Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Precipitate Labor and Delivery
Caricato da
myer pasandalan0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
8 visualizzazioni2 paginegdfgdf
Titolo originale
Alara
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentogdfgdf
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
8 visualizzazioni2 paginePrecipitate Labor and Delivery
Caricato da
myer pasandalangdfgdf
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
Precipitate labor and delivery Nursing diagnosis:
-occurs within 3 hours from onset of
contraction to the delivery of the baby. Uterine rupture:
Causes:
Signs and symptoms:
Rate of cervical dilatation 5cm.hr or - Tearing of scar from previous C/S
faster in nullipara - Prolonged laor, malpresentation
10cm per hour in multipara - Overdistention
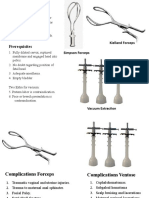
Desire to push - Unwise use of oxytocin. Forceps and
Hypertonic contractions vacuum extraction.
Intense pain more than normal
Restlessness. S and S:
Impending uterine rupture
Predisposing factors: - Pathologic retraction ring
1. Multiparity - Strong uterine contractions without
2. Maternal fatigue previous brief labor cervical dilatation
3. Age >35: younger than 20 #prepare fo CS
Precipitating: If uterus should rupture;
1. Induction of labor 1. Sudden severe pain during a strong
2. Hypertonic contraction labor contraction
3. Multiple gestation 2. Tearing or popping sensation in the
4. Adequate pelvis and small fetus abdomen.
5. Anxiety and stress
Types of rupture:
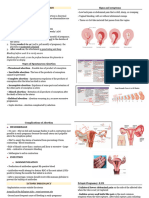
Complication: Complete
Maternal: - Goes through endometrium,
1. Uterine rupture myometrium and perimetrium.
2. Laeration of birth canal - Uterine contractions stop
3. Pp haemorrhage - Signs of shock
4. AFE - Change in abdominal contour
Fetal: - Fetal parts are palpable thru the
5. hypoxia abdominal wall.
6. Infection intracranial bleeding Incomplete:
- Leaves the perimetrium intact
Management: - Persistent tenderness over the lower
Tocolytics – medical segment.
Episiotomy as necessary – surgical - Disorganized uterine patter
- Fetal bradycardia.
EMERGENCY DELIVERY OF AN INFANT
1. Pant and blow Management:
2. Do not prevent birth of the baby 1. Blood transfusion and IVF. Admin
3. Maintain sterile environment 2. )2 inhalation
4. Handle the delivery 3. E laparotomy
Important consideration: come to the hospital 4. Emotional support
at first sign of labor
INVERSION OF THE RUPTURE
Cause:
1. Application of traction to the Causes:
umbilical cord. Retain placental fragments
2. Application of rupture to the fundus Infection
when the uterus is not contracted Sub involution of uterus
3. If placenta Is attached to the fundus.
Signs and symptoms:
- Sudden gush of blood from the vagina
- Fundus is not palapable in the
abdomen
- Signs of shock
Interventions:
1. Do not attempt to replace an
inversion
2. Never attempt to remove the
placenta if it is still attached
3. Do not give oxytocin
4. O2 inhalation and assess vital sings
5. General anesthesia or tocolytic IV
6. Make an attempt to reposition the
uterus
7. Oxytocic after manual replacement
8. Antibiotic
9. C/S during future pregnancies.
POST PARTUM COMPLICATIONS:
1. Hemorrhage
2. Infection
3. Thromboembolic disorder
4. Psychiatric disorders.
POST PARTUM HEMORHAGE:
- Decreased in the haematocrit of 10
percent or greater after delivery.
-
Types:
a. Early PP hemorhage: first 24
hours
Causes:
Uterine atony
Laceration and hematoma of birth canal
Inversion o uterus
b. Late PP haemorrhage: after 24 hrs
– 4 wsks
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Painful Coitus or Dyspareunia, A Simple Guide To Causative DiseasesDa EverandPainful Coitus or Dyspareunia, A Simple Guide To Causative DiseasesNessuna valutazione finora
- ConstipationDocumento3 pagineConstipationmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Antenatal management and statisticsDocumento64 pagineAntenatal management and statisticsHasan Dahamsheh100% (4)
- ALL Ob-Gyn McqsDocumento297 pagineALL Ob-Gyn McqsPreeti ChouhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal Problems With PowerDocumento2 pagineMaternal Problems With PowerAlex CvgNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2 NCM 109 - Complications During Pregnancy, Labor and Delivery and Postpartum PeriodsDocumento10 pagine2.2 NCM 109 - Complications During Pregnancy, Labor and Delivery and Postpartum PeriodsSittie Haneen TabaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Abnormal ObstetricsDocumento286 pagineAbnormal ObstetricsJen Ilagan100% (3)
- MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSINGDocumento40 pagineMATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSINGArlyn Faith AlvarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Equine Reproductive Physiology, Breeding, and Stud ManagementDocumento383 pagineEquine Reproductive Physiology, Breeding, and Stud Managementfrancisco_aguiar_22100% (2)
- Postpartum ComplicationsDocumento21 paginePostpartum ComplicationsRoccabeth Villanueva100% (1)
- Complaint For Damages SampleDocumento4 pagineComplaint For Damages SampleJubelee Anne Patangan100% (2)
- Antepartum HaemorrhageDocumento74 pagineAntepartum HaemorrhageApex College of Nursing100% (1)
- Complaint For Damages SampleDocumento4 pagineComplaint For Damages Samplemyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Abnormal Uterine Action GuideDocumento27 pagineAbnormal Uterine Action Guidetanmai noolu100% (1)
- Nursing Care of Postpartum ComplicationsDocumento13 pagineNursing Care of Postpartum ComplicationsLyca Mae AurelioNessuna valutazione finora
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyDocumento20 pagineBleeding in Early Pregnancynanapet80Nessuna valutazione finora
- Delivery Room Write-UpDocumento42 pagineDelivery Room Write-UpDyanne BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Postpartum ExaminationDocumento10 paginePostpartum ExaminationKrystelle Jade LabineNessuna valutazione finora
- Complications of PostpartumDocumento10 pagineComplications of PostpartumJecel Eran100% (1)
- HSG Guide Provides Insights on Hysterography ProcedureDocumento89 pagineHSG Guide Provides Insights on Hysterography Proceduregrahapuspa17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Postpartum ComplicationsDocumento16 paginePostpartum Complicationshoohoo100% (1)
- Complications of PostpartumDocumento10 pagineComplications of PostpartumAlverastine AnNessuna valutazione finora
- MCN MidtermDocumento3 pagineMCN MidtermPaul Jhon Vergara67% (3)
- Uterine MYOMADocumento5 pagineUterine MYOMARoss Manalang100% (2)
- Physiology of Normal LabourDocumento29 paginePhysiology of Normal LabournamitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Incomplete AbortionDocumento22 pagineIncomplete AbortionAJ Dalawampu100% (2)
- HIGH RISK AND SICK MOTHER 5PsDocumento16 pagineHIGH RISK AND SICK MOTHER 5Psbaracream.exeNessuna valutazione finora
- A 3.1 Sudden Pregnancy Complications PDFDocumento47 pagineA 3.1 Sudden Pregnancy Complications PDFCamille Joy BaliliNessuna valutazione finora
- High Risk Postpartum Client ReviewerDocumento6 pagineHigh Risk Postpartum Client ReviewerArianJubaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Puerperium ManagementDocumento19 paginePuerperium ManagementDavina DakapNessuna valutazione finora
- SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF BLEEDING DURING PREGNANCYDocumento6 pagineSIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF BLEEDING DURING PREGNANCYSherylou Kumo SurioNessuna valutazione finora
- MCN ObDocumento7 pagineMCN ObJoshua SaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Cmca2 (Prelim) 2Documento16 pagineCmca2 (Prelim) 2NOEL YRIGONNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Topics at RiskDocumento5 pagine2 Topics at RiskGeraldine PatayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Instruments & IndicationsDocumento11 pagineInstruments & IndicationsZiyad100% (2)
- Abortion: PathophysiologyDocumento3 pagineAbortion: PathophysiologyEdmund Lominoque LamelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Means Ebesate Montebon Patigayon Ulile TitoDocumento38 pagineMeans Ebesate Montebon Patigayon Ulile TitoJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNessuna valutazione finora
- Handouts of Complications of PostnatalDocumento12 pagineHandouts of Complications of PostnatalAshish GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abnormality in PowerDocumento29 pagineAbnormality in PowerGerald BatugalNessuna valutazione finora
- Abnormality in PowerDocumento29 pagineAbnormality in Powermark OrpillaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER III Postpartum ComplicationsDocumento15 pagineCHAPTER III Postpartum Complicationsjacobprince0016Nessuna valutazione finora
- maternalDocumento6 paginematernalBlessed Glaiza MarianoNessuna valutazione finora
- MCN NotesDocumento20 pagineMCN NotesLiamLexus JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Signs Indicating Possible Complications of PregnancyDocumento6 pagineSigns Indicating Possible Complications of Pregnancygerald polopotNessuna valutazione finora
- High Risk Ob Notes 1Documento20 pagineHigh Risk Ob Notes 1pinpindalgoNessuna valutazione finora
- Gestational Conditions HandoutDocumento17 pagineGestational Conditions HandoutFilamae Jayahr Caday100% (4)
- Module 5 - MCN TransesDocumento6 pagineModule 5 - MCN TransesCarl UyNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Multiple Pregnancies and DeliveriesDocumento31 pagineManaging Multiple Pregnancies and Deliveriesmustafe omarNessuna valutazione finora
- Displacement of The UterusDocumento32 pagineDisplacement of The UterusRaja100% (1)
- Management of Breast EngorgementDocumento81 pagineManagement of Breast EngorgementNavid BabluNessuna valutazione finora
- Types and Management of AbortionDocumento6 pagineTypes and Management of AbortionJan Vincent BallesterosNessuna valutazione finora
- Postpartum Complications: Ahmed AliDocumento36 paginePostpartum Complications: Ahmed AliPeter Osundwa KitekiNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 - MCN TransesDocumento6 pagineModule 5 - MCN TransesCarl UyNessuna valutazione finora
- Abnormal Uterine Contractions: Causes, Types & ManagementDocumento68 pagineAbnormal Uterine Contractions: Causes, Types & ManagementDrPreeti Thakur ChouhanNessuna valutazione finora
- High Risk PregnancyDocumento104 pagineHigh Risk PregnancyNovelyn PuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abortion HandoutDocumento3 pagineAbortion HandoutShena Mie Adis ValleceraNessuna valutazione finora
- Abnormalities of The Puerperium: Puerperal PyrexiaDocumento28 pagineAbnormalities of The Puerperium: Puerperal Pyrexiadrravindermehetrey100% (2)
- Lecture 2 MidtermDocumento65 pagineLecture 2 MidtermKyla Desiree BedienesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care of High-Risk Labor and DeliveryDocumento165 pagineNursing Care of High-Risk Labor and DeliveryMelchor Felipe SalvosaNessuna valutazione finora
- AbortionDocumento28 pagineAbortionlordgoncarNessuna valutazione finora
- Those Related To The Pregnant State: AbortionDocumento43 pagineThose Related To The Pregnant State: AbortionJohannah DaroNessuna valutazione finora
- High Risk of PregnancyDocumento16 pagineHigh Risk of PregnancyGeraldine PatayanNessuna valutazione finora
- 109Documento3 pagine109Angel MoncadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Obstructed Labor & Prolonged LaburDocumento22 pagineObstructed Labor & Prolonged LaburOmari Kabelwa100% (1)
- Definition of Premature Rapture of Membrane (Documento3 pagineDefinition of Premature Rapture of Membrane (Merly Grael LigligenNessuna valutazione finora
- Case 1 AbortionDocumento18 pagineCase 1 AbortionEduard GarchitorenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Perineal LacerationDocumento16 paginePerineal Lacerationbasman1212Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pathology of Pregnancy and Delivery: Lecture On Pathological Anatomy For The 3-rd Year StudentsDocumento35 paginePathology of Pregnancy and Delivery: Lecture On Pathological Anatomy For The 3-rd Year StudentsRodriguez Vivanco Kevin DanielNessuna valutazione finora
- client-with-difficlut-labor-and-deliveryDocumento68 pagineclient-with-difficlut-labor-and-deliveryKristine BacaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentasi Blok 2.3 Modul 3Documento34 paginePresentasi Blok 2.3 Modul 3Andrew StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- Complication During Labor DeliveryDocumento68 pagineComplication During Labor DeliveryEllie ELLNessuna valutazione finora
- A Woman Who Develops A Complication of PregnancyDocumento24 pagineA Woman Who Develops A Complication of PregnancyLady Jane CaguladaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of The Urinary System: Patient's Name / Room No. - 1Documento2 pagineAnatomy of The Urinary System: Patient's Name / Room No. - 1myer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Drugs and IVDocumento2 pagineSummary of Drugs and IVmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Assessment IIDocumento5 pagineNursing Assessment IImyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Meds New FormatDocumento2 pagineSummary of Meds New Formatmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- MSU-IIT Nursing Student Assignment LoadDocumento2 pagineMSU-IIT Nursing Student Assignment Loadmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluationmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- MSU-IIT Nursing Student Assignment LoadDocumento2 pagineMSU-IIT Nursing Student Assignment Loadmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of SystemDocumento2 pagineReview of Systemmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Risperidine: Disturbed Thought Process Related To Neurological DisturbancesDocumento3 pagineRisperidine: Disturbed Thought Process Related To Neurological Disturbancesmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluationmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Group F DXDocumento2 pagineGroup F DXmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory and Diagnostic ProcedureDocumento5 pagineLaboratory and Diagnostic Proceduremyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Narrative PathophysiologyDocumento5 pagineNarrative Pathophysiologymyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and PhysioDocumento2 pagineAnatomy and Physiomyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluationmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresDocumento6 pagineDiagnostic and Laboratory Proceduresmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDocumento4 pagineHemorrhagic Strokemyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Discharge Plan: Drug/S Indication/S Dosage Route FrequencyDocumento3 pagineDischarge Plan: Drug/S Indication/S Dosage Route Frequencymyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineDrug Studymyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Schizophrenia: I. IdentificationDocumento3 pagineSchizophrenia: I. Identificationmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- DKKDNDDocumento14 pagineDKKDNDmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineDrug Studymyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Management 1Documento5 pagineCase Management 1myer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Somatoform Disorders: I. IdentificationDocumento1 paginaSomatoform Disorders: I. Identificationmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Eating DisordersDocumento1 paginaEating Disordersmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Personality DisordersDocumento2 paginePersonality Disordersmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Valle 2013Documento21 pagineValle 2013Karisma NandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study of Cesarean SectionDocumento9 pagineCase Study of Cesarean SectionErika Joy Imperio0% (1)
- ICD 10 GinekologiDocumento15 pagineICD 10 GinekologiMario Aphin NgNessuna valutazione finora
- Antenatal Assessment and Exercise DemonstrationDocumento46 pagineAntenatal Assessment and Exercise DemonstrationPragati BholeNessuna valutazione finora
- 1a. Obstetric Emergencies Koros E.KDocumento225 pagine1a. Obstetric Emergencies Koros E.KSalman KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation On Hysterosalpingography: BY Mahmud M Alkali I.D: 12/01/09/069 Radiography, Unimaid. 2014/2015 SESSIONDocumento23 paginePresentation On Hysterosalpingography: BY Mahmud M Alkali I.D: 12/01/09/069 Radiography, Unimaid. 2014/2015 SESSIONMubarak M AlkaliNessuna valutazione finora
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocumento17 pagineHow Do Organisms ReproduceBighnaraj ParichhaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.mal PresentationDocumento75 pagine1.mal PresentationhabtamuNessuna valutazione finora
- Baby dumping prevention through education, support servicesDocumento9 pagineBaby dumping prevention through education, support servicesMadhiea Omrienaez100% (1)
- Effects of The Treatment Method of Reproductive Performance in Cows With Retention of Fetal MembranesDocumento10 pagineEffects of The Treatment Method of Reproductive Performance in Cows With Retention of Fetal MembranesAlberto BrahmNessuna valutazione finora
- Discuss Each Aspect of Uterine ContractionsDocumento2 pagineDiscuss Each Aspect of Uterine ContractionsChristianne CapuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cesarean SectionDocumento110 pagineCesarean SectionyordiNessuna valutazione finora
- تحشيش instrumentsDocumento24 pagineتحشيش instrumentsMohamed FlefelNessuna valutazione finora
- Intrapartum-Unit ExamDocumento2 pagineIntrapartum-Unit ExamChris AnnNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing care for reproductive health issuesDocumento100 pagineNursing care for reproductive health issuesHassen ZabalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Health: Infatuation or Crush Is The State of BeingDocumento13 pagineHealth: Infatuation or Crush Is The State of BeingJuan Jaylou AnteNessuna valutazione finora
- Cow ReproductiveDocumento5 pagineCow Reproductiveastyrafe100% (1)
- Carski Rez Po VejnovicuDocumento48 pagineCarski Rez Po VejnovicuAndreyKovacevicNessuna valutazione finora
- Gynae CompilationDocumento787 pagineGynae CompilationMajgsjqNessuna valutazione finora
- Krok 2 Bases of Obstetrics & GynecologyDocumento152 pagineKrok 2 Bases of Obstetrics & GynecologyDae ShimNessuna valutazione finora