Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
C Programming Arrays: How To Declare An Array in C?
Caricato da
Nadun RathnayakeDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
C Programming Arrays: How To Declare An Array in C?
Caricato da
Nadun RathnayakeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
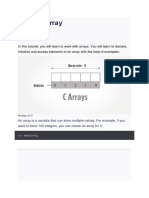
C Programming Arrays
In this article, you will learn to work with arrays. You will learn to declare, initialize and, access array elements
with the help of examples.
An array is a collection of data that holds fixed number of values of same type. For example: if you want to
store marks of 100 students, you can create an array for it.
float marks[100];
The size and type of arrays cannot be changed after its declaration.
Arrays are of two types:
1. One-dimensional arrays
2. Multidimensional arrays (will be discussed in next chapter)
How to declare an array in C?
data_type array_name[array_size];
For example,
float mark[5];
Here, we declared an array, mark, of floating-point type and size 5. Meaning, it can hold 5 floating-point values.
Elements of an Array and How to access them?
You can access elements of an array by indices.
Suppose you declared an array mark as above. The first element is mark[0], second element is mark[1] and so
on.
Few key notes:
Arrays have 0 as the first index not 1. In this example, mark[0]
If the size of an array is n, to access the last element, (n-1) index is used. In this example, mark[4]
Suppose the starting address of mark[0] is 2120d. Then, the next address, a[1], will be 2124d, address
of a[2] will be 2128d and so on. It's because the size of a float is 4 bytes.
How to initialize an array in C programming?
It's possible to initialize an array during declaration. For example,
int mark[5] = {19, 10, 8, 17, 9};
Another method to initialize array during declaration:
int mark[] = {19, 10, 8, 17, 9};
Here,
mark[0] is equal to 19
mark[1] is equal to 10
mark[2] is equal to 8
mark[3] is equal to 17
mark[4] is equal to 9
How to insert and print array elements?
int mark[5] = {19, 10, 8, 17, 9}
// insert different value to third element
mark[3] = 9;
// take input from the user and insert in third element
scanf("%d", &mark[2]);
// take input from the user and insert in (i+1)th element
scanf("%d", &mark[i]);
// print first element of an array
printf("%d", mark[0]);
// print ith element of an array
printf("%d", mark[i-1]);
Example: C Arrays
// Program to find the average of n (n < 10) numbers using arrays
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int marks[10], i, n, sum = 0, average;
printf("Enter n: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
for(i=0; i<n; ++i)
{
printf("Enter number%d: ",i+1);
scanf("%d", &marks[i]);
sum += marks[i];
}
average = sum/n;
printf("Average marks = %d", average);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter n: 5
Enter number1: 45
Enter number2: 35
Enter number3: 38
Enter number4: 31
Enter number5: 49
Average = 39
Important thing to remember when working with C arrays
Suppose you declared an array of 10 elements. Let's say,
int testArray[10];
You can use the array members from testArray[0] to testArray[9].
If you try to access array elements outside of its bound, let's say testArray[12], the compiler may not show
any error. However, this may cause unexpected output (undefined behavior).
Before going further, check out these array articles:
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Visual FoxPro To Visual Basic NET 2004 PDFDocumento1.535 pagineVisual FoxPro To Visual Basic NET 2004 PDFxsHaDoWnxNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Computer Programming ProgrammingDocumento54 pagineIntroduction To Computer Programming ProgrammingSushma VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- JIRA Tutorial: What Is JIRA Software?Documento9 pagineJIRA Tutorial: What Is JIRA Software?sudarshanNessuna valutazione finora
- 50 Web Developer Interview Questions For Sure SuccessDocumento14 pagine50 Web Developer Interview Questions For Sure SuccessRaghu GowdaNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT II Arrays and StringsDocumento30 pagineUNIT II Arrays and StringsSivasathiya G100% (1)
- ASPICEDocumento3 pagineASPICEJosephNessuna valutazione finora
- Online Shoe Shopping DocumentDocumento62 pagineOnline Shoe Shopping DocumentBharathiNessuna valutazione finora
- C Arrays - Declare, Initialize and Access Elements With ExamplesDocumento4 pagineC Arrays - Declare, Initialize and Access Elements With ExamplessudhirNessuna valutazione finora
- WINSEM2021-22 BCSE102L TH VL2021220504672 2022-03-01 Reference-Material-IDocumento12 pagineWINSEM2021-22 BCSE102L TH VL2021220504672 2022-03-01 Reference-Material-IavogadroangsterNessuna valutazione finora
- C Programming ArraysDocumento6 pagineC Programming ArrayshaldersubhasNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To ArraysDocumento10 pagineIntroduction To ArraysAmlan SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- ArraysDocumento15 pagineArraysAbhijit Kumar GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Language Programming: Lesson 6Documento19 pagineLanguage Programming: Lesson 6Mariane CarandangNessuna valutazione finora
- WINSEM2020-21 CSE1002 LO VL2020210504934 Reference Material I 16-Feb-2021 4 C ArraysDocumento18 pagineWINSEM2020-21 CSE1002 LO VL2020210504934 Reference Material I 16-Feb-2021 4 C ArraysVickyNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit II ArraysDocumento36 pagineUnit II ArraysBhuma Naga PavanNessuna valutazione finora
- C Lesson#6 (Fin)Documento20 pagineC Lesson#6 (Fin)devora aveNessuna valutazione finora
- Python by DR SabDocumento14 paginePython by DR SabDukkyNessuna valutazione finora
- Topik 7 Array BaruDocumento14 pagineTopik 7 Array BaruMuhammad izroilNessuna valutazione finora
- C Programming Arrays: Declaration of One-Dimensional ArrayDocumento3 pagineC Programming Arrays: Declaration of One-Dimensional ArrayJohn Mark CarpioNessuna valutazione finora
- ARRAYSDocumento10 pagineARRAYSMohammedtajuddin TajuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Array 1Documento34 pagineArray 1Jatin GargNessuna valutazione finora
- PC Unit 6Documento7 paginePC Unit 6krishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- ArrayDocumento15 pagineArrayadarsh rajNessuna valutazione finora
- ch05 (1) - ArraysDocumento17 paginech05 (1) - ArraysSamantha MorinNessuna valutazione finora
- Array in CDocumento3 pagineArray in CMoshiur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- CPPS Unit 3Documento7 pagineCPPS Unit 3jsanandkumar22Nessuna valutazione finora
- PSP M-3Documento15 paginePSP M-3Dhanush RNessuna valutazione finora
- AARYSANDSTRINGSDocumento27 pagineAARYSANDSTRINGSmaneskin488Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6 ArraysDocumento18 pagineUnit 6 ArraysSakar SapkotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cseb114: Principle of Programming: Chapter 8: ArraysDocumento30 pagineCseb114: Principle of Programming: Chapter 8: ArraysMei GuanNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT-2 C Prog.Documento18 pagineUNIT-2 C Prog.Raghuvanshmani RajNessuna valutazione finora
- ArrayDocumento4 pagineArrayMS KABILANNessuna valutazione finora
- C ArraysDocumento18 pagineC Arraysraeljohn273Nessuna valutazione finora
- Arrays-1Documento46 pagineArrays-1Malavika VipinNessuna valutazione finora
- Pps Using C r20 - Unit-3Documento20 paginePps Using C r20 - Unit-3Raj AryanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter7 ArraysDocumento26 pagineChapter7 Arrayshisham_eyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of ArrayDocumento6 pagineProperties of Arraysonali guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Arrays in CDocumento27 pagineArrays in CGarimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Array - in C ProgrammingDocumento7 pagineArray - in C Programmingshakti brata naikNessuna valutazione finora
- Single Dimensional ArraysDocumento11 pagineSingle Dimensional Arraysissei dragneelNessuna valutazione finora
- C-Arrays & Strings and FunctionsDocumento33 pagineC-Arrays & Strings and FunctionsSambhaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-3: ArraysDocumento36 pagineUnit-3: ArraysChinnari ChinnuNessuna valutazione finora
- Array in C++Documento19 pagineArray in C++Shweta ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- C Arrays: Unit IxDocumento13 pagineC Arrays: Unit IxKim John NunezNessuna valutazione finora
- PPSC Unit 3 Lesson NotesDocumento14 paginePPSC Unit 3 Lesson NotesHermione GrangerNessuna valutazione finora
- 11-Array-After Mid-2Documento8 pagine11-Array-After Mid-2SaifNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer ProjectDocumento17 pagineComputer ProjectSaloni NandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Eceg 1052 CH 4Documento25 pagineEceg 1052 CH 4CHARANessuna valutazione finora
- Slide6 ArraysDocumento23 pagineSlide6 ArraysAnurag BandyopadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-I Arrays and Strings Arrays: DefinitionDocumento44 pagineUnit-I Arrays and Strings Arrays: Definitionsolai rajNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture VDocumento26 pagineLecture VSalim IsyakuNessuna valutazione finora
- C Programming LanguageDocumento113 pagineC Programming LanguageCarlos VillamizarNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is An Array?: Int Float Char Int Int 100 100 Roll - No (100) 100 100 0 Roll - No (0) Roll - No (1) Roll - No (99) Roll - No (100) 0Documento6 pagineWhat Is An Array?: Int Float Char Int Int 100 100 Roll - No (100) 100 100 0 Roll - No (0) Roll - No (1) Roll - No (99) Roll - No (100) 0zahoorNessuna valutazione finora
- PSP Module-3-NotesDocumento36 paginePSP Module-3-NotesloxxNessuna valutazione finora
- C ArraysDocumento7 pagineC ArraysRavenTaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 of CS 112Documento18 pagineModule 1 of CS 112Gerry BlackNessuna valutazione finora
- ARRAY&STRINGDocumento19 pagineARRAY&STRINGChanchal GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- C Prog Notes All UnitesDocumento220 pagineC Prog Notes All UnitesAashiQ ShayarNessuna valutazione finora
- Here We Go Through Some Valid Array DeclarationDocumento37 pagineHere We Go Through Some Valid Array DeclarationSravani VankayalaNessuna valutazione finora
- BasuDocumento14 pagineBasubasavarajparapur514Nessuna valutazione finora
- DITG 1113:: Array (Part 1)Documento54 pagineDITG 1113:: Array (Part 1)siti nur rahmahNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4Documento18 pagineUnit 4dawnglianiNessuna valutazione finora
- C Programming UNIT 3.2 ArraysDocumento20 pagineC Programming UNIT 3.2 ArraysrishikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Arrays: Store A Single Value at A Time Store Roll No. of 100 Students?Documento17 pagineArrays: Store A Single Value at A Time Store Roll No. of 100 Students?Mohd UmairNessuna valutazione finora
- Ascential DataStage 7.5.x Server Job Developers GuideDocumento776 pagineAscential DataStage 7.5.x Server Job Developers GuideSrinivasa Kumar Gullapalli67% (3)
- The Foundational Lessons of The Program Will Be Delivered Over ADocumento33 pagineThe Foundational Lessons of The Program Will Be Delivered Over AAzka FairuzulNessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Hacker MindsetDocumento8 pagine07 Hacker Mindsetchampubhaiya8Nessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2. Introduction To Software EngineeringDocumento52 pagineWeek 2. Introduction To Software EngineeringJim Colin PeñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Web Tech Slip SolutionsDocumento47 pagineAdvanced Web Tech Slip SolutionsAbhinav DakshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Soumya Brata BiswasDocumento3 pagineSoumya Brata BiswasMitali MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- AdasDocumento1 paginaAdasPradnya TantarpaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrating Apache Nifi With External API'sDocumento4 pagineIntegrating Apache Nifi With External API'sMario SoaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Data Structure PDFDocumento35 pagineChapter 1 - Introduction To Data Structure PDFSyira RzliNessuna valutazione finora
- Vmware Cloud Disaster Recovery DatasheetDocumento2 pagineVmware Cloud Disaster Recovery DatasheetOrchidaceae PhalaenopsisNessuna valutazione finora
- Havij Help EnglishDocumento46 pagineHavij Help EnglishMuhd Daniel AsyraafNessuna valutazione finora
- Built-Ins, Packages, Constants, and Syntax PDFDocumento7 pagineBuilt-Ins, Packages, Constants, and Syntax PDFAdolfoJiménezNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Sepm Unit 1Documento43 pagineNotes Sepm Unit 1Abdul Wasiq KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 NetworkingDocumento21 pagineChapter 2 Networkingvibz99Nessuna valutazione finora
- ProgrammingGuide HealthDataDocumento59 pagineProgrammingGuide HealthDataözlemArtuk100% (1)
- Lab 05 - Dropbox QuestionsDocumento2 pagineLab 05 - Dropbox QuestionsPreet DhillonNessuna valutazione finora
- Slot20 Assembly01 27 SlidesDocumento28 pagineSlot20 Assembly01 27 SlidesTriết Nguyễn MinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle Inventory SetupsDocumento3 pagineOracle Inventory SetupsVenkat ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- PWP ReportDocumento9 paginePWP ReportPriyankaNessuna valutazione finora
- Database Assignment 2Documento5 pagineDatabase Assignment 2NyoniTrinosNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity #1.3: Advantages of C++ LanguageDocumento2 pagineActivity #1.3: Advantages of C++ Languagesay whhhuuutNessuna valutazione finora
- PHP Session: Prepared By: Prof. Disha H. ParekhDocumento11 paginePHP Session: Prepared By: Prof. Disha H. ParekhKavisha PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Blue Print: Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Chandigarh RegionDocumento2 pagineBlue Print: Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Chandigarh RegionAmisha DalalNessuna valutazione finora
- OBIEE 11g Query LoggingDocumento3 pagineOBIEE 11g Query Loggingcboss911Nessuna valutazione finora
- New South Wales Public SchoolDocumento42 pagineNew South Wales Public SchoolDEVANSHU SHARMANessuna valutazione finora