Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Alternative Centres of Power
Caricato da
Sameena Siraj0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
30 visualizzazioni11 pagineAlternative Centres of Power
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoAlternative Centres of Power
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
30 visualizzazioni11 pagineAlternative Centres of Power
Caricato da
Sameena SirajAlternative Centres of Power
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 11
Association of South-East
Asian Nations (ASEAN)
Lesson 3
By,
Sameena
To start by..
• Lets take a look at the political map of the world.
• Which countries would fall in the southeastern region of Asia?
• Before and during the Second World War, this region of Asia suffered the
economic and political consequences of repeated colonialisms, both
European and Japanese.
The problems faced..
• At the end of the war, it confronted problems of nation-building, the
ravages of poverty and economic backwardness;
• And the pressure to align with one great power or another during the Cold
War.
• This was a recipe for conflict, which the countries of Southeast Asia could
ill afford.
An alternative..
• Efforts at Asian and Third World unity, such as the Bandung
Conference and the Non-Aligned Movement, were ineffective in
establishing the conventions for informal cooperation and interaction.
• Hence, the Southeast Asian nations sought an alternative by establishing
the Association for South East Asian Nations (ASEAN).
The member countries..
• ASEAN was established in 1967 by five countries of this region —
Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand — by signing
the Bangkok Declaration.
• The objectives of ASEAN were primarily to accelerate economic growth
and through that ‘social progress and cultural development’.
The second objective..
• A secondary objective was to promote regional peace and stability based on
the rule of law and the principles of the United Nations Charter.
• Over the years, Brunei Darussalam, Vietnam, Lao PDR, Myanmar (Burma)
and Cambodia joined ASEAN taking its strength to ten.
• Unlike the EU there is little desire in ASEAN for supranational structures
and institutions.
The ASEAN way..
• ASEAN countries have celebrated what has become known as the ‘ASEAN
Way’, a form of interaction that is informal, non-confrontationist and
cooperative.
• The respect for national sovereignty is critical to the functioning of
ASEAN.
• With some of the fastest growing economies in the world, ASEAN
broadened its objectives beyond the economic and social spheres.
The three pillars..
• In 2003, ASEAN moved along the path of the EU by agreeing to
establish an ASEAN Community comprising three pillars,
• Namely, the ASEAN Security Community, the ASEAN Economic
Community and the ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community.
Thank you ☺
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Solution Manual For Database Systems Design Implementation and Management 10th EditionDocumento13 pagineSolution Manual For Database Systems Design Implementation and Management 10th EditionChris Harris0% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Time Wise ItineraryDocumento3 pagineTime Wise ItineraryKeshav BahetiNessuna valutazione finora
- China-The Land That Failed To Fail PDFDocumento81 pagineChina-The Land That Failed To Fail PDFeric_stNessuna valutazione finora
- US Hegemony in World PoliticsDocumento14 pagineUS Hegemony in World PoliticsSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- US As A Hegemonic StateDocumento11 pagineUS As A Hegemonic StateSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- End of BipolarityDocumento12 pagineEnd of BipolaritySameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- US As A Hegemonic PowerDocumento8 pagineUS As A Hegemonic PowerSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- US Hegemony in World PoliticsDocumento14 pagineUS Hegemony in World PoliticsSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- Alternative Centres of PowerDocumento12 pagineAlternative Centres of PowerSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- End of BipolarityDocumento6 pagineEnd of BipolaritySameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Questions - 2 Markers: Lesson 14 By, SameenaDocumento7 paginePractice Questions - 2 Markers: Lesson 14 By, SameenaSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- New International Economic Order (NIEO) : Lesson 10 By, SameenaDocumento8 pagineNew International Economic Order (NIEO) : Lesson 10 By, SameenaSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- Cold WarDocumento12 pagineCold WarSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- CW 12 PDFDocumento8 pagineCW 12 PDFSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- India and The Cold War: Lesson 12 By, SameenaDocumento8 pagineIndia and The Cold War: Lesson 12 By, SameenaSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cold War: Lesson 3 By, SameenaDocumento8 pagineThe Cold War: Lesson 3 By, SameenaSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cuban Missile Crisis: Lesson 2 By, SameenaDocumento8 pagineThe Cuban Missile Crisis: Lesson 2 By, SameenaSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- US Hegemony in World PoliticsDocumento10 pagineUS Hegemony in World PoliticsSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cold War: Lesson 4 By, SameenaDocumento8 pagineThe Cold War: Lesson 4 By, SameenaSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cold War Era: Lesson 1 By, SameenaDocumento11 pagineThe Cold War Era: Lesson 1 By, SameenaSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- US Hegemony in World PoliticsDocumento14 pagineUS Hegemony in World PoliticsSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- US Hegemony in World PoliticsDocumento14 pagineUS Hegemony in World PoliticsSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cold War Era: Lesson 1 By, SameenaDocumento11 pagineThe Cold War Era: Lesson 1 By, SameenaSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- US Hegemony in World PoliticsDocumento11 pagineUS Hegemony in World PoliticsSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- US Hegemony in World PoliticsDocumento10 pagineUS Hegemony in World PoliticsSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- US Hegemony in World PoliticsDocumento11 pagineUS Hegemony in World PoliticsSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- RiseDocumento7 pagineRiseSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- PerceptionDocumento24 paginePerceptionSameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- Sampling Design Sample Size and Determination: Team 10 Chandini - 063 KAVYA - 072 Meghana - 078 SAMEENA - 083Documento2 pagineSampling Design Sample Size and Determination: Team 10 Chandini - 063 KAVYA - 072 Meghana - 078 SAMEENA - 083Sameena SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- Barro and Grossman - A General Disequilibrium Model of Income and Employment PDFDocumento12 pagineBarro and Grossman - A General Disequilibrium Model of Income and Employment PDFDouglas Fabrízzio CamargoNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Scheme of Studyb - SC (Hons.) Agri Economics (UAF)Documento15 pagineRevised Scheme of Studyb - SC (Hons.) Agri Economics (UAF)Irfy BegNessuna valutazione finora
- Maruti CaseDocumento5 pagineMaruti CaseBishwadeep Purkayastha100% (1)
- 25-JUNE-2021: The Hindu News Analysis - 25 June 2021 - Shankar IAS AcademyDocumento22 pagine25-JUNE-2021: The Hindu News Analysis - 25 June 2021 - Shankar IAS AcademyHema and syedNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - Money Creation & Framwork of Monetary Policy1Documento6 pagineChapter - Money Creation & Framwork of Monetary Policy1Nahidul Islam IUNessuna valutazione finora
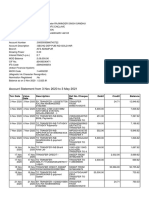
- Account Statement From 3 Nov 2020 To 3 May 2021: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceDocumento8 pagineAccount Statement From 3 Nov 2020 To 3 May 2021: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceRajwinder SandhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Mission Report2Documento8 pagineFinal Mission Report2api-3701155100% (4)
- Capsim Success MeasuresDocumento10 pagineCapsim Success MeasuresalyrNessuna valutazione finora
- Forklift Driving Training MalaysiaDocumento2 pagineForklift Driving Training MalaysiaIsogroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual For Macroeconomics For Today 10th Edition Irvin B TuckerDocumento6 pagineSolution Manual For Macroeconomics For Today 10th Edition Irvin B TuckerKelly Pena100% (31)
- UPODocumento3 pagineUPOcaue69343Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notice of Ex Parte IEPDocumento9 pagineNotice of Ex Parte IEPonell.soto653Nessuna valutazione finora
- T1 General PDFDocumento4 pagineT1 General PDFbatmanbittuNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Data About Swiss Grid PDFDocumento7 pagineComplete Data About Swiss Grid PDFManpreet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Plastics Give A Helpful HandDocumento10 pagine1 Plastics Give A Helpful HandNIranjanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Analysis of NestleDocumento40 pagineMarketing Analysis of NestleFaizanSheikh100% (3)
- CSR 2Documento7 pagineCSR 2Shravan RamsurrunNessuna valutazione finora
- Portfolio Management ASSIGN..Documento23 paginePortfolio Management ASSIGN..Farah Farah Essam Abbas HamisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Borjas 2013 Power Point Chapter 8Documento36 pagineBorjas 2013 Power Point Chapter 8Shahirah Hafit0% (1)
- Drivers of International BusinessDocumento38 pagineDrivers of International BusinessAKHIL reddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Operation Flood White Revolution Muhammad Ali 2007-Va-378 Bs (Hons) Dairy TechnologyDocumento23 pagineOperation Flood White Revolution Muhammad Ali 2007-Va-378 Bs (Hons) Dairy TechnologyShawn MathiasNessuna valutazione finora
- Mind Map Cost of ProductionDocumento1 paginaMind Map Cost of ProductionDimas Mahendra P BozerNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Strategy An OverviewDocumento13 pagineMarketing Strategy An OverviewRobin PalanNessuna valutazione finora
- SWOT-ToWS Analysis of LenovoDocumento2 pagineSWOT-ToWS Analysis of Lenovoada9ablao100% (4)
- Study On The Thermal Pyrolysis of Medical Waste (Plastic Syringe) For The Production of Useful Liquid Fuels PDFDocumento53 pagineStudy On The Thermal Pyrolysis of Medical Waste (Plastic Syringe) For The Production of Useful Liquid Fuels PDFaysarNessuna valutazione finora
- TC2014 15 NirdDocumento124 pagineTC2014 15 Nirdssvs1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Midc MumbaiDocumento26 pagineMidc MumbaiparagNessuna valutazione finora