Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Geometry Scope and Sequence - 60
Caricato da
api-189090943Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Geometry Scope and Sequence - 60
Caricato da
api-189090943Copyright:
Formati disponibili
BCCS Math Scope and Sequence
GRADE 10 Geometry MA FRAMEWORKS
Unit 1: Basics of Geometry (Chapter 1) MA Standard(s)
POWER STANDARD: Solve for unkowns using segment and
angle relationships
a.) Identify and use the appropriate notation for basic terms (point,
line, plane, collineary points, coplanar points, line segment,
endpoints, ray, initial point, oppostie rays) G.G.1
b.) Use the segment addition postulate to determine distances G.G.12
c.) Use the Distance Formula to measure distances G.G.12
d.) Determine the midpoint of a segment using the Midpoint Formula G.G.12
e.) Determine the endpoints of a segment when given one endpoint
and midpoint. G.G.12
f.) Determine the measure of an angle using the Angle Addition
Postulate G.G.6
g.) Classify angles (acute, right, obtuse, straight) G.G.6
h.) Identify vertical angles and linear pairs G.G.6
i.) Identify complementary and supplementary angles G.G.6
j.) Solve for unknowns using segment and angle bisectors G.G.6
Auxilliary Standards
k.)……………………………………………………………………. G.G.4
l.) ……………………………………………………………………… G.G.4
m.) ……………………………………………………………………… G.G.4
POWER STANDARD: Predict future terms in a pattern
a.) Identify and describe patterns AI.P.1
b.) Use inductive reasoning to make conjectures G.G.2
Unit 2: Circles and Polygons (1.7 & 11.4-11.6, 12.2-12.6)
POWER STANDARD: Find and use measures of perimeter,
circumference, and area of common geometric figures.
a.) Calculate the perimeter and area of a square, rectangle, triangle,
and circle G.M.1
b.) Apply a general problem-solving plan to word problems dealing
with perimeter and area
c.) …………………………………………………………….. G.M.1
d.) Use circumference …... to solve real-life problems G.M.1
e.) Calculate the area of a sector of a circle G.M.2
f.) Determine the area of regions composed of multiple polygons and
circles G.M.2
g.) Calculate geometric probability using segments and polygons
POWER STANDARD: Find and use measures of lateral areas,
surface areas, and volumes of prisms, pyramids, spheres,
cyclinders, and cones
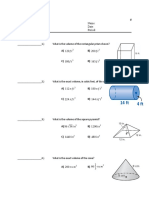
a.) Find the surface area of a prism, cylinder, pyramid, cone, and
sphere G.M.2
b.) Determine the surface area of objects composed of two prisms,
cylinders, pyramids, cones, or spheres G.M.2
c.) Calculate the volume of prism, cylinder, pyramid, cone, and
sphere G.M.2
d.) Determine the volume of objects composed of two prisms,
cylinders, pyramids, cones, or spheres G.M.2
e.) Use dimensional analysis for unit conversion and verify that
expressions and equations make sense G.M.5
Auxilliary Standards
f.) ……………………………………………………………………. G.M.3
g.)……………………………………………………………………. G.M.4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Ccgps CRCT Math 7th Grade Geometry Review PacketDocumento9 pagineCcgps CRCT Math 7th Grade Geometry Review PacketOishin MariscalNessuna valutazione finora
- FL Geo CorrelationsDocumento13 pagineFL Geo CorrelationsValleyNessuna valutazione finora
- IB Grade 9 Math Book-Chapter8Documento62 pagineIB Grade 9 Math Book-Chapter8aa1cc2100% (3)
- Math Final Geometry Standards 4 - 2 - 2018Documento9 pagineMath Final Geometry Standards 4 - 2 - 2018Luke ThorneNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry BookDocumento249 pagineGeometry BookMarizza Bailey100% (1)
- 1 Chapter 4 Study GuideDocumento3 pagine1 Chapter 4 Study Guide瀬黒愛済見Nessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Maths Term 4 Unit Plan 2021Documento3 pagine10 Maths Term 4 Unit Plan 2021Jeremy JaquesNessuna valutazione finora
- Add Maths Form 4Documento10 pagineAdd Maths Form 4Azrul AkmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Convergence ChartDocumento2 pagineConvergence Chartapi-310264286Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH5 - Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento33 pagineCH5 - Trigonometric Functionsmalik4164512095Nessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Scaffolding FrameworkDocumento10 pagineGeometry Scaffolding FrameworkMelanieNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 3 Outcomes 2014 2015Documento3 pagineMath 3 Outcomes 2014 2015api-271055898Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1819-Geom-Pre-TestDocumento7 pagine1819-Geom-Pre-Testapi-426721162Nessuna valutazione finora
- Third Term SS 1 Mathematics Lesson Note 1Documento3 pagineThird Term SS 1 Mathematics Lesson Note 1DanielNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan GET SP Grade 8 Mathematics Term 2 Week 4 GEOMETRY OF STRAIGHT LINESDocumento25 pagineLesson Plan GET SP Grade 8 Mathematics Term 2 Week 4 GEOMETRY OF STRAIGHT LINESAishvarya RashmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6 Test Review15-16Documento7 pagineUnit 6 Test Review15-16Micaela KNessuna valutazione finora
- Edmentun - GeometryDocumento5 pagineEdmentun - GeometryLeandro SafraNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Trigonometry 1 Course Notes & Exercise BookeltDocumento98 pagine01 Trigonometry 1 Course Notes & Exercise BookeltCobraコブラNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 1.1Documento6 pagineTutorial 1.1Lauren ChuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Performance IndicatorsDocumento10 pagineGeometry Performance IndicatorsSravan Kumar ChallojuNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.4 Trigonometric Functions of General Angles-Fall 2020Documento10 pagine7.4 Trigonometric Functions of General Angles-Fall 2020ali alqahtaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Measure and Trigonometry Worksheet-638493004971812022Documento10 pagineCircular Measure and Trigonometry Worksheet-638493004971812022ayh.alrashdiNessuna valutazione finora
- CT GeometryDocumento2 pagineCT Geometryak dNessuna valutazione finora
- MHF4U+6 1+-+assessmentDocumento9 pagineMHF4U+6 1+-+assessmentyao fengNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 1330Documento2 pagineMath 1330Siddharth VNessuna valutazione finora
- M Nov 2003Documento2 pagineM Nov 2003Leonardo TiabaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Final Exam: Multiple ChoiceDocumento15 pagineGeometry Final Exam: Multiple ChoicedanitNessuna valutazione finora
- GI LAB Manual PDFDocumento25 pagineGI LAB Manual PDFasdfghjNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Enrichment Packet - Answer Key PDFDocumento30 pagineGeometry Enrichment Packet - Answer Key PDFlesNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Review Student Jan 2018 GeometryDocumento4 pagineExam Review Student Jan 2018 Geometryapi-286302284Nessuna valutazione finora
- Math 5 Q3 ST#2Documento4 pagineMath 5 Q3 ST#2Gladish AnsubanNessuna valutazione finora
- Metrology Part 2Documento7 pagineMetrology Part 2Amar ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Metrology Part 2Documento7 pagineMetrology Part 2Shanawas Abdul RazakNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Worksheet 1 - AnglesDocumento13 pagineGeometry Worksheet 1 - AnglesAlexaNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Maths Term 4 Unit PlanDocumento3 pagine10 Maths Term 4 Unit PlanJeremy JaquesNessuna valutazione finora
- GeometryDocumento62 pagineGeometryRamana ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Xz≃Tm: Δ Mnp ∠ N=34° ∠ Xzy ≃∠ StmDocumento4 pagineXz≃Tm: Δ Mnp ∠ N=34° ∠ Xzy ≃∠ StmNATHANIEL GALOPONessuna valutazione finora
- Summative Test No. 4Documento5 pagineSummative Test No. 4Shaine Dzyll KuizonNessuna valutazione finora
- GED102 Week 5 WGN - ANTEDocumento5 pagineGED102 Week 5 WGN - ANTEArsen Rae M. ANTENessuna valutazione finora
- Shape and SpaceDocumento7 pagineShape and Spaceapi-65563698Nessuna valutazione finora
- Summative Test No. 2 Grade V - MathDocumento3 pagineSummative Test No. 2 Grade V - MathAileen Magbanua ArcaNessuna valutazione finora
- CE11 CE MATH 113A Mathematics in Modern World Trigonometry and Analytic GeometryDocumento2 pagineCE11 CE MATH 113A Mathematics in Modern World Trigonometry and Analytic GeometryJoshua John JulioNessuna valutazione finora
- Geoide MarottaVidotti2017 PDFDocumento20 pagineGeoide MarottaVidotti2017 PDFmarottagsaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1982 2170 BCG 23 03 00520Documento19 pagine1982 2170 BCG 23 03 00520marottagsaNessuna valutazione finora
- MSE21016711 Week 5Documento34 pagineMSE21016711 Week 5s.macharia1643Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 6 Suppl WkstsDocumento15 pagineCH 6 Suppl WkstsZahedah SataryNessuna valutazione finora
- Carnegie Learning CCSS GeometryDocumento30 pagineCarnegie Learning CCSS GeometryjaysakeNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento2 pagineUntitledapi-63318741Nessuna valutazione finora
- G P H S A U: Eometry Atterson IGH Chool LL NitsDocumento11 pagineG P H S A U: Eometry Atterson IGH Chool LL NitsNicholas YatesNessuna valutazione finora
- Yearly Plan Mathematics T 2013Documento22 pagineYearly Plan Mathematics T 2013Tan Chin HuatNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Physical Quantities and Units: Cambridge International AS and A Level Physics 9702 Syllabus Syllabus ContentDocumento23 pagine1 Physical Quantities and Units: Cambridge International AS and A Level Physics 9702 Syllabus Syllabus ContentRabin BajgainNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Review For Assessment PDFDocumento5 pagineUnit 1 Review For Assessment PDFAnjhang Estipular QuiñonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Practical 3Documento8 paginePhysics Practical 3geoffrey osuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Third Summative Test in Math Vi - q3Documento3 pagineThird Summative Test in Math Vi - q3Hrrym Ramirez100% (1)
- 2-Math Term - 2 Practice Worksheet 2 GeometryDocumento5 pagine2-Math Term - 2 Practice Worksheet 2 GeometryDr. Saqib RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- High School Geometry Curriculum: Course Description: This Course Involves The Integration of Logical Reasoning andDocumento52 pagineHigh School Geometry Curriculum: Course Description: This Course Involves The Integration of Logical Reasoning andenglishabraham24Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alg 2 Aiit.13 Aiit.14 Aiit.15 Aiit.16 Trig Test 1 Unit Circle Mostly Test Study Guide PDFDocumento6 pagineAlg 2 Aiit.13 Aiit.14 Aiit.15 Aiit.16 Trig Test 1 Unit Circle Mostly Test Study Guide PDFEugene ChungNessuna valutazione finora
- 663 Chemical Technology 3rd SemDocumento28 pagine663 Chemical Technology 3rd SemNasim UddinNessuna valutazione finora
- 663 Chemical Technology 3rd SemDocumento28 pagine663 Chemical Technology 3rd SemNasim UddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan - DilationsDocumento1 paginaLesson Plan - Dilationsapi-189090943Nessuna valutazione finora
- Get Your Brain in Shape!: Name: - 5.11 DilationsDocumento7 pagineGet Your Brain in Shape!: Name: - 5.11 Dilationsapi-189090943Nessuna valutazione finora
- Name: - Geometry CP Boston Collegiate Charter School Final Exam Ms - Touhey Multiple Choice (30 Points)Documento39 pagineName: - Geometry CP Boston Collegiate Charter School Final Exam Ms - Touhey Multiple Choice (30 Points)api-189090943Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final - '08-'09 - Modified IIDocumento39 pagineFinal - '08-'09 - Modified IIapi-189090943Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final - '08-'09-1Documento36 pagineFinal - '08-'09-1api-189090943Nessuna valutazione finora
- Read A Table: Name: - 3.17 Exit Ticket Criteria For MATH SuccessDocumento1 paginaRead A Table: Name: - 3.17 Exit Ticket Criteria For MATH Successapi-189090943Nessuna valutazione finora
- Things I Should Know by The End of Unit OneDocumento2 pagineThings I Should Know by The End of Unit Oneapi-189090943Nessuna valutazione finora
- Term 4 Kca - D and SDocumento7 pagineTerm 4 Kca - D and Sapi-189090943Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1.) 2.) Complete A Pictograph 3.) Identify: Name: - 3.17 Do NowDocumento7 pagine1.) 2.) Complete A Pictograph 3.) Identify: Name: - 3.17 Do Nowapi-189090943Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Quiz 2 (Surface Area and Volume)Documento5 paginePractice Quiz 2 (Surface Area and Volume)Natalia ArmozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Virtual Learning: Grade 7 / Volume of Triangular PrismDocumento11 pagineMath Virtual Learning: Grade 7 / Volume of Triangular PrismTru ManNessuna valutazione finora
- Pothuaud 2008Documento13 paginePothuaud 2008putu juniNessuna valutazione finora
- PDFDocumento14 paginePDFBibhuti B. Bhardwaj100% (1)
- Physics Chapter-1 Questions : Made By: M.farhan The Physics Teacher: Wahidullah HassanDocumento5 paginePhysics Chapter-1 Questions : Made By: M.farhan The Physics Teacher: Wahidullah HassanMohamadNessuna valutazione finora
- 1012 ChemistryDocumento182 pagine1012 ChemistryDuslius Smerkys100% (2)
- 10th Grade Physics - Unit 1Documento25 pagine10th Grade Physics - Unit 1Alice ScarletNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Suppression System of A Small-Scale LNG Loading Facility at PT Badak NGLDocumento8 pagineFire Suppression System of A Small-Scale LNG Loading Facility at PT Badak NGLT. LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Jlhhvalue Based Questions Class-12Documento16 pagineJlhhvalue Based Questions Class-12jitender8Nessuna valutazione finora
- American Handbook of Psychiatry 3Documento2.365 pagineAmerican Handbook of Psychiatry 3richuNessuna valutazione finora
- ICEM CFD Introductory Course: Volume MeshingDocumento23 pagineICEM CFD Introductory Course: Volume MeshingBharath DvNessuna valutazione finora
- Is 4179 1967 PDFDocumento48 pagineIs 4179 1967 PDFSneha RaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 and 2 AssessmentDocumento5 pagineLesson 1 and 2 AssessmentleleNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter:4 Reciprocating Air Compressors: B) Based On Number of Stages: I. IIDocumento14 pagineChapter:4 Reciprocating Air Compressors: B) Based On Number of Stages: I. IIKrishna ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W3Documento8 pagineDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W3JannahNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential VaporisationDocumento8 pagineDifferential VaporisationMohd RafiqNessuna valutazione finora
- ANSYS Forte Best PracticesDocumento48 pagineANSYS Forte Best PracticesReza JazayeriNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge IGCSE International Mathematics Paper 41 Summer 2013Documento16 pagineCambridge IGCSE International Mathematics Paper 41 Summer 2013mpoer72850% (1)
- Lab Report 7Documento3 pagineLab Report 7Kamran AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Lab Java Fundamentals Lab ObjectivesDocumento6 pagineChapter 2 Lab Java Fundamentals Lab ObjectivesammyNessuna valutazione finora
- 2020-2016 Price List Rev 1 PDFDocumento42 pagine2020-2016 Price List Rev 1 PDFN SNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Outcomes:: The Learner Demonstrates Understanding of Key Concepts of MeasurementsDocumento34 pagineLearning Outcomes:: The Learner Demonstrates Understanding of Key Concepts of MeasurementsMaricris Galachico GaraoNessuna valutazione finora
- Batching of Dosing Chemicals For BoilersDocumento4 pagineBatching of Dosing Chemicals For BoilersDavid Muñoz CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Q4 ST 1 GR.6 Math With TosDocumento3 pagineQ4 ST 1 GR.6 Math With TosSusan M. PalicpicNessuna valutazione finora
- Scientific Calculator LessonsDocumento74 pagineScientific Calculator LessonsMujib Kazi100% (1)
- Properties of SLGDocumento2 pagineProperties of SLGXinyi ZhouNessuna valutazione finora
- Accumulator SizingDocumento6 pagineAccumulator Sizingtankimsin100% (2)
- 5.4.A CalculatingPropertiesSolidsDocumento6 pagine5.4.A CalculatingPropertiesSolidsJunaid SiddiqiNessuna valutazione finora
- DukungalatDocumento6 pagineDukungalatridhoniNessuna valutazione finora
- MMEN 226 - Worked Examples On Change in Dimensions, Set 6Documento10 pagineMMEN 226 - Worked Examples On Change in Dimensions, Set 6nattydreadfathelahNessuna valutazione finora