
auditable and provides an uncensored truth.
In public blockchain, for any transactions we have to spend our real money to purchase respecting cryptocur-
rency of blockchain. Cryptocurrnecy in India, for example ethereum is neither illegal nor accepted. So it is
controversial to use public blockchain for deployment of contracts.
The sole distinction between public and private blockchain is related to who is allowed to participate in
the network, execute the consensus protocol and maintain the shared ledger. A public blockchain network
is completely open and anyone can join and participate in the network. The network typically has an
incentivizing mechanism to encourage more participants to join the network. Bitcoin is one of the largest
public blockchain networks in production today.
One of the drawbacks of a public blockchain is the substantial amount of computational power that is
necessary to maintain a distributed ledger at a large scale. More specifically, to achieve consensus, each node
in a network must solve a complex, resource-intensive cryptographic problem called a proof of work to ensure
all are in sync.
Another disadvantage is the openness of public blockchain, which implies little to no privacy for transactions
and only supports a weak notion of security. Both of these are important considerations for enterprise use
cases of blockchain.
A private blockchain network requires an invitation and must be validated by either the network starter
or by a set of rules put in place by the network starter. Businesses who set up a private blockchain, will
generally set up a permissioned network. This places restrictions on who is allowed to participate in the
network, and only in certain transactions. Participants need to obtain an invitation or permission to join.
The access control mechanism could vary: existing participants could decide future entrants; a regulatory
authority could issue licenses for participation; or a consortium could make the decisions instead. Once an
entity has joined the network, it will play a role in maintaining the blockchain in a decentralized manner.
Advantages of Private Blockchains:
• Private Blockchains are decentralized peer-to-peer networks
• Participation in the network is allowed to only members
• Membership is totally controlled by the central consortium
• Fundamentally you will know with whom you are working with
• Execution of the protocol requires invitation
• Maintenance of the ledger needs validation
• Transactions are quick and highly confidential
• Transactions are operated by the controlling organization
• Strength varies according to the use
• Increased stability and scalability
• They are permissioned
• Transactions are censorable
We can use private/permissionless blockchain in our project. In which fake cryptocurrency or no cryptocurrency
are required to perform transtaction and for validation of transactions. There are many blockchains available
which doesn’t use cryptocurrency like Corda and Hyperledger(which is developed by IBM).
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Block ChainDocumento16 pagineBlock ChainNirnay PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain TechnologyDocumento33 pagineBlockchain Technologypawar143omkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of BlockchainsDocumento6 pagineTypes of Blockchainsmeghanavalli2003Nessuna valutazione finora
- 06 - BCT - Different Types of BlockchainsDocumento13 pagine06 - BCT - Different Types of BlockchainsJoel SamuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - 1 NotesDocumento14 pagineUnit - 1 NotesFbz AriNessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain Chapter1&2Documento26 pagineBlockchain Chapter1&2sachinkhote40Nessuna valutazione finora
- Crypto Currency UNIT - 1 NOTESDocumento14 pagineCrypto Currency UNIT - 1 NOTESanishshree1207Nessuna valutazione finora
- BlockChain Technologies (20CS32015)Documento16 pagineBlockChain Technologies (20CS32015)srinivas kanakalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain TechnologyDocumento14 pagineBlockchain TechnologyRobsen MergaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 Consortium BlockchainDocumento29 pagineModule 4 Consortium BlockchainDishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3Documento44 pagineUnit 3Abhishek KasurdeNessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain and Operation ManagementDocumento18 pagineBlockchain and Operation ManagementFatma HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- BlockchainDocumento5 pagineBlockchainGood for NothingNessuna valutazione finora
- MB NotesDocumento19 pagineMB NotesBhavik UpadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain As An Enabling TechnologyDocumento10 pagineBlockchain As An Enabling Technology0928PRIYANSHI CHUTANINessuna valutazione finora
- Block ChainDocumento9 pagineBlock ChainNurul Rofifah MNessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain TechnologyDocumento20 pagineBlockchain Technologyabreham ashebirNessuna valutazione finora
- BCT Unit-1Documento43 pagineBCT Unit-1raginiguntupalli12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain: The Distributed LedgerDocumento5 pagineBlockchain: The Distributed LedgerKSHITIJ PANDEYNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento8 pagineChapter 1nishant tomarNessuna valutazione finora
- BT Unit 3rd NotesDocumento8 pagineBT Unit 3rd NotesTom JerryNessuna valutazione finora
- Block ChainDocumento14 pagineBlock Chainiqbal ishak100% (1)
- Blockchain: A Guide To Blockchain, The Technology Behind Bitcoin, Ethereum And Other Cryptocurrency: Blockchain, #1Da EverandBlockchain: A Guide To Blockchain, The Technology Behind Bitcoin, Ethereum And Other Cryptocurrency: Blockchain, #1Nessuna valutazione finora
- FOB Chapter-2Documento27 pagineFOB Chapter-2Pratik KhuntNessuna valutazione finora
- Block Chain CourseDocumento6 pagineBlock Chain CoursePrince StefanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 1Documento35 pagineUnit 2 1rocky2003rajkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Contemporary Issues in Management 2Documento13 pagineContemporary Issues in Management 2joseph mbuguaNessuna valutazione finora
- BCT 2Documento25 pagineBCT 2khalidsherzai67Nessuna valutazione finora
- Block Chain Fundamentals and HyperledgerDocumento42 pagineBlock Chain Fundamentals and HyperledgerFatema TurnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain Technology: Submitted By, Sayog DongaDocumento19 pagineBlockchain Technology: Submitted By, Sayog Dongasayog dongaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 BlockchainsDocumento26 pagine1 BlockchainsJuma SohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Block Chain Architecture Design-1Documento21 pagineBlock Chain Architecture Design-1Mayank GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- BlockChain TechnologyDocumento43 pagineBlockChain TechnologyHarish AugadNessuna valutazione finora
- Feasibility StudyDocumento29 pagineFeasibility StudyKhairun NatsirunNessuna valutazione finora
- On Block ChainDocumento16 pagineOn Block Chainshaik ashraffNessuna valutazione finora
- Block Chain Architecture DesignDocumento18 pagineBlock Chain Architecture DesignMayank GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Benefits of Blockchain TechnologyDocumento3 pagineBenefits of Blockchain TechnologydhoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Block ChainDocumento12 pagineBlock ChainISHA AGGARWALNessuna valutazione finora
- Block ChainDocumento60 pagineBlock Chainromeesh jainNessuna valutazione finora
- Block Chain: BY Mohamed Safwan A Kavin Manoj C M Cse Ii Year Gce, SalemDocumento21 pagineBlock Chain: BY Mohamed Safwan A Kavin Manoj C M Cse Ii Year Gce, SalemMohamed safwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain TechnologyDocumento2 pagineBlockchain TechnologydhoniNessuna valutazione finora
- BlockchainDocumento11 pagineBlockchainanilkumarak9532Nessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain for Beginners: Understand the Blockchain Basics and the Foundation of Bitcoin and CryptocurrenciesDa EverandBlockchain for Beginners: Understand the Blockchain Basics and the Foundation of Bitcoin and CryptocurrenciesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (7)
- Module 3 Private Blockchain SystemDocumento34 pagineModule 3 Private Blockchain SystemDishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain Technology PPT Project Final EditDocumento17 pagineBlockchain Technology PPT Project Final EditHACKERS HOVELNessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain Note by HasanDocumento6 pagineBlockchain Note by HasanMd.HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain Notes B Tech AKTU by Krazy Kreation (Kulbhushan)Documento2 pagineBlockchain Notes B Tech AKTU by Krazy Kreation (Kulbhushan)RahulMondol100% (1)
- Blockchain TechnologyDocumento2 pagineBlockchain Technologyriley zeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 UpdatedDocumento113 pagineUnit 1 Updatedsaurabh tiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Block Chain ArchitectureDocumento2 pagineBlock Chain Architecturectl designerNessuna valutazione finora
- Block Chain PowerPoint TemplatesDocumento15 pagineBlock Chain PowerPoint TemplatesKim Clint DuhaylungsodNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Key Blockchain Features You Need To Know NowDocumento26 pagine6 Key Blockchain Features You Need To Know NowBankole AyoadeNessuna valutazione finora
- LMS 13Documento11 pagineLMS 13prabakar1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 BADDocumento12 pagineUnit 1 BADVasu AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Block ChainDocumento11 pagineBlock ChainPratibhaNessuna valutazione finora
- BT ReductionDocumento6 pagineBT Reduction21U338 Ashish waghNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Blockchain-1Documento5 pagineUnit 1 Blockchain-1merimarji6265Nessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain and Its Main ApplicabilityDocumento17 pagineBlockchain and Its Main ApplicabilityBrigs MastermindNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1Documento9 pagineAssignment 1Sarfirey GamersNessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain TechnologyDocumento8 pagineBlockchain Technology20CM052-Shravani Shinganwadikar. CMNessuna valutazione finora
- Access 2002 Programming by ExampleDocumento574 pagineAccess 2002 Programming by ExampletfmconsultNessuna valutazione finora
- Iphone RestaurarDocumento3 pagineIphone RestaurarBobadilla Y Merino Abogados AsociadosNessuna valutazione finora
- Dca Note BookDocumento88 pagineDca Note BookŚîbá ĐõräNessuna valutazione finora
- Mc-Simotion Scout ConfiguringDocumento298 pagineMc-Simotion Scout ConfiguringBruno Moraes100% (1)
- PPTDocumento81 paginePPTSmart DiamondNessuna valutazione finora
- APAC AU 5 MayDocumento90 pagineAPAC AU 5 MayvietanhpsNessuna valutazione finora
- SRS Health Management SystemDocumento6 pagineSRS Health Management SystemRonith SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To FMEDocumento129 pagineIntro To FMEDennie AndresNessuna valutazione finora
- Cover LetterDocumento2 pagineCover Letterpechan07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rules of MathDocumento2 pagineRules of MathSheilaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Manual For Biochemistry ProtocolsDocumento7 pagineA Manual For Biochemistry ProtocolsLauryn HemmerlingNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Doc Project of Training and PlacementDocumento60 pagineFinal Doc Project of Training and PlacementPreeti Dahiya100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Basic Signaling ProceduresDocumento68 pagineChapter 6 Basic Signaling ProceduresEfosa AigbeNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 7 1st Term English 2017 Vembadi GirlsDocumento6 pagineGrade 7 1st Term English 2017 Vembadi GirlsWael M. Alsawi0% (1)
- A Monte Carlo Simulation Method For System Reliability AnalysisDocumento9 pagineA Monte Carlo Simulation Method For System Reliability AnalysisMinho LawNessuna valutazione finora
- Stat FitDocumento112 pagineStat FitedwinwwillanNessuna valutazione finora
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocumento2 pagineNew Microsoft Office Word Documentvarunft1Nessuna valutazione finora
- XSD TutorialDocumento48 pagineXSD TutorialashokmvanjareNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication Error PDFDocumento3 pagineCommunication Error PDFAJDaajhhkNessuna valutazione finora
- Comp Arch Syllabus 6-29-2017Documento4 pagineComp Arch Syllabus 6-29-2017Karthikeya MamillapalliNessuna valutazione finora
- Sub Net Mask Cheat SheetDocumento3 pagineSub Net Mask Cheat SheetjorgelanfrediNessuna valutazione finora
- Storage Support Method: From TheDocumento10 pagineStorage Support Method: From Thesumanya kumariNessuna valutazione finora
- Fujitsu Scanner - Emulation Mode SetupDocumento3 pagineFujitsu Scanner - Emulation Mode Setupmohsen3310Nessuna valutazione finora
- Distributing Notes Clients Automatically: PaperDocumento64 pagineDistributing Notes Clients Automatically: PaperDharathi Nirmala SNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless & Mobile Comm CLOs GCUFDocumento1 paginaWireless & Mobile Comm CLOs GCUFTayyab HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Error Handling in PHPDocumento18 pagineError Handling in PHPVinit Vini JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Extract PDF ReferencesDocumento2 pagineExtract PDF ReferencesKellyNessuna valutazione finora
- Emerging Technology Workshop COLADocumento3 pagineEmerging Technology Workshop COLARaj Daniel Magno58% (12)
- Cs6503 Toc Unit 1 VBDocumento58 pagineCs6503 Toc Unit 1 VBAppasami G100% (1)
- White Paper Du-Huawei For 5G Core Network Evolution v12Documento34 pagineWhite Paper Du-Huawei For 5G Core Network Evolution v12flatelecom938100% (1)