Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
X X X X: Retyped by Tan Sze Haun, Page: 1 / 6
Caricato da
david70830chanTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
X X X X: Retyped by Tan Sze Haun, Page: 1 / 6
Caricato da
david70830chanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Putrajaya Addmaths Trial 2010 Paper 1
1. The function f maps x to y and the function h maps y to z.
f g
State (a) f 1 (3) and (b) h f (7) x y z
2. 4 7 3 11
The function g 1 ( x ) , x k.
2x 1
(a) State the value of k. (b) Find g ( x ) .
3. The information is about the function h and the inverse 2
function h 1 ( x ) . Find the values of a and b. h : x 4 a x , and h 1 : x 2b x
3
4. Given the quadratic equation 3 x ( x 2) 3 x( x 2), find
(a) the sum of roots. (b) the product of roots.
5. If the quadratic equation x 2 2 x 3 k has no roots, find the range of values of k .
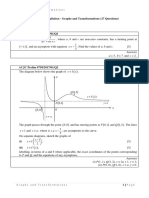
6. The diagram shows the graph of a quadratic function g(x) = 2(x – m)2 – 3, where m is a constant. The
curve y = g(x) has the maximum point (2, n), where n is a constant. State
y
(a) the value of m, (b) the value of n,
(c) The equation of the axis of symmetry. O ( 2, n ) x
●
7. Find the range of values of x if x( x 4) 5 2 x .
8. 1
Solve the equation 2 3 x 5 x 1
.
4
9. Given that log 2 p q 6 7 log 2 p log 2 q , express q in terms of p.
10. The sum of the first n term of an arithmetic progression is given by S n 2 n 2 5 n . Find
(a) the first term, (b) the common difference.
11. Fifth term of a geometric progression is 20. The sum of the fifth term and the sixth term is 10.
(a) Find the first term and the common ratio of the progression,
(b) Find the sum to infinity of the progression.
12. y q
The variables x and y are related by the equation 2
px , where p y
x x
x
and q are constants. Diagram shows the straight line obtained by
y (2,6)
plotting against x 2 .
x
y q
(a) Express the equation 2
px to the linear form. x2
x x O (4, 0)
(b) Find the value of p and of q .
13. Diagram shows a straight line passing through P0, 6 and Q3,0 . y Q (3, 0)
x y O
(a) Write down the equation of the straight line PQ in the form 1 x
a b
(b) A point S x, y moves such that SQ 2 SP . Find the equation of the
locus of S . P (0, 6)
Retyped by Tan Sze Haun, Page : 1 / 6
14. The following information refers to the equation of two straight lines, EF and GH which are
perpendicular to each other. Express t in terms of k .
EF : y = 2tx + k ; GH : y = (k 3)x + t , where k and t are constants
15. Diagram show two vector OP and PR . Express
P (5, 2) y
(a) OP in the form xi y j ,
x
(b) (b) PR in the form . O x
y
P 5z
~
3 R
S
4y
~
16. Diagram shows a quadrilateral PQRS . Express RS in terms of x , y and z .
Q R
3x
~
17. Solve the equation 2 tan x cot x 1 for 0 o x 360 o
18. Diagram shows two sectors MON and POQ of two M
concentric circles with centre O , where MOQ and PON are P
straight lines. Given ON r cm , OP r 3 cm and O
1.3 rad
perimeter of the diagram is 42.9.Find the value of r , in cm.
N Q
19. Given the curve y 2 x 1 , find the gradient of the curve at x 1 .
5
20. 6
Two variables, x and x, are related by the equation y , Express, in terms of p, the approximate
x2
change in y, when x changes from 3 to 3 p , where is a small value.
21. Given that
3
h ( x ) dx 5 , , find the value of if
3
1 1 [ 2 x k h ( x ) ] dx 10 .
22. A set of five numbers has a mean of 8.
(a) Find x .
(b) When a number m is taken out of this set, the new mean is 7.5. Find the value of m.
23. A bag contains x red marbles, 5 blue marbles and 4 green marbles. When a marble is drawn at random
from the bag, the probability that it is red marble is 25%. Find the value of x.
24. There are 4 cars, A , B , C and D and 3 vans, X ,Y and Z in a used car shop. Diagram shows five
parking lots. Find
(a) the number of ways for a man to buy two cars and a van from the shop.
(b) the number of ways of arranging the vehicles if 3 cars and 2 vans
Van
Van
have to be arranged in the parking lots as shown.
Car
Car
Car
25. X is a continuous random variable of a normal distribution with a mean of 45 and a standard deviation
of . Find the value of when P ( x 50 ) 0.2061.
Retyped by Tan Sze Haun, Page : 2 / 6
Putrajaya Addmaths Trial 2010 Paper 2
1. Solve the simultaneous equations h 2 k 3 and h ( h k ) 2 h 1.
2. Given a function y 3 4 x 5 x 2 .
(a) By using the completing the square method, determine the turning point of the function y .
(b) If x 2 3 k , where k is a constant, is the axis of symmetry, calculate the value of k .
(c) Hence sketch the graph of y 3 4 x 5 x 2 for 2 x 3.
3. Ali and David start to save money at the same time.
(a) Ali saves RM x in the first month and his saving increases constantly by RM y every subsequent
month.He saves RM 200 in the sixth month and the total saving for first 12 month is RM 2 520.
Find the values of x and y.
(b) David saves RM 200 in the first month and his savings increases constantly by RM 10 every
subsequent month.Find the value of n when both of them save the same amount of money in n t h
month.
4. (a) Prove that 1 tan 2 x sec 2 x .
(b) Sketch the graph of y 2 sin x 2 for 0 x 2.
(c) Hence, using the same axes, sketch a suitable straight line to find the number of solutions for the
x
equation sin x 1 for 0 x 2. State the number of solutions.
2
5. Table shows the frequency distribution of
weight for 20 students. Find Weight (kg) Number of students
(a) the mean. 30 – 34 3
(b) The interquatile range.
35 – 39 5
40 – 44 8
45 – 49 4
6. Diagram shows a trapezium PQRS. It is given that
3 7
Q R
PQ 4 y , P S 8 x , P M P S and Q R P S .
4 8
N
(a) Express P R in terms of x and y .
(b) Point N lies inside the trapezium PQRS such that
M N k P Q and k is a constant.
P S
(i) Express P N in terms of k , x and y . M
(ii) Hence, if the points P, N and R are collinear, find the value of k .
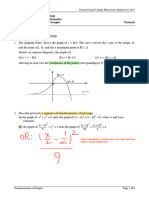
7. (a) Diagram shows a shaded region bounded by the curve
y
y 4 x 2 , the y-axis and the line y k . Given that the
volume of the solid generated when the shaded region yis 4 x 2
revolved 360‚ about the y-axis is 2 unit 3 , find the value of
k.
5 1 y=k
(b) A curve with minimum point , 4 has a gradient
6 4
function mx – 5. Find O x
(i) value of m.
(ii) equation of the curve.
Retyped by Tan Sze Haun, Page : 3 / 6
8. Table shows the values of two variables, x and y obtained from an experiment. Variable x and y are
related by the equation y 10 k c x , where k and c are Constants.
x 15 20 25 30 35 40
y 0.15 0.38 0.95 2.32 5.90 14.80
(a) Based on the table, construct a table for the value of log 10 y .
(b) Plot log 10 y against x , using a scale of 2 cm to 5 unit on the x-axis and 2 cm to 0.5 unit on the
log 10 y axis. Hence, draw the line of best fit.
(c) Use the graph in 8(b) to find the value of
(i) k.
(ii) c
(iii) x when y = 10.
y
9. Diagram shows P(4, 2) , Q (8, 4) and R (5, 9) are the midpoints of the B
sides of the triangle ABC. R
(a) Find the gradient of PQ.
A
(b) Find the equation of the straight line AC .
(c) Find the equation of the perpendicular bisector of the line AC. Q
(d) A point k moves such that its distance from Q is always 6 units. Find P
the equation of the locus of k x
10. Diagram shows a semicircle with centre O and radius 7 cm. The
chord PR is extended to S such that PQ = PS and sector SPQ is S
drawn with P as a centre and PQ as its radius. Given that arc PR R
is 14 cm. Find
(a) the angle of SPQ in radians,
(b) the area , in cm2 ,of PRO ,
(c) the area , in cm2 , of the shaded region.
P Q
O
11. (a) In a survey carried out in a college, it is found that 90% of the students like to read newspapers.
Six students are chosen at random from the college. Find the probability that
(i) exactly 2 students like to read newspapers.
(ii) more than half of the students like to read newspapers.
(b) A survey on body-mass is done on a group of students. The mass of a student is normally
distributed with a mean of 45 kg and a standard deviation of 12 kg.
(i) If a student is chosen at random, find the probability that his mass is more than 54 kg.
(ii) Given that 8% of the students have a mass of less than m kg, find the value of m.
12. An object moves along a straight line from a fixed point A. Its velocity, v ms 1 , is given by
v 16 t 4 t 2 , where t is the time, in seconds, after leaving the point A. (Assume motion to the right is
positive.) Find
(a) the initial velocity, in ms 1 , of the object,
(b) the distance , in m , travelled during the third second,
(c) the time intervals during which the objects moves towards the left.
Retyped by Tan Sze Haun, Page : 4 / 6
13. Diagram shows a quadrilateral ABCD.
(a) Calculate D 4 cm
(i) the length , in cm , of BD, C
(ii) BCD,
(b) Point D’ lies on BD such that CD’ = CD. 7 cm
8 cm
(i) sketch ΔBCD’, 100‚
(ii) hence, find the area, in cm 2, of BCD’.
A B
5 cm
14. A computer company offers two types of computer courses ‘Internet for Beginners’ and ‘Introduction
to Excel’ , with a monthly tuition fee of RM 120 and RM 80 respectively. The number of participants
for course ‘Internet for Beginners’ is and for course ‘Introduction to Excel’ is . The enrolment of the
participants is based on the following constraints:
I : There are at least 30 participants registered for the course ‘Introduction to Excel’.
II : There are at most 100 participants registered for both courses.
III : The number of participants registered for ‘Introduction to Excel’ is at least two times
the number of participants registered for ‘Internet for Beginners’.
(a) Write three inequalities, other than and , which satisfy all the above
constraints.
(b) By using a scale of 2 cm to 10 participants on both axes, construct and shade the region R
that satisfies all the above constraints.
(c) By using your graph from (b), find
(i) the range of the number of participants for course ‘Introduction to Excel’ if the number
of participants for course ‘Internet for Beginners’ is 25.
(ii) the maximum total fees per month that can be collected by the company.
15. Table shows the prices and the prices indices for the four ingredients, P, Q, R and S, used in making a
type of drink. The pie chart which represents the relative amount of the ingredients P, Q, R and S, used
in making these drink.
Price per litre (RM) Price index in the year 2006
Ingredient
Year 2004 Year 2006 based on the year 2004.
55 66
50 70 140
40 60 150
20 125
(a) Find the values of and of b.
(b) Calculate the composite index for the cost of making the
drink in the year 2006 based on the year 2004. P
(c) The composite index for the cost of making the drink
increased by 10% from the year 2006 to the year 2008. 150‚
Calculate
(i) the expected composite index for year 2008 based on 60 ‚
S
the year 2004.
(ii) hence, calculate the corresponding cost of a bottle of 30 ‚ Q
the drink in the year 2008 if the cost in the year 2004
is RM 20. R
Retyped by Tan Sze Haun, Page : 5 / 6
Putrajaya Add Maths Trial 2010 Paper 1 – Answers
1. (a) 7 (b) 11 9. q 8 p 2 15. (a) 5 i 2 j (b) 5
5
1 4x 10. (a) 3 (b) 4
2. (a) k (b) g(x)
2 2x 16. 4 x 3 y 5 z
1
1 11. (a) r , a 320
3. a 6 and b 2 17. 45, 153.43, 225, 333.43
12 1
(b) 213
3 18. 8 19. 10
4 2
4. (a) (b)
3 3 y 4 2
12. (a) px2 q 20. p 21.
x 9 5
5. k > 2 (b) p = 3, q = 12
22. (a) 40 (b) 10
6. (a) m = 2 (b) n = 3 13. (a) x y 1
(c) x = 2 3 6 23. 3
2 2
(b) x y 2 x 16 y 45 0
1 24. (a) 18 (b) 144
7. 1 < x < 5 8. x
5 14. t 1
2(k 3) 25. 6.098
Putrajaya Add Maths Trial 2010 Paper 2 – Answers
1 1 4 1
1. h 2 , k , 9. (a) m PQ (b) 3 y 5 x 26
3 2 3 2 (c) 2
2 19 (c) 5 y 3 x 2 (d) x2 + y2 - 16x - 8y + 44 = 0
,
2 19 4 5 5
2. (a) , (b) k
5 5 5 10. (a) 0.571 (b) 22.28 (c) 32.41
3. (a) x = 100, y = 20 11. (a) (i) 0.001215 (ii) 0.98415
(2, 9) (b) (i) o.2266 (ii) m = 28.13
(b) n = 11
y
(3, 54) 12. (a) 0 (b) 14.67 (c) t > 4
4
x
4. (b) y 13. (a) 10.80 (b) 157.24‚ (c) (i)
2 (c) (ii) 1.528
2 solutions C
5. (a) 40.25
O 0.5 1.5 2 x
(a ) y 30,
(b) 7.375 D' B
x y 100
14.
(a ) P R 7 x 4 y y 2x
(c ) (i) 50 y 75 (ii) RM 9320
6. 6
(b) (i) P N 6 x 4 k y (ii) k
7
15. (a) a = 120, b = 25 (b) 130
(c) 143 (d) RM 28.60
7. (a) k = 2 (b) (i) m = 6 (ii) y 3x2 5x 13
6
8. (c) (i) k = 2.00 (ii) c = 1.2 (iii) x = 37.5
lg y -0.82 -0.42 -0.02 0.37 0.77 1.17
Retyped by Tan Sze Haun, Page : 6 / 6
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Topic 6 - Paper 1Documento7 pagineTopic 6 - Paper 1Ing Ding LonNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM 2010 Paper 1Documento3 pagineSPM 2010 Paper 1kysim100% (1)
- Linear Law BIDocumento17 pagineLinear Law BInorazizikdhNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Law QuestionDocumento13 pagineLinear Law QuestionFardeena DaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Equation of ParabolaDocumento3 pagineEquation of Parabolaleahpillay463Nessuna valutazione finora
- School 1 PDFDocumento8 pagineSchool 1 PDFnishtha kawatraNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM 2019Documento6 pagineSPM 2019Hui JingNessuna valutazione finora
- Jan 2005 Core 1 PaperDocumento4 pagineJan 2005 Core 1 PaperNisanthJoelNessuna valutazione finora
- PA CombinedDocumento9 paginePA CombinedumbfkamaldeenNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento8 pagineChapter 1TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Topical Test LINEAR LAWDocumento2 pagineTopical Test LINEAR LAWSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz Ch6Documento2 pagineQuiz Ch6Samuel Sim Shien ShuangNessuna valutazione finora
- Negeri Sembilan 2010 P1Documento3 pagineNegeri Sembilan 2010 P1kysimNessuna valutazione finora
- Tarea 2 de Derivadas 2 PDFDocumento6 pagineTarea 2 de Derivadas 2 PDFOscarDaniel Tello ChinguelNessuna valutazione finora
- HL Calculus 1 Bank PDFDocumento4 pagineHL Calculus 1 Bank PDFibrahim fadelNessuna valutazione finora
- C4 Mock Paper - V1Documento4 pagineC4 Mock Paper - V1circuspunkNessuna valutazione finora
- FunctionsDocumento31 pagineFunctionsysheng98Nessuna valutazione finora
- OSM ConsolEx 4B07 7b lv2 eDocumento4 pagineOSM ConsolEx 4B07 7b lv2 e林俊佑Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Paper Ib Coordinate Geometry (2D &3D) and Calculus. TIME: 3hrs Max. Marks.75Documento17 pagineMathematics Paper Ib Coordinate Geometry (2D &3D) and Calculus. TIME: 3hrs Max. Marks.75UB SANKARNessuna valutazione finora
- WS FunctionsDocumento8 pagineWS FunctionsasmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions and Equations PracticeDocumento2 pagineFunctions and Equations PracticeHarveen Kaur AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- QP G11 MathematicsDocumento10 pagineQP G11 Mathematicsmourees karanNessuna valutazione finora
- PureMaths1976 Pastpaper P2Documento4 paginePureMaths1976 Pastpaper P2wltfNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 H2 Prelim (Graphs and Transformations)Documento21 pagine2017 H2 Prelim (Graphs and Transformations)toh tim lamNessuna valutazione finora
- 1) GivenDocumento11 pagine1) Givenibrahim fadelNessuna valutazione finora
- Differentiation P 2Documento3 pagineDifferentiation P 2Salmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- MathHL QB3 T2Documento25 pagineMathHL QB3 T2Nikola PetrovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Pure Mathematics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 1: Algebra and FunctionsDocumento2 paginePure Mathematics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 1: Algebra and FunctionsThi Hanh Nguyen LeNessuna valutazione finora
- Add Maths Practice Set 12Documento6 pagineAdd Maths Practice Set 12Athanaseus ShazamNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 - Linear LawDocumento4 pagine10 - Linear LawJASON_INGHAMNessuna valutazione finora
- Quadratic Function WorksheetDocumento3 pagineQuadratic Function Worksheetbader alsaloumNessuna valutazione finora
- Addmath ExerciseDocumento1 paginaAddmath Exercisemaieqa87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Form 4: Chapter 2 Quadratic EquationsDocumento3 pagineForm 4: Chapter 2 Quadratic Equationsnani98Nessuna valutazione finora
- DHS H2 2021 Prelim P1Documento5 pagineDHS H2 2021 Prelim P1猪猪侠Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rotation of Axes PDFDocumento9 pagineRotation of Axes PDFJohn Paul TolinNessuna valutazione finora
- HCI 2023 H2 Maths PromoDocumento7 pagineHCI 2023 H2 Maths PromoMarcus LinNessuna valutazione finora
- C4 Solomon J Question PaperDocumento4 pagineC4 Solomon J Question PaperSachitra WijethungaNessuna valutazione finora
- PPMP Soalan KulaiDocumento7 paginePPMP Soalan KulaiAidil-Nur ZainalNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Law NewDocumento6 pagineLinear Law NewAnisha GillNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM 2013 (Edited)Documento5 pagineSPM 2013 (Edited)Hui JingNessuna valutazione finora
- Simultaneous Equations: M N N MDocumento12 pagineSimultaneous Equations: M N N MHadibahHarunNessuna valutazione finora
- Repaso Derivada - Integrales PDFDocumento7 pagineRepaso Derivada - Integrales PDFFelipe AndradeNessuna valutazione finora
- PureMaths1979 Pastpaper P2Documento3 paginePureMaths1979 Pastpaper P2wltfNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 TestDocumento2 pagineUnit 1 TestKostas KostaNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM 2015Documento6 pagineSPM 2015Hui JingNessuna valutazione finora
- (Total 6 Marks) : IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Documento146 pagine(Total 6 Marks) : IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Keya SanghviNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch3 Polynomial Func Test ADocumento3 pagineCh3 Polynomial Func Test Aarcherk06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transformations of Graphs TutorialDocumento9 pagineTransformations of Graphs Tutoriallbwnb.68868Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ibsl-2 Epg q1Documento4 pagineIbsl-2 Epg q1María Cecilia García ArangoNessuna valutazione finora
- IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Documento32 pagineIB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1ibrahim fadelNessuna valutazione finora
- Mixed Exam-Style Questions On DifferentiationDocumento2 pagineMixed Exam-Style Questions On Differentiationsamsweet96Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Table Shows The Three Equations of Straight Line, AB, CD and EFDocumento6 pagine1 Table Shows The Three Equations of Straight Line, AB, CD and EFKatherinaNessuna valutazione finora
- X and y Are Related by The Equation: Linear Law Paper 1Documento5 pagineX and y Are Related by The Equation: Linear Law Paper 1Loh Chee WeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Quadratic SL Q PDFDocumento15 pagineQuadratic SL Q PDFSamar GoelNessuna valutazione finora
- Year 12 Term 2 Assessment 2007 - EXTENSION II: Question 2 (B) Continued On Next PageDocumento3 pagineYear 12 Term 2 Assessment 2007 - EXTENSION II: Question 2 (B) Continued On Next Pagenoah smithNessuna valutazione finora
- REVISIONARY AM 1 (Ii)Documento2 pagineREVISIONARY AM 1 (Ii)LAKIESHANessuna valutazione finora
- PureMaths1978 Pastpaper P2Documento3 paginePureMaths1978 Pastpaper P2wltfNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 Ajc jc1 PromoDocumento5 pagine2017 Ajc jc1 PromoE M Meng QuekNessuna valutazione finora
- Cohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)Da EverandCohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Da EverandNonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Louis B. RallNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ On Graph TheoryDocumento3 pagineMCQ On Graph TheorySubrata MahapatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lets22 Ultimate Math FinalDocumento30 pagineLets22 Ultimate Math FinalJudie Jane MuegaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.14.4 Test (TST) - Shapes (Test)Documento10 pagine3.14.4 Test (TST) - Shapes (Test)Bumble BeanNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Larson SolDocumento108 pagine7 Larson SolCrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Yao D.D., Zheng S.-Dynamic Control of Quality in Production-Inventory Systems-Springer (2002)Documento229 pagineYao D.D., Zheng S.-Dynamic Control of Quality in Production-Inventory Systems-Springer (2002)Vsauce FansNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental Mathematics Marathon Semi-Final 2012 PowerpointDocumento42 pagineMental Mathematics Marathon Semi-Final 2012 Powerpointrishie1Nessuna valutazione finora
- D18NNDocumento372 pagineD18NNMarius GherguNessuna valutazione finora
- PWNSAT 2023 SyllabusDocumento5 paginePWNSAT 2023 SyllabusBaby SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Archibald Fripp Dr. Archibald Fripp is an electrical engineer and materials scientist. He was a senior scientist at NASA and managed many space shuttle experiments. He retired from NASA in 1998 but st.pdfDocumento346 pagineArchibald Fripp Dr. Archibald Fripp is an electrical engineer and materials scientist. He was a senior scientist at NASA and managed many space shuttle experiments. He retired from NASA in 1998 but st.pdfprashantnasaNessuna valutazione finora
- 8TH Worksheet in Statistic and Probability 11Documento4 pagine8TH Worksheet in Statistic and Probability 11Kim DahyunNessuna valutazione finora
- MCH3008 Lab ProjectDocumento4 pagineMCH3008 Lab ProjectEJAZ AHMADNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths - English Medium 2 To 5Documento8 pagineMaths - English Medium 2 To 5TNGTASELVASOLAINessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture NotesDocumento108 pagineLecture NotesjohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Module in Trigonometry MidtermsDocumento45 pagineModule in Trigonometry MidtermsEUGENE D. GABRIEL, MSENessuna valutazione finora
- 1745806749maths Class Ix Periodic Test II Exam Sample Paper 02Documento5 pagine1745806749maths Class Ix Periodic Test II Exam Sample Paper 02AdtNessuna valutazione finora
- Surds Practice WorksheetDocumento2 pagineSurds Practice Worksheetimaad malikNessuna valutazione finora
- Ma110 Course Outline 1 1Documento4 pagineMa110 Course Outline 1 1HarrisonNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Center CaseDocumento13 pagineComputer Center CaseNguyễn LâmNessuna valutazione finora
- Management Science - Final Exam With AnswersDocumento11 pagineManagement Science - Final Exam With AnswersAuroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Number SystemsDocumento30 pagineUnit 1 Number SystemsAnurag GoelNessuna valutazione finora
- Best PracticeDocumento4 pagineBest Practiceapi-229152558Nessuna valutazione finora
- CK 12 Middle School Math Concepts Grade 6 B v51 z63 s1Documento1.213 pagineCK 12 Middle School Math Concepts Grade 6 B v51 z63 s1navigator86100% (2)
- MATH 4 - 4th Q-Worksheet6Documento2 pagineMATH 4 - 4th Q-Worksheet6Chery LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple-Choice Test Nonlinear Regression Regression: Complete Solution SetDocumento12 pagineMultiple-Choice Test Nonlinear Regression Regression: Complete Solution SetPankaj KaleNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 31197-Atnaa 768532-1199308Documento21 pagine10 31197-Atnaa 768532-1199308Roy TufailNessuna valutazione finora
- Set Cse Ca 1Documento13 pagineSet Cse Ca 1Bhumika BiyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Ross12e - CHAPTER 4 - NMIMS - Practice Problems and Solutions For ClassDocumento8 pagineRoss12e - CHAPTER 4 - NMIMS - Practice Problems and Solutions For Classwander boyNessuna valutazione finora
- Exponential Generating Function PDFDocumento2 pagineExponential Generating Function PDFKristinNessuna valutazione finora
- Y9 Solving PBLDocumento19 pagineY9 Solving PBLhoneyoopsyaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Universal Evangelical Christian School Inc. S.Y. 2018 - 2019 Second Periodical Examination Math - 4-BDocumento2 pagineUniversal Evangelical Christian School Inc. S.Y. 2018 - 2019 Second Periodical Examination Math - 4-BJurelieNessuna valutazione finora