Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Nuclear Power Plant
Caricato da
LJCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Nuclear Power Plant
Caricato da
LJCopyright:
Formati disponibili
LARA JANE A.
LOPEGA
CE501-CE51FB2
Nuclear power plant
Nuclear power plants are a type of power plant that uses the process of nuclear fission in
order to generate electricity. They do this by using nuclear reactors in combination with the
Rankine cycle, where the heat generated by the reactor converts water into steam, which spins a
turbine and a generator. Nuclear power provides the world with around 11% of its total
electricity, with the largest producers being the United States and France.
Aside from the source of heat, nuclear power plants run very similar to coal-fired power
plants. They require different safety measures however, since the use of nuclear fuel has vastly
different properties from coal or other fossil fuels. They get their thermal power from splitting
the nuclei of atoms in their reactor core, with uranium being the dominant choice of fuel in the
world today. Thorium also has potential use in nuclear power production; however it is not
currently in use. Below is the basic operation of a boiling water power plant, which shows the
many components of a power plant, along with the generation of electricity.
A nuclear reactor produces and controls the release of energy from splitting the atoms of
certain elements. In a nuclear power reactor, the energy released is used as heat to make steam to
generate electricity. (In a research reactor the main purpose is to utilise the actual neutrons
produced in the core. In most naval reactors, steam drives a turbine directly for propulsion.)
The principles for using nuclear power to produce electricity are the same for most types
of reactor. The energy released from continuous fission of the atoms of the fuel is harnessed as
heat in either a gas or water, and is used to produce steam. The steam is used to drive the turbines
which produce electricity (as in most fossil fuel plants).
LARA JANE A. LOPEGA
CE501-CE51FB2
The world's first nuclear reactors operated naturally in a uranium deposit about two
billion years ago. These were in rich uranium orebodies and moderated by percolating rainwater.
The 17 known at Oklo in west Africa, each less than 100 kW thermal, together consumed about
six tonnes of that uranium. It is assumed that these were not unique worldwide.
The nuclear power plant consists of two main buildings: Containment building (houses
Nuclear Reactor) and Turbine building (houses Turbo Generator). The containment building is
the key building of the nuclear island. It is an air-tight building, which houses a nuclear reactor
and its pressurizer, reactor coolant pumps, steam generators, and other equipment or piping that
might otherwise release fission products to the atmosphere in the event of an accident. Such
buildings are usually made of steel-reinforced concrete.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Siemen 94.2Documento18 pagineSiemen 94.2Thanapaet Rittirut100% (4)
- Final Written Report TemplateDocumento23 pagineFinal Written Report TemplateLJNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Rubric For SO (B) Problem AnalysisDocumento1 paginaEngineering Rubric For SO (B) Problem AnalysisLJNessuna valutazione finora
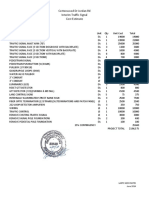
- Cottonwood DR Jordan RD Interim Traffic Signal Cost EstimateDocumento1 paginaCottonwood DR Jordan RD Interim Traffic Signal Cost EstimateLJNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: Rebekah Elegado Program/Year: Bsce/FirstDocumento1 paginaName: Rebekah Elegado Program/Year: Bsce/FirstLJNessuna valutazione finora
- Shear and TorsionDocumento2 pagineShear and TorsionLJNessuna valutazione finora
- 938 Aurora Boulevard Cubao Quezon City: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesDocumento6 pagine938 Aurora Boulevard Cubao Quezon City: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesLJNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer For RCDDocumento2 pagineReviewer For RCDLJNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydroelectric Power PlantDocumento2 pagineHydroelectric Power PlantLJNessuna valutazione finora
- Recycle Glass BottlesDocumento2 pagineRecycle Glass BottlesLJNessuna valutazione finora
- Len 260 WP Monocrystaline 2019Documento2 pagineLen 260 WP Monocrystaline 2019anggitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentasi Coal MILL Pulverizer Modeling AwalDocumento26 paginePresentasi Coal MILL Pulverizer Modeling Awalbhisma aktaNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated Plasma Fuel Cell Process (IPFC)Documento39 pagineIntegrated Plasma Fuel Cell Process (IPFC)Krishna KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- A Case Study On Thermodynamic Analysis of Cogeneration Power Plant (IRJET-V2I9163)Documento5 pagineA Case Study On Thermodynamic Analysis of Cogeneration Power Plant (IRJET-V2I9163)luis hyungNessuna valutazione finora
- Power - October 2013 PDFDocumento92 paginePower - October 2013 PDFisosicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineer's Guide To Level Measurement For Power and Steam MeasurementDocumento262 pagineEngineer's Guide To Level Measurement For Power and Steam Measurementvlcmstne04100% (1)
- Operation and Maintenance Schedule of A Steam Turbine Plant and Flow DiagramDocumento100 pagineOperation and Maintenance Schedule of A Steam Turbine Plant and Flow DiagramGirish Oniyil100% (1)
- World Renewable Energy Congress VIII BOOK OF ABSTRACTSDocumento646 pagineWorld Renewable Energy Congress VIII BOOK OF ABSTRACTSKanoe FabrikNessuna valutazione finora
- LPG Air Mixing 2 A3Documento1 paginaLPG Air Mixing 2 A3ambientinstal instalNessuna valutazione finora
- GE Energy: Gas Turbine (60Hz)Documento2 pagineGE Energy: Gas Turbine (60Hz)Rolando Antonio Cuenca PironaNessuna valutazione finora
- Frequently Asked Questions: About Solar PowerDocumento2 pagineFrequently Asked Questions: About Solar PowerService Solahart 081313462267Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity Sector Opportunity in The Philippines - May 2017 PDFDocumento27 pagineElectricity Sector Opportunity in The Philippines - May 2017 PDFGrace PatagocNessuna valutazione finora
- Fan Flow Calculation For FBC BoilerDocumento3 pagineFan Flow Calculation For FBC BoilerOmprakaash MokideNessuna valutazione finora
- GE Model DesignationDocumento6 pagineGE Model DesignationJerry IrawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Analysis of A 1MW Grid-Connected Solar PV System in GhanaDocumento23 pagineDesign and Analysis of A 1MW Grid-Connected Solar PV System in GhanaAgus SalimNessuna valutazione finora
- Wind Turbine Power PlantDocumento8 pagineWind Turbine Power PlantShailesh SankdasariyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ongrid PVDocumento9 pagineOngrid PVbhushanNessuna valutazione finora
- M Mahfoz C.V 20 Nov StartupDocumento4 pagineM Mahfoz C.V 20 Nov StartupelrajilNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Rate Vs LoadDocumento8 pagineHeat Rate Vs LoadVenkateswara Rao DoodalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Sciences: Current Flow Analysis of PV Arrays Under Voltage Mismatch Conditions and An Inverter FailureDocumento12 pagineApplied Sciences: Current Flow Analysis of PV Arrays Under Voltage Mismatch Conditions and An Inverter Failurekarus shaneNessuna valutazione finora
- M. S. Bidve Engineering College, Latur: CertificateDocumento30 pagineM. S. Bidve Engineering College, Latur: CertificateShubham GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Energy PDFDocumento13 pagineSolar Energy PDFryanNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Energy EPIADocumento76 pagineSolar Energy EPIAjaviNessuna valutazione finora
- CCGT Network Rev 1Documento1 paginaCCGT Network Rev 1projectmanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary Flare Gas Monetization ProjectsDocumento2 pagineSummary Flare Gas Monetization Projectssvnaik14Nessuna valutazione finora
- Propane Regulators - LP Gas Pressure RegulationDocumento2 paginePropane Regulators - LP Gas Pressure RegulationkuraimundNessuna valutazione finora
- Nrel CSP 1Documento1 paginaNrel CSP 1Arvind YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Meeting Mingguan Pembangunan Epf Lokasi Jati Asri, Akasia Bagus Dan Bambu BesarDocumento38 pagineMeeting Mingguan Pembangunan Epf Lokasi Jati Asri, Akasia Bagus Dan Bambu BesarAditya FathurachmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Energy Technology: January 2020Documento10 pagineSolar Energy Technology: January 2020Habes NoraNessuna valutazione finora