Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
How To Design Concrete Structures Using Eurocode 2
Caricato da
אחמד סלאח כאמלTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
How To Design Concrete Structures Using Eurocode 2
Caricato da
אחמד סלאח כאמלCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
Example (1) :-
Using ultimate limit state design method, design and draw cross section for the
short columns given P D.L=1500 KN & live loads PL.L= 700 KN.The concrete
characterisitic strength fcu is 25 N /mm2 while the stress proof fy is 240 N /mm2
(1-a) A square tied column
(1-b) A rect . tied column having a width of 0.30m
(1-c) A circular tied column .
(1-d) A spiral circular column
(1-e) A spiral square column .
Solution :-
Since PL.L < 0.75 PD.L. ………………………………Code (3-2-1-1-2 -)ب
Pu = 1.5 ( PD.L+ PL.L ) = 1.5 (1500+700) =3300 kN.
Using code equation (4-12-a) for tied column.
Pu= 0.35 fcu Ac + 0.67 fy Asc
3300 x 103 =0.35 x 25 Ac + 0.67 x 240 x Asc
Let Asc= 0.01 Ac
3300 x 103 =0.35 x 25 Ac + 0.67 x 240 x 0.01 Ac
Ac req = 318594.3 mm2
(1-a) Square Tied Column ( b b )
Ac req = b b =318594 mm2 b = 564.5 mm
Choose b = 600mm Ac chosen = 360000mm2
Asc = 0.01 Ac req =3186 mm2
>0.008 Ac req = 2550 mm2
>0.006 A c chosen = 2160 mm2 O.K. …….…………...Code ( 6-4-7- 1 -)أ
Choose 16 16 ( Asc chosen = 3216 mm2 )
Stirrups
Smax = max. spacing between stirrups ……………………………..Code (6-4-7-)ز
b=600 mm
= smaller 15 col =15 X 16 =240 mm
200 mm 60cm
Use S = 200mm
^
30cm
Stirrup diameter ( st min ) 2x5 8/m'
60cm
8mm
st min = bigger 16 16
col /4 =16/4 =4 mm 25cm
^
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 1
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
Use st = 8 mm & spacing 200mm Use stirrups 5 8 /m
Vstirrups = Volume of stirrups / m
= 5 [ 4 550 +4 390 ] 50.3
Vc = Volume of concrete = 600 6001000 = 360x106 mm3
Vstirrups / Vc = 0.263 % > 0.25 % O.K. ………………………….Code ( 6-4-7-)ح
Note :
If the percentage is less than 0.25% , volume of stirrups should be increased by
increasing the diameter , No. of branches and No . of stirrups / m (descreaing S )
( 1-b ) Rectangular Tied Column :-
Acreq = b t = 318594 mm2
For b = 300 mm t = 1062 mm 3x5 8/m'
16 16
t = 1100 mm Ac chosen330000 mm 2
30cm
Asc= 0.01 318594 = 3186 mm2
> 0.008 Ac req 110cm
> 0.006 Ac chosen O.K.
choose 16 16 ( Asc= 3216 mm2 ) .
Stirrups let stirrups 5 8/ m …….(Smax & st min as case (1-a) )
Vstirrups = 50.3 5 [ 2(250 +1050 ) +2 2 ( 250 +150 )] = 105630 mm2
Vc =30 110100 =330x106 mm3
Vstirrups / Vc =0.32 % > 0.25 % O.K .
(1-c ) Circular Tied Column
16 16
Ac req = Dc 2/4 =318594 mm2
Dc =637 mm Dc = 650 mm 65cm
Ac chosen =331800 mm2
Asc =3186 mm2
> 0.008 X 318594 mm2
>0.006 X331800 mm2 O.K 10 8/m'
or 6 10/m'
Choose 16 16 (A sc = 3216 mm2 )
Stirrups
Vc = 331800 1000 = 331.8 x106 mm3
Vstirrups = 5 50.3 600 = 474066.33 mm3
Vst / Vc = 0.143% < 0.25 % Increase stirrups
Using stirrups 8 with spacing S
Vst= (0.25 /100) 331.8 x106 =( 1000/s) 50.3 600
S =1140 cm Stirrups 10 8/ m (s=100 mm )
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 2
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
Or use stirrups 10
S = 178 mm use stirrups 6 10/m ( S=166.6 mm )
(1-d) Circular Spiral Columns
Using code equations ( 4-12-b ) & (4-12-c )
Pu = 0.35 fcu Ak +0.67 fy A sc + 1.38 fysp . Vsp ………………………………...(1)
Pu = 0.4 fcu Ac + 0.76 fy As ……………………………………………………(2)
Using equation (2)
Let Asc = 1.0 % Ac = 0.01 Ac ….…Code (6-4-7- – أ2) 14 16
cm
3300 103 = 0.4 25 Ac +0.76 240 0.01 Ac Dc = 60
cm
55
Ac = 279093.3 mm2 = Dc2 / 4
=
k
D
Dc 600 mm Ac = 282740 mm2
Spiral
Asc = 1/100 Ac = 2791mm2 8/ 3.75cm
Choose (14 16 ) ( Asc = 2814 mm2)
Dk = Dc-50 =550 mm 3.75cm
Ak = Dk2 /4 = 237583 mm2
sp = Asc /Ak = 1.2 % O.K. ………………………………… Code (6-4-7-– أ2)
Sub. in equation ( 1)
3300 103 = 0.35 25 237583 + 0.67 240 2814 + 1.38 240 Vsp
Vsp = 2321 mm2 sp = Vsp/Ak = 2321 /237583 = 9.77x10-3
sp min = 0.36 (fcu / fysp )(( Ac/Ak)-1 ) = 7.13 x10-3 ………………Code Eq. (4.12-e)
< sp O.K.
Use sp = 9.77x10-3
Vsp = Dk Asp /p let sp = 8 mm
Asp = 50.3 mm2
p = Dk . Asp / Vsp = 550 50.3 /2321 = 37.5 mm
30mm < p < 80 mm …………………………………………..Code ( 6-4-7-) ك
Spiral 8 /37.5 mm
(1-e) Spiral Square Column :
As given in (1-d)
Ac = 279100 mm2 = b b b = 528.3 mm
Choose b = 550 mm Ac = 302500 mm2
Asc = 1416 =2814 mm2
Dk = b-50 = 500 mm
Ak= Dk2/4 = 196350 mm2
sc = Asc / Ak = 1.4% > 1.2 %
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 3
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
Using eq . (4-12-b)
3300 103 = 0.35 25196350 0.672402814 1.38240Vsp
55cm
Vsp = 3410 mm2 sp = Vsp / Ak =0.0174
14 16
sp min =0.36 ( 25 /240 ) ((302500 /196350 )-1) = 0.02 > sp
Spiral
Use sp = sp min = 0.02 Vsp = 0.02 196350 = 3930 mm2
cm
10/ 3cm
55cm
50
Vsp = Dk .Asp /p
=
k
D
Use spiral 8 Asp = 50.3 mm2
p = 19 mm < 30 mm add. 4 16
Use spiral 10 Asp = 78.5 mm 2 5 8/m'
add.
p = 31.0 mm use pitch = 30.0 mm Spiral 10 /30 mm
Note
Additional reinfocement 4 16 & stirrups 5 8 /m should be used to achieve the square shape
Example (2) :
Calculate the vertical reiforcement Asc and the spirals inside a circular spiral column
having a diameter Dc equal to 600 mm , to carry a factorized load Pu of 3200 KN,
knowing that fcu = 25 N/mm2 & fy = fyp = 280 N/mm2
Solution
For spiral column
(a) Pu = 0.4 fcu Ac + 0.76 fy Asc
3200 1000 =0.4 25 6002/4+ 0.76 280 Asc
Asc = 1750 mm2 Asc min= 0.01Ac = 2827 mm2
Asc = Asc min = 2827 mm2 choose Asc =12 18 (=3048 mm2)
(b) Pu =0.35 fcu Ak + 0.67 fy Asc +1.38 fyp Vsp
3200 103 = 0.35 25 (550)2/4 + 0.67 280 3048 +1.38 280 Vsp
Vsp =1422 mm2
Vsp min = spminAk = 0.36 (25/280 ) ((6002 /5502)–1 ) (550)2 /4 =1452 mm2
Vsp min > Vsp
Vsp = 1452 mm2 = Dk Asp /p for Asp = 50.3 mm2 ( 8 mm)
p = 60.0 mm (30< p< 80 mm O.K. )
p = 60 mm Use spiral 8 /60 mm
Example (3):
For a braced column subjected to Pu = 1500 kN, and having a cross section 250 x 500
mm , it is required to check if the column is short or long and calculate :-
Addititional moments – if any – due buckling in each direction knowing that the clear
height in both direction ( Ho) is equal to 5.00 m . The end condition according to
Egyptian code is as given in the table
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 4
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
b- direction T- direction
Case
Top end Bottom end top end Bottom end
A 1 1 2 2
B 2 1 1 1
C 2 2 2 1
Solution :
Using table (9-9)
K (case 1-1) = 0.75 , k (case 1-2 ) = 0.80 , k (case 2-2 )=0.85
He =k. Ho & = He /b ( b- direction ) & = He / t ( t-direction )
If 15 ( table 6-7 ) No buckling occurs in this direction
If 15 30 ( table 6-8 ) buckling occurs in this direction
If >30 the column dimension in this direction should be increased
b /2000 ( b- direction )
t / 2000 ( t- direction )
Mu add = P.
Case b- direction t- direction
K He M add K He (mm) M add
(mm) mm) (kN.m) mm) (kN.m)
A 0.75 3750 Zero Zero 0.85 4250 8.5 zero zero
B 0.80 4000 32.0 4.80 075 3750 7.5 zero zero
C 0.85 4250 36.13 5.42 0.80 4000 8.0 zero zero
Column is considered short for case (a) only and the reinforcement may be calculated
using code (equation 4-12 a ) for cases (b & c ) ,the column is considered as long
(slender column )and subjected to Pu in addition to Madd as shown .
M add ( case b or c )
b
Example (4) :
If the clear height (He ) in t – direction changed to be 10.0 m instead of 5.00 m in
example (3) re-check the buckling of the columns given before
Solution :
The solution in b-direction will be as before
For t- direction
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 5
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
Case (a)
He = 0.85 10000 =8500 mm =17 > 15
= (17)2 x 500 /2000 = 72.25 mm M add
(t)
Madd = 108.4 kN.m.
So, the column will be subjected to Pu and Madd as shown
M add
Case (b)
(b)
He = 0.75 10000 =7500 mm = 7500/500 =15
=0.0 Madd =0.0
The column will be subjected to Pu and Madd as shown
Case (c)
He = 0.8 10000 = 8000 mm M add
(c)
=8000/500 = 16>15
= (16)2 500 /2000 = 64.0 mm M add
(t)
Madd = 1500 x 0.064 = 96.0 kN.m.
The column will be subjected to Pu in addition
to biaxial moments (Madd in both directions as shown) .
Note : If the system is unbraced in example (3) or example (4) all columns in the
system should be studied together in two global till getting the average deformation
(av ) for all columns in each direction (i.e no individual column calculation should be
done as given later in example (10)
Example (5)
Using code tables (4-9) & (4-10 ) , find the ratio He / Ho for the given cases
Case Col dimen Bottom end Top end System
a 250x500 Foundation beam250x600 braced
b 500x500 beam250x400 beam250x600 braced
c 250x800 beam250x700 beam250x500 unbraced
d 250x500 Beam 250x400 slabs only (ts= 200 mm ) unbraced
Solution :
The end conditions given by the code are as follows
Case (1) : Columns are connected monolotically to foundations or slabs or
beams with ts or tb column dimension in the direction considered
Case (2) : Columns are connected monolotically to slabs or beams with ts or tb
less than the column dimension in the direction considered
Case (3) Hinged connection as for precast systems
Case (4) : Free end as for cantilever columns
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 6
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
There cases should be studied for each direction of the column
Case b-direction t-direction
b Bot- End Top-End He t Bot- End Top-End He
(mm) tb Case tc case Ho (mm) tb Case tb case Ho
a 250 Found 1 600 1 0.75 500 Found 1 600 1 0.75
b 500 400 2 600 1 0.80 500 400 2 600 1 0.80
c 250 700 1 500 1 1.20 800 700 2 500 2 1.50
d 250 400 1 200 2 1.30 500 400 2 200 2 1.50
Note :-
The system may be braced in one direction and unbraced in other direction and so, the
ratio ( He / Ho ) must be calculate individually in each direction according to the system
type ( braced or un-braced ) in the direction considered (b or t) as will be given in
example (8)
Example 6:
Check if the building shown in fig is considered braced or unbraced
Data :
No . of floors = 6 floors Y
5.0 5.0
Total building height = 19m
C1 C2 C1
C1 = 400 400 mm . total load / floor = 150 kN.
C2 = 250600 mm . Total load / floor = 320 kN. 3.0
W1= 250x3000 mm. Total load / floor = 640 kN 2.0
W1 X
Core thickness = 300 mm 3.0 W1
0.779
2.0
Core load = 400 kN. / floor 0.3 1.4 0.3
Concrete strength fcu = 25 N /mm2 3.0
C1 C2 C1
Solution
Total load = 6 [ 4 (150) + 2(320) + 2(640) +400 ] = 17520 kN.
Inertia about X- X axis for W1
Ix = 250 x 30003 /12 = 562.5x 109 mm4
Neglect the inertia about Y- Y axis for W1
C.G for the core
A1 =300 X 2000 = 600000 mm2
A2 = 300 X 1400 = 420000 mm2
A total = 2 X 600000 + 420000 = 1620000 mm2
Y = (2 X 600000 X 1000 + 420000 X 150) / 1620000=779.6 mm
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 7
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
Inertia about X- X axis for Core:
Ix =2 [300 X (2000)3/12 +600000 (1000-779.6)2] +1400 X (300)3/12
+ 420000 (779.6 –150 )2 = 627,927,770,000 mm4
Inertia about Y- Y axis for Core:
Iy = 2[2000 X (300) 3 /12 +600000 (850 )2] +300 X (1400 )3 /12 =9.446x1011 mm4
Ix total = 562.5x 109 + (627,927,770,000)
= 1.19043 x 1012 mm4
E 4400 25 22000 N / mm2 ................................................................Code Eq (4 61)
Iy total = 9.446x1011 mm4
In x- direction: - the inertia is taken about Y axis
In y- direction: - the inertia is taken about X axis
ΣN
αH ............................................................................. Code Eq.(art.6 5 4)
ΣEI
As the building more than four stories then it will considered braced only if
17520000
y 19000 0.491 0.6 ............................ (braced )
22000 1.19043 x 1012
17520000
x 19000 0.551 0.6 ...................... (braced )
22000 9.446x1011
The building is considered braced in Y direction ( around x axis )
The building is considered braced in X direction ( around y axis )
Example (7)
The following figure shows a sectional elevation of a column in a building braced
in the two directions .
0.6
b = 0.25
t
Ho = 6 - 0.6
= 5.4 m
6.00
x x
Sec ( x - x )
0.6
It is required to design the column with separate stirrups knowing that :
- width of column = 250 mm
- depth of all beams = 600 mm
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 8
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
- fcu = 25 N/mm2 fy = 360 N/mm2 Pu = 2900 kN
First Estimate of the cross sections dimensions
Assuming the column to be subjected to axid load only then :
Pu = 0.35 fcu Ac + 0.67 fy Asc …………………..………….… Code Eq ( 4.12 a)
Ac
Assume Asc then :
100
0.67
P Ac [0.35 f cu fy]
100
0.67
Ac [8.75 360]
100
11.162 Ac
2900 1000
Ac 259810 250 1050 mm 2
11.162
Buckling calculations :-
1- In plane buckling (t-direction )
Top end condition : (tc=1050)> (tb=600 ) case (2)
Bottom end condition : (tc=1050)> (tb=600 ) case (2)
He
0.85 .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... .. Codetable (6 9)
Ho
He 0.85 540 4590 mm
He 4590
b 4.37
b 1050
b 15 the column is short in this direction.......... .......... ....... Codetable (6 7)
2- Out of plane buckling ( b-direction )
Top end condition : (tc = 250 ) < ( tb =600 ) case (1)
Bottom end condition : ( tc =250 ) < (tb =600 ) case (1)
He = 0.75 5400 = 4050 mm
H 405
b e 16 .2
b 25
15 the columnis long in this direction
b
b 2 .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... ...... Code Eq.(6.37 )
2000
(16 .2) 2 250
32 .8 mm
2000
Madd = P.……………………………………………….………..Code Eq.(6.36)
Madd = 2900 0.0328 = 95.1 kN.m
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 9
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
Design of column
Pu =2900 kN , Mu = 95.1 kN.m ( out of plane B.M )
Designing the section using the Interaction Diagram in chart 38 :
Pu 2900 1000
0.44
f cu t b 25 1050 250
Mu 95 .1 10 6
0.058
f cu t b2 25 1050 (250 )2
Get 3.6
f cu10 4 0.9 %
As As bt 2363 mm 2
Use 5 25 (Top and Bottom)
25 5
( Note that 0.8)
25
25cm
10 25
105cm
Example (8)
Design sec A-A in the frame shown in figure. Assume the frame is braced in y direction
(out of plane ) and unbraced in – x direction (its plane )
Data
fcu = 25 N/mm2 . fy =240 N/mm2 Pu = 1565.0 kN
As the column has a variable cross , section , so an average value ( t avg ) will be used for
buckling calculation , while the actual section ( t=100cm ) is used in designing sec A-A
The average thickness for buckling may be taken at 2/3h
tavg = 600+400 (2/3) =867 mm
refer to table (6-10)as the frame is unbraced in x- direction
case (3) at bottom and case (1) at top …………………..k = 1.6
Ho = 7.6 + 1- 0.6 = 8.0 m
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 10
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
700 700 KN.m 100
700 700
80 120
A
A A
340
80 760 cm 700
Ho
340cm
80 100
60 100cm
x - direction
35
y - direction
SEC A - A
He = 1.6 (8) = 12.8 m
12800
14.76 10 ( table(6 7))
867
(14.76) 2 (0.867)
0.0944
2000
Muy (add)= 0.0944 (1565) = 147 kN.m
Muy (tot)= 700 + 147 = 847 kN.m
In most cases the additional moment in Y- direction equal to Zero or equal to small
values and can be neglected
1565 x 1000
k 0.179
25x (350)x 1000
=0.9 fy =240 N/mm2 =0.6 …………..Chart No. 19 page 24
ρ= 2.5
= 2.5 (250)10-4 =0.00625
As = 0.00625 (35) 100 = 2187 mm2 …………………..(5 25)
A\s= 0.6 (2187) = 1312.5 mm2…… …….……….(3 25)
As (min ) = [ 0.25 + 0.052 ( 14.76 )] 350 (1000 ) /100= 3550 mm2 ...Code Eq. (6-45)
As (total) = 3928 mm2 ( 8 25 ) > As (min )
100cm
35cm
5 25
4 12 3 25
5 8/m'
Another Solution :
Use chart with uniform steel No. 11 page 16, =0.9 , fy = 240 N/mm2
K= 0.179, k ( e/t) =0.097
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 11
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
= 5……………………… =5(25)10-4 = 0.0125
As (total ) = 0.0125 (350) 1000 = 4375 cm2
12 22
As ( chosen ) = ( 4560 mm2) 12 22
In Y- direction
Refer to table ( 6-9) as the frame is braced
in Y- direction . K= 0.75
He = 0.75 (3.40 ) = 2.55m ( since t b > b col ) case (1) 5 8/m'
2.55
7.30 15 (short column)
0.35
Example (9)
Design the exterior column shown in figure (A) ( column C1)
Data
fcu = 20 N / mm2 fy =240 N / mm2
PD.L = 500 kN , PL.L =500 kN
Assume that the building is braced
3.00
3.00
C1 C1
30x30
3.00
3.00
1 3
2 25x60
4.00
6.00 6.00
40x40 A
wL2
12 w t/m'
Solution :
6000 L
slab 2.0 one way slab
3000
Wus = 1.4 [ 0.10 (25000 ) + 2000] + 1.6 (2150 ) = 9750 N/m2
Wub = 1.4 (25) 0.25 (0.6) +3 (9.75) = 34.5 kN/m2
34.5 * (6) 2
Mf = = 103.5 kN.m
12
K= stiffness of the member
= 4EI/ L ( for member fixed from both ends )
We can also use relative stiffness as all member from concrete ( having the same ends)
Relative stiffness = I/L …………… …………(Fixed – Fixed )
= 3I/ (4 L) ………………….( Fixed – Hinged )
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 12
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
From code for two bays or more , the moment over column ends can be calculated as
k n i k
n k r M f ..............where K r n
k k
follows (code table 6-11)
This calculations are illustrated in a tabulated form
No. Section I L K Kr = k/ k M= Kr (Mf)
300 300 6.75 x 10
8
1 3000 225,000 0.149 15.5
400 400 21.33 x 10 4000 533,250
8
2 0.353 36.5
3 250 600 45 x 108 6000 750,000 0.498 51.5**
k = 1,508,250 M = 103.5
40
4 18
8 16
40
5 8/m'
Ho = 4.0, He = 0.75 (4.0) = 3.0m
Use chart No. 11 page 16
3.0
7.5 10 ( short column )
0.40
Pu 1.4 (500) 1.6 (500) 1500 kN
1500 1000
k 0.468
20 x ( 400) x 400
e 36.5 106
k. 0.028
t 20 x ( 400) x 400 2
M
e u 0.024m
P
u
emin bigger of 0.02or 0.05b
emin 0.02m
e emin
ecc . sec tion
= 8.0 ………………………………tot =8 (20)10-4=0.016
As ( total ) = 0.016 (400) (400) = 2560 mm2
As (chosen) = 2732 cm2 (4 18 +8 16 )
** Note : The value of the moment transferred to beam ( 51.5 kN.m. ) is in a good
agreement with the value of the assumed – ve bending on beam edges suggested by the
code
(WL 2 /24) = 34.5 (6)2 /24 = 51.7 kN.m.
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 13
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
Example (10)
The following figure represents a structural plan and sectional elevation of a five – story
residential building , Given that :
b= 250 mm , fcu , =25 N / mm2, fy = 360 N / mm2, all beams are 250x500, typical floor
height = 3m, and loads on beams Wd = 20 kN / m andW1 = 10 kN/m .
It is required to :
1) Calculate the straining actions for column C1 through C6 at the ground floor
2) Design column C6.
A B C D E
4.00 4.00 4.00 4.00
4.00
1 1
0.5m
C3 C2 C1
4.00
2 2
C6 C5 C4
4.00
Ho = 4.25m
Pd =650 kN Pd =1000 kN Pd =1000 kN
PL =400 kN PL =600 kN PL =600 kN
3 3
0.25
4.00
0.00
y Pd =400 kN Pd =650 kN Pd =650 kN
PL =300 kN PL =400 kN PL =400 kN
4 4 -0.75
Semell 25x60
x A B C D E
-1.75
Structural plan of a five-story building
First Estimation of columns dimensions :
The cross sections of columns can be first estimated by considering them subjected to
axial loads only as following :
Pu= 0.35 fcu Ac + 0.67 fy Asc …………………...………………. Code Eq.( 4.12.a)
Ac
Assume Asc then :
100
0.67
Pu A c [0.35 f cu fy ]
0.67
100
Ac [8.75 360] 11.162 Ac
100
C1 250 400
C2 , C3 , and C4 250 550
C5 and C6 250 850
Check of building bracing :
The building has not any walls or cores for bracing.
So, the building is unbraced in both X & Y directions.
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 14
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
X- direction :
Column Homm Top* Bottom* He Hemm bmm He mm * * *
Ho
**
End End b
Cond Cond.
C1 4250 1 1 1.2 5100 250 20.4 52
C2 4250 1 1 1.2 5100 250 20.4 52
C3 4250 1 1 1.2 5100 250 20.4 52
C4 4250 2 1 1.3 5525 550 10.05 27.8
C5 4250 1 1 1.2 5100 250 20.4 52
C6 4250 2 1 1.3 5525 850 6.5 18
* Code item : 6-4-5-1 ** Code Table :6-10 *** Code Equation : 6-37
av = 43.76mm My ) add = 0.04376(P)
.
Column C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6
(M)yD.L add 17.5 28.5 28.5 28.5 43.8 43.8
(M)yL.L add 13.1 17.5 17.5 17.5 26.3 26.3
Y- direction
Column Homm. Top Bottom He He mm Bmm He mm * * *
Ho
**
End End b
Cond Cond
C1 4250 1 1 1.2 5100 400 12.75 32.5
C2 4250 2 1 1.3 5525 550 10.05 27.8
C3 4250 2 1 1.3 5525 550 10.05 27.8
C4 4250 1 1 1.2 5100 250 20.4 52
C5 4250 2 1 1.3 5525 850 6.5 18
C6 4250 1 1 1.2 5100 250 20.4 52
4 32.5 (4 2) 27.8 4 52 4 18 2 52
av
20
* Code item : 6-4-5-1 ** Code Table : 6-10 *** Code Equation : 6-37
av = 34 mm.
Mx ) add = 0.034(P)
Column C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6
( M)D.L 13.6 22.1 22.1 22.1 34 34
(M) L.L 10.2 13.6 13.6 13.6 20.4 20.4
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 15
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
Edge Columns
C2 and C3 in Y- direction & C4 in X- direction
For edge columns another bending moments must be calculated these bending moment
results from the frame action between the beams and the columns . In other words , the
deflection of the end beam causes a rotation in the connection between the beam and the
column consequently causes bending moments in the column .
C1 (Both x – direction and Y- direction )
1) In y – direction
250 400 3
u 1 1.33 x 10 9 mm 4
12
1.33 x 10 9
26.7 ( )
Mx) D. L 4.75 5.4 kN.m
1.33 x 10 9 1.33 x 10 9 2.604 x 10 9
( )( )( )
4.75 3 4
1.33 x 10 9
13.3 ( )
M y ) L. L 4.75 2.7kN.m
1.33 x 10 9 1.33 x 10 9 2.604 x 10 9
( )( )( )
4.75 3 4
250 5003
Ib 2604167000 mm4
12
250 5503
I u I1 3466146000 mm4
12
20 42
Mf ) D. L 26.7kN .m
12
In X- direction
400 250 3
Iu Il 520833333 mm 4
12
520833333
26.7 ( )
M x ) D. L 4.75 3.1 kN.m
520833333 520833333 2604167000
( )( )( )
4.75 3 4
520833333
13.3 ( )
M x ) L. L 4.75 1.6kN.m
520833333 520833333 2604167000
( )( )( )
4.75 3 4
Design of column C6
PD.L.= 1000 kN PL.L = 600 kN
MY) D.L.=43.8 kN.m MY)L.L = 26.3 kN.m
Mx)D.L = 34 kN.m Mx)L.L = 20.4 kN.m
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 16
Faculty of Engineering THIRD YEAR CIVIL-2016
Cairo University REINFORCED CONCRETE
STR 302B
Pu =1.4 (1000) +1.6(600) =2360 KN.m
Mxu = 1.4 (34)+ 1.6 (20.4) = 80.2 KN.m ex = Mxu / Pu = 0.034m > ex min *
MYu = 1.4 (43.8) + 1.6 (26.3) = 103.KN.m ey = Myu / Pu = 0.044m > ey min **
To Design a column subjected to biaxial bending moment, a simplified method in the
code item (6-4-6) can be used in which the column may be designed as if it was
subjected to uniaxial bending moment but after multiplying this moment by a
magnification factor as follows .
Pu 2360 1000
0.44
f cu b a 25 250 850 M xu
0.48
M xu 80.2 M yu
a
356.4 kN .m
a 0.225 b
M yu 103.4
125.3 kN .m M xu
b 0.825
M M
xu yu
a b
.
25
16 18
85
Reinforcement Details
b = 850, b = 825 mm. a= 250 , a =225 mm.
Using Chart No. 17 get =7
= ƿ fcu 10-4 =1.75 %
As (total ) = 3719 mm2 Use 16 18 (Uniformly Distributed )
as follows :
Designed for M xu
a
M xu M yu ............................................................................ Code Eq. (6 43)
M xu
b
225
80.2 0.48 x x 103.4 93.7 kN .m.
825
0.025 0.025
* ex min bigger 0.02 m ,* * ey min bigger 0.0425m
0.05 * 0.25 0.0125 0.05 0.85
Pu 2360 1000
0.44
f cu b a 25 250 850
M xu 93.7 106
0.07
f cu b a 2
25 850 2502
R. Concrete STR302B SOLVED EXAMPLES PREPARED BY CONCRETE STAFF Page 17
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Celebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985Da EverandCelebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5.3 Slab 5.3.1 Slab: Office Area: Ref. Calculation OutputDocumento27 pagine5.3 Slab 5.3.1 Slab: Office Area: Ref. Calculation OutputNH SyzlnNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 One Way SlabDocumento4 pagine7 One Way SlabPronay DhakNessuna valutazione finora
- NumericalDocumento24 pagineNumericalDIMariaAUnitedNessuna valutazione finora
- Example For CH-2Documento25 pagineExample For CH-2antenehNessuna valutazione finora
- One Way Slab ExampleDocumento18 pagineOne Way Slab Examplegizachewgirma551Nessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Continuous Beams PDFDocumento4 pagineDesign of Continuous Beams PDFBlend DlerNessuna valutazione finora
- RC Example ES-EN Code-1Documento17 pagineRC Example ES-EN Code-1Firomsa EntertainmentNessuna valutazione finora
- Slab Design WakandziwqreDocumento12 pagineSlab Design WakandziwqreTinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trapezoidal Combind FootingDocumento8 pagineTrapezoidal Combind FootingMarciano John100% (1)
- One Way & 2way Slab Desi̇gnDocumento24 pagineOne Way & 2way Slab Desi̇gnObsii W Busha LaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Design of SlabsDocumento3 pagineAnalysis and Design of Slabsdhanya1995100% (1)
- Limit State DesignDocumento85 pagineLimit State Designkeshav1980Nessuna valutazione finora
- Manyam Dr.s House 2.5Documento33 pagineManyam Dr.s House 2.5Durga Rama Swamy KalvakolanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter One in Elastic Moment RedistributionDocumento8 pagineChapter One in Elastic Moment RedistributionHaftom GebreegziabiherNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.1 Two-Way Slab - pp.194-206 - CIVL3320 - 2017-04-03Documento13 pagine10.1 Two-Way Slab - pp.194-206 - CIVL3320 - 2017-04-03Mk2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Memo STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS II - SAN2601 Assignments 2020Documento28 pagineMemo STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS II - SAN2601 Assignments 2020Rachel Du PreezNessuna valutazione finora
- TR 334 Tutorial-1Documento5 pagineTR 334 Tutorial-1Adaminovic MrishoNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank: Cem701 Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures Ii Unit 1Documento7 pagineQuestion Bank: Cem701 Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures Ii Unit 1RaNessuna valutazione finora
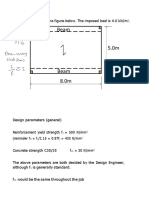
- Example: Design The Beams in The Figure Below. The Imposed Load Is 4.0 KN/MDocumento28 pagineExample: Design The Beams in The Figure Below. The Imposed Load Is 4.0 KN/MSarah HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Ribbed Slab 1Documento20 pagineRibbed Slab 1ephrem100% (2)
- Example 2 Simply Supported Beam - Flanged Section PDFDocumento7 pagineExample 2 Simply Supported Beam - Flanged Section PDFWee Ren100% (1)
- 11 - Flexural Strength Capacity-Code ComparisonsDocumento18 pagine11 - Flexural Strength Capacity-Code Comparisonsothman okNessuna valutazione finora
- Sa-2 Kani's Method ObjDocumento7 pagineSa-2 Kani's Method Objnirmalraj100% (2)
- Reinforced Concrete Slab Design - BS 8110Documento8 pagineReinforced Concrete Slab Design - BS 8110Rosaline MainaNessuna valutazione finora
- Example and ExerciseDocumento7 pagineExample and ExercisesamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Example 1 ': σ σ on faces near water face) on faces away σ water faceDocumento4 pagineExample 1 ': σ σ on faces near water face) on faces away σ water faceyenebeb tarikuNessuna valutazione finora
- Concrete Column Design - Design ChartsDocumento6 pagineConcrete Column Design - Design ChartsSajid Mehmood100% (1)
- Hydro Assignment #3Documento5 pagineHydro Assignment #3Kishan Madhoo100% (1)
- Design and Calibration of A Linear Proportional Weir For Flow Control FacilitiesDocumento5 pagineDesign and Calibration of A Linear Proportional Weir For Flow Control FacilitiesBenjamín Andres Lagos BerriosNessuna valutazione finora
- One Way Slab Design 3Documento3 pagineOne Way Slab Design 3Kenneth Peña JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- by Compression of The Water in The PoresDocumento16 pagineby Compression of The Water in The PoresAsifAliNessuna valutazione finora
- Behavior of Two Way SlabsDocumento18 pagineBehavior of Two Way Slabsnirmal sutharNessuna valutazione finora
- RCDDocumento1 paginaRCDShakir Naim Che ManNessuna valutazione finora
- Fa D F B: Example 1Documento19 pagineFa D F B: Example 1Sevet Gnow DrachirNessuna valutazione finora
- This Study Resource Was: Transition CurvesDocumento7 pagineThis Study Resource Was: Transition CurvesJoe NjoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Column Design Design of Short Braced ColumnsDocumento17 pagineColumn Design Design of Short Braced ColumnsPimpa MwiingaNessuna valutazione finora
- Slender ColumnsDocumento15 pagineSlender Columnskh.mitesh1904100% (1)
- Slabs FinalDocumento30 pagineSlabs FinalMwa100% (1)
- Civil Engg Materials Lab ManualDocumento34 pagineCivil Engg Materials Lab ManualAli RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical Behavior of Concrete-Encased CFST Columns Under Cyclic Lateral Loading, 2016 (Wei-Wu Qian)Documento15 pagineAnalytical Behavior of Concrete-Encased CFST Columns Under Cyclic Lateral Loading, 2016 (Wei-Wu Qian)Phan Đào Hoàng Hiệp100% (1)
- Ipt Design WorkDocumento43 pagineIpt Design WorkMorice RwakataleNessuna valutazione finora
- Moment Distribution Method - TutorialDocumento4 pagineMoment Distribution Method - TutorialEr. Rajendra Acharaya100% (1)
- Hawassa University: Department of Hydraulic and Water Resources EngineeringDocumento2 pagineHawassa University: Department of Hydraulic and Water Resources EngineeringAmanuel AlemayehuNessuna valutazione finora
- Important RCC Questions-Short and LongDocumento15 pagineImportant RCC Questions-Short and LongmailjoelsamuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Design of SlabsDocumento6 pagineAnalysis and Design of SlabsricardoNessuna valutazione finora
- CIV 3164-Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures-I: Department of Civil, Environmental and Geomatics EngineeringDocumento52 pagineCIV 3164-Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures-I: Department of Civil, Environmental and Geomatics EngineeringHakuna MatataNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydraulic Structure PPTSummer MaterialDocumento397 pagineHydraulic Structure PPTSummer MaterialZelalem A.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Isolated - Foundation Design ES en 2015Documento10 pagineIsolated - Foundation Design ES en 2015Dino AbdelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Beams To BS 8110Documento14 pagineDesign of Beams To BS 8110YAHAMPATH ARACHCHIGE PASAN MADURA YahampathNessuna valutazione finora
- RCC32 Ribbed Slabs (A & D)Documento23 pagineRCC32 Ribbed Slabs (A & D)jaffnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of First Floor Slab MKD: S2-S2 Continous Slab Materials UsedDocumento18 pagineDesign of First Floor Slab MKD: S2-S2 Continous Slab Materials UsedNawaz Zac0% (1)
- មេកានិចដី PDFDocumento107 pagineមេកានិចដី PDFMen Keo RathaNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepared BY Dr. Mohammed Kadhum FekheraldinDocumento55 paginePrepared BY Dr. Mohammed Kadhum Fekheraldinhemantkle2uNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE 2306 NOTES I Jan2014Documento22 pagineECE 2306 NOTES I Jan2014TinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Design of Biaxial RC ColumnsDocumento14 pagineComparative Design of Biaxial RC ColumnsMouhamad WehbeNessuna valutazione finora
- One Way Solid SlabDocumento26 pagineOne Way Solid SlabalaajabbarNessuna valutazione finora
- Detail Design of ColumnDocumento7 pagineDetail Design of ColumnAmit TharuNessuna valutazione finora
- Column (1) SRCDocumento17 pagineColumn (1) SRCpratik ranaNessuna valutazione finora
- Footing Subjected To Eccentric LoadingDocumento5 pagineFooting Subjected To Eccentric LoadingPratik DhariwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Soft Story PDFDocumento7 pagineSoft Story PDFאחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S1674987114001327 MainDocumento12 pagine1 s2.0 S1674987114001327 Mainאחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- First Page PDFDocumento1 paginaFirst Page PDFאחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory NA en 1991 EnuDocumento29 pagineTheory NA en 1991 EnutzzutzuNessuna valutazione finora
- Rehabilitation of RC STRUCTURES - 2nd AssignmentDocumento14 pagineRehabilitation of RC STRUCTURES - 2nd Assignmentאחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- Links ProvidedDocumento1 paginaLinks Providedאחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- Hollow Sections ConnectionsDocumento4 pagineHollow Sections Connectionsאחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- Behavior of Diagonal Knee Moment End-Pla PDFDocumento188 pagineBehavior of Diagonal Knee Moment End-Pla PDFאחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- Soft Story PDFDocumento7 pagineSoft Story PDFאחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- FE Civil CBT Specs PDFDocumento4 pagineFE Civil CBT Specs PDFkyleNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods of Solving Number TheoriesDocumento404 pagineMethods of Solving Number Theoriesאחמד סלאח כאמל100% (1)
- B C OFS F: Terzaghi's Bearing Capacity TheoryDocumento1 paginaB C OFS F: Terzaghi's Bearing Capacity Theoryאחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- 3D Closet ModelDocumento1 pagina3D Closet Modelאחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- Sesam ProgramDocumento2 pagineSesam ProgramMarco MorrisNessuna valutazione finora
- S OFS F: Ettelment Hallow OundationsDocumento1 paginaS OFS F: Ettelment Hallow Oundationsאחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- Course 4 (E)Documento45 pagineCourse 4 (E)אחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate Results and Design ForcesDocumento10 paginePlate Results and Design Forcesthirumalaichettiar100% (1)
- Course 1 (E)Documento60 pagineCourse 1 (E)אחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- Course 1 (E)Documento60 pagineCourse 1 (E)אחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- Tank Design: EN 1993 4 2 Eurocode 3Documento31 pagineTank Design: EN 1993 4 2 Eurocode 3אחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- Shape Factors For Bearing Capacity EquationsDocumento1 paginaShape Factors For Bearing Capacity Equationsعبدالوهاب بركاتNessuna valutazione finora
- Depth Factors For Bearing Capacity Equations: Values of D (Inside Table) D /BDocumento1 paginaDepth Factors For Bearing Capacity Equations: Values of D (Inside Table) D /Bאחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- Cons Setlm EqsDocumento2 pagineCons Setlm Eqsאחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- Course 3 (E)Documento56 pagineCourse 3 (E)אחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture03 Types of Foundations PDFDocumento45 pagineLecture03 Types of Foundations PDFאחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- Stabilitate en 2019Documento79 pagineStabilitate en 2019אחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- El-Sayed Bahaa Machaly-Behavior, Analysis and Design of Steel Work Connections. 3-Faculty of Engineering Cairo University (2008)Documento474 pagineEl-Sayed Bahaa Machaly-Behavior, Analysis and Design of Steel Work Connections. 3-Faculty of Engineering Cairo University (2008)אחמד סלאח כאמל100% (1)
- Theory of Structures EL-Dakhakhni P.2 CH.6Documento34 pagineTheory of Structures EL-Dakhakhni P.2 CH.6אחמד סלאח כאמלNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Design Concrete Structures Using Eurocode 2Documento104 pagineHow To Design Concrete Structures Using Eurocode 2Adil Javed Chaudhary97% (36)
- Expenses Claims Data BaseDocumento30 pagineExpenses Claims Data BaseJay BongNessuna valutazione finora
- BIM Capability - SLABS EngineeringDocumento12 pagineBIM Capability - SLABS EngineeringShabbir LokhandwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- HM Esc: For DN 100 See HMESC 840202 SeriesDocumento8 pagineHM Esc: For DN 100 See HMESC 840202 SeriesNam Nguyen VanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hindu College of Design, Architecture & Planning, Industrial Area, SONEPAT-131001Documento1 paginaHindu College of Design, Architecture & Planning, Industrial Area, SONEPAT-131001charuNessuna valutazione finora
- AE For Provn of Shed at Entry GateDocumento15 pagineAE For Provn of Shed at Entry GatePARMESHWAR KUMAR VERMANessuna valutazione finora
- Critical Regionalism: Studies On Contemporary Residential Architecture of Khartoum - SudanDocumento14 pagineCritical Regionalism: Studies On Contemporary Residential Architecture of Khartoum - SudanMaha Omer BaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Steel For CRCP Reinforcement (IRC-118-2015)Documento6 pagineDesign of Steel For CRCP Reinforcement (IRC-118-2015)Sneh KhandelwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Internship at Simplex Infrastructure LTDDocumento46 pagineInternship at Simplex Infrastructure LTDSanthosh HMNessuna valutazione finora
- Koflan Catalogue Taps October 2022Documento12 pagineKoflan Catalogue Taps October 2022Benjamin ngilaNessuna valutazione finora
- NSC LWD TP 105 - Tree Plan GFC R1-ModelDocumento1 paginaNSC LWD TP 105 - Tree Plan GFC R1-ModelSachin GandhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mies Van Der Rohe and The Philosophy of WorkDocumento5 pagineMies Van Der Rohe and The Philosophy of WorkLira CroninNessuna valutazione finora
- Rahmath Saidabad QuotationDocumento4 pagineRahmath Saidabad Quotation43MOHAMMED SIDDIQ MOHIUDDINNessuna valutazione finora
- BSR 2019Documento109 pagineBSR 2019aflal100% (3)
- SR Activity Godrej Query Pil Response Dr. Fixit Fastflex - Pull Off Adhesion 1Documento3 pagineSR Activity Godrej Query Pil Response Dr. Fixit Fastflex - Pull Off Adhesion 1শুভাশীষ গাঙ্গুলীNessuna valutazione finora
- Dams in Nashik DistrictDocumento15 pagineDams in Nashik DistrictNikhilNessuna valutazione finora
- PresentationDocumento28 paginePresentationMike Schaeffer100% (1)
- 2 PDFDocumento41 pagine2 PDF123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Palestine Building CodesDocumento20 paginePalestine Building Codesrami zughayar100% (1)
- Project Brief of VedapatashalaDocumento2 pagineProject Brief of VedapatashalaStructural Dept. SatyaVaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Tara Residences BrochureDocumento9 pagineTara Residences BrochureRochelle Ciudad BaylonNessuna valutazione finora
- Cladding Installation: Cembrit CembonitDocumento39 pagineCladding Installation: Cembrit CembonitVranceanu Vlad-gabrielNessuna valutazione finora
- ShotcreteDocumento26 pagineShotcreteMohamed Nk100% (1)
- Location: Chennai Outer Ring Road Project: Ashoka Buildcon LTDDocumento22 pagineLocation: Chennai Outer Ring Road Project: Ashoka Buildcon LTDrushikshNessuna valutazione finora
- HAMPIDocumento13 pagineHAMPIJoseph Kurian Mullasseril50% (2)
- Crawl Space Plastic Visqueen ProjectsDocumento1 paginaCrawl Space Plastic Visqueen ProjectsRahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Reinforced Concrete DesignDocumento29 pagineReinforced Concrete DesignChristian Angelo ButacNessuna valutazione finora
- Shotcrete - Advanced Technology in Civil Engineering: Chandra Pratap Singh, Nishant Rana, Siddhant RanaDocumento4 pagineShotcrete - Advanced Technology in Civil Engineering: Chandra Pratap Singh, Nishant Rana, Siddhant RanaRajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Green Building MaterialDocumento22 pagineGreen Building MaterialAmrutha PavithranNessuna valutazione finora
- Molo MansionDocumento1 paginaMolo MansionKryla Anika JamerlanNessuna valutazione finora
- There-Is-There-Are DirectionsDocumento1 paginaThere-Is-There-Are DirectionsLaura BarraganNessuna valutazione finora