Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Conversion Table
Caricato da
Vembricha NindyaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Conversion Table
Caricato da
Vembricha NindyaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
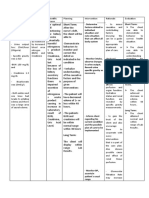
Equivalent Surface Area Dosage Conversion Factors
This table gives approximate factors for converting doses expressed in terms of mg/kg from
one species to an equivalent surface area dose expressed as mg/kg in the other species
tabulated. The assumptions and constants of the paper by Freireich EJ, et al, 1966 are used.
TO
Mouse 20 g Rat 150 g Monkey 3 kg Dog 8 kg Man 60 kg
Mouse 1 1/2 1/4 1/6 1/12
Rat 2 1 1/2 1/4 1/7
FROM
Monkey 4 2 1 3/5 1/3
Dog 6 4 1 2/3 1 1/2
Man 12 7 3 2 1
Ex: Given a dose of 50 mg/kg in the mouse, what is the appropriate dose in the monkey
assuming equivalency on the basis of mg/m2? 50 mg/kg x 1/4 = 13 mg/kg.
Representative Surface Area to Weight Ratios [km] for Various Species1
Species Body Weight [kg] Surface Area [sq. m.] km factor
Mouse 0.02 0.0066 3.0
Rat 0.15 0.025 5.9
Monkey 3.0 0.24 12
Dog 8.0 0.40 20
Human, Child 20 0.80 25
Human, Adult 60 1.6 37
1
Freireich, EJ, et al. Quantitative comparison of toxicity of anticancer agents in mouse, rat,
dog, monkey and man. Cancer Chemother Rep.1966;50(4):219-244.
Ex: To express a mg/kg dose in any given species as the equivalent mg/sq.m. dose, multiply
the dose by the appropriate km factor. In adult humans, 100 mg/kg is equivalent to 100
mg/kg x 37 kg/sq.m. = 3700 mg/sq.m.
DTP/DCTD/NCI/NIH/DHHS
http://dtp.nci.nih.gov
Guidance Posted August 2007
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Buangan Dari Dose EscalationDocumento3 pagineBuangan Dari Dose EscalationAgung OppoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1471-7899-jrf 15 1 029Documento4 pagine1471-7899-jrf 15 1 029Eng.Químico SCNessuna valutazione finora
- IJMPR0101007Documento6 pagineIJMPR0101007IJMPR JournalNessuna valutazione finora
- Anxiolytic Activity of Fennel Fruit Soxhlet in MiceDocumento3 pagineAnxiolytic Activity of Fennel Fruit Soxhlet in MiceOthman JerbiNessuna valutazione finora
- Backup of LD50 Report Nguyen - Alice - 99141754Documento8 pagineBackup of LD50 Report Nguyen - Alice - 99141754Alice NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Artigo AntônioDocumento17 pagineArtigo AntônioHenry Daniel Ruiz AlbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Black Bengal GoatsDocumento10 pagineBlack Bengal GoatsMaruf KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Measuring Water Potential in Potato Tubers LABDocumento10 pagineMeasuring Water Potential in Potato Tubers LABMonica Paris SisourathNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.6.4 Practice - Modeling - Linear, Quadratic, and Exponential Functions (Practice)Documento9 pagine3.6.4 Practice - Modeling - Linear, Quadratic, and Exponential Functions (Practice)johnnyhockey91Nessuna valutazione finora
- Act 9Documento9 pagineAct 9Deasserei TatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Animal BreedingDocumento8 pagineOverview of Animal BreedingAP Opto SistNessuna valutazione finora
- Dose CalculationDocumento20 pagineDose CalculationratheeshkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of The Teratogenicity of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-P-Dioxin in The RatDocumento8 pagineStudy of The Teratogenicity of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-P-Dioxin in The RatscribdmyprintsNessuna valutazione finora
- 2020-Acetamiprid RatasDocumento10 pagine2020-Acetamiprid RatasNuria Areli Márquez PérezNessuna valutazione finora
- A28 (Tavuk Karaciğer Kemik EurPoulSci)Documento9 pagineA28 (Tavuk Karaciğer Kemik EurPoulSci)cht aytNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculations in Toxicology and Determination of Median Effective and Median Lethal DosesDocumento3 pagineCalculations in Toxicology and Determination of Median Effective and Median Lethal DosesHammad KingNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No. 3Documento45 pagineExperiment No. 3api-3728522Nessuna valutazione finora
- 32 Schlegel0Documento6 pagine32 Schlegel0cristina_gomhNessuna valutazione finora
- Glifosato Test Estres OxidativoDocumento8 pagineGlifosato Test Estres OxidativodborghiNessuna valutazione finora
- Anim 1014behaviour and Assessment and Management of Welfare in PracticeDocumento83 pagineAnim 1014behaviour and Assessment and Management of Welfare in Practicemurse101Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Exercise 3 Tabular PresentationDocumento2 pagineLab Exercise 3 Tabular PresentationgaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Breeding MethodsDocumento186 pagineAnimal Breeding MethodsAmanuel AsratNessuna valutazione finora
- Normal Reference Ranges in Pregnancy - UpToDateDocumento14 pagineNormal Reference Ranges in Pregnancy - UpToDateopenid_nF8LPWdRNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 5 - Predator Prey RelationshipsDocumento4 pagineExercise 5 - Predator Prey RelationshipsAlaniss Viveca AgnoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Three: Risk Indicators For Displaced Abomasum On Herd LevelDocumento12 pagineChapter Three: Risk Indicators For Displaced Abomasum On Herd LevelfrankyNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Dosing ChartDocumento2 paginePediatric Dosing Chartblueash44Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 24Documento16 pagineChap 24Phú NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Does Mosquito Mass-Rearing Produce An Inferior Mosquito?: Malaria JournalDocumento8 pagineDoes Mosquito Mass-Rearing Produce An Inferior Mosquito?: Malaria JournalNur AriviantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Tribulus Terrestris Extract On Semen Quality and Serum Total Cholesterol Content in White Plymouth Rock-Mini CocksDocumento8 pagineEffect of Tribulus Terrestris Extract On Semen Quality and Serum Total Cholesterol Content in White Plymouth Rock-Mini CocksyigalbyNessuna valutazione finora
- Deer Pellet ProjectDocumento13 pagineDeer Pellet ProjecttquelchNessuna valutazione finora
- Antimetastatic ActivDocumento5 pagineAntimetastatic ActivwxcvbnnbvcxwNessuna valutazione finora
- ' - Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn., 1968, 173, No 2. 316: A Comparative Behavioral OF Ditran AND LSD in Mice, DogsDocumento11 pagine' - Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn., 1968, 173, No 2. 316: A Comparative Behavioral OF Ditran AND LSD in Mice, DogsahalbersNessuna valutazione finora
- Predator Prey SimulationDocumento2 paginePredator Prey SimulationMaggie WaltersNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti-Inflammatory: Activity of The Steroid Alkaloid Glycoside, TomatineDocumento8 pagineAnti-Inflammatory: Activity of The Steroid Alkaloid Glycoside, TomatineTrimaryantiNessuna valutazione finora
- 473 845 1 SM PDFDocumento7 pagine473 845 1 SM PDFDodi JajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Insecticidal Effects of The Insect Growth Regulators Methoprene and Pyriproxyfen On The Cat Flea - Kawada 1996Documento4 pagineInsecticidal Effects of The Insect Growth Regulators Methoprene and Pyriproxyfen On The Cat Flea - Kawada 1996Camyla NunesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Replacement of Corn Silage by Treated and Untreated Whole Crop Triticale Silage in Diets of Fattening Male CalvesDocumento2 pagineThe Replacement of Corn Silage by Treated and Untreated Whole Crop Triticale Silage in Diets of Fattening Male CalvesDaniel PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolizable Energy of Corn, Soybean Meal and Wheat For Laying HensDocumento7 pagineMetabolizable Energy of Corn, Soybean Meal and Wheat For Laying HensBAUTISTA TERRONES GILMERNessuna valutazione finora
- Feeding Behavior of Giant Gourami, Osphronemus Gouramy (Lacepede) LarvaeDocumento4 pagineFeeding Behavior of Giant Gourami, Osphronemus Gouramy (Lacepede) LarvaeMuhammad Faroq Abu Wildan100% (1)
- Worm Lab For Environmental Science ClassDocumento2 pagineWorm Lab For Environmental Science Classoscarwu1Nessuna valutazione finora
- DISTOCIDDocumento2 pagineDISTOCIDmahgadNessuna valutazione finora
- DSE Ratings Revised September 2019Documento2 pagineDSE Ratings Revised September 2019GwyddonNessuna valutazione finora
- Antimicrobial Nazar PDFDocumento5 pagineAntimicrobial Nazar PDFSyufyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fantz 1953Documento4 pagineFantz 1953Desarrollo Cognitivo CAMYPNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 1007%2FBF01234480Documento13 pagine10 1007%2FBF01234480Mukthar FitzsimmonsNessuna valutazione finora
- Inter SHDocumento6 pagineInter SHAkmal FadilandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Effects of Different Feed Forms On Performance in Broiler ChickensDocumento5 pagineEffects of Different Feed Forms On Performance in Broiler ChickensKhaeraniMahdinurAwliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Edgar1990-The Use of The Size-Structure of Benthic Macrofaunal Communities To Estimate Faunal BiomassDocumento20 pagineEdgar1990-The Use of The Size-Structure of Benthic Macrofaunal Communities To Estimate Faunal BiomassLeandro EspíndolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantification of Cry1Ac Protein Over Time in Different Tissues of BT Cotton HybridsDocumento2 pagineQuantification of Cry1Ac Protein Over Time in Different Tissues of BT Cotton HybridsMuhammad Ehetisham Ul HaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Normal Blood Chemistry of The Saker Falcon Falco CherrugDocumento5 pagineNormal Blood Chemistry of The Saker Falcon Falco CherrugMunzir KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Drosophila Final DraftDocumento8 pagineDrosophila Final DraftJessica NelsonNessuna valutazione finora
- IQ-CRO Recommended Dose Volumes For Common Laboratory Animals June 2016Documento5 pagineIQ-CRO Recommended Dose Volumes For Common Laboratory Animals June 2016Juan CarNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug CalculationDocumento58 pagineDrug CalculationInsatiable CleeNessuna valutazione finora
- Stats - 78 ProblemsDocumento1 paginaStats - 78 ProblemsHafizah HalimNessuna valutazione finora
- Use of Mannan Oligosaccharides During Post Weaning Enteric Syndrome in Rabbits Effect On in Vivo Performance From 35 To 60 DaysDocumento4 pagineUse of Mannan Oligosaccharides During Post Weaning Enteric Syndrome in Rabbits Effect On in Vivo Performance From 35 To 60 DaysErwin Luis KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 5Documento14 pagineLecture 5Teflon SlimNessuna valutazione finora
- G2910 Heritability and Its Use in Animal Breeding - University of Missouri ExtensionDocumento8 pagineG2910 Heritability and Its Use in Animal Breeding - University of Missouri ExtensionAlbyziaNessuna valutazione finora
- Artificial Spawning and Larvae Performance of Three Indonesian Mahseer SpeciesDocumento9 pagineArtificial Spawning and Larvae Performance of Three Indonesian Mahseer SpeciesboonyongchiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Aac00370 0083Documento6 pagineAac00370 0083Caustic ToxicNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 - Logical ReasoningDocumento7 pagine01 - Logical ReasoningLester Ryan ElcanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical Exposition TextDocumento6 pagineAnalytical Exposition TextTimothy VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- Hotel Hygiene & Housekeeping Development DutiesDocumento14 pagineHotel Hygiene & Housekeeping Development DutiesMunhasib ElahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Erythrocytosis PolycythemiaDocumento2 pagineErythrocytosis PolycythemiaNeoMedica100% (2)
- Professional Disclosure StatementDocumento2 pagineProfessional Disclosure Statementapi-323266047Nessuna valutazione finora
- Article Breast Ultrasound - Why and When by Dr. HombalDocumento2 pagineArticle Breast Ultrasound - Why and When by Dr. HombalDomica DavisNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Selected Sanjeevini Combinations SSCDocumento1 paginaList of Selected Sanjeevini Combinations SSCsatyr7020% (1)
- Sexual Reproductive Health Program FGM and Child Early/Forced Marriage (FGM and CEFM) ProjectDocumento4 pagineSexual Reproductive Health Program FGM and Child Early/Forced Marriage (FGM and CEFM) ProjectOmar Hassen100% (1)
- PASSMED MRCP MCQs-DERMATOLOGY PDFDocumento53 paginePASSMED MRCP MCQs-DERMATOLOGY PDFFatima Ema100% (5)
- Canadas Food Guide Serving SizesDocumento2 pagineCanadas Food Guide Serving SizesVictor EstradaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case 10: Placenta Previa: ST ND RDDocumento6 pagineCase 10: Placenta Previa: ST ND RDMengda ZhangNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health Nursing Approach: Mrs - Neethu Vincent Asst Professor KVM College of NursingDocumento21 pagineCommunity Health Nursing Approach: Mrs - Neethu Vincent Asst Professor KVM College of NursingNeethu VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 1Documento11 paginePresentation 1api-300463091Nessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 5 Food and Beverage Operations ManagementDocumento5 pagineUNIT 5 Food and Beverage Operations Managementchandni0810Nessuna valutazione finora
- Empirically Supported Complexity: Rethinking Evidence-Based Practice in PsychotherapyDocumento6 pagineEmpirically Supported Complexity: Rethinking Evidence-Based Practice in PsychotherapyPedro VargasNessuna valutazione finora
- Desi1219 DossierDocumento82 pagineDesi1219 DossierJuy HuyNessuna valutazione finora
- Protecting and Supporting Vulnerable Groups Through The Covid-19 CrisisDocumento28 pagineProtecting and Supporting Vulnerable Groups Through The Covid-19 CrisisPacuto Ngos SolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- CURRICULUM VITAE Netra June 2017Documento10 pagineCURRICULUM VITAE Netra June 2017Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt LtdNessuna valutazione finora
- UK Guidelines Iron Deficiency in Pregnancy PDFDocumento34 pagineUK Guidelines Iron Deficiency in Pregnancy PDFYoga Rhamada SiregarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sex Differences in Brain Anatomy - National Institutes of Health (NIH)Documento4 pagineSex Differences in Brain Anatomy - National Institutes of Health (NIH)Ryan BurtonNessuna valutazione finora
- Short TermDocumento2 pagineShort TermJamaica Leslie NovenoNessuna valutazione finora
- IGC3 Exam Template 2Documento17 pagineIGC3 Exam Template 2mibshNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation of Prosthetic Marginal Fit and Implant SurvivalDocumento12 pagineEvaluation of Prosthetic Marginal Fit and Implant SurvivalGustavo IsmaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomic Therapy English PDFDocumento339 pagineAnatomic Therapy English PDFBabou Parassouraman100% (3)
- Dialog Perawat Dan PerawatDocumento5 pagineDialog Perawat Dan PerawatnandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Procedural Dermatology CmeDocumento3 pagineProcedural Dermatology CmePadmapriya SrinivasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Foster 2013Documento38 pagineFoster 2013Rahmi YuliastantriNessuna valutazione finora
- ACSM's Complete Guide To Fitness & Health, 2nd EditionDocumento449 pagineACSM's Complete Guide To Fitness & Health, 2nd EditionRitaMata95% (22)
- PSMT Finals ReviewerDocumento67 paginePSMT Finals ReviewerPALATTAO, AUBRIE L. BSMT2-8Nessuna valutazione finora
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessDa Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (33)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeDa EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceDa EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (18)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldDa EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (597)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomDa EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (216)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseDa EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (52)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDa EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceDa EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDa EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (393)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainDa EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (111)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedDa EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesDa EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (397)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionDa EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (812)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainDa EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (65)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveDa EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (66)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemDa EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (116)
- Remnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsDa EverandRemnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (3)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildDa EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (44)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignDa EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (19)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindDa EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (93)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueDa EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (38)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorDa EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNessuna valutazione finora