Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Justine May Arcos: Types
Caricato da
JenniferFajutnaoArcosTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Justine May Arcos: Types
Caricato da
JenniferFajutnaoArcosCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Justine May Arcos
Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actinand myosin that slide past
one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce
force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement
of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive
system via peristalsis.
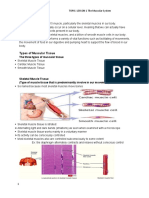
Types
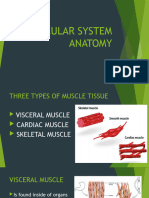
The body contains three types of muscle tissue: (a) skeletal muscle, (b) smooth muscle, and (c) cardiac muscle. (Same
magnification)
Muscle tissue is a soft tissue, and is one of the four fundamental types of tissue present in animals. There are three types
of muscle tissue recognized in vertebrates:
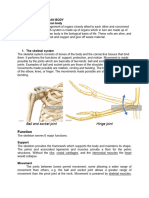
Skeletal muscle or "voluntary muscle" is anchored by tendons (or by aponeuroses at a few places) to bone and is
used to effect skeletal movement such as locomotion and in maintaining posture. Though this postural control is
generally maintained as an unconscious reflex, the muscles responsible react to conscious control like non-postural
muscles. An average adult male is made up of 42% of skeletal muscle and an average adult female is made up of
36% (as a percentage of body mass).[5]
Smooth muscle or "involuntary muscle" is found within the walls of organs and structures such as
the esophagus, stomach, intestines, bronchi, uterus, urethra, bladder, blood vessels, and the arrector piliin the skin
(in which it controls erection of body hair). Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is not under conscious control.
Cardiac muscle (myocardium), is also an "involuntary muscle" but is more akin in structure to skeletal muscle, and is
found only in the heart.
Muscular system
The muscular system consists of all the muscles present in a single body. There are approximately 650 skeletal muscles
in the human body,[12] but an exact number is difficult to define. The difficulty lies partly in the fact that different sources
group the muscles differently and partly in that some muscles, such as palmaris longus, are not always present.
A muscular slip is a narrow length of muscle that acts to augment a larger muscle or muscles.
The muscular system is one component of the musculoskeletal system, which includes not only the muscles but also the
bones, joints, tendons, and other structures that permit movement.
The three types of muscle (skeletal, cardiac and smooth) have significant differences. However, all three use the
movement of actin against myosinto create contraction. In skeletal muscle, contraction is stimulated by electrical
impulses transmitted by the nerves, the motoneurons (motor nerves) in particular. Cardiac and smooth muscle
contractions are stimulated by internal pacemaker cells which regularly contract, and propagate contractions to other
muscle cells they are in contact with. All skeletal muscle and many smooth muscle contractions are facilitated by
the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
Exercise is often recommended as a means of improving motor skills, fitness, muscle and bone strength, and joint
function. Exercise has several effects upon muscles, connective tissue, bone, and the nerves that stimulate the
muscles. One such effect is muscle hypertrophy, an increase in size. This is used in bodybuilding.
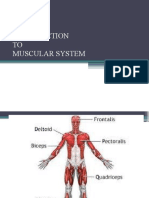
The biceps, also biceps brachii is a two-headed muscle that lies on the upper arm between the shoulder and the
elbow. Both heads arise on the scapula and join to form a single muscle belly which is attached to the upper
forearm. While the biceps crosses both the shoulder and elbow joints, its main function is at the elbow where it
flexes the forearm and supinates the forearm. Both these movements are used when opening a bottle with a
corkscrew: first biceps unscrews the cork (supination), then it pulls the cork out (flexion)
The triceps, also triceps brachii (Latin for "three-headed muscle of the arm"), is a large muscle on the back of the upper
limb of many vertebrates. It is the muscle principally responsible for extensionof the elbow joint (straightening of the arm).
Skeletal
relating to or functioning as a skeleton.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Reading 4 The Muscular SystemDocumento16 pagineReading 4 The Muscular Systemlephuongvy1406Nessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular SystemDocumento7 pagineMuscular Systemchristianoliver.aceroNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle SystemDocumento7 pagineMuscle System910907Nessuna valutazione finora
- Human AnatomyDocumento7 pagineHuman AnatomydecastroghislaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2 FIT MEDocumento7 pagineTopic 2 FIT MESleepy HeadNessuna valutazione finora
- Make-Up of The Human BodyDocumento7 pagineMake-Up of The Human BodyMariam GamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Four: Muscular System: Cilia Flagellum AmoeboidDocumento7 pagineUnit Four: Muscular System: Cilia Flagellum AmoeboidKath RubioNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Human Anatomy 1Documento55 pagineBasic Human Anatomy 1ZzzNessuna valutazione finora
- K00429 - 20180831110050 - Muscular SystemDocumento14 pagineK00429 - 20180831110050 - Muscular Systemroesil juniNessuna valutazione finora
- The Muscular SystemDocumento8 pagineThe Muscular SystemMika SaldañaNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular SystemDocumento9 pagineMuscular SystemFrely Jane PanilagaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sistem Otot Muskular 2 (Muscular System)Documento38 pagineSistem Otot Muskular 2 (Muscular System)PaRaDoX eLaKSaMaNaNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Map: Smooth or Visceral MuscleDocumento2 pagineBody Map: Smooth or Visceral MuscleFani Try Utami BoedaxRed'waterzzNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT-6 Muscular SystemDocumento48 pagineUNIT-6 Muscular SystemChandan ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- MYOLOGYDocumento20 pagineMYOLOGYNatty ChikumbaNessuna valutazione finora
- PE20#1 The Muscular SystemDocumento146 paginePE20#1 The Muscular SystemJasmine GañganNessuna valutazione finora
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocumento4 pagineNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Muscular SystemDocumento14 pagineThe Muscular SystemOana Maria FrancNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular System Anatomy Muscle TypesDocumento5 pagineMuscular System Anatomy Muscle TypesĘđı AzøıcăNessuna valutazione finora
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocumento5 pagineNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- MUSCLESDocumento6 pagineMUSCLESTishonna DouglasNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular System AnatomyDocumento12 pagineMuscular System AnatomyTishonna DouglasNessuna valutazione finora
- Body SystemDocumento22 pagineBody SystemNAWRAS ALAZZAMNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles EngDocumento3 pagineMuscles Engkaneki.ghoul1710Nessuna valutazione finora
- Human SkeletalDocumento17 pagineHuman SkeletalMa Kristine CabyaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Unit 6 - The Muscular SystemDocumento9 pagineAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Unit 6 - The Muscular Systemnur100% (1)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Muscular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionDa EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Muscular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Summary of Muscular System 4Documento4 pagineSummary of Muscular System 4api-253866502100% (1)
- The Muscylar SystemDocumento31 pagineThe Muscylar SystemXavier Mark BeatingoNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular-System-Handouts - BiologyDocumento7 pagineMuscular-System-Handouts - BiologyApril Joy T. GrijaldoNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMDocumento20 pagineModule 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - 6 Muscular SystemDocumento17 pagineUnit - 6 Muscular SystemChandan ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Education ClassDocumento8 pagineHealth Education ClassAlicia ValverdeNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles in The Body 20121Documento14 pagineMuscles in The Body 20121Elpi Amelia PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- Ilovepdf Merged 1 13Documento13 pagineIlovepdf Merged 1 13Abdulrahman UdayNessuna valutazione finora
- HCP MODULE 11 Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento9 pagineHCP MODULE 11 Musculoskeletal SystemLHYRA KATHLEEN LOPEZNessuna valutazione finora
- DefinitionDocumento9 pagineDefinitionaimiorreNessuna valutazione finora
- AnatomyDocumento17 pagineAnatomyAb To zine doNessuna valutazione finora
- The Muscular System-251606Documento8 pagineThe Muscular System-251606sselt gayNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.3 Bones Muscles and JointsDocumento5 pagine9.3 Bones Muscles and JointsDerick NKANDU KALUBANessuna valutazione finora
- Naw TrainingDocumento34 pagineNaw Trainingganesh pNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular SystemDocumento1 paginaMuscular SystemKareen ArnaizNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Body Muscles by Alijan BadalzadehDocumento11 pagineHuman Body Muscles by Alijan BadalzadehElican BedelZadehNessuna valutazione finora
- Human BodyDocumento10 pagineHuman BodyspgmaniarunagiriNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissuesDocumento10 pagineAnimal TissuesAlvin PaboresNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Form A Healthy Lifestyle and Muscle GroupsDocumento14 pagineHow To Form A Healthy Lifestyle and Muscle GroupsRhea SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Bones, Muscles, and Joints: What Are Bones and What Do They Do?Documento4 pagineBones, Muscles, and Joints: What Are Bones and What Do They Do?Rolavilla BartolomeNessuna valutazione finora
- Textos I Medicina Level I 2020Documento18 pagineTextos I Medicina Level I 2020Valeria DonzelliNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular System AnatomyDocumento23 pagineMuscular System Anatomymichaelryann madayagNessuna valutazione finora
- AssignmentFile 18 06032024133208Documento15 pagineAssignmentFile 18 06032024133208kartikbansal232007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biological Systems and Processes BookletDocumento31 pagineBiological Systems and Processes Bookletapi-422428700100% (1)
- Muscle Ligaments & TendonsDocumento5 pagineMuscle Ligaments & TendonsMahnoor JawadNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphy Muscular SystemDocumento54 pagineAnaphy Muscular SystemZosia SageNessuna valutazione finora
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento2 pagineMusculoskeletal SystemJames Wilstar Delicano SandovalNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular SystemDocumento41 pagineMuscular SystemGem Rose UretaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Do You Call The Arrowed Part?Documento13 pagineWhat Do You Call The Arrowed Part?Earl GenodipaNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular SystemDocumento8 pagineMuscular SystemZoological science classesNessuna valutazione finora
- Document 6Documento10 pagineDocument 6shivalee.abirajNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular System FunctionDocumento2 pagineMuscular System FunctionLachlan PalmerNessuna valutazione finora
- From Error To Error, One Discovers The Entire Truth. - Sigmund FreudDocumento1 paginaFrom Error To Error, One Discovers The Entire Truth. - Sigmund FreudJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Acctg Writing GuideDocumento1 paginaAcctg Writing GuideJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Anna Mitz Resume 2018Documento2 pagineAnna Mitz Resume 2018JenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Infotech College of Art and Science: Student Information System Surname First Name Middle Name AddressDocumento2 pagineInfotech College of Art and Science: Student Information System Surname First Name Middle Name AddressJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Abm FDocumento2 pagineAbm FJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- The Internet and Online BehaviorDocumento10 pagineThe Internet and Online BehaviorJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment in Tax 102 What Is Transfer?Documento5 pagineAssignment in Tax 102 What Is Transfer?JenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Friday NightDocumento11 pagineFriday NightJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Junior Philippine Institute of Accountants: La Consolacion University PhilippinesDocumento2 pagineJunior Philippine Institute of Accountants: La Consolacion University PhilippinesJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: Napoleon C. Lomotan Professor: Dean Cordova Year and Section: BSA-4A Date: January 23, 2019Documento6 pagineName: Napoleon C. Lomotan Professor: Dean Cordova Year and Section: BSA-4A Date: January 23, 2019JenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Friday NightDocumento1 paginaFriday NightJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: Napoleon C. Lomotan Professor: Dean Cordova Year and Section: BSA-4A Date: January 23, 2019Documento6 pagineName: Napoleon C. Lomotan Professor: Dean Cordova Year and Section: BSA-4A Date: January 23, 2019JenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Regional Conference For Central and Eastern Europe and Central AsiaDocumento1 paginaRegional Conference For Central and Eastern Europe and Central AsiaJenniferFajutnaoArcos0% (1)
- Name: Napoleon C. Lomotan Professor: Dean Cordova Year and Section: BSA-4A Date: January 23, 2019Documento6 pagineName: Napoleon C. Lomotan Professor: Dean Cordova Year and Section: BSA-4A Date: January 23, 2019JenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Friday NightDocumento1 paginaFriday NightJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- AngelesDocumento11 pagineAngelesJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Kap - BienDocumento1 paginaKap - BienJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Justine May Arcos: TypesDocumento2 pagineJustine May Arcos: TypesJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Artikel 3 PDFDocumento14 pagineArtikel 3 PDFJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Movement Enhancement: Justine May Arcos CBET 19 - 101 ADocumento2 pagineMovement Enhancement: Justine May Arcos CBET 19 - 101 AJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Body-Table Di Pa FinalDocumento4 pagineBody-Table Di Pa FinalJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Submitted To: Ms. Princess Serdina Submitted By: Danica Mae MapaDocumento3 pagineSubmitted To: Ms. Princess Serdina Submitted By: Danica Mae MapaJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Junior Philippine Institute of Accountants: La Consolacion University PhilippinesDocumento2 pagineJunior Philippine Institute of Accountants: La Consolacion University PhilippinesJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Debut ScriptDocumento5 pagineDebut ScriptJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- System Analysis and Design TutorialDocumento71 pagineSystem Analysis and Design TutorialPralay BiswasNessuna valutazione finora
- Submitted To: Ms. Princess Serdina Submitted By: Danica Mae MapaDocumento3 pagineSubmitted To: Ms. Princess Serdina Submitted By: Danica Mae MapaJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- 2551q BIR FormDocumento2 pagine2551q BIR FormJenniferFajutnaoArcos0% (1)
- 1601e PDFDocumento2 pagine1601e PDFJanKhyrelFloresNessuna valutazione finora
- FallacyDocumento3 pagineFallacyJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- CPT Session 1 - GMFADocumento23 pagineCPT Session 1 - GMFAAgrashek TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Medical Terminology A Word Building Approach 7th Edition RiceDocumento24 pagineTest Bank For Medical Terminology A Word Building Approach 7th Edition RiceMaryJohnsonafrz100% (37)
- Lower Limb MusclesDocumento8 pagineLower Limb Musclesbilal_kmu020% (1)
- Trainer ResourceDocumento24 pagineTrainer ResourceRicky Wu100% (4)
- Tendon Transfers Part I.Documento9 pagineTendon Transfers Part I.Abdelaziz AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles of MasticationDocumento6 pagineMuscles of MasticationAbdallah Essam Al-ZireeniNessuna valutazione finora
- WhitfieldR PS2016 PostSymposium HandoutsDocumento18 pagineWhitfieldR PS2016 PostSymposium Handoutsdeemoney3Nessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Pilates Foundation and Mat v202001Documento98 pagine01 Pilates Foundation and Mat v202001Yulia LarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Leanbody Labrada CalendarDocumento3 pagineLeanbody Labrada CalendarJaviDiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanism of Muscle Contraction ReviewerDocumento5 pagineMechanism of Muscle Contraction ReviewerMerli Ann Joyce Caldito100% (1)
- Muscular System of Frog Autofit To ContentsDocumento3 pagineMuscular System of Frog Autofit To ContentsBanana LatteNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct Lateral Approach Hardinge Approach Hip Replacement ObDocumento8 pagineDirect Lateral Approach Hardinge Approach Hip Replacement ObhaminatrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Try Out Anatomi 1Documento4 pagineTry Out Anatomi 1maha candraNessuna valutazione finora
- Musculoskeletal Imaging, The Essentials - Chew (2019)Documento1.309 pagineMusculoskeletal Imaging, The Essentials - Chew (2019)Cheyenne RahimiNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomechanics of Knee JointDocumento123 pagineBiomechanics of Knee JointSIBASIS PATTANAYAKNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular System: MusclesDocumento19 pagineMuscular System: MusclesChristelle Marie De GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Shreddin8 Muscle AnatomyDocumento16 pagineShreddin8 Muscle Anatomysambelov100% (2)
- Functional Neuromuscular AnatomyDocumento56 pagineFunctional Neuromuscular AnatomyΒασίλης Βασιλείου100% (3)
- Tavi's 8-Weeks Booty Builder ProgramDocumento111 pagineTavi's 8-Weeks Booty Builder Programsndx87y9vhNessuna valutazione finora
- Penatalaksanaan Fisioterapi Pada KasusDocumento8 paginePenatalaksanaan Fisioterapi Pada KasusWidya SyahdilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomi Ankle 1Documento114 pagineAnatomi Ankle 1Zera DirgantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Pelvic Muscles TrimmedDocumento6 paginePelvic Muscles TrimmedDelfin UrbanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle MechanicsbDocumento15 pagineMuscle MechanicsbTamas KalmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdominal IncisionDocumento23 pagineAbdominal IncisiondinahzrNessuna valutazione finora
- (RP FPT Novice-Intermediate) 4x - Full BodyDocumento46 pagine(RP FPT Novice-Intermediate) 4x - Full BodyMichaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Anterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossaDocumento24 pagineAnterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossaShahid MaqboolNessuna valutazione finora
- The Lifters Muscle ManualDocumento50 pagineThe Lifters Muscle ManualMir TastanNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise Therapy Old PapersDocumento8 pagineExercise Therapy Old PapersJust ChepthunnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle ContractionDocumento21 pagineMuscle ContractionMarilyn GumeyiNessuna valutazione finora
- Repiratory System: Presented by Group 3: Lacap, Lopez, Medina, MarceloDocumento8 pagineRepiratory System: Presented by Group 3: Lacap, Lopez, Medina, MarceloAj LacapNessuna valutazione finora