Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Unit 5 Tissues
Caricato da
hollyCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Unit 5 Tissues
Caricato da
hollyCopyright:
Formati disponibili
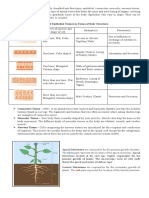
Unit 5: Anatomy and Physiology
Tissues
There are many different types of tissues. They are all made up of hundreds of cells with little
variation between the cells, regarding both structure and function. This results in a tissue that has
one main task. There are various ways in how tissues can form. There is a specific technique called
tissue culture (do some research into this)
Epithelial tissue: is a thin layer of tissue which usually lies on top of other tissues or organs. They
protect said tissues from chemical or physical damage. There are different types of epithelial tissue.
Some examples of this tissue in humans are in the mouth, windpipe and food canal. Functions are to
protect from the outside world (skin), it helps with absorption (stomach and intestinal lining), filters
(kidneys) and it secretes (creates glands). It’s closely attached to form the protective barrier. Always
has one free surface open to outside the body or inside an internal organ. Part of this tissue is always
on the outside of the organ or skin. It always has one fixed section to connective tissue. It has lots of
nerves in it. It’s very good at regenerating (sunburn or cuts etc.)
Connective tissues: these tissues lie beneath the epithelia tissues connecting different parts of the
internal structure. Various types of cells lie in a background material known as a matrix. The matrix
may be liquid as in blood, a jelly like material, as in areolar tissue (white material that binds muscle
groups, blood vessels and nerves together), firm as in cartilage or hard as in bone. The matrix of
tissue is usually secreted by the connective tissue cells. Its functions are to wrap around, cushion and
protect organs, it stores all nutrients, acts as an internal support for organs and can run through the
organs to give it strength.
Muscle tissues: three different types, smooth (involuntary- no control) cardiac (involuntary control)
and skeletal muscle tissue (voluntary- have control). In muscle tissue you can expect to find other
types of cells like blood vessels and nerves. They are formed like a sheet and are elastic, so they can
easily go back to shape after being stretched. They are not just found in arms and legs. They can be
found elsewhere, for example in the stomach muscle movement will crush food. Is referred as an
excitable tissue which can respond to stimuli. Smooth muscle- organ walls and blood vessels,
involuntary, spindle shaped cells to push things through organs. Skeletal muscle- large body muscles,
voluntary, packed in bundled and attached to bone foe movement. Cardiac muscle- heart wall,
involuntary, intercalculated discs connecting cells for synchronised contractions during a heartbeat.
Nervous tissues: is only found in the central nervous system, which consists of the brain, spinal cord
and nerves. Receives stimuli from external and internal sources creating consistency, coordination
and communication between different parts of the body. Interprets stimuli from the sense organs so
that vision, hearing, smell and the other senses can become apparent.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- External and Internal Anatomy of FISHDocumento22 pagineExternal and Internal Anatomy of FISHsheil.cogayNessuna valutazione finora
- Ann. Din. Biochem.: Regulation of Calcium MetabolismDocumento22 pagineAnn. Din. Biochem.: Regulation of Calcium MetabolismAzmi FarhadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 2 Nervous SystemDocumento2 pagineActivity 2 Nervous SystemElaine BaratitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Human Histology LDocumento32 pagineIntroduction To Human Histology LAhmed JawdetNessuna valutazione finora
- Advance Nursing Practice: KMC College of Nursing, MeerutDocumento50 pagineAdvance Nursing Practice: KMC College of Nursing, MeerutJyoti Prem UttamNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 1/4: (2012/case 1)Documento8 pagineSection 1/4: (2012/case 1)LoNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 5 Science Classwork 091020Documento3 pagineClass 5 Science Classwork 091020Rakesh AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Manual Zoology-1Documento86 paginePractical Manual Zoology-1Ayesha Mirza100% (2)
- Structured - Biology HLDocumento14 pagineStructured - Biology HLnur shahirahNessuna valutazione finora
- Race-5 - Respiration in Plants and Animals - (ASE)Documento3 pagineRace-5 - Respiration in Plants and Animals - (ASE)Uma AllakondakarNessuna valutazione finora
- The Parts of The Human Reproductive System and Their FunctionsDocumento13 pagineThe Parts of The Human Reproductive System and Their FunctionsRhodora Rendon OrizonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Year 10 DPP Biology Term 3 Exam RevisionDocumento8 pagineYear 10 DPP Biology Term 3 Exam RevisionPoojit VenugopalaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Case of Giant Pleomorphic Adenoma of The Parotid GlandDocumento3 pagineA Case of Giant Pleomorphic Adenoma of The Parotid GlandmitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocumento33 pagineHuman Anatomy and Physiology NotesFLORLYN VERALNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuby5 20 AutoImmunity PDFDocumento19 pagineKuby5 20 AutoImmunity PDFASDASDDD2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Martini FAP7 ch1Documento41 pagineMartini FAP7 ch1Muhammad Na'imNessuna valutazione finora
- AnaPhy ReviewerDocumento2 pagineAnaPhy ReviewerNashleyah AnayatinNessuna valutazione finora
- The Circulatory SystemDocumento8 pagineThe Circulatory Systemrosario marcelaNessuna valutazione finora
- GENBIO1 HandoutDocumento2 pagineGENBIO1 HandoutZaza May VelascoSbNessuna valutazione finora
- Wolf Motor Function Test WMFTDocumento1 paginaWolf Motor Function Test WMFTTadeja Hernja Rumpf100% (1)
- CellsDocumento19 pagineCellsAulia Safri NahriyahNessuna valutazione finora
- OjasDocumento66 pagineOjasVineeth Vini100% (1)
- WOAg B7 My 1 HJmy GGN EYOFDocumento41 pagineWOAg B7 My 1 HJmy GGN EYOFandrewmanshionNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 - Respiratory SystemDocumento24 pagineChapter 7 - Respiratory Systemchloe06muller.mNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell PlantDocumento7 pagineCell PlantEbiz MarkNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure and Function: Powerpoint Presentations Prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State UniversityDocumento96 pagineCell Structure and Function: Powerpoint Presentations Prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State UniversityVia SongcalNessuna valutazione finora
- Section: Mental & Reasoning Ability: Question ID: 1034353300 Status: Not Attempted and Chosen OptionDocumento46 pagineSection: Mental & Reasoning Ability: Question ID: 1034353300 Status: Not Attempted and Chosen OptionPiyush TannuNessuna valutazione finora
- Frog DissectionDocumento4 pagineFrog Dissection2110038Nessuna valutazione finora
- MRI TextbookRecommendationsDocumento1 paginaMRI TextbookRecommendationsChris SacconeNessuna valutazione finora
- HeartDocumento28 pagineHeartZahidKhanNessuna valutazione finora