Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
11 Eco PP ch2 1 PDF
Caricato da
Gamer Channel0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
37 visualizzazioni4 pagineTitolo originale
11_eco_pp_ch2_1.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
37 visualizzazioni4 pagine11 Eco PP ch2 1 PDF
Caricato da
Gamer ChannelCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 4
CBSE
Class 11 Economics
Practice Paper-1
Ch-02 Consumer's Behaviour & Theory of Demand
Short Answer type Questions (3-4 Marks)
Ques 1. Explain the law of diminishing marginal utility with the help of a utility schedule.
Ques 2. Explain consumers equilibrium with utility approach in case of single good.
Ques 3. What do you mean by budget line? What are the reasons of change in budget line?
Ques 4. Explain the relationship between total utility and marginal utility with the help of
schedule.
Or
What changes will take place in total utility when –
(a) Marginal utility curve remains above X–axis
(b) Marginal utility curve touches X–axis
(c) Marginal utility curve lies below X–axis.
Ques 5. State three features of indifference curve.
Ques 6. Why does two indifference curves not intersect each other?
Ques 7. Under what situations there will be parallel shift in budget line?
Ques 8. Explain the effect of a rise in the prices of ‘related goods’ on the demand for a good
X.
Ques 9. Why does demand of a normal good increases due to increase in consumer’s
income?
Ques 10. State elasticity of demand of followings :
(a) Luxurious goods
(b) Goods of alternate use
(c) Necessity goods.
Ques 11. Distinguish between expansion of demand and increase in demand with the help of
diagram.
Ques 12. Measure Price Elasticity of Demand on the following points of a straight line
demand curve :
(a) Centre point of the demand curve.
(b) Demand curve intercepting y-axis
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 1 / 4
(c) Demand curve intercepting x-axis.
Ques 13. Distinguish between change in demand and change in quantity demanded.
Ques 14. What will be the effect of following on elasticity of demand.
(a) time factor (b) nature of the product.
Ques 15. What will be the slope of demand curve under following situations.
(a) Perfectly elastic demand
(b) Perfectly inelastic demand
(c) Unit elastic demand.
Ques 16. State the factors of rightward shift of demand curve. Explain any one.
Ques 17. State the factors of leftward shift of demand curve. Explain any one.
Ques 18. How does ‘a proportion of income spent on a good’ affect elasticity of demand.
Ques 19. What will be elasticity of demand if
(a) Total expenditure increases due to increase in price.
(b) Total expenditure increases due to fall in price.
Ques 20. When price of a good is Rs. 7 per unit a consumer buys 12 units. When price falls to
Rs. 6 per unit he spends Rs. 72 on the good. Calculate price elasticity of demand by using the
percentage method. comment on the likely shape of demand curve based on this measure of
elasticity.
Ques 21. A consumer buys 10 units of a good at a price of Rs. 9 per unit. At price of Rs. 10 per
unit he buys 9 units. What is price elasticity of demand? Use expenditure approach Comment
on the likely shape of demand curve on the basis of this measure of elasticity.
Ques 22. A consumer buys 20 units of a good at a price of Rs. 5 per unit. He incurs an
expenditure of Rs. 120 when he buys 24 units. Calculate price elasticity of demand of the
percentage method. Comment on the likely shape of demand curve based on this
information.
Ques 23. When the price of a commodity falls by Rs. 2 per unit, its quantity demanded
increases by 10 units. Its price elasticity of demand is (–) 1. Calculate its quantity demanded
at the price before change which was Rs. 10 per unit.
Ques 24. The price elasticity of demand of a commodity is –0.5. At a price of Rs. 20 per unit,
total expenditure on it is Rs. 2,000. Its price is reduced by 10 percent. Calculate its demand at
the reduced price.
H.O.T.S.
Ques 25. State four determinants of price elasticity of demand.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 2 / 4
Ques 26. Differentiate between Normal goods and Inferior goods
Ques 27. Differentiate between Complementary goods and substitute goods.
Ques 28. Why should the budget line be tangent to the indifference curve at the point of
consumer’s equilibrium.
Ques 29. Why does consumer stop consumption in case where marginal utility is less than
price of a good?
Ques 30. What is budget line? Why is it negatively stopped?
Ques 31. A consumer consumes only two goods x & y. state & explain the conditions of
consumer’s equilibrium with the help of utility analysis.
Ques 32. Explain the conditions determining how many units of a good the consumer will
buy at a given price.
Ques 33. Define marginal rate of substitution. Explain why is an indifference curve convex?
LONG QUESTIONS (6 MARKS)
Ques 1. Explain the conditions of consumer’s equilibrium with the help of the indifference
curve analysis. Represent the same in a diagram.
Ques 2. Explain the determination of consumers equilibrium with the help of a schedule in
case of two commodities by using utility approach.
Ques 3. Why does demand curve slope downward?
Ques 4. Explain the determinants of price elasticity of demand.
Ques 5. With the help of diagrams, explain the effect of following changes on the demand of
a commodity.
(a) A fall in the income of its buyer.
(b) A rise in price of complementary good.
Ques 6. What are the conditions of consumer’s equilibrium under the indifference curve
approach? What changes will take place if the conditions are not fulfilled to reach
equilibrium?
Ques 7. Explain the three properties of indifference curve.
H.O.T.S.
Ques 8. With the help of numerical example measure price elasticity of demand in the
following conditions by total expenditure method :
(i) Demand falls when price is constant.
(ii) Price falls while demand is constant.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 3 / 4
Ques 9. Whether the following statements are true or false? Give reasons.
(i) Two indifference curves never intersects each other.
(ii) Income effect of inferior good is positive.
(iii) Change in quantity demanded is the explanations of law of demand.
Ques 10. Explain the concept of marginal rate of substitution (MRS) by giving an example.
What happens to MRS when consumer moves downwards along the indifference curve? Give
reasons for your answer.
Ques 11. Following statements are true or false give reasons :
(i) Increase in number of consumers shifts the demand curve rightward.
(ii) The demand of a commodity becomes elastic if its substitute good is available in the
market.
(iii) The price elasticity of demand is equal to unity at a point situated in the middle of a
straight line demand curve.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 4 / 4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Basic Carding Tutorial PDFDocumento2 pagineBasic Carding Tutorial PDFTeodor Tiron87% (15)
- Microeconomics Problems SetDocumento33 pagineMicroeconomics Problems SetBeri Z HunterNessuna valutazione finora
- 0 - Business Studies (Class 12) Mind Map-1 PDFDocumento14 pagine0 - Business Studies (Class 12) Mind Map-1 PDFGamer Channel67% (6)
- 0 - Business Studies (Class 12) Mind Map-1 PDFDocumento14 pagine0 - Business Studies (Class 12) Mind Map-1 PDFGamer Channel67% (6)
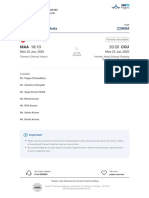
- Chennai To Kolkata Z2IR8M: Air Asia I5-557Documento3 pagineChennai To Kolkata Z2IR8M: Air Asia I5-557Gamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics - Undergraduate Essays and Revision NotesDa EverandMicroeconomics - Undergraduate Essays and Revision NotesNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotisserie Affair Deli Marketing PlanDocumento41 pagineRotisserie Affair Deli Marketing PlanAri EngberNessuna valutazione finora
- REEBOKDocumento90 pagineREEBOKManoranjan Singh75% (4)
- REEBOKDocumento90 pagineREEBOKManoranjan Singh75% (4)
- Case Study KarimRamziDocumento10 pagineCase Study KarimRamziToufik Akhdari0% (1)
- Microeconomics and Behavior 9th Edition Frank Solutions ManualDocumento25 pagineMicroeconomics and Behavior 9th Edition Frank Solutions ManualDeborahWestwdzt96% (51)
- Nivea Is Widely Known Especially in Skin Care and Beauty ProductsDocumento3 pagineNivea Is Widely Known Especially in Skin Care and Beauty ProductsMyra AbbasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual For Microeconomics and Behavior 9th Edition Frank 0078021693 9780078021695Documento36 pagineSolution Manual For Microeconomics and Behavior 9th Edition Frank 0078021693 9780078021695brianrobertsonogknfzetxw100% (22)
- Paper EconomicsDocumento2 paginePaper EconomicsVAIBHAVNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics Question BankDocumento3 pagineMicroeconomics Question BankGeneral DhruvNessuna valutazione finora
- Eco Class Xii WorksheetsDocumento20 pagineEco Class Xii WorksheetsNeeraj TyagiNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics Principles and Applications 6th Edition Hall Solutions Manual DownloadDocumento15 pagineMicroeconomics Principles and Applications 6th Edition Hall Solutions Manual DownloadGerald Washing100% (20)
- SPSCHD23 Dec 20191242677Documento2 pagineSPSCHD23 Dec 20191242677Jugadu GenerationNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-II Consumer's EquilibriumDocumento1 paginaUnit-II Consumer's Equilibriumanushkac537Nessuna valutazione finora
- Consumers Equi and DemandDocumento37 pagineConsumers Equi and DemandDimple BhattNessuna valutazione finora
- Maximize satisfaction with consumer choicesDocumento19 pagineMaximize satisfaction with consumer choicesBishawnath RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- ABM 311 (Introductory Microeconomic Theory) 1. Module 3 Consumer Choice and Demand: The Indifference Curve ApproachDocumento5 pagineABM 311 (Introductory Microeconomic Theory) 1. Module 3 Consumer Choice and Demand: The Indifference Curve ApproachIrene PacunayenNessuna valutazione finora
- AQS1104200512 Principles of MicroeconomicsDocumento2 pagineAQS1104200512 Principles of MicroeconomicsPhainos Simon GwariNessuna valutazione finora
- IB Economics Teacher Resource 3ed Paper 1 AnswersDocumento19 pagineIB Economics Teacher Resource 3ed Paper 1 AnswersIzyan LiraniNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of MicroeconomicsDocumento3 pagineFundamentals of MicroeconomicsYou TubeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cavendish University Zambia Microeconomics Assignment FeedbackDocumento12 pagineCavendish University Zambia Microeconomics Assignment FeedbackAndrewNessuna valutazione finora
- pt1ch02 PDFDocumento8 paginept1ch02 PDFsmcNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank Economics - Micro and StatisticsDocumento21 pagineQuestion Bank Economics - Micro and StatisticsAvijit RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- CMYK Sample PaperDocumento1 paginaCMYK Sample PaperAnkur GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 12 Economics Question Paper 2019 PDFDocumento21 pagineCBSE Class 12 Economics Question Paper 2019 PDFVaishali AggarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- CJC Prelim h2 Econs p2 Answers 2016Documento41 pagineCJC Prelim h2 Econs p2 Answers 2016Yan Shen TanNessuna valutazione finora
- ZMJCF SL80 CDocumento11 pagineZMJCF SL80 CbilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Economics and Bangladesh Economy (PBE) IntroductionDocumento5 paginePrinciples of Economics and Bangladesh Economy (PBE) IntroductionZonal office ChapainawbagnajNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics Theory and Applications With Calculus 3rd Edition Perloff Solutions ManualDocumento36 pagineMicroeconomics Theory and Applications With Calculus 3rd Edition Perloff Solutions Manualsiphilisdysluite7xrxc100% (27)
- Dwnload Full Microeconomics Theory and Applications With Calculus 3rd Edition Perloff Solutions Manual PDFDocumento36 pagineDwnload Full Microeconomics Theory and Applications With Calculus 3rd Edition Perloff Solutions Manual PDFependymaspritelywuuurq100% (14)
- 200ECN Jan 2017 - Model Answer (All Questions)Documento11 pagine200ECN Jan 2017 - Model Answer (All Questions)phuongfeoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Theory of Consumer Behaviour: Property 1: Completeness. If An Individual Can Rank Any Pair of BundlesDocumento27 pagineThe Theory of Consumer Behaviour: Property 1: Completeness. If An Individual Can Rank Any Pair of BundlesprabodhNessuna valutazione finora
- Econ Unit 1Documento18 pagineEcon Unit 1sadNessuna valutazione finora
- Dwnload Full Microeconomics and Behavior 9th Edition Frank Solutions Manual PDFDocumento35 pagineDwnload Full Microeconomics and Behavior 9th Edition Frank Solutions Manual PDFreneestanleyf375h100% (9)
- Microeconomics and Behavior 9th Edition Frank Solutions ManualDocumento35 pagineMicroeconomics and Behavior 9th Edition Frank Solutions Manualbejumbleaugitexy08y100% (22)
- Microeconomics Midterm Exam QuestionsDocumento2 pagineMicroeconomics Midterm Exam QuestionsNatia KakuliaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Microeconomics Key Notes CH 02 Theory of Consumer BehaviourDocumento11 pagine12 Microeconomics Key Notes CH 02 Theory of Consumer BehaviourRaunit SethiNessuna valutazione finora
- Business EconomicsDocumento2 pagineBusiness EconomicsGuruKPONessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer EquilibriumDocumento28 pagineConsumer EquilibriumRupesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- NIT Rourkela Economics Exam QuestionsDocumento2 pagineNIT Rourkela Economics Exam QuestionsPrarabdha SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Preferences and Choice Chapter AnalysisDocumento22 pagineConsumer Preferences and Choice Chapter AnalysisDrGarima Nitin SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of Demand and Consumer BehaviorDocumento24 pagineTheory of Demand and Consumer Behaviorsikandar aNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro EconomicsDocumento1 paginaMicro EconomicsGuruKPONessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Micro Economics Question Bank Ist SemDocumento3 paginePrinciples of Micro Economics Question Bank Ist Semyjayasanka588Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 8Documento35 pagineUnit 8pakhi rawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical and Descriptive QuestionsDocumento2 pagineAnalytical and Descriptive QuestionsAbhisek MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Essay Exercise - Indifference Curve AnalysisDocumento7 pagineEssay Exercise - Indifference Curve AnalysisYashjeet Gurung RCS KJNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics Theory and Applications With Calculus 3rd Edition Perloff Solutions ManualDocumento13 pagineMicroeconomics Theory and Applications With Calculus 3rd Edition Perloff Solutions ManualMichaelMeyerfisp100% (47)
- PK Work Sheet Economics Class 11Documento5 paginePK Work Sheet Economics Class 11Krish PatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- SKRastogi - Teaching Note - Lancaster Consumption TechnologyDocumento6 pagineSKRastogi - Teaching Note - Lancaster Consumption TechnologyHemant KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Abm Module 3 NewDocumento21 pagineAbm Module 3 NewAiza BelandoNessuna valutazione finora
- P - VTH Sem Question BankDocumento2 pagineP - VTH Sem Question BankTheodorah MbedziNessuna valutazione finora
- Indifference CurvesDocumento49 pagineIndifference CurvesMuhammad BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics Principles and Applications 6th Edition Hall Solutions Manual 1Documento9 pagineMicroeconomics Principles and Applications 6th Edition Hall Solutions Manual 1earl100% (51)
- Microeconomics Principles and Applications 6Th Edition Hall Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento30 pagineMicroeconomics Principles and Applications 6Th Edition Hall Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFlonnie.lotts387100% (12)
- TheoryofDemand IIIDocumento24 pagineTheoryofDemand IIIepic gamerNessuna valutazione finora
- Distinguish Between Cardinal and Ordinal Approach To Explain The ConsumerDocumento10 pagineDistinguish Between Cardinal and Ordinal Approach To Explain The ConsumerPoonam ThapaNessuna valutazione finora
- C 3 AC ' C C: Hapter Onsumer S Onstrained HoiceDocumento3 pagineC 3 AC ' C C: Hapter Onsumer S Onstrained HoiceMaggiehoushaimiNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading 12b CFAL1 EconDocumento38 pagineReading 12b CFAL1 EconSteve Sambu JrNessuna valutazione finora
- Cobecon - Consumer Behavior Reviewer.1.2022-23Documento5 pagineCobecon - Consumer Behavior Reviewer.1.2022-23Joshua KhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics For Today 8Th Edition Tucker Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento28 pagineMicroeconomics For Today 8Th Edition Tucker Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFlonnie.lotts387100% (11)
- Microeconomics For Today 8th Edition Tucker Solutions Manual 1Documento7 pagineMicroeconomics For Today 8th Edition Tucker Solutions Manual 1david100% (48)
- Microeconomics 8th Edition Perloff Solutions ManualDocumento36 pagineMicroeconomics 8th Edition Perloff Solutions Manualanthonytodd5jbw100% (25)
- Current Affairs 11-08-2021Documento4 pagineCurrent Affairs 11-08-2021Gamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebook by Witloof: Earn Money by Playing Fortnite 10-100 / WeekDocumento2 pagineEbook by Witloof: Earn Money by Playing Fortnite 10-100 / WeekGamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Affairs 09-08-2021Documento2 pagineCurrent Affairs 09-08-2021Gamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- Intergovernmental Panel On Climate ChangeDocumento3 pagineIntergovernmental Panel On Climate ChangeGamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- TimetableDocumento1 paginaTimetableGamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- Cbse Geography Sample Paper Class 12 2019-20Documento10 pagineCbse Geography Sample Paper Class 12 2019-20Bhola DoleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bangalore FruitsDocumento6 pagineBangalore FruitsMahesh GNessuna valutazione finora
- Cbse Geography Sample Paper Class 12 2019-20Documento10 pagineCbse Geography Sample Paper Class 12 2019-20Bhola DoleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bba Syllabus PDFDocumento73 pagineBba Syllabus PDFGamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Paper Sample Paper Solution Set 4Documento14 pagineCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Paper Sample Paper Solution Set 4Gamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- Dummy PDF File SampleDocumento1 paginaDummy PDF File SampleGamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- 3c964527-b7cc-4ddb-aadf-8269f0ad9270Documento5 pagine3c964527-b7cc-4ddb-aadf-8269f0ad9270Gamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- Time: 3 Hrs Max. Marks: 100 Class: Xi Annual Examination Jan, 2019 General InstructionsDocumento4 pagineTime: 3 Hrs Max. Marks: 100 Class: Xi Annual Examination Jan, 2019 General InstructionsGamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- English Question Paper 2010Documento7 pagineEnglish Question Paper 2010ShrikantNessuna valutazione finora
- HackDocumento4 pagineHackGamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- Keac 105Documento20 pagineKeac 105Gamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 10 SolutionsDocumento18 pagineClass 10 SolutionsGamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank Rekonsiliasi PDFDocumento31 pagineBank Rekonsiliasi PDFSekar Ayu Kartika SariNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Eco PP ch2 1Documento23 pagine11 Eco PP ch2 1Gamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 4Documento4 pagineMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 4Gamer ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- Viner Cost Curves and Supply CurvesDocumento25 pagineViner Cost Curves and Supply CurvesZenobio FarfNessuna valutazione finora
- ThelerougecandycompanyDocumento4 pagineThelerougecandycompanyAreeba.SulemanNessuna valutazione finora
- Frequently Asked Questions Transition From UL 508C To UL 61800-5-1Documento6 pagineFrequently Asked Questions Transition From UL 508C To UL 61800-5-1nomeacueroNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprehensive Variance Analysis Journal EntriesDocumento9 pagineComprehensive Variance Analysis Journal EntriesNovel LiaNessuna valutazione finora
- History and Definition of Eco-EfficiencyDocumento6 pagineHistory and Definition of Eco-EfficiencyRodrigo Alejandro Hurtado ValdiviaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Entrepreneur Networks. Final VerDocumento26 pagine6 Entrepreneur Networks. Final VerSAURAV SAURAVNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations Management: Location StrategiesDocumento18 pagineOperations Management: Location StrategiesRavi JakharNessuna valutazione finora
- Women Entrepreneurs in IndiaDocumento33 pagineWomen Entrepreneurs in Indiaritesh1991987Nessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of SBI and PNBDocumento100 pagineComparison of SBI and PNBMukeshKumar100% (2)
- 02062019105858t13pdxmwzeiag20kby Estatement 052019 997 PDFDocumento3 pagine02062019105858t13pdxmwzeiag20kby Estatement 052019 997 PDFNikhil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Agency v4Documento59 pagineAgency v4Roxanne Daphne Ocsan LapaanNessuna valutazione finora
- Teoria Do MSR ADocumento4 pagineTeoria Do MSR AAlexandre Valeriano da SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study 1Documento5 pagineCase Study 1Abubakar MoazzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Asset Quality, Credit Delivery and Management FinalDocumento21 pagineAsset Quality, Credit Delivery and Management FinalDebanjan DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Principles For Industrie 4.0 Scenarios: A Literature ReviewDocumento16 pagineDesign Principles For Industrie 4.0 Scenarios: A Literature ReviewRogério MaxNessuna valutazione finora
- CV of Faysal AhamedDocumento2 pagineCV of Faysal AhamedSyed ComputerNessuna valutazione finora
- KFC Case Study by MR OtakuDocumento36 pagineKFC Case Study by MR OtakuSajan Razzak Akon100% (1)
- Oranjolt - Rasn-WPS OfficeDocumento3 pagineOranjolt - Rasn-WPS OfficeKaviya SkNessuna valutazione finora
- Glass Manufacture BrochureDocumento4 pagineGlass Manufacture BrochureCristian Jhair PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- DTC Agreement Between Cyprus and United StatesDocumento30 pagineDTC Agreement Between Cyprus and United StatesOECD: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and DevelopmentNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample of Application Letter and CVDocumento4 pagineSample of Application Letter and CVSaleh Al ArifinNessuna valutazione finora
- Distridution and Channel MemberDocumento6 pagineDistridution and Channel Memberabdulhaq4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Flavia CymbalistaDocumento3 pagineFlavia Cymbalistadodona7772494Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tamaño de Los Data Files (DBA - DATA - FILES)Documento9 pagineTamaño de Los Data Files (DBA - DATA - FILES)Frank HackNessuna valutazione finora
- Aud589 (Pya 2019 Dec)Documento7 pagineAud589 (Pya 2019 Dec)amirah zahidahNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminology Test - Petty CashDocumento2 pagineTerminology Test - Petty CashStars2323100% (1)
- FM11 CH 10 Capital BudgetingDocumento56 pagineFM11 CH 10 Capital Budgetingm.idrisNessuna valutazione finora