Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Liver Cancer
Caricato da
Tarantado67%(3)Il 67% ha trovato utile questo documento (3 voti)
462 visualizzazioni1 paginaHCC is a malignant tumor of hepatocellular origin that develops in patients with risk factors such as alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis, and metabolic liver disease. Grossly, HCC can undergo hemorrhage and necrosis because of a lack of fibrous stroma. There are 3 growth patterns exhibited by HCC: solitary mass - Often large Multifocal or nodular pattern - Multiple nodules Diffuse - Multiple, small
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoHCC is a malignant tumor of hepatocellular origin that develops in patients with risk factors such as alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis, and metabolic liver disease. Grossly, HCC can undergo hemorrhage and necrosis because of a lack of fibrous stroma. There are 3 growth patterns exhibited by HCC: solitary mass - Often large Multifocal or nodular pattern - Multiple nodules Diffuse - Multiple, small
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
67%(3)Il 67% ha trovato utile questo documento (3 voti)
462 visualizzazioni1 paginaLiver Cancer
Caricato da
TarantadoHCC is a malignant tumor of hepatocellular origin that develops in patients with risk factors such as alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis, and metabolic liver disease. Grossly, HCC can undergo hemorrhage and necrosis because of a lack of fibrous stroma. There are 3 growth patterns exhibited by HCC: solitary mass - Often large Multifocal or nodular pattern - Multiple nodules Diffuse - Multiple, small
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
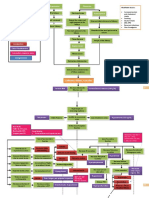
LIVER CANCER
Pathophysiology
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a malignant tumor of hepatocellular origin that
develops in patients with risk factors such as alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis, and
metabolic liver disease. It can also occur, rarely, in patients with normal liver
parenchyma.2
Grossly, HCC can undergo hemorrhage and necrosis because of a lack of fibrous
stroma. Vascular invasion, particularly of the portal system, is common. Invasion of the
biliary system is less common. Aggressive HCC can cause hepatic rupture and
hemoperitoneum.
There are 3 growth patterns exhibited by HCC:
• Solitary mass - Often large
• Multifocal or nodular pattern - Multiple nodules
• Diffuse - Multiple, small foci scattered diffusely throughout the liver
Microscopically, HCC cells resemble normal hepatocytes and can be confused with
cells of hepatic adenoma. Tumors that are more differentiated can produce bile.
HCC can produce alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) as well as other serum proteins.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 2019 Auto Truck Key Blank Reference PDFDocumento188 pagine2019 Auto Truck Key Blank Reference PDFAlbert RodaNessuna valutazione finora
- Glomerulonephritis-1 (Dr. Soffa)Documento58 pagineGlomerulonephritis-1 (Dr. Soffa)Rahmailla Khanza Diana FebriliantriNessuna valutazione finora
- MedSurg Notes - Cancer of The LiverDocumento2 pagineMedSurg Notes - Cancer of The LiverMae CeaesarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pancreatic Cancer - PresentationDocumento71 paginePancreatic Cancer - PresentationMavy CantonNessuna valutazione finora
- Liver CancerDocumento27 pagineLiver CancerKoRnflakes100% (4)
- Pathophysiology of NephrosclerosisDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of NephrosclerosisJessica Damasen Caballero0% (1)
- Pahtophysiology of EsrdDocumento5 paginePahtophysiology of EsrdCarl JardelezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Anthony Alexander University of The West Indies at MonaDocumento40 pagineUpper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Anthony Alexander University of The West Indies at MonaAy Alex0% (1)
- 2 6 7 HypervolemiaDocumento4 pagine2 6 7 HypervolemiaMaica LectanaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Role of IT in TQM L'Oreal Case StudyDocumento9 pagineThe Role of IT in TQM L'Oreal Case StudyUdrea RoxanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Liver CancerDocumento44 pagineLiver CancerEjay Jacob Ricamara50% (2)
- CholelithiasisDocumento3 pagineCholelithiasisMIlanSagittarius0% (1)
- Bladder CancerDocumento1 paginaBladder CancerCarmina AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Diverticular DiseaseDocumento8 pagineDiverticular Diseasenurse_enzo100% (1)
- Liver Case StudyDocumento6 pagineLiver Case StudyGhulam MustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cancer of The ColonDocumento8 pagineCancer of The Colonnot your medz duranNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Acute CholecystitisDocumento21 pagine2 Acute CholecystitisEtteh MaryNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP AgnDocumento2 pagineNCP Agnj3nann3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final Major Case StudyDocumento17 pagineFinal Major Case Studyapi-546876878Nessuna valutazione finora
- Addison'sDocumento4 pagineAddison'sKoRnflakesNessuna valutazione finora
- Stomach CancerDocumento7 pagineStomach CancerSyazmin KhairuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Breast Cancer Case StudyDocumento5 pagineBreast Cancer Case StudyFrancesca ElixirNessuna valutazione finora
- CholelithiasisDocumento6 pagineCholelithiasismarkzamNessuna valutazione finora
- V. Pathophysiology Modifiable: Non - ModifiableDocumento2 pagineV. Pathophysiology Modifiable: Non - ModifiableMary Grace BanezNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS)Documento21 pagineHyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS)Malueth AnguiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedDocumento2 paginePathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hepatomegaly: Clinical ApproachDocumento22 pagineHepatomegaly: Clinical ApproachPooja ShashidharanNessuna valutazione finora
- Esophagea L Cancer: By: Krizzia S. Bunagan-Legasi, RNDocumento20 pagineEsophagea L Cancer: By: Krizzia S. Bunagan-Legasi, RNAnn SalvatierraNessuna valutazione finora
- Path o PhysiologyDocumento9 paginePath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study 18 CKDDocumento7 pagineCase Study 18 CKDapi-301049551Nessuna valutazione finora
- By: Leila Floresca Esteban BSNIII-BDocumento38 pagineBy: Leila Floresca Esteban BSNIII-BMonica Morales100% (2)
- SimvastatinDocumento1 paginaSimvastatinLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaDocumento10 paginePathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNessuna valutazione finora
- My Case Study of Liver CirrhosisDocumento13 pagineMy Case Study of Liver Cirrhosisdysphile100% (1)
- Voglibose PiDocumento2 pagineVoglibose PiAmit KhuntNessuna valutazione finora
- Management For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocumento3 pagineManagement For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiamarivohNessuna valutazione finora
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDocumento2 pagineScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology and Schematic Diagram of Typhoid FeverDocumento3 paginePathophysiology and Schematic Diagram of Typhoid FeverCyrus De AsisNessuna valutazione finora
- Gastrectomy Post OpDocumento5 pagineGastrectomy Post Opfeirri100% (4)
- CholelithiasisDocumento5 pagineCholelithiasisrgflores1979100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Gastrointestinal Bleeding Secondary To Bleeding PolypsDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Gastrointestinal Bleeding Secondary To Bleeding PolypsGinoTevesNessuna valutazione finora
- PUCAN, Julienne BSN III-D - SGD - HYPO&HYPERCHLOREMIADocumento10 paginePUCAN, Julienne BSN III-D - SGD - HYPO&HYPERCHLOREMIAJulienne PucanNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study ReportDocumento23 pagineCase Study Reportapi-290866384Nessuna valutazione finora
- HypopituitarismDocumento2 pagineHypopituitarismAnne de VeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Kidney Disease Secondary To Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocumento84 pagineChronic Kidney Disease Secondary To Type 2 Diabetes Mellituswar5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes InsipidusDocumento48 pagineDiabetes InsipidusAhmed Fraz MamoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Liver Cirrhosis Care PlanDocumento3 pagineLiver Cirrhosis Care PlanWendy EscalanteNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP CvaDocumento4 pagineNCP CvaMariquita BuenafeNessuna valutazione finora
- Care of Clients With Problems in Cellular Aberrations Key TermsDocumento2 pagineCare of Clients With Problems in Cellular Aberrations Key Termsjoyrena ochondraNessuna valutazione finora
- HyperphosphatemiaDocumento2 pagineHyperphosphatemiatephNessuna valutazione finora
- Hepatocellula R CarcinomaDocumento45 pagineHepatocellula R Carcinomamhean azneitaNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Digestion and Bowel Elimination 2019 (Nursing) Geriatric NursingDocumento44 pagine11 Digestion and Bowel Elimination 2019 (Nursing) Geriatric NursingDarla SaulerNessuna valutazione finora
- HCVD KoDocumento10 pagineHCVD KoMarianne BaquilalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modified Radical MastectomyDocumento6 pagineModified Radical Mastectomymetch isulatNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDocumento3 pagineHypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDiane-Richie PezLo100% (1)
- Predisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento52 paginePredisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseSaad MotawéaNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Liver: Dr. I Made Naris Pujawan, M.Biomed, SP - PADocumento19 pagineThe Liver: Dr. I Made Naris Pujawan, M.Biomed, SP - PAAnonymous D29e00Nessuna valutazione finora
- k8 Tumors of The Liver and Billiary TractDocumento39 paginek8 Tumors of The Liver and Billiary Tractinstagram googleNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Stage Liver Diseases (2) - HMUDocumento31 pagine3rd Stage Liver Diseases (2) - HMUjwan ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Liver CancerDocumento51 pagineLiver Cancerrizkahmed332Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of PudDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of PudAngel-Jeh De Guzman100% (1)
- Liver Cancer Pathophysiology: Predisposing FactorDocumento3 pagineLiver Cancer Pathophysiology: Predisposing FactorTarantado100% (2)
- Chron's Disease 2Documento3 pagineChron's Disease 2TarantadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Top Performing Schools in November 2008 NLEDocumento19 pagineTop Performing Schools in November 2008 NLETarantadoNessuna valutazione finora
- NURSE Board Exam November 2008 ResultsDocumento790 pagineNURSE Board Exam November 2008 ResultsstuffednurseNessuna valutazione finora
- COE301 Lab 2 Introduction MIPS AssemblyDocumento7 pagineCOE301 Lab 2 Introduction MIPS AssemblyItz Sami UddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment # 1 POMDocumento10 pagineAssignment # 1 POMnaeemNessuna valutazione finora
- New Horizon Public School, Airoli: Grade X: English: Poem: The Ball Poem (FF)Documento42 pagineNew Horizon Public School, Airoli: Grade X: English: Poem: The Ball Poem (FF)stan.isgod99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lords of ChaosDocumento249 pagineLords of ChaosBill Anderson67% (3)
- Green ChemistryDocumento17 pagineGreen ChemistryAaditya RamanNessuna valutazione finora
- System Administration ch01Documento15 pagineSystem Administration ch01api-247871582Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Impact of Online Games To The AcademicDocumento20 pagineThe Impact of Online Games To The AcademicJessica BacaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 184 Учебная программа Английский язык 10-11 кл ОГНDocumento44 pagine184 Учебная программа Английский язык 10-11 кл ОГНзульфираNessuna valutazione finora
- JurnalDocumento12 pagineJurnalSandy Ronny PurbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Job Stress InterventionsDocumento5 pagineJob Stress InterventionscocaralucamihaelaNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Prepare Adjusting Entries - Step-By-Step (2023)Documento10 pagineHow To Prepare Adjusting Entries - Step-By-Step (2023)Yaseen GhulamNessuna valutazione finora
- 06.21.2010 - Historic Treasure of Jewish Life and Culture Gifted To UC BerkeleyDocumento2 pagine06.21.2010 - Historic Treasure of Jewish Life and Culture Gifted To UC BerkeleymagnesmuseumNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydraulic Excavator: Engine WeightsDocumento28 pagineHydraulic Excavator: Engine WeightsFelipe Pisklevits LaubeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62Documento12 pagineCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62EffNessuna valutazione finora
- Major Chnage at Tata TeaDocumento36 pagineMajor Chnage at Tata Teasheetaltandon100% (1)
- Mat101 w12 Hw6 SolutionsDocumento8 pagineMat101 w12 Hw6 SolutionsKonark PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Vermicomposting Learning ModulesDocumento6 pagineVermicomposting Learning ModulesPamara Prema Khannae100% (1)
- Dental Clinic - Floor Plan R3-2Documento1 paginaDental Clinic - Floor Plan R3-2kanagarajodisha100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: DR - Wasfi Dhahir Abid AliDocumento9 paginePathophysiology: DR - Wasfi Dhahir Abid AliSheryl Ann PedinesNessuna valutazione finora
- Vialyn Group ResearchDocumento17 pagineVialyn Group ResearchVial LynNessuna valutazione finora
- NRNP PRAC 6665 and 6675 Focused SOAP Note ExemplarDocumento6 pagineNRNP PRAC 6665 and 6675 Focused SOAP Note ExemplarLogan ZaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Time-Temperature Charge Function of A High Dynamic Thermal Heat Storage With Phase Change MaterialDocumento15 pagineTime-Temperature Charge Function of A High Dynamic Thermal Heat Storage With Phase Change Materialgassoumi walidNessuna valutazione finora
- A Database For Handwritten Text Recognition ResearchDocumento5 pagineA Database For Handwritten Text Recognition Researchtweety492Nessuna valutazione finora
- Norm ANSI PDFDocumento1 paginaNorm ANSI PDFAbdul Quddus Mat IsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Objective-C Succinctly PDFDocumento110 pagineObjective-C Succinctly PDFTKKNessuna valutazione finora
- Porsche Dealer Application DataDocumento3 paginePorsche Dealer Application DataEdwin UcheNessuna valutazione finora
- Montessori Vs WaldorfDocumento4 pagineMontessori Vs WaldorfAbarnaNessuna valutazione finora