Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Physics
Caricato da
youssefDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Physics
Caricato da
youssefCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Math: Grade 1, Semester 1
Math: Grade 1, Semester 2
Math: Grade 2, Semester 1
Math: Grade 2, Semester 2
Math: Grade 3, Semester 1
Math: Grade 3, Semester 2
Printed on October 15, 2015
Math: Grade 1, Semester 1
Matter, Form and Function
Big Idea: We use mathematical modeling with a variety of classes of functions to solve applications such as in
biology and finance, and to form a basis for the study of mechanics and calculus.
MA.1.01 - Create, interpret and analyze trigonometric ratios that model real-world situations. (Week 01 -
Week 05)
Essential Questions: ‣ "Why is modeling an indispensable tool?
‣ Why do we represent phenomena in multiple ways?"
Skills:
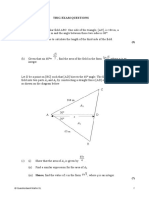
‣ A. Sine, cosine, and tangent ratios and Pythagorean Theorem
‣ B. Define the six trigonometric functions in terms of right triangles.
‣ C. Determine which quadrants have positive and negative trigonometric values
‣ D. Derive sine and cosine law
‣ E. Solving triangles (using law of sine and cosine)
‣ F. Use the law of sines, law of cosines to solve applied problems.
‣ G. Use the inverses of the sine, cosine, and tangent to solve problems.
Concepts:
‣ A. Unit circle
‣ B. Six trigonometric functions
‣ C. Related angles
‣ D. Sine law , cos law
‣ E. Angle of elevation and angle of depression
Evidence:
Problem Set 1.8 - BA #3, ST #6d
Problem Set 3.1 - BA #6, 10, ST #9
Problem Set 3.2 - BA #5, ST #7c
Problem Set 3.3 - BA #7, ST #8
Problem Set 3.6 - BA #1, ST # 8
Texts & References: Math Connections 2a sections 1.8, 3.1 - 3.4 , 3.6, 3.7
See materials in Unit Materials folder:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/0B9KK7ZY6QeS3dGlETUVNQ0c2em8
Capstone Connection: Determine the dimensions of the sustainable houses
Grand Challenge Connections: Improve the use of alternative energies to reduce our reliance on extracted
fuel sources,Increase efficient use of our land through improved use of arid areas,Increase industrial base
for Egypt,Recycle and retain garbage for recycling
Topic: Right triangle trig
MA.1.02 - Apply the relationships between 2-D and 3-D objects in modeling situations (Week 06 - Week 10)
Printed on October 15, 2015
Essential Questions: Why is the world 3-D?
Skills:
‣ A. Draw 2-D cross-sections of a representation of a 3-D object.
‣ B. Identify three dimensional objects created by rotations of two dimensional objects
‣ C. Describe 3-D shapes
‣ D. Create 3-D shapes
Concepts:
‣ A. Cross section
‣ B. 2-Dimensional objects
‣ C. 3-Dimensional objects
‣ D. Classifying regular polyhedra
Evidence:
Problem Set 5.1 BA:p 466 # 1 a, b, ST:466 # 1 c
Assessment in "2D Representations of 3D Objects"
Texts & References: Math Connections Geometry 2b Section 5.1
See materials in the Unit Materials Folder:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/0B10u0LfTYd6hflM3QkZnM0JCM1B6bzR5T3F6dktnN0RkdFBJb3RpS
XdBLTRuMlVIbVZGWW8
Capstone Connection: Building house
Grand Challenge Connections: Reduce urban congestion and its impact,Increase opportunities for
Egyptians to stay and work in Egypt
Topic: 2-D/3-D Objects
MA.1.03 - Understand similarity and use the concept for scaling to solve problems (Week 06 - Week 10)
Essential Questions: Why are relationships predictable?
Skills:
‣ A. Determine axes of similarity
‣ B. Draw the image of a shape (using reduction and magnification)
‣ C. Solve problems and applications using proportionality theorems
‣ D. Prove the angle bisector theorem
‣ E. Stretching and Shrinking Angles and Areas
‣ F. Stretching and Shrinking Volumes
‣ G. Finding the scaling factor(area and volume)
‣ H. Solve problems related to geometric shapes "
Concepts:
‣ A. Similarity
‣ B. Transformation( reduction and magnification)
‣ C. Proportionality
‣ D. Parallel lines and proportional parts
‣ E. Angle bisectors
Evidence:
Geometry Packet Basic Application- page 4, page 16 #7, page 25 bottom chart
Geometry Packet Strategic Thinking Pages 12, 18
Printed on October 15, 2015
Math Connections Geometry 2a, 2.10 BA - #5
Geometry Packet Strategic Thinking page 31 #4, page 36, page 38
Texts & References: Geometry Packet in the Unit Materials Folder pages 1 to 25
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/0B10u0LfTYd6hfkllWmNyWHcwRDdRWXJ5T05peldMVFBtemtscTczU
1lDaEVvaWo4aTZ6bDg
Math Connections 2a 1.10
Math Connections Geometry 2a, 2.9, 2.10
Geometry Packet in the Unit Materials Folder pages 27 to 38
Capstone Connection: Building house
Grand Challenge Connections: Reduce urban congestion and its impact,Increase opportunities for
Egyptians to stay and work in Egypt,Increase industrial base for Egypt,Recycle and retain garbage for
recycling
Topic: Similarity, scaling
MA.1.04 - Apply volume formulas (pyramid, cones, spheres, prisms) (Week 06 - Week 10)
Essential Questions: How does what we measure influence how we measure?
Skills:
‣ A. Derive the formulas of areas and volumes
‣ B. Determine area and volume of different shapes and figures
‣ C. Determine volume of a composite figures
Concepts:
‣ A. Area
‣ B. Volume
‣ C. Composite figures
Evidence:
Math Connections 5.3 Basic Application #3
Math Connections 5.4 Strategic Thinking #7
Texts & References: Math Connections 2b 5.3-5.4
See materials in Unit Materials folder:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/0B10u0LfTYd6hfjJHNDFJTGpkVlQ1S040Z2JIOWhRS3JENkFQUzNV
VzdZNEM2QlNLckU1Mlk
Capstone Connection: Building house
Grand Challenge Connections: Reduce urban congestion and its impact,Increase opportunities for
Egyptians to stay and work in Egypt
Topic: Volume
MA.1.05 - Create, interpret and analyze functions, particularly linear and step functions that model real-world
situations. (Week 11 - Week 13)
Essential Questions: ‣ Why is modeling an indispensable tool?
Printed on October 15, 2015
‣ Why do we represent phenomena in multiple ways?
‣ How does data help make sense of the world around us?
Skills:
‣ A. Given data, create functions that model applied situation. Calculate a least squares regression
line, understand its properties, compute and interpret correlation for data
‣ B. Interpret the functions based on the real-world situation they model
‣ C. Analyze the functions and their characteristics. Explain the different properties of the algebraic
function and its graph.
‣ D. Identify, interpret and describe real-world step functions
‣ E. Analyze direct and inverse variations based on the real-world situation they model.
‣ F. Graph linear, piecewise, absolute value and step functions
‣ G . Find the inverse of some functions algebraically and graphically and determine if the inverse is
a function. (Also: Distinguish between "inverse variation" and "inverse function.")
‣ H. Solve real life application on functions
Concepts:
‣ A. Linear functions
‣ B. Piecewise function
‣ C. Absolute-Value Functions
‣ D. STEP function
‣ E. Direct variation
‣ F. Inverse variation
‣ G. Regression
‣ H. Correlation
‣ I. Correlation coefficient
‣ j. Slope
‣ K. Intercepted part
‣ L. Composition of Functions
‣ M.Translation of linear function
Evidence:
Quiz : https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/0B9KK7ZY6QeS3NGZVd25rbWhmS2c
Math Connections 1a
Basic Application Problem Set 4.5 #1
Strategic Thinking Problem Set 4.5 #6
Math Connections 1b
Basic Application Problem Set 6.1 #2, Problem Set 6.3 # 3, Problem Set 6.4 #6 a through c, Problem set 6.6
# 2 (any of them)
Strategic Thinking Problem Set 6.1 #8, Problem Set 6.4 #6 d, Problem Set 6.6 #6c
Texts & References: Math Connections 1A 3.4 - 3.6, 4.4 - 4.5
Math Connections 1B 6.1 - 6.4, 6.6
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=npBg0Ynv4D0
See material in Unit Materials folder
Capstone Connection: Building house
Printed on October 15, 2015
Grand Challenge Connections: Reduce urban congestion and its impact,Increase opportunities for
Egyptians to stay and work in Egypt
Applications: PH.1.08, PH.1.09, PH.1.11, PH.1.12, ME.1.02, ME.1.04, CH.3.15,
Topic: linear, piecewise, absolute value
MA.1.06 - Analyze, display and describe quantitative data with a focus on standard deviation. (Week 14 -
Week 14)
Essential Questions: ‣ How can graphical displays be manipulated to present misleading
information?
‣ How can data analysis be used to predict future happenings?
‣ Does the data always lead to the truth? Why or why not?
Skills:
‣ A. Describe the overall pattern (shape, center, spread) of a distribution and identify any major
departures from the pattern (like outliers).
‣ B. Make a histogram, dotplot, boxplot or stemplot to display small sets of data and interpret the
data.
‣ C. Identify the shape of a distribution (symmetric or skewed) from a dotplot, stemplot, or histograms
‣ D. Calculate and interpret measures of center (mean, median) and spread (IQR, standard
deviation).
‣ E. Use appropriate graphs and numerical summaries to compare distributions of quantitative
variables.
Concepts:
‣ A. Shape, center, spread
‣ B. Outliers
‣ C. histogram
‣ D. Dotplot
‣ E. Boxplot
‣ F. Stemplot
‣ G. Skewed
‣ H. Symmetric
‣ I. IQR
‣ J. Standard deviation
Evidence:
The Practice of Statistics
Section (1-2) Exercises
Basic Application #38 a
Strategic Thinking #49b
section (1-3) Exercises
Basic Application Check Your Understanding #1,2,3
Strategic Thinking #98b, c
Chapter 1 Chapter Review Exercises
Printed on October 15, 2015
Strategic Thinking R1.3
Texts & References: Starnes, Daren - Tabor, Josh - Yates, Daniel - Moore, David, The Practice of
Statistics, New York: W.H. Freeman, 2015, 5th Edition
Exploring Data (Chapter 1)
Capstone Connection: geometry and measurement
Grand Challenge Connections: Address the exponential population growth and prepare for the
impact,Improve the use of alternative energies to reduce our reliance on extracted fuel sources,Reduce
urban congestion and its impact,Increase opportunities for Egyptians to stay and work in Egypt,Increase
industrial base for Egypt
Topic: Quantitative data
Printed on October 15, 2015
Math: Grade 1, Semester 2
Energy Force and Power
Big Idea: We use mathematical modeling with a variety of classes of functions to solve applications such as in
biology and finance, and to form a basis for the study of mechanics and calculus.
MA.1.07 - Create, interpret and analyze quadratic functions that model real-world situations. (Week 01 -
Week 04)
Essential Questions: ‣ Why do we need an imaginary world?
‣ How can things be real and imaginary?
Skills:
‣ A. Use first and second differences to create models that represent data
‣ B. Interpret the functions based on the real-world situation they model.
‣ C. Analyze the functions and their characterisitcs. Explain the different properties of the algebraic
function and its graph
‣ D. Review solving quadratic equations using completing squares
‣ E. Find the inverse of a quadratic function graphically and algebraically (completing the square) and
determine how to make the inverse a function.
‣ F. Graph quadratic function
‣ G. Relation between roots of quadratic function and the coefficient
‣ H. Form Quadratic equation
‣ I. Related roots
‣ J. Parabola: focus, directrix,
‣ K.Write quadratic equation in parabolic form
‣ L. Real life application on parabola
‣ M. Use the quadratic formula to find real solutions to quadratic equations; identify graphically and
algebraically when a quadratic equation has no real solution
‣ N. Use the quadratic formula to find complex solutions to quadratic equations
‣ O. Represent complex numbers three ways: as ordered pairs, graphically on the coordinate plane,
and in the form a+bi
‣ I. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide complex numbers
Concepts:
‣ A. Quadratic Function
‣ B. First and second differences
‣ C. Completing the square
‣ D.complex numbers
‣ E. parabola
‣ F. Focus
‣ G. Argand diagram
‣ H. related roots
Evidence:
Math Connections 3A Algebra 2 Basic Application Problem Set 1.2 #5a
Math Connections 3A Algebra 2 Basic Application Problem Set 1.5 #3
Printed on October 15, 2015
Math Connections 3A Algebra 2 Strategic Thinking Problem Set 1.2 #5a, #5c
Math Connections 3A Algebra 2 Strategic Thinking Problem Set 1.5 #5
Texts & References: Math Connections 3A Algebra 2 sections 1.2, 1.3 pages 11 - 36
Math Connection Algebra 1B Sections 8.4
Math Connections 3A Algebra 2 sections 1.5
See materials in Unit Materials folder
Capstone Connection: using the graphs of quadratic function in modeling solar cell
Grand Challenge Connections: Reduce urban congestion and its impact,Increase opportunities for
Egyptians to stay and work in Egypt
Applications: PH.1.10, PH.1.08, PH.1.09, PH.1.11, PH.1.12, ME.1.04,
Topic: Quadratic function
MA.1.08 - Create, interpret and analyze exponential and logarithmic functions that model real-world
situations. (Week 05 - Week 07)
Essential Questions: ‣ "Why is modeling an indispensable tool?
‣ Why do we represent phenomena in multiple ways?
‣ How does data help make sense of the world around us?
‣ Why do we need laws/rules?"
Skills:
‣ A. Use different properties of exponential and logarithmic functions
‣ B. Interpret and manipulate rational exponents
‣ C. Use exponential functions to describe growth and decay ratios
‣ D. Construct exponential growth and decay functions to fit given data
‣ E. Solve compound interest problems.
‣ F. Reveal and explain different properties of the exponential function and its graph
‣ G. Graph exponential functions, find its domain and range
‣ H. Describe the inverse of an exponential function as a logarithm
‣ G. Graph logarithmic functions, find its domain and range.
‣ I. prove the logarithm rules
‣ J. solve logarithmic and exponential equations
‣ K. solve real life application
Concepts:
‣ A. Exponential functions
‣ B. Logarithmic function
‣ C. Growth
‣ D. Decay
Evidence:
Basic Application - Math Connections 3A Problem Set 2.8 p.213, # 3a, b or Quiz in Unit Materials folder:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/0B9KK7ZY6QeS3cEpJZGlYNzFzWVk
Strategic Thinking - Math Connections 3A Problem Set 2.6 p.197, 6d, e, Math Connections 3a P.221 #10 d,
e, Math Connections 3a Problem Set 2.8p.213, 3c, d
Printed on October 15, 2015
Texts & References: Math Connections 3a sections 2.1 - 2.8 and pages 217-226
http://betterlesson.com/community/document/219143/unit-08-
day-06-notes-guided-practice-properties-of-logs-logarithms-
pdf
For graph: https://www.desmos.com/calculator
See materials in Unit Materials folder:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/0B9KK7ZY6QeS3cEpJZGlYNzFzWVk
Capstone Connection: inform alternative energy geometries, using graphs in solar cells
Grand Challenge Connections: Reduce urban congestion and its impact,Improve Sources of Clean
Water,Reduce pollution fouling our air water and grounds
Applications: CH.2.03, PH.1.11, PH.1.12, PH.1.09, PH.1.08, ES.3.06, ES.2.09, CH.1.06,
Topic: Exponential, Logarithmic
MA.1.09 - Create, interpret and analyze trigonometric functions that model real-world situations. (Week 08 -
Week 11)
Essential Questions: ‣ Why is modeling an indispensable tool?
‣ Why do we represent phenomena in multiple ways?
Skills:
‣ A. Relate the coordinates of points on the unit circle to the sine and cosine of angles
‣ B. Extend the domain of trigonometric functions using the unit circle (convert between radians and
degrees)
‣ C. Draw and identify positive, negative, and co-terminal angles of rotation
‣ D. Describe the inverses of the sine, cosine and tangent functions and explain the relationship
between sine, cosine, tangent and their inverses
‣ E. Identify different characteristics of sine, cosine and tangent functions: shape, domain, range,
amplitude, intercepts, max/min, period, asymptotes.
‣ F Use technology to explore and analyze various functions..
‣ G. Describe the transformations that shift and stretch a trigonometric function
‣ H Interpret the functions created based on the real-world situation they model.
Concepts:
‣ A. Trigonometric functions.
‣ B. Coordinates
‣ C. Graphs of sine, cosine and tangent functions
‣ D. Inverses of the sine, cosine and tangent functions
‣ E. Shape, domain, range, amplitude, intercepts, max/min, period, asymptotes.
‣ F. Domain of trigonometric functions
‣ G. Positive, negative, and co-terminal angles of rotation
‣ H. Shift and stretch a trigonometric function
Evidence:
Math Connections Book 3A
Basic Application: P.274 #2a,b,c P.280 #10a,b,c,d
Printed on October 15, 2015
Strategic Thinking: P.264 #3 P274 #2d,e, #3b P.280 #10e,f P.289 #6b
Texts & References: Math Connections 3a sections 3.1 - 3.6
Capstone Connection: inform alternative energy geometries, using graphs in solar cells
Grand Challenge Connections: Reduce urban congestion and its impact,Increase industrial base for Egypt
Topic: Trigonometric graphs
MA.1.10 - Prove and apply trigonometric identities (Week 08 - Week 11)
Essential Questions: Can things change and still be the same?
Skills:
‣ A. Derive and apply the Pythagorean Identities
‣ B. Manipulate and apply cofunction Identities"
Concepts:
‣ A. Trigonometric identities
‣ B. Pythagorean Identities
‣ C. Cofunction Identities
Evidence:
Basic Application: Math Connections 3A Algebra 2
Page 315 3.47 any of those problems
Strategic Thinking: Students create a trigonometric identity that involves cosine, sine and tangent.
Texts & References: Math Connections 3A Algebra 2 pages 307 - 316
Capstone Connection: inform alternative energy geometries.
Grand Challenge Connections: Increase industrial base for Egypt
Topic: Trigonometric identities
MA.1.11 - Create, interpret and analyze systems of linear functions that model real-world situations. (Week
12 - Week 14)
Essential Questions: ‣ Why is modeling an indispensable tool?
‣ Why do we represent phenomena in multiple ways?
‣ How do humans make informed decisions, given multiple options?
‣ What factors affect our decisions and how dothese factors relate to mathematical models?
Skills:
‣ A. Solve a system of two equations and two unknowns by graphing and algebraic methods
‣ B. Interpret the solution of a system in context of the situation
‣ D. Represent a system as a matrix
‣ E. Apply matrix operations to solve a system
‣ F. Use matrices to represent real-world situations and interpret their solution
‣ G. Reduce matrices to RREF and interpret the meaning
‣ H. Determine and interpret optimal solutions and the constraints to real-world situations using
Linear Programming
‣ I Write objective functions
Concepts:
‣ A. System
Printed on October 15, 2015
‣ B. System of equations
‣ C. Unknowns
‣ D. Graphing methods
‣ E. Algebraic methods
‣ F. Matrix
‣ G. Operations
‣ A. Linear Programming
‣ B. Objective functions
‣ C. Feasible regions
‣ D. Constraints
‣ E. Optimal solution
Evidence:
Math Connections Geometry 2B Basic Application Problem Set 6.4 #7a
Math Connections Geometry 2B Basic Application Page 631, #6.49
Math Connections Algebra 2 3A Basic Application Page 332 # 3 a, b
Math Connections Algebra 2 3A Basic Application Page 352 # 3 a, b
Math Connections Geometry 2B Strategic Thinking Problem Set 6.4 #7b
Math Connections Geometry 2B Strategic Thinking Page 631, #6.50
Math Connections Algebra 2 3A Basic Application Page 352 # 3c
Texts & References: Math Connections 2b, sections 6.1 - 6.5
Math Connections 3a sections 4.1 - 4.4
Capstone Connection: Modeling with Energy
Grand Challenge Connections: Address the exponential population growth and prepare for the
impact,Improve the use of alternative energies to reduce our reliance on extracted fuel sources,Increase
industrial base for Egypt
Topic: Systems, determinant, constraint
MA.1.12 - Apply determinants and their properties in real-world situations (Week 12 - Week 14)
Essential Questions: ‣ Why use shortcuts?
‣ Why is it essential to have different ways of reaching solutions?
Skills:
‣ A. Use the properties of determinants to determine the value of a determinant
‣ B. Solve real-world applications of determinants particularly finding the area of parallelogram and
triangle.
‣ C. Solve a system of linear equations using Cramer's Rule
Concepts:
‣ A. Determinants
‣ B. Value of a determinant
‣ C. Area, parallelogram and triangle.
‣ D. Matrices
‣ E. System of equations
Printed on October 15, 2015
‣ F. Cramer's Rule
Evidence:
Unit in Materials Folder: Determinants
Basic Application: Page 24 #41 - 48
Basic Application: Page 25 #59
Strategic Thinking: Page 26 #76
Strategic Thinking: Page 26 # 78
Texts & References: See materials in Unit Materials Folder: Determinants
Practice Problems: Determinants, Area, and Volume Formative Assessment Problems.
Capstone Connection: inform alternative energy geometries.
Grand Challenge Connections: Improve Sources of Clean Water,Increase industrial base for Egypt
Applications: PH.2.02,
Topic: Determinant, Cramer's Rule
Printed on October 15, 2015
Math: Grade 2, Semester 1
Change, Equilibrium and Cycles
Big Idea: The study of probability enables prediction of the future.
MA.2.01 - Create, interpret and analyze polynomial and absolute value functions that model real-world
situations. (Week 01 - Week 04)
Essential Questions: ‣ Why is modeling an indispensable tool?
‣ Why do we represent phenomena in multiple ways?
Skills:
‣ A. Reveal and explain different properties of the algebraic function and its graph
‣ B. Model real-world situations using polynomial and absolute value functions.
‣ C. Perform operations with polynomials
‣ D. Find the roots of polynomial equations algebraically
‣ E. Construct a polynomial curve through specific points on a horizontal line
‣ F. Understand how the degree of the function determines the attributes of a graph. (turning points,
symmetry, even/odd)
‣ G. Find the inverse graphically and algebraically of a function
‣ H. Identify and use the reciprocal function and the absolute value function
Concepts:
‣ A. Polynomial
‣ B. Absolute value,
‣ C. Inverse of a function
‣ D. Algebraic function
‣ E. Operations with polynomials
‣ F. Roots of polynomial equations
‣ G. Polynomial curve
‣ H. Polynomial functions.
‣ I. Degree of the function
‣ J. Attributes of a graph. (turning points, symmetry, even/odd)
Evidence:
Recall: p. 88 #2e, #4
Basic Application: p.76 #2, p.97 #8
Strategic Thinking: p.76 #7, p.109 #6b, p.110 #7e
Texts & References: Math Connections 1b pages 667 - 676
Math Connections 3a Chapter 1.7 - 1.10
Capstone Connection: Apply to water treatment analysis if appropriate
Grand Challenge Connections: Improve Sources of Clean Water
Topic: Polynomial Function, Absolute Value Function
MA.2.02 - Create, interpret and analyze rational functions that model real-world situations. (Week 05 - Week
06)
Printed on October 15, 2015
Essential Questions: ‣ Why is modeling an indispensable tool?
‣ Why do we represent phenomena in multiple ways?
Skills:
‣ A. Reveal and explain different properties of the algebraic function and its graph
‣ B. Model real-world situations using rational functions.
‣ C. Factor and simplify all rational polynomial expressions completely and describe the process.
‣ D. Describe and sketch rational functions, their zeros and their asymptotes.
Concepts:
‣ A. Rational polynomial expressions
‣ B. Sketch rational functions,
‣ C. Vertical asymptotes of rational functions .
‣ D. Horizontal asymptotes of rational functions
Evidence:
Recall: Activity (7.65)#1a, p.653 #5, p.681 #5
BA: Activity (7.65) #1b, p.654 #6, p.678 #7.88
ST: 3. For what positive number is the sum of the number and its reciprocal smallest?
(Answer: If x is the number, then is the reciprocal. Therefore the sum of a number and its reciprocal is
represented by . Graph the function for positive x-values. The minimum occurs at the point (1,2).) OR
Texts & References: Math Connections 3b Chapter(7-8) pages 643 - 654
Math Connections 3b pages 673-681 operations with rational expressions
Capstone Connection: Apply to water treatment analysis if appropriate
Grand Challenge Connections: Improve Sources of Clean Water,Increase industrial base for
Egypt,Reduce pollution fouling our air water and grounds
Topic: Rational functions, asymptotes
MA.2.03 - Represent, analyze and solve counting problems (Week 07 - Week 10)
Essential Questions: ‣ Is order really important?
‣ Why predict the future
Skills:
‣ A. Use the Fundamental Counting Principle to solve counting problems
‣ B. Use permutations to solve counting problems
‣ C. Solve counting problems where some elements are alike
‣ D. Solve counting problems in which order is not important
‣ E. Determine a combination of n objects taken r at a time
‣ F. Use factorials count combinations
Concepts:
‣ A. Fundamental Counting Principle
‣ B. Permutations
‣ C. Combinations
‣ D. Factorials
Evidence:
Printed on October 15, 2015
Recall: p. 408#5
BA: p.408 # 6, p. 424 #4a
ST: p. 424 #6, #7
Texts & References: Math Connections 1b Chapter 7.3
Math Connections 3B Chapter 5.2, 5.4
Capstone Connection: Apply to water treatment analysis if appropriate
Grand Challenge Connections: Improve Sources of Clean Water,Increase industrial base for Egypt
Topic: Permutations, Combinations
MA.2.04 - Know and apply the Binomial Theorem (Week 11 - Week 11)
Essential Questions: ‣ Is order really important?
‣ Why predict the future
Skills:
‣ A. Know and understand the binomial theorem and row sums (Pascal's Triangle)
‣ B. Explain the expansion of (x+y)^n in powers of x and y for a positive integer n, where x and y are
any numbers.
Concepts:
‣ A. Pascal's Triangle
‣ B. Binomial Theorem
Evidence:
Recall:ِOnline Quiz http://www.cliffsnotes.com/math/algebra/algebra-ii/additional-topics/quiz-binomial-
coefficients-and-the-binomial-theorem
BA:
ST:
Texts & References: Math Connections 3a - pages 87 and 89
http://www.mathcentre.ac.uk/resources/tests/swf/Algebra/Exercises/2-05ae.swf
Capstone Connection: Apply to water treatment analysis if appropriate
Grand Challenge Connections: Improve Sources of Clean Water
Topic: Binomial Theorem, Pascal's Triangle
MA.2.05 - Use rules of probability to solve problems and predict behavior. (Week 12 - Week 14)
Essential Questions: ‣ What is fair?
‣ What is luck?
‣ What would the world be without risk?
Skills:
‣ A. Explain probability as a numerical description, between 0 and 1, of the likelihood of an event
‣ B. Interpret probability as a long run relative frequency
‣ C. Draw tree diagrams to represent and solve counting problems
‣ D Determine a set of possible outcomes
‣ E. Use fundamental counting principal to solve problems
‣ F. Use the rules of probability to compute probabilities of compound events in a uniform probability
Printed on October 15, 2015
model.
‣ G. Calculate expected values and use them to solve problems (heritable traits and diseases)
Concepts:
‣ A. Probability
‣ B. Prediction
‣ C. Event
‣ D. Likelihoods
‣ E. Tree diagram
‣ F. Independent
‣ G. Conditional
‣ H. Compound events Probability
‣ I. Expected values
Evidence:
Recall : p.435 #6
BA : p. 564 #2a - f, p.597 #6, #7, p.446 #6
ST :p.564 #2g, p.598 #7.86
Texts & References: Math Connections 1b sections 7.4 - 7.6 and pages 593 - 600
Math Connections 3b sections 5.5 and 5.7 and pages 469 - 471
Capstone Connection: Apply to efficacy of treatment and contamination (LD50)
Grand Challenge Connections: Improve Sources of Clean Water
Topic: Probability, likelihood, independent/dependent events
Printed on October 15, 2015
Math: Grade 2, Semester 2
Systems and Feedback
Big Idea: Differential calculus enables greater application of classes of functions studied in grade 1.
MA.2.06 - Identify and analyze continuity and limits and connect them to graphs of functions. (Week 01 -
Week 03)
Essential Questions: ‣ Why do we need limits?
‣ How close is close?
Skills:
‣ A. Determine and prove the limit of a function at a given x value if it exists, including limits involving
infinity. If not, explain, why?
‣ B. Differentiate between step, infinite and removable discontinuity
‣ C. When given a function, explain why it might not be continuous by using the definition of
"continuity" and determining which part(s) of the definition is not met.
‣ D. Given certain characteristics, sketch a graph.
Concepts:
‣ A. Limits
‣ B. Continuity
‣ C. Discontinuity: step, infinite and removable
Evidence:
Recall : p.43 #9, 10, p.64 R1,
Basic application: p.44 #19, P.68 #T9, p.70 #T18
Strategic thinking: p. 45 #23, p.67 #3, Exploration 2-5a #7, p.70 #T16
Texts & References: Foerster Calculus Concepts and Applications: Chapter 2
Foerster Calculus Concepts and Applications: Exploration 2-1a, 2-2a, 2-3a, 2-3b, 2-3b, 2-4a, 2-5a, 2-7a, 2-
7b
Capstone Connection: graphical representation of new business numbers
Grand Challenge Connections: Increase industrial base for Egypt
Topic: Continuity, Limits
MA.2.07 - Given the equation of a function, apply the derivative of that function to solve real-world problems.
(Week 04 - Week 06)
Essential Questions: ‣ How do you know if the information you have is enough, too little or too
much?
‣ When is it better to memorize and when is it better to understand?
Skills:
‣ A. Given the equation of a function, calculate and analyze the derivative at a given point
algebraically, numerically and graphically.
‣ B. Graph the function and its derivative function and draw conclusions about the relationship
between the derivative function and the original function.
Printed on October 15, 2015
‣ C. Determine f ' (x) given a power function, using the properties of differentiation in a real world
situation.
‣ D. Determine the derivative of a composite function using the chain rule and apply this to real-world
situations.
‣ E. Determine the derivative using the product and quotient rule and apply to situations.
‣ F. Use "differentiability implies continuity."
‣ G. Apply the Mean Value Theorem and Rolle's Theorem to determine the location at which the
instantaneous rate of change is identical to the average rate of change in problem situations.
Concepts:
‣ A. Derivative
‣ B. Limit
‣ C. Difference quotient
‣ D. Power Function
‣ E. Reducing the exponent
‣ F. Differentiation
‣ G. Composite function.
‣ H. Chain rule.
‣ I. Quotient Rule
‣ J. Derivative function
‣ K. Rolle's Theorem
‣ L. Mean Value Theorem
‣ M. Instantaneous rate of change
‣ N. Average rate of change
Evidence:
Recall : p. 76 #5,9,12 p.90 #11, #18 p.105 #2
Basic application:p. 77 #16e p.91 #29 Also see "MA 2.07 Basic Application Problem" in materials folder
(blue)
Strategic thinking: p.78 #20 p.92 #38 Exploration 3-3b #3, #4 p.106 #29d
Texts & References: Foerster Calclus Concepts and Applications: Chapter 3 3.1 - 3.4, 3.7
Foerster Calclus Concepts and Applications: Chapter 4 Sections 4.1 - 4.3, 4.6, 5.5
(P. 131-141 - 153-159, 211-220)
Foerster Calclus Concepts and Applications: Exploration 3-2a, 3-3a, 3-3b, 3-4a, 3-7a, 4-2a, 4-3a, 4-6a, 4-
6b, 5-5a
Capstone Connection: Rate of change applied to growth numbers for a new business
Grand Challenge Connections: Improve Sources of Clean Water,Increase industrial base for Egypt
Topic: Differentiation, Chain rule
MA.2.08 - Analyze the rates of change of a sinusoidal, exponential and logarithmic functions in real-world
problems. (Week 07 - Week 09)
Essential Questions: ‣ How do you know if the information you have is enough, too little or too
much?
‣ When is it better to memorize and when is it better to understand?
Skills:
Printed on October 15, 2015
‣ A. Define the derivatives of the sin and cosine functions.
‣ B. Differentiate each of the six trigonometric functions
‣ C. Analyze the derivative and graph of a sinusoidal function in terms of the motion of an object
‣ D. Given an exponential or logarithmic function find its' derivative function algebraically
‣ E Find and use the derivative of the natural logarithm"
‣ F. Use and apply the derivative of an exponential function to calculate population, compound
interest and depreciation.
Concepts:
‣ A. Rates of change
‣ B. Exponential and logarithmic functions
‣ C. Derivatives
‣ D . Differentiability
‣ E. Derivative function algebraically
‣ F. Derivative of the natural logarithm"
‣ G. Trigonometric functions
‣ H. Logarithmic differentiation
‣ i. L'Hopital's Rule"
Evidence:
*****Please provide evidence.
Texts & References: Foerster Calculus Chapter 3
3.6, 3.8, 3.9, 3.10, 4.4, 4.5
Foerster Calculus Concepts and Applications: Exploration 3-6a, 3-8a, 3-9a, 4-5a
Capstone Connection: apply rates to periodic functions of business (supply, product, cash flow).
Grand Challenge Connections: Increase opportunities for Egyptians to stay and work in Egypt,Increase
industrial base for Egypt
Topic: Derivatives
MA.2.09 - Apply the indefinite integral to model and solve problems (Week 10 - Week 12)
Essential Questions: ‣ When can an action be undone?
‣ Is the whole the sum of its parts? Or, is the whole greater than the sum of its parts? Or is the whole
less than the sum of its parts?
Skills:
‣ A. Use the definite integral to find the area of a region between two graphs, to find displacement
given the velocity.
‣ B. Use properties of indefinite and definite integral
‣ C. Use Reimann sums
‣ D. Use Fundamental theorem of Calculus
‣ E. Use integrals in applied problem situations: area, displacement given velocity, work and heat
problems.
Concepts:
‣ A. indefinite integral
‣ B. integration of power function
‣ C. integration of trigonometric functions
Printed on October 15, 2015
‣ D. integration of exponential function e^x , a^x
Evidence:
Recall :problem 11, 12
Basic application:problem 4, 5, 6
Strategic thinking: problem 10, 20, 21
*****Please provide page numbers for the evidence.
Texts & References: Foerster Calculus Concepts and Applications: Chapter 5
5.2 - 5.4, 5.6-5.8
Foerster Calculus Concepts and Applications: Exploration 5-2a, 5-2b, 5-4a, 5-6a, 5-6b, 5-7a, 5-8a
Capstone Connection: Model accumulated production and/or sales, or technical applications associated
with the new business.
Grand Challenge Connections: Improve Sources of Clean Water,Increase industrial base for Egypt
Topic: Indefinite integral, displacement
MA.2.10 - Analyze the distribution of data with a focus on normal distribution (Week 13 - Week 14)
Essential Questions: ‣ Why is the normal distribution essential?
‣ How does one asses normality?
Skills:
‣ A. Use percentiles to locate individual values within distributions of data.
‣ B. Interpret a cumulative relative frequency graph.
‣ C. Find the standardize value of an observation. Interpret z-scores in context.
‣ D. Describe the effect of adding, subtracting, multiplying by, or dividing by a constant on the shape,
center, and spread of a distribution of data.
‣ E. Approximately locate the median and the mean on a density curve.
‣ F. Use the standard Normal distribution to calculate the proportion of values in a specific interval.
‣ G. Use the standard Normal distribution to determine a z-score from a percentile.
Concepts:
‣ A. Percentiles
‣ B. Cumulative relative frequency graph
‣ C. z-scores
‣ D. Density curve
‣ E. Standard Normal Distribution
Evidence:
Section (2-1) page 99-103 problem 1-32
Section (2-2) page 128-133
*****Please provide specific items for the evidence and distinguish between recall, basic application and
strategic thinking.
Texts & References: Practice of Statistics
Grand Challenge Connections: Address the exponential population growth and prepare for the
impact,Improve the use of alternative energies to reduce our reliance on extracted fuel sources,Reduce
urban congestion and its impact,Increase opportunities for Egyptians to stay and work in Egypt,Increase
industrial base for Egypt
Topic: Data Distribution, Normal, z-score
Printed on October 15, 2015
Printed on October 15, 2015
Math: Grade 3, Semester 1
Communication, Sensing, Information, Informatics
Big Idea: Behavior of functions can be either differentiable or integral.
MA.3.01 - Determine and use the implicit differentiation and apply this method to solve real-world problems.
(Week 01 - Week 02)
Essential Questions: ‣ How do you know if the information you have is enough, too little or too
much?
‣ When is it better to memorize and when is it better to understand?
Skills:
‣ A. Find the derivative y with respect to x, and show by graphing that the answer is reasonable.
‣ B. Use the derivative of an implicit function to analyze a graph."
Concepts:
‣ A, Implicit relation
‣ B. Implicit function
‣ C. Derivative of an implicit function
Evidence:
Can be found on pages 172 through 174
Recall (quick review 1 - 9)
BA (Q1 - Q24)
ST(Q27 - 28)
Texts & References: Foerster Calculus Concepts and Applications Section 4-8 p169-174
Foerster Calculus Concepts and Applications Exploration 4-8a
Capstone Connection: communication and information transfer rates
Grand Challenge Connections: Increase opportunities for Egyptians to stay and work in Egypt,Reduce
pollution fouling our air water and grounds
Topic: Implicit differentiation
MA.3.02 - Represent and use complex numbers (Week 03 - Week 07)
Essential Questions: ‣ Why do we need an imaginary world?
‣ How can things be real and imaginary?
Skills:
‣ A. Perform operations with complex numbers
‣ B. Graphically represent complex numbers and their operations on the Argand diagram
‣ C. Find the conjugate of a complex number and use it to find moduli and quotients of complex
numbers
Concepts:
‣ A. Complex numbers
Printed on October 15, 2015
‣ B. Demoivre
‣ C. Binomial
‣ D. Euler's Rule
‣ E. Argand plan
Evidence:
Recall
BA
ST
*****Please complete the evidence of learning section.
Texts & References: Math Connections Book 3A 1.5 pages 48 – 56
In the Unit Materials folder, “Complex Numbers Part 1 – student materials”
“Complex Numbers Part 1 – teacher directions”
Capstone Connection: Electromagnetic communication represented by complex numbers, or any periodic
function that can be represented by and exponential with complex arguments.
Grand Challenge Connections: Improve the use of alternative energies to reduce our reliance on extracted
fuel sources,Reduce pollution fouling our air water and grounds
Topic: Complex numbers, Demoivre, Euler's Rule
MA.3.03 - Use complex numbers in trigonometric identities (Week 08 - Week 10)
Essential Questions: ‣ Why do we need an imaginary world?
‣ How can things be real and imaginary?
Skills:
‣ A. Graph using both rectangular and polar coordinates.
‣ B. Prove and use DeMoivre's theorem.
‣ C. Find the nth roots of unity
Concepts:
‣ A. Polar coordinates
‣ B. DeMoivre's Theorem
‣ C. nth roots of unity
Evidence:
Recall
BA
ST
*****Please provide specific evidence.
Texts & References: In the Unit Materials folder, “Complex Numbers Part 2”
Capstone Connection: Electromagnetic communication represented by complex numbers, or any periodic
function that can be represented by and exponential with complex arguments.
Grand Challenge Connections: Improve the use of alternative energies to reduce our reliance on extracted
fuel sources,Reduce pollution fouling our air water and grounds
Topic: Polar coordinates, nth roots of unity
MA.3.04 - Analyze the behavior of functions by investigating critical points using first and second derivatives.
(Week 11 - Week 12)
Printed on October 15, 2015
Essential Questions: ‣ Why is position important?
‣ What makes something critical?
Skills:
‣ A. Determine if the y-value is a local max or min
‣ B. Determine point of inflection
‣ C. Sketch the graph and/or find the equation of the function given the local (relative) max or min
‣ and critical point.
‣ D. Determine concavity
Concepts:
‣ A. Local max or min
‣ B. Point of inflection
‣ C. Critical point
‣ D. Concavity
Evidence:
BA: 21-26 (8-2)
St: 1-20, 27-46 (8-2)
*****Please be more specific as to what items in this section will be basic application and what will be
Strategic Thinking.
Texts & References: Foerster Calculus - Concepts and Applications Section 8.2
Foerster Calculus - Concepts and Applications - Exploration 8-2a, 8-2b
Capstone Connection: Information transfer rates, minima and maxima
Grand Challenge Connections: Increase opportunities for Egyptians to stay and work in Egypt,Recycle and
retain garbage for recycling
Topic: Concavity, critical pints
MA.3.05 - Given a solid or plane figure, analyze the derivative to determine maximum or minimum value and
to solve real-world problems. (Week 13 - Week 14)
Essential Questions: When is is better to know the maximum or the minimum?
Skills:
‣ A. Maximize/minimize perimeter, area, and volume.
‣ B. Maximize/minimize costs of materials
‣ C. Maximize/minimize cross-sectional areas"
Concepts:
‣ A. Perimeter
‣ B. Area
‣ C. Volume
‣ D. Costs of materials
‣ E. Cross-sectional areas
Evidence:
problem set (8-3)
*****Please provide more specific evidence
Texts & References: Foerster Calculus - Concepts and Applications Section 8.3
Printed on October 15, 2015
Foerster Calculus - Concepts and Applications Exploration 8-3a, 8-3b
Capstone Connection: Information transfer rates, minima and maxima
Grand Challenge Connections: Increase opportunities for Egyptians to stay and work in Egypt,Recycle and
retain garbage for recycling
Topic: Maximize, minimize
Printed on October 15, 2015
Math: Grade 3, Semester 2
Theories, Models and Data
Big Idea: Behavior of functions can be either differentiable or integral. Determinates and their properties help
scientists and mathematicians model life problems. 3-D shapes, concepts and theorem are critical tools in the
representation of objects in real life.
MA.3.06 - Analyze motion using a derivative: distance, displacement, acceleration, velocity. (Week 01 -
Week 02)
Essential Questions: ‣ When can an action be undone?
‣ Is the whole the sum of its parts? Or, is the whole greater than thesum of its parts? Or is the whole
less than the sum of its parts?
Skills:
‣ A. Given a function, analyze displacement and distance
‣ B. Calculate average velocity and use in problem solving situation
Concepts:
‣ A. Velocity
‣ B. Acceleration
‣ C. Displacement
‣ D. Average velocity
Evidence:
ST: (10-1) 1-5 & (10-2) 1-16
*****Please provide recall and basic application evidence. Also, reexamine the items that are listed as
strategic thinking. Some might be recall or basic application.
Texts & References: Foerster Calculus - Concepts and Applications
Sections 3.5, 10.1, 10.2, 10.3
Foerster Calculus - Concepts and Applications Exploration 3-5a, 3-5b, 10-2a, 10-3a
Grand Challenge Connections: Increase opportunities for Egyptians to stay and work in Egypt,Recycle and
retain garbage for recycling
Topic: Displacement, velocity, acceleration, distance
MA.3.07 - Write, solve (graphically and algebraically) and apply differential equations in a real-world
situation. (Week 03 - Week 06)
Essential Questions: Why predict?
Skills:
‣ A. Use resulting differential equations as a mathematical model to make predictions and
interpretations of real-world situations, including: population growth and decay problems, bacterial growth,
predator-prey problem, etc.
‣ B. Find the graphical solutions of differential equations by using Slope Fields
‣ C. Demonstrate an understanding of slope field by first calculating dy/dx and verifying with the
graph
Printed on October 15, 2015
‣ D. Use Euler's method for solving a differential equation numerically.
‣ E. Apply understanding of differential equations to real world problem solving
Concepts:
‣ A. Differential equation
‣ B. Slope fields
‣ C. Euler's method
‣ D. Population growth
‣ E. Decay
‣ F. Predator-prey
Evidence:
St: (7-2) 1-11 & (7-3) 1-10 & (7-4) 1-14 & (7-5) 1-12
*****Please provide recall and basic application evidence. Are ALL of the items at the end of these units
going to be assessed as strategic thinking items or should we consider just some of them.
Texts & References: Foerster Calculus - Concepts and Applications Sections 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5
Foerster Calculus - Concepts and Applications Exploration 7-2a, 7-3a, 7-4a, 7-4b, 7-5a
Grand Challenge Connections: Increase opportunities for Egyptians to stay and work in Egypt,Recycle and
retain garbage for recycling
Topic: Differential Equations, slope fields
MA.3.08 - Recognize and justify when to use a particular technique of integration and apply to real-world
situations (Week 07 - Week 10)
Essential Questions: ‣ How do we choose what to use?
‣ When are techniques more efficient?
Skills:
‣ A. Integrate by parts, rapid repeated addition of parts
‣ B. Integrate odd and even powers of trigonometric functions
‣ C. Integrate by Trigonometric Substitution
‣ D. Resolve an integrand into partial fractions and find the integral
‣ E. Given an improper interval, determine whether it converges or diverges.
Concepts:
‣ A. Integration
‣ B. Integration by parts
‣ C. Trigonometric substitution
‣ D. Converges
‣ E. Diverges
Evidence:
BA: (9-2) 1-10 & (9-3) 1-38 & (9-5) 1-30 & (9-10) 1-20
ST:(9-1) 1-7 & (9-3) 39-49 & (9-5) 31-37 & (9-6) 1-35 & (9-7) 1-24 & (9-10) 21-28
*****Please choose some of the items as evidence. It would be very cumbersome to assess the students on
ALL of the items.
Texts & References: Foerster Calculus - Concepts and Applications Sections 9.1 - 9.7 and 9.10
Foerster Calculus - Concepts and Applications Exploration 9-3a, 9-4a, 9-5a, 9-5b, 9-6a, 9-7a, 9-10a, 9-11a
(in 9-11a only those that items that apply)
Printed on October 15, 2015
Grand Challenge Connections: Increase opportunities for Egyptians to stay and work in Egypt,Recycle and
retain garbage for recycling
Topic: techniques of integration
MA.3.09 - Determine and use orthogonal projections of a point and a line onto a line or plane. (Week 11 -
Week 12)
Essential Questions: What constitutes a relationship?
Skills:
‣ A. Find the measure of angle between two skew lines
‣ B. Find the measure of the dihedral angle
‣ C. Find the length of the projections
Concepts:
‣ A. Skew lines
‣ B. Dihedral angle
‣ C. Projections
Evidence:
Selected items from Algebra and Solid Geometry PAGES 249 - 258
*****Please be more specific in the evidence section.
Texts & References: See blue folder for materials.
Algebra and Solid Geometry - General Secondary Certificate Second Stage - Chapter 2
Grand Challenge Connections: Increase opportunities for Egyptians to stay and work in Egypt,Recycle and
retain garbage for recycling
Topic: Orthogonal projections
Printed on October 15, 2015
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- McGraw-Hill - Data Management (Full Textbook Online)Documento664 pagineMcGraw-Hill - Data Management (Full Textbook Online)Varun Shah81% (16)
- Regents Exams and Answers Geometry Revised EditionDa EverandRegents Exams and Answers Geometry Revised EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Land SurveyingDocumento6 pagineLand Surveyingapi-289190212Nessuna valutazione finora
- g8 Ms Mastering Mct2 SeDocumento80 pagineg8 Ms Mastering Mct2 SeShorya Kumar100% (2)
- Visual Strategy: Strategy Mapping for Public and Nonprofit OrganizationsDa EverandVisual Strategy: Strategy Mapping for Public and Nonprofit OrganizationsValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Pyramid Algorithms: A Dynamic Programming Approach to Curves and Surfaces for Geometric ModelingDa EverandPyramid Algorithms: A Dynamic Programming Approach to Curves and Surfaces for Geometric ModelingNessuna valutazione finora
- Hs Geometry PDFDocumento26 pagineHs Geometry PDFapi-255155256Nessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced AutoCAD® 2017: Exercise WorkbookDa EverandAdvanced AutoCAD® 2017: Exercise WorkbookValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- Spreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis A Practical Introduction To Business Analytics 8th Edition Ragsdale Test BankDocumento16 pagineSpreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis A Practical Introduction To Business Analytics 8th Edition Ragsdale Test Bankraymondfarrellpkbqzjotas100% (16)
- Introduction to Integral Calculus: Systematic Studies with Engineering Applications for BeginnersDa EverandIntroduction to Integral Calculus: Systematic Studies with Engineering Applications for BeginnersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Introduction To Graph TheoryDocumento47 pagineIntroduction To Graph TheoryJan Lemuel T. Gonzalvo100% (2)
- K To 12 Grade 8 Math Module Part 2Documento90 pagineK To 12 Grade 8 Math Module Part 2Drei78% (9)
- Business Analytics - Chapter 1 Testbank - GroupDocumento14 pagineBusiness Analytics - Chapter 1 Testbank - GroupKhaleel AbdoNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Complex Binary Number SystemsDocumento4 pagineIntroduction To Complex Binary Number SystemsDebajyoti DattaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics For Olympiads and Talent Search Competitions For Class 7 - NodrmDocumento498 pagineMathematics For Olympiads and Talent Search Competitions For Class 7 - NodrmNEET/AAIMS COMPLETE PREPARATION100% (1)
- Math 9 TestDocumento2 pagineMath 9 TestJerson Yhuwel100% (2)
- Math - LO-2018Documento34 pagineMath - LO-2018Omar Ayman Mahmoud EssaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial of OOS With JavaDocumento5 pagineTutorial of OOS With JavaTiwari AnuragNessuna valutazione finora
- Math (Grade 1, Semester 1) : Right Triangle TrigonometryDocumento51 pagineMath (Grade 1, Semester 1) : Right Triangle TrigonometryhenryNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - Quiz 3 Instructions - Set O Group of 4hDocumento3 pagine2 - Quiz 3 Instructions - Set O Group of 4hKimberly IgnacioNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Download Spreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis A Practical Introduction To Business Analytics 8th Edition Ragsdale Test BankDocumento36 pagineFull Download Spreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis A Practical Introduction To Business Analytics 8th Edition Ragsdale Test Bankmatthewfem6v100% (24)
- Math (Grade 1, Semester 1) : Right Triangle TrigonometryDocumento10 pagineMath (Grade 1, Semester 1) : Right Triangle TrigonometryAbo Alphotoh GamingNessuna valutazione finora
- Document Answer KeyDocumento8 pagineDocument Answer Keymariam51321Nessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Spreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis A Practical Introduction To Management Science 6th Edition Ragsdale DDocumento36 pagineTest Bank For Spreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis A Practical Introduction To Management Science 6th Edition Ragsdale Dcestui.shote7a36100% (38)
- ESFTMA PublishedDocumento21 pagineESFTMA PublishedKiên Lê TrungNessuna valutazione finora
- Choosing The Best PlanDocumento6 pagineChoosing The Best Planmariam51321Nessuna valutazione finora
- High School Geometry Days 102-112Documento49 pagineHigh School Geometry Days 102-112eclecticOTANessuna valutazione finora
- CAPE Pure Math Unit 1 (2012)Documento25 pagineCAPE Pure Math Unit 1 (2012)Brodrick100% (2)
- University of Derby School of Electronics, Computing and Mathematics In-Course Assignment SpecificationDocumento5 pagineUniversity of Derby School of Electronics, Computing and Mathematics In-Course Assignment Specificationسید کاظمیNessuna valutazione finora
- Calc Ap SyllabusDocumento4 pagineCalc Ap Syllabusapi-239856705Nessuna valutazione finora
- Statistics: Grade 3, Semester 1 Statistics: Grade 3, Semester 2Documento7 pagineStatistics: Grade 3, Semester 1 Statistics: Grade 3, Semester 2youssefNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Algebra/Trigonometry: 2.1. Numbers, Number Systems and Number RelationshipsDocumento5 pagineAdvanced Algebra/Trigonometry: 2.1. Numbers, Number Systems and Number RelationshipsAustin ChiversNessuna valutazione finora
- Photogrammetry OrientationDocumento6 paginePhotogrammetry OrientationNurlaili Khalip0% (1)
- Thesis CH 35Documento7 pagineThesis CH 35jenniferbrowncary100% (1)
- Geometry Enrichment Packet - Answer Key PDFDocumento30 pagineGeometry Enrichment Packet - Answer Key PDFlesNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment OosDocumento4 pagineAssignment OosNiki Malhotra0% (1)
- Curriculum Map Math 7+ 16-17Documento1 paginaCurriculum Map Math 7+ 16-17st72136Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introductory Mathematical Analysis For Business Economics and The Life and Social Sciences 14th Edition Paul Test BankDocumento44 pagineIntroductory Mathematical Analysis For Business Economics and The Life and Social Sciences 14th Edition Paul Test Bankjesselact0vvk100% (28)
- Introductory Mathematical Analysis For Business Economics and The Life and Social Sciences 14Th Edition Paul Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento52 pagineIntroductory Mathematical Analysis For Business Economics and The Life and Social Sciences 14Th Edition Paul Test Bank Full Chapter PDFmrissaancun100% (9)
- HW 22 220Documento3 pagineHW 22 220Sourodipto RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Spring Unit 8Documento32 pagineSpring Unit 8Bala SubramanianNessuna valutazione finora
- Math LOs For 3 YearsDocumento51 pagineMath LOs For 3 Yearsahmedelmelegy850Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2008math App Work11Documento10 pagine2008math App Work11api-335213081Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dsa Lab Manual Bcsl305Documento96 pagineDsa Lab Manual Bcsl305pavannithin2004Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet 01Documento2 pagineSheet 01TimoNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface Reconstruction ThesisDocumento33 pagineSurface Reconstruction ThesisalexNessuna valutazione finora
- Six Sigma End Term Test Jan-May 2007-Pattern 1Documento8 pagineSix Sigma End Term Test Jan-May 2007-Pattern 1Vijayasekar100% (2)
- Geometry in Art Assignment 2018Documento4 pagineGeometry in Art Assignment 2018api-332361871Nessuna valutazione finora
- CAD IntroductionDocumento21 pagineCAD IntroductionAmritansh RanjanNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 533 ProjectDocumento4 pagineMath 533 ProjectNot listingNessuna valutazione finora
- Tybsc-It Sem6 Pgis Nov19Documento2 pagineTybsc-It Sem6 Pgis Nov19farji4433Nessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Posing With Technology EnvironmentDocumento6 pagineProblem Posing With Technology EnvironmentHaile YidegNessuna valutazione finora
- 2003 03 01 MathModelingDocumento29 pagine2003 03 01 MathModeling'Nabeela MahmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Omputing Corner Omputing Corner: More Statistical Nuggets With A Graphics CalculatorDocumento6 pagineOmputing Corner Omputing Corner: More Statistical Nuggets With A Graphics CalculatoropurataNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 12 Mathematics Board Project 1 Details 2023-2024Documento3 pagineGrade 12 Mathematics Board Project 1 Details 2023-2024progamerdk576Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Designing Substansial Task To Utilize ICT in Math LessonsDocumento9 pagineChapter 8 Designing Substansial Task To Utilize ICT in Math LessonsNadia SefianyNessuna valutazione finora
- CEE4100 01 Homework 06 2013 Fall SchedulingDocumento8 pagineCEE4100 01 Homework 06 2013 Fall Schedulingjhnelson2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- Business Analytics - Final Exam August 2022Documento3 pagineBusiness Analytics - Final Exam August 2022Romar PogoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification, Parameter Estimation and State Estimation: An Engineering Approach Using MATLABDa EverandClassification, Parameter Estimation and State Estimation: An Engineering Approach Using MATLABValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Thematic Cartography, Cartography and the Impact of the Quantitative RevolutionDa EverandThematic Cartography, Cartography and the Impact of the Quantitative RevolutionNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistics: Grade 3, Semester 1 Statistics: Grade 3, Semester 2Documento7 pagineStatistics: Grade 3, Semester 1 Statistics: Grade 3, Semester 2youssefNessuna valutazione finora
- LibraryDocumento45 pagineLibraryyoussefNessuna valutazione finora
- Topical Outlines of STEM CoursesDocumento7 pagineTopical Outlines of STEM CoursesyoussefNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer ScienceDocumento14 pagineComputer ScienceyoussefNessuna valutazione finora
- PhysicsDocumento37 paginePhysicsyoussefNessuna valutazione finora
- Capstone: Grade 1, Semester 1 Capstone: Grade 1, Semester 2 Capstone: Grade 2, Semester 1 Capstone: Grade 2, Semester 2 Capstone: Grade 3, Semester 1Documento26 pagineCapstone: Grade 1, Semester 1 Capstone: Grade 1, Semester 2 Capstone: Grade 2, Semester 1 Capstone: Grade 2, Semester 2 Capstone: Grade 3, Semester 1youssefNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz Grade11 MathDocumento6 pagineQuiz Grade11 MathyoussefNessuna valutazione finora
- B2 Alphabetical Wordlist Unit 4Documento6 pagineB2 Alphabetical Wordlist Unit 4youssefNessuna valutazione finora
- Great English - Grammar Rules, Reference Lists and General Knowledge - Isabel UysDocumento10 pagineGreat English - Grammar Rules, Reference Lists and General Knowledge - Isabel UysyoussefNessuna valutazione finora
- School Calendar 2017/2018 First Term: Portfolio DeliverDocumento1 paginaSchool Calendar 2017/2018 First Term: Portfolio DeliveryoussefNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Year Exams From1980 To 1995Documento43 pagine3rd Year Exams From1980 To 1995youssefNessuna valutazione finora
- Vedic Maths1Documento2 pagineVedic Maths12010vjNessuna valutazione finora
- CircleDocumento17 pagineCircleFOCUSNessuna valutazione finora
- Zimsec Nov 2008 p1 Abnd 2Documento13 pagineZimsec Nov 2008 p1 Abnd 2Emily NcubeNessuna valutazione finora
- PolynomialsDocumento17 paginePolynomialschand7790100% (3)
- Applied Calculus 5th Edition Hughes Hallett Solutions ManualDocumento35 pagineApplied Calculus 5th Edition Hughes Hallett Solutions Manualsaxonpappous1kr6f100% (12)
- Math Lesson WorksheetDocumento5 pagineMath Lesson Worksheetapi-283894138Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tracking Test 1-Version A: Time Allowed: 60 Minutes. 50 MarksDocumento5 pagineTracking Test 1-Version A: Time Allowed: 60 Minutes. 50 Marksrama singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Solving Quadratics by Factorising 1 PDFDocumento3 pagineSolving Quadratics by Factorising 1 PDFcarolinethami13Nessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Root - A Simple and Useful Mathematical ConceptDocumento6 pagineDigital Root - A Simple and Useful Mathematical ConceptKaushik RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Quant Checklist 460 by Aashish Arora For Bank Exams 2024Documento110 pagineQuant Checklist 460 by Aashish Arora For Bank Exams 2024sharpleakeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering MathematicsDocumento140 pagineEngineering MathematicsRohit SenNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics: Engineering ©©©©©© Medical Work ©©©©©©©© Law ©© Science ©Documento8 pagineMathematics: Engineering ©©©©©© Medical Work ©©©©©©©© Law ©© Science ©Jheanelle Andrea GodoyNessuna valutazione finora
- LESSON NO. 13: Finding The Equation of A Quadratic Function Content StandardDocumento5 pagineLESSON NO. 13: Finding The Equation of A Quadratic Function Content StandardRonald AlmagroNessuna valutazione finora
- fx-115ES fx-991ES: User's GuideDocumento75 paginefx-115ES fx-991ES: User's Guideapi-294268347Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - Simplification PDFDocumento31 pagineChapter 2 - Simplification PDFBhushan PawarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2 Trigonometric SubstitutionDocumento2 pagine2.2 Trigonometric Substitutioncory kurdapyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics P2 Nov 2016 Memo Afr & EngDocumento26 pagineMathematics P2 Nov 2016 Memo Afr & EngThabiso Jimmy LengwateNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 01Documento111 pagineModule 01Aemin IhtishamNessuna valutazione finora
- Year 10 International Maths Revision ListDocumento3 pagineYear 10 International Maths Revision ListAmy KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Worked SolutionsDocumento177 pagineChapter 1 Worked Solutionscormac molloyNessuna valutazione finora
- Argentina Team Selection Test 2010Documento2 pagineArgentina Team Selection Test 2010Karn Kumar0% (1)
- Secondary Mathematics Scheme of Work: Stage 8Documento18 pagineSecondary Mathematics Scheme of Work: Stage 8E EmmanuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Sin and Cos Rule Exam QuestionsDocumento4 pagineSin and Cos Rule Exam QuestionsKavya KishoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Curriculum Guide Grade10Documento7 pagineMath Curriculum Guide Grade10Lauresta L. JeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow ChartDocumento2 pagineFlow ChartBoopathy S SomasundaramNessuna valutazione finora
- Cartesian Coordinate SystemDocumento11 pagineCartesian Coordinate SystemAmar GillNessuna valutazione finora
- C PROGRAMMES - SET-1 - GECR GEEK - UpdatedDocumento8 pagineC PROGRAMMES - SET-1 - GECR GEEK - Updatedyash gamingNessuna valutazione finora