Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
A Study of Abrasive Jet Machining
Caricato da
Advanced Research PublicationsCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
A Study of Abrasive Jet Machining
Caricato da
Advanced Research PublicationsCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Research Article
A Study of Abrasive Jet Machining
Gulshan Kumar1, Monu Kumar2, Kulwinder Singh3, Ravi pal Rana4, Suraj Tiwari5
Abstract
Abrasive jet machining falls under a category of mechanical process or it is an unconventional and non-
traditional manufacturing process. In this machining fine abrasive grades or particles in a jet of inert gas
hit the work piece at very high velocity (usually in the order of 200-400 m/sec). This high velocity of jet of
abrasives causing the material removals from the workpiece in the form of chips. This are very effectively
removes hard or brittle materials. This is use for cutting, cleaning, polishing, au etching. This effectively
work on glass, silicon, tungsten and ceramic because these all under categories of hard and brittle material.
This machining is not suitable for soft materials like aluminum, rubber etc. Because abrasive particles
get plunged into the material, which provide additional operation like cleaning. In abrasive jet machining
varies process parameter such as abrasive, gas, nozzle and velocity of fluid are usual. This paper give u
perfect knowledge about the abrasive jet machining. In this machining varies abrasive are aluminium
oxides and silicon carbide. This is under a category of conventional abrasive. In some new machine cubic
boron and diamonds used
Keywords: Abrasive jet machining, friability, material removal rate, abrasive standoff distance
Introduction
In abrasive jet machining, final shape of the product or workpiece is for make into desired shape by high velocity
definition are suggested by various author about the abrasive jet machining. The abrasive particles coming from the
nozzle strike the surface of the workpiece with vary high velocity usually 200-400m/sec. The distance of abrasive particles
is 0.025mm and air is discharges at several atmospheres pressure [1]. The abrasives are of shape sharp edges. When
the sharp shape of abrasive strikes the workpiece, it removes the material in the form of small chip or discontinuous
chip. Because hard material always produces a discontinuous chip when it is under cutting operation. The sharp edge
of the abrasive after cutting operation converts in spherical shape and do not use again because its cutting capacity
reduces. The various process parameter that are used in abrasive jet machining which are discussed in this paper.
The various definition of abrasive jet machining given by various author. Abrasive are widely used on various machine
process, and it effectively produce holes of intricate shape and provide close tolerances that are regularly for producing
the engineering components [2]. Abrasives jet machining is a non-traditional manufacturing process that is include the
cleaning of surface, sand blasting and cutting etc. [3]. AJM also known as pencil blasting, abrasive micro blasting [4].
Abrasive jet machining is an efficient non-traditional process for machining brittle and hard material and heat sensitive
materials, in which material is removal from the work surfaces by mechanical erosion. Mechanical erosion caused by
imparting of high velocity abrasive particles mixed with compressed air [5].
Mechanism
various author suggest mechanisms used in abrasive machining. Finnie [6] suggest that mechanism of material removal
for ductile material is by plastic deformation and fracture. Mechanism of MRR is mainly depend upon the flow rate and
size of abrasive particles [7]. Standoff distance effect the MRR and penetration rates.
1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Students, Mechanical Engineering, GNA University, Phagwara, Punjab, India.
Correspondence: Gulshan Kumar, Mechanical Engineering, GNA University, Phagwara, Punjab, India.
E-mail Id: gulshankumar2695@gmail.com
Orcid Id: http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3040-237X
How to cite this article: Kumar G, Kumar M, Singh K et al. A Study of Abrasive Jet Machining. J Adv Res Appl Mech Compu Fluid
Dyna. 2017; 4(3): 9-14.
E ISSN: 2349-7661 l P ISSN: 2394-7055
© ADR Journals 2017. All Rights Reserved.
Kumar G et al. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Mech. Compu. Fluid Dyna. 2017; 4(3)
Figure 1.Abrasive Jet Machining
C. N. Insulli [8] material is removed from the surface of shape of the abrasive flow rate and pressure and velocity of
workpiece by the impingement of the abrasive particles carrier gas. The abrasive particles are irregular in shape and
of very fine in shape. These abrasive particles move with consist of short edges which perform the cutting operation.
a very high velocity through the nozzle along with the
high stream of gas. When the abrasive particles having Effect of various parameter on material removal rate
sharp edges strike the brittle and hard material with a high
velocity, it makes dents into the material and again strike Before discussing the process parameter first we understand
the workpiece it the material from the workpiece. The wear what are process parameter. Process parameter are that
out particles is carried away from the workpiece by the air parameter which are control by manually during the
or gas. The MRR of abrasive jet machining [9] Rahul Jain. machining operation. Such as the abrasive flow rate, velocity
of fluid, gas, geometry of nozzle.
MRR = K N δ^3
K = constant • Abrasives- commonly used abrasives in manufacturing
N = no. of abrasive particles imparting per unit time are as follows.
d = diameter of abrasive particles • Conventional abrasive- in conventional abrasives
v = velocity of abrasive aluminium oxide and silicon carbide is used.
H = hardness of work material. • Super abrasives- In which cubic baron carbide and
diamond is used.
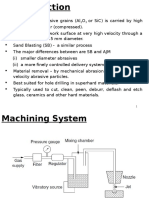
In AJM, gas (nitrogen or carbon di oxide or air) is supplied
under a very high pressure. After it passed through the In conventional machining process cutting tool material
filter and regulator, it passed to a mixing chamber. Mixing is harder than the workpiece. After a number of use it is
chamber containing the abrasive particles which are re shape on grinding wheel in case of lathe machine. But
vibrating at a very high frequency by the vibration source. in non-conventional machining abrasive are used which
After moving through the mixing chamber, the gas along is harder than cutting tool material used in conventional
with the abrasive particles passes on to a nozzle. Nozzle is manufacturing process. Super abrasives are harder than
made of tungsten carbide and diameter of about 0.45mm. the conventional abrasives, but its cost is high. In spite
The nozzle tip distance is used in abrasive jet machining is of hardness of abrasive, another important property of
0.81mm. the various further which influence the material abrasives is its friability. Friability is the ability of abrasive
rate, geometry of cut, surface roughness and nozzle wear growing to fracture (breakdown) into smaller pieces. This
rate are standoff distance, composition, strength, size and property gives the abrasive self-sharping fractures [9].
Figure 2.Mixing ratio and Abrasive mass flow rate dependence of mrr
E ISSN: 2349-7661 l P ISSN: 2394-7055 10
J. Adv. Res. Appl. Mech. Compu. Fluid Dyna. 2017; 4(3) Kumar G et al.
Abrasive are found in nature are made by synthetically now rate of the gas, when the fraction of mass of abrasives in
a day. Abrasive found in nature are as follow. the flowing gas increases, the material removal rate of
firstly increases, but further mass of abrasives in the jet
Energy increases, it reaches a maximum and then falls.
Corundum (alumina)
Quartz Mixing ratio = volume of flow rate abrasives / volume flow
Diamond rate of gas
Sand stone.
When we increase mass flow rate of abrasives particles
Diamond is common abrasives that produced by the beyond a particles limit. It will result in a decreases the
industry as well as obtained from the nature. Corundum available energy for cutting action and automatically the
which is obtained from the nature, but now a day this are material removal rate [10]
manufactured from bauxite artificial abrasives.
Gas
• Silicon carbide (sic)
• Aluminium oxide MRR directly influences by the air or gas pressure. Material
• Artificial diamond. removal rate is directly proportional to the air or gas
pressure. [11] composition of gas also effects the MRR.
These are the abrasives also use in grinding wheel. No High pressure of gas or high velocity of gas obviously causes
mind diameter of abrasive is normally used is 10-15 µm a low material removal rate.
in abrasive jet machining. Abrasives particles are not used
again and again because of the following reasons. Nozzle
• Cutting capacity decreases after the one application. The nozzle is the most important element in the AJM.
Sharp edges of the abrasive are eliminated. Abrasives grains strikes the workpiece after it is passed
• Surface roughness is poor when we use abrasives again through nozzle. Nozzle is always in contact with the
and again. abrasives grains. Nozzle increases the velocity of abrasives
particles.
Abrasives flow rate influences by the pressure and flow
Figure 3.Model depicting AJM
Normally wc or sapphire is used. At the end of the nozzle, Standoff & Nozzle tip distance
small hole called orifice is kept cross sectional area of the
orifice is either rectangular or circular. The life of the nozzle These are distance between the nozzle tip and the
is not very long, after a number of uses it is replaced with workpiece. Both are the something. It largely effect on
a new one. Life of the nozzle in abrasive jet machining is the material removal rate in AJM. MRR increases up to
difficult to achieve, but various investigator suggest the certain limit with increases of nozzle tip distance. After
nozzle life. A wc nozzle lasts between 12 hour to 13 hour, that limit, constant MRR is obtained, but further decreases.
whereas a sapphire nozzle lasts for 300 hour approximately.
11 E ISSN: 2349-7661 l P ISSN: 2394-7055
Kumar G et al. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Mech. Compu. Fluid Dyna. 2017; 4(3)
Nozzle tip distance not only effect the material removal optimum performance NTD of 0.25 to 0.75 is provided [11].
rate, it also effect the shape and size (diameter) of cut. For
Figure 4.Effect of Nozel Tip distance
Velocity of fluid (carrier gas) the concept of abrasive jet cutting as a practical alternative
for traditional machine shapes [13]. End seal of Dr Johan
The velocity of the carrier gas also effects on the MRR. to develop a system which eliminate the noise, dust and
With the abrasive particles density, velocity of carrier gas expertise demanded by abrasive jet at that time. In the last
changes. When the abrasive particles density is gradually two decades, heavily deal of research and development in
increased, the exit velocity will go on decreasing. It is due AJM is contributed or provides.
to the fact that fluid kinetic energy is used or utilized for
conveying the abrasive particles. Literature Review
Advantages of AJM In this section, various author gives the result of abrasive jet
machining. Experiment related to MRR by various research
• AJM can cut holes of intricate shapes in hard material has been conducts. Various author gives the influencing
• There is no contact between the tool and the workpiece factor that effects the MRR. R. Bal Subramanian at [14] said
• Surface finish obtained by AJM is very high than that increases the size of particles, the material removal
conventional machining operation rate in near to the centre line of jet drastically increases,
• Power consumption is low but near the periphery material removal rate very less. As
• Capital cost is low the nozzle tip distance increases, material removal rate also
increases when we increase jet velocity near the centre
Limitations of AJM line, MRR near to the centre line of jet increases. But the
MRR nearer to the periphery of the jet decreases. When
• MRR is low
we increase jet velocity, the radius of edge and entry side
• It cannot be best suited for machining soft material
diameter increase. It is also increase the MRR.
• Wear rate of nozzle is high
• Process cause the pollute environment, so that dust Jukti Prasad panday [15] taken the experiment (practical)
collecting system is required on glass work piece using aluminium oxide as an abrasive
powder. To study MRR and over cut, experiment was
Application
done by considering nozzle tip distance and procedure as
• Electronic devices [12] bulter,1980 Wikipedia machining or process parameter. From the experiment,
• Deburring of plastics i.e. gives that both pressure and nozzle tip distance are
• Making on electronic products important for MRR and only pressure as a significant
• Making of nylon and Teflon parts role in over cut. He said that individual optimal setting
• Cutting of thin and fragile component of parameters is taken out to decreases the over cut and
increases the MRR.
Background
Mr. Barker Chandra [16] studied the material removal
This machining technology was first started by Franz to cut rate varied according to the variation in has pressure and
laminated paper tubes in 1968 and as a commercial system hole diameter accordingly to change in standoff distance.
was first introduced I 1983. Abrasive jet was born in 1980 by He gives the various practical on wok piece material glass
the garnet abrasive was abbey to the water stream. In the alumina as a abrasive powder.
easily 1990, Dr. Johan Olsen began to explore and explain
E ISSN: 2349-7661 l P ISSN: 2394-7055 12
J. Adv. Res. Appl. Mech. Compu. Fluid Dyna. 2017; 4(3) Kumar G et al.
Rahul Jain [18] various results have been conducted. Typical decreases various graph as already discussed on this
MRR is 16 cubic mm per minute for cutting glass and concept.
minimum width of cut can be 0.1mm. accuracy of 0.1mm • MRR is directly proportion to the gas pressure. If we
and surface roughness of 0.2µm to 1.5µm size particles increase the gas pressure, MRR also increase and
can be attained. decrease when gas pressure decrease.
• If we increase the standoff distance various shape of
Dr.A.k. Paul et al [19]. Taken the experiment on the influence the cut or geometry of cut is achieved. The NTD not
of pressure of the carrier gas on the MRR in AJM.Experiment effect only the material removal rate, but also the
are developed in porcelain and silicon carbide as a abrasive shape and size of cavity produced.
particles. Experiment are conducted at various pressure. • Velocity of fluid (carrier gas) also of feed the MRR in
It was observed that with increase the grain size, material abrasive jet machine.
removal rate increase and also increase with the nozzle
diameter. MRR also increase with increase of SOD at a In the end, we can say that AJM is very helpful to procedure
particular pressure. desire surface finish, close tolerance than the conventional
manufacturing process. It consumes less time, MRR is
A el- domiaty [20] et al conducted the experiment on high than traditional machining. AJM is very helpful to
drilling of glass with varying thickness by the use of AJM. increase the production rate of industry and reduces the
With the help of this practical he determines machinability difficulty in machining process which are obtained during
under different process parameters. He could do that the conventional machining process.
when we increase the diameter of nozzle, abrasive flow
rate corresponding increase which leads to more material References
removal rate. They developedan experiment and theoretical
analysisto calculate the MRR. 1. Rahul Jain, author of book unconventional
manufacturing process (2011-1-1).
ShripadChopard et al [21]. Said that any material can 2. Dr. Mark J. Jackson and Dr. J. PaulsDavin, editors of
be cut or machined by AJM.ie harder material like steel, machining with abrasives (2011).
titanium laminates flammable materials cut thin stuff or 3. Yasser M. Ali and Jun wangle, author of impact abrasive
thick stuff brittle or fragile material like glass, ceramic, machining (June,2010).
quartz and stone etc. 4. Wikipedia.com.
5. AnuTomy and S Hire math (Dec., 2016).
Zhang et al [22] developed a new method called micro 6. I Finnie, erosion of surface by solid ductile material
abrasive intermittent jet abrasive (MAIJM)in which first (1960).
compressed air is mixed with abrasive is strike on workpiece 7. Rahul Jain, authors of book unconventional
in first cycle and air alone is discharged to remove abrasive manufacturing process (2011-1-1).
particles in hole in second half cycle. 8. C. N. Insulli, abrasive jet machining (1967).
9. Rahul Jain. Author of book unconventional
Ray and Paul [23] gives report that use of sic abrasive manufacturing process (2011-1-1).
particles with grain size 80 micron to 120 microns is very 10. Manjeet Kumar panday(march,2016) effect of abrasive
effective results for machining hard and brittle material flow rate and mixing ratio on MRR.
like porcelain. 11. Mechteacher.com.
Conclusion 12. Butler,1980, Dom brow ski, 1983.
13. TejasPawer, SwapnilWagh, Rohitshinde (deptt. of
According to various books and research paper, lot of mechanical engineering) international journal of
work on the abrasive jet machining has already home.A engineering research and general science volume 3,
new technology come into existence in world. Various issuse3, May-June 2015. ISSN20912730
parameter like abrasive (flow rate, size and shape), nozzle 14. R. Balasubramaniam, Krishan, N. Rama Krishan, a
(standoff distance) velocity of carrier gas, in abrasive jet empirical study on the generation of edge machining in
machining which are distance in this articles. Abrasive AJM external deburring. J. Mater process, technical.99
jet machining involves a number of complex mechanism. (2000) 49.
In short (conclusion) has been explained on the AJM. 15. Jukti Prasad Panday, optimization and effect of
Parameter used in AJM are abrasive flow rate, size and controlling parameter on AJM. International journal
shape of abrasive. The gas pressure, the nozzle, nozzle tip of engineering research and application ISSN: 2248-
distance, velocity of carrier gas. 9622, vol.4, issue(version1), march,2014.
16. ]Mr. Bhaskar Chandra, a study of effect of process
• When we increase the abrasive flow rate, material parameter of AJM. international journal of engineering
removal rate increase, but after a certain valve it and technology. Vol3, app.504-513, jan.2011.
13 E ISSN: 2349-7661 l P ISSN: 2394-7055
Kumar G et al. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Mech. Compu. Fluid Dyna. 2017; 4(3)
17. A Ghobiety. Effect of particles size distribution vol.3, pp.57-63, Aug.2009.
on surface profile journal of material processing 21. Shripadchopade, Sagerkauthalkar, Dr. pushpendra
technology 209 PP.6067-6077, 2009. Kumar Sharma. International journal of modern
18. Rahul Jain, author of book unconventional engineering research, vol.3, issue 3. May-june.2013.
manufacturing process (2011-1-1). 22. L. Zhang, T. Kuriyagawa, Y. Yasutomi and J. Zhao,
19. [19] Dr. A. k. Paul &R. K. Roy “some studies on Abrasive “Investigation into micro abrasive intermittent jet
jet machining the Journal of theInstitution of Engineers machining,” International Journal of Machine Tools &
(India) Vol 68 part PE 2 November 1987 Manufacture, Vol. 45, pp.873–879, 2005204.
20. A. El-Domiaty, H. M. Abd El-Hafez and M.A. Shaker. 23. P K, Paul A. K. (1987), ―Some Studies on Abrasive Jet
„„Drilling of Glass Sheets by Abrasive Jet Machining. ‟‟ Machining‖, Journal of the Institutions of
World Academy science, Engineering and Technology, 24. Engineers, (India), Vol. 68, PP.27-30204.
E ISSN: 2349-7661 l P ISSN: 2394-7055 14
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 1997 - Handbook of Stainless SteelsDocumento1.078 pagine1997 - Handbook of Stainless SteelsFrancisco PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDocumento30 pagineAbrasive Jet MachiningMr PotatoNessuna valutazione finora
- 4a AjmDocumento13 pagine4a AjmHARSHVARDHAN SINGH RATHORENessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDocumento9 pagineAbrasive Jet MachiningArko MazumderNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet Machining: Dr. Harlal S. Mali, MNIT JaipurDocumento12 pagineAbrasive Jet Machining: Dr. Harlal S. Mali, MNIT JaipurAbinash GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDocumento29 pagineAbrasive Jet MachiningSRIKANTH PATELNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 11Documento28 pagineUnit 11Akash KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and fabrication of an abrasive jet machineDocumento4 pagineDesign and fabrication of an abrasive jet machineDishant ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet Machining (Ajm) : Pressure Energy of The Carrier Gas or Air To Its Kinetic EnergyDocumento20 pagineAbrasive Jet Machining (Ajm) : Pressure Energy of The Carrier Gas or Air To Its Kinetic EnergyMr Yasin Mech StaffNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Non-Traditional Machining ProcessesDocumento57 pagineIntroduction to Non-Traditional Machining ProcessesramadanNessuna valutazione finora
- AJMDocumento20 pagineAJMAkshay MuleNessuna valutazione finora
- UCMP II UnitDocumento59 pagineUCMP II Unit18R21A0310 BIYYALA SHESHAGIRINessuna valutazione finora
- 02-Non-traditional-machining -2Documento10 pagine02-Non-traditional-machining -2Mas ArifinNessuna valutazione finora
- Ajm - 1st Lecture Chapter2Documento16 pagineAjm - 1st Lecture Chapter2KAMALJEET SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDocumento23 pagineAbrasive Jet MachiningLeo Jose100% (1)
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDocumento13 pagineAbrasive Jet MachiningParshva KhatadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- AJM: Abrasive Jet Machine Process OverviewDocumento16 pagineAJM: Abrasive Jet Machine Process OverviewKunal KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Fabrications of Abrasive Jet Machine: Presented byDocumento31 pagineDesign and Fabrications of Abrasive Jet Machine: Presented byAnuj TripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Me2026 - Unconventional Machining ProcessesDocumento77 pagineMe2026 - Unconventional Machining ProcessesRashida BegumNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDocumento5 pagineAbrasive Jet Machiningsudhanshu kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet Machining (Ajm) : Dept. of ME, ACEDocumento8 pagineAbrasive Jet Machining (Ajm) : Dept. of ME, ACEJabir 08Nessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDocumento10 pagineAbrasive Jet MachiningFadlanbunglonNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM) : Dr. Venkaiah NDocumento24 pagineAbrasive Jet Machining (AJM) : Dr. Venkaiah NAkshay ManiyarNessuna valutazione finora
- PC Me 701Documento32 paginePC Me 701Prabhat RoutNessuna valutazione finora
- AjmDocumento22 pagineAjmsuneel kumar rathoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Water Jet Machining Guide: Equipment, Parameters & ApplicationsDocumento21 pagineAbrasive Water Jet Machining Guide: Equipment, Parameters & ApplicationsDarsh MenonNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Advanced Machining Processes Are ImportantDocumento38 pagineWhy Advanced Machining Processes Are ImportantLavishNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - AJM Process PDFDocumento11 pagine1 - AJM Process PDFRaj VeerNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDocumento37 pagineAbrasive Jet MachiningPola Vamsi RahulNessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Traditional Machining: Abrasive Jet Machining GuideDocumento13 pagineNon-Traditional Machining: Abrasive Jet Machining GuideKurniawan ChaniagoNessuna valutazione finora
- NMCOE4054ijarseDocumento5 pagineNMCOE4054ijarseUsman AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM) : Material RemovalDocumento23 pagineAbrasive Jet Machining (AJM) : Material RemovalHemanth Rama Krishna YernagulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM) Process OverviewDocumento31 pagineAbrasive Jet Machining (AJM) Process OverviewAbhishek KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro Machining Processes: Welcome To The Course ONDocumento65 pagineMicro Machining Processes: Welcome To The Course ONAshit RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet and Water Jet Machining Mp2Documento50 pagineAbrasive Jet and Water Jet Machining Mp2Drew LadlowNessuna valutazione finora
- Persentasi B.inggris 2Documento17 paginePersentasi B.inggris 2Mustakim AnsoriNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Fabrication of Abrasive Jet MachiningDocumento5 pagineDesign and Fabrication of Abrasive Jet MachiningDarko MarjanovicNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On Surface Roughness in Abrasive Waterjet Machining Process Using Artificial Neural Networks and Regression Analysis MethodDocumento4 pagineA Study On Surface Roughness in Abrasive Waterjet Machining Process Using Artificial Neural Networks and Regression Analysis MethodronNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment No 01 Abrasive Jet MachineDocumento3 pagineAssignment No 01 Abrasive Jet MachineChirag BotkondleNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Flow MachiningDocumento12 pagineAbrasive Flow MachiningfhjNessuna valutazione finora
- Unconventional Machining ProcessesDocumento64 pagineUnconventional Machining Processesdeepak kantipudiNessuna valutazione finora
- SujitDocumento24 pagineSujitNehul PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Nozzle Design and Material in Abrasive Jet Machining Process - A ReviewDocumento9 pagineNozzle Design and Material in Abrasive Jet Machining Process - A ReviewRajiv RanjanNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis On Abrasive Jet MachiningDocumento4 pagineThesis On Abrasive Jet Machiningfjcz1j5g100% (2)
- 1 s2.0 S1755581722000165 MainDocumento11 pagine1 s2.0 S1755581722000165 MainFabio RustowNessuna valutazione finora
- A N A F I C F U D A F F M: Ovel Pproach For Inishing Nternal Omplex Eatures Sing Eveloped Brasive LOW Inishing AchineDocumento8 pagineA N A F I C F U D A F F M: Ovel Pproach For Inishing Nternal Omplex Eatures Sing Eveloped Brasive LOW Inishing AchinePramendra7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Non Conventional Machining MethodsDocumento24 pagineNon Conventional Machining MethodsGaurav Nigam100% (1)
- USM IntroductionDocumento28 pagineUSM IntroductionPuqing JiangNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDocumento12 pagineAbrasive Jet MachiningTejas SuratiNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Manufacturing Technology - Lecture 5Documento36 pagineIntroduction To Manufacturing Technology - Lecture 5venkat4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM) : A Seminar OnDocumento14 pagineAbrasive Jet Machining (AJM) : A Seminar OnAkshatshuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Fabrication of Abrasive Glass Cutting Machine Using Compressed AirDocumento4 pagineDesign and Fabrication of Abrasive Glass Cutting Machine Using Compressed AirSujit SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter2 - AJMDocumento13 pagineChapter2 - AJMravish kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 Study On The Modeling Method and Influencing Paramteres of SanblastingDocumento19 pagine2022 Study On The Modeling Method and Influencing Paramteres of SanblastingJakub GrzelkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM) : Unit 3Documento54 pagineAbrasive Jet Machining (AJM) : Unit 3Satish SatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-5 6Documento12 pagineUnit-5 6chiranthanchiru332Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrostatic and Hydro-Testing in the Oil and Gas FieldDa EverandHydrostatic and Hydro-Testing in the Oil and Gas FieldValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- Rock Blasting - A Practical Treatise On The Means Employed In Blasting Rocks For Industrial PurposesDa EverandRock Blasting - A Practical Treatise On The Means Employed In Blasting Rocks For Industrial PurposesNessuna valutazione finora
- Laryngeal Neuroendocrine Tumor - An Atypical PresentationDocumento3 pagineLaryngeal Neuroendocrine Tumor - An Atypical PresentationAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Disseminated Histoplasmosis in An Immunocompetent Host Presenting As Pyrexia of Unknown Origin (PUO)Documento4 pagineDisseminated Histoplasmosis in An Immunocompetent Host Presenting As Pyrexia of Unknown Origin (PUO)Advanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Turmeric - Its Applications in DentistryDocumento4 pagineTurmeric - Its Applications in DentistryAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Delayed Diagnosis of Scrub Typhus in Dengue Epidemic: A Case ReportDocumento3 pagineDelayed Diagnosis of Scrub Typhus in Dengue Epidemic: A Case ReportAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Association of Epicardial Fat With Metabolic Syndrome in Indian PopulationDocumento6 pagineAssociation of Epicardial Fat With Metabolic Syndrome in Indian PopulationAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Delayed Diagnosis of Hemophilia B Presenting With HematemesisDocumento3 pagineDelayed Diagnosis of Hemophilia B Presenting With HematemesisAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Utility of Acute-Phase Reactants in MedicineDocumento4 pagineClinical Utility of Acute-Phase Reactants in MedicineAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Stroke As The Initial Presentation of Takayasu Arteritis: Rare But Not InfrequentDocumento4 pagineAcute Stroke As The Initial Presentation of Takayasu Arteritis: Rare But Not InfrequentAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Association of Epicardial Fat With Metabolic Syndrome in Indian PopulationDocumento6 pagineAssociation of Epicardial Fat With Metabolic Syndrome in Indian PopulationAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyrotoxic Periodic Paralysis As A Presentation of Thyrotoxicosis: A Case ReportDocumento4 pagineThyrotoxic Periodic Paralysis As A Presentation of Thyrotoxicosis: A Case ReportAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Symmetrical Lipomatosis With Involvement of TongueDocumento3 pagineMultiple Symmetrical Lipomatosis With Involvement of TongueAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Progressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis in An Immunocompetent Host With Reversible CD4 LymphocytopeniaDocumento4 pagineProgressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis in An Immunocompetent Host With Reversible CD4 LymphocytopeniaAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Celiac Disease With Balanced TranslocationDocumento3 pagineCeliac Disease With Balanced TranslocationAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Waterborne Food Poisoning Outbreak of Bacillus Cereus in Primary School Sabah East MalaysiaDocumento8 pagineWaterborne Food Poisoning Outbreak of Bacillus Cereus in Primary School Sabah East MalaysiaAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Pancytopenia in Cytophagic Histiocytic PanniculitisDocumento3 paginePancytopenia in Cytophagic Histiocytic PanniculitisAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Systemic Variety of Anaplastic Large - Cell LymphomaDocumento3 pagineSystemic Variety of Anaplastic Large - Cell LymphomaAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Association of Xenobiotic Metabolizing Gene Polymorphisms and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Indian PopulationDocumento10 pagineAssociation of Xenobiotic Metabolizing Gene Polymorphisms and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Indian PopulationAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Unusual Extrahepatic Manifestations of Hepatitis C InfectionDocumento4 pagineUnusual Extrahepatic Manifestations of Hepatitis C InfectionAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Faces of HIV in A Single Patient: Case StudyDocumento3 pagineDifferent Faces of HIV in A Single Patient: Case StudyAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulmonary Lymphangiomyomatosis: A Rare Disease Responsive To ProgesteroneDocumento2 paginePulmonary Lymphangiomyomatosis: A Rare Disease Responsive To ProgesteroneAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Bilateral Ptosis in An Adult Following Wasp Sting With Spontaneous RecoveryDocumento3 pagineBilateral Ptosis in An Adult Following Wasp Sting With Spontaneous RecoveryAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Deep Vein Thrombosis in TuberculosisDocumento3 pagineDeep Vein Thrombosis in TuberculosisAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Autonomic Dysfunction in Acromegaly: A Case ReportDocumento5 pagineAutonomic Dysfunction in Acromegaly: A Case ReportAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Primary Tubercular Abscess of Thigh in An Immunocompetent IndividualDocumento4 paginePrimary Tubercular Abscess of Thigh in An Immunocompetent IndividualAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin D Supplementation Improves Bone Mineral Density in Patients With HyperthyroidismDocumento7 pagineVitamin D Supplementation Improves Bone Mineral Density in Patients With HyperthyroidismAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- An Epidemiological Cross - Sectional Comparative Study of Morbidity Profile in An Automobile Manufacturing UnitDocumento5 pagineAn Epidemiological Cross - Sectional Comparative Study of Morbidity Profile in An Automobile Manufacturing UnitAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Remission in Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus PatientDocumento3 pagineComplete Remission in Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus PatientAdvanced Research Publications100% (1)
- Pharmacovigilance in India: A Rising Concern Towards Safe Medication UseDocumento6 paginePharmacovigilance in India: A Rising Concern Towards Safe Medication UseAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Monitoring of Blood Pressure Using Invasive or Non-Invasive Method in Critically Ill Patients: A ReviewDocumento4 pagineMonitoring of Blood Pressure Using Invasive or Non-Invasive Method in Critically Ill Patients: A ReviewAdvanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- An Epidemiology of Reported Needlestick Injuries Among Health Care Workers in Sabah Health Government Facilities From 1999 - 2008Documento10 pagineAn Epidemiology of Reported Needlestick Injuries Among Health Care Workers in Sabah Health Government Facilities From 1999 - 2008Advanced Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Stainless Steel Grade 630Documento6 pagineStainless Steel Grade 630mazaher.ramazaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm B150-2003 PDFDocumento6 pagineAstm B150-2003 PDFRashedul HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Preparation For Construction PDFDocumento61 pagine02 Preparation For Construction PDFMiguel David100% (2)
- Fire Rated Sandstone FRP Door BrochureDocumento2 pagineFire Rated Sandstone FRP Door BrochureSpecial-Lite DoorsNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - CompositesDocumento42 pagineChapter 2 - CompositesAmmar SafwtNessuna valutazione finora
- Injection Quill Assembly Piping Data SheetDocumento4 pagineInjection Quill Assembly Piping Data SheetsudjonoNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm A771Documento5 pagineAstm A771Cristian OtivoNessuna valutazione finora
- RT&HT As Per IBRDocumento2 pagineRT&HT As Per IBRSitaram JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quotation For Layer Equipment With Capacity 55000 Hens - Janey PDFDocumento16 pagineQuotation For Layer Equipment With Capacity 55000 Hens - Janey PDFNasim KurdistanNessuna valutazione finora
- New Ligao City HallDocumento45 pagineNew Ligao City HallrrpenolioNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines For Listing & Registration of Prods & SupplierDocumento142 pagineGuidelines For Listing & Registration of Prods & SuppliermsnirosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aeroquip - Formed Metal Tubing Design RulesDocumento21 pagineAeroquip - Formed Metal Tubing Design RulesbenNessuna valutazione finora
- NHA concrete pouring permitDocumento8 pagineNHA concrete pouring permiterjieNessuna valutazione finora
- AnnealingDocumento9 pagineAnnealingRathne AbeynayakeNessuna valutazione finora
- Slide Plate ApplicationsDocumento2 pagineSlide Plate ApplicationsvietrossNessuna valutazione finora
- Porosity of Electroless Nickel Coatings Investigated Using Different Porosity Tests and Their ApplicationDocumento6 paginePorosity of Electroless Nickel Coatings Investigated Using Different Porosity Tests and Their ApplicationAnnie LauNessuna valutazione finora
- Ce 6506 Construction Techniques, Equipments and PracticesDocumento5 pagineCe 6506 Construction Techniques, Equipments and PracticesDuraid FalihNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 14 BaDocumento6 pagineChapter 14 BaNaeemSiddiquiNessuna valutazione finora
- Technique # 1. Leftward or Forward Welding:: AdvertisementsDocumento2 pagineTechnique # 1. Leftward or Forward Welding:: AdvertisementszombieNessuna valutazione finora
- Piping 2Documento7 paginePiping 2Jeffrey SsalonNessuna valutazione finora
- Methodologies For Repair of Cracks in PQC in Concrete PavementsDocumento9 pagineMethodologies For Repair of Cracks in PQC in Concrete PavementsADC PLNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion Test by Gravimetric MethodDocumento3 pagineCorrosion Test by Gravimetric MethodShanti Kiran ZNessuna valutazione finora
- Check List For Site Construction WorksDocumento65 pagineCheck List For Site Construction WorksUmar Farooq91% (11)
- UNit 3 Part A RevisedDocumento76 pagineUNit 3 Part A Revisedraymon sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and fabrication of groove press toolDocumento47 pagineDesign and fabrication of groove press toolBharathi ChegueweraNessuna valutazione finora
- OPSS 791 Nov2014Documento6 pagineOPSS 791 Nov2014Muhammad UmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Concrete Masonry SpecificationsDocumento4 pagineConcrete Masonry SpecificationsGlenda CambelNessuna valutazione finora
- Cutting Tool and Tool GeometryDocumento58 pagineCutting Tool and Tool Geometry18033 S.M RahatNessuna valutazione finora
- Saej 524 V 002Documento5 pagineSaej 524 V 002Marcos Verissimo Juca de PaulaNessuna valutazione finora