Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Level One Curriculum Framework: Teacher Effectiveness Measure (
Caricato da
Vivanie YanireeTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Level One Curriculum Framework: Teacher Effectiveness Measure (
Caricato da
Vivanie YanireeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Level One Curriculum Framework
INTRODUCTION
The Shelby County Schools (SCS) World Language Program fully embraces a performance-driven curriculum that
is focused on two guiding principles:
1. Learning episodes and ultimately the curricula that guides these episodes must be student-
centered, and
2. World Language learning should focus on building measurable proficiency for real world
purposes.
Our students are our most important customers; therefore “real world” is dictated by the students’ perspective.
Real world is also defined as learning tasks and situations that students would actually experience in the real
world. While fanciful and imaginary scenarios can be fun and entertaining ultimately achieving immediate
attentiveness from most students, the necessary meaningful context the brain needs to retain information is
lacking and subsequently does not yield the retention necessary for building proficiency. It should be noted that
the following curricula topics have been developed with kids in mind and through focus groups with actual SCS
students.
Secondly, research provides multiple compelling rationales for focusing on performance driven programs. We
acknowledge this is a departure from traditional teaching methods and is a paradigm shift for many teachers as
this was not the way we learned languages. The recent national focus on growth (in addition to achievement)
supports this paradigm shift and departure from traditional methods to both grow our students and to grow
ourselves as professionals. We acknowledge that this is a shift and fully support the growth of you as a
professional through a concerted effort and focus on high-yield, model teaching practices.
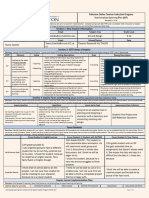
The Teacher Effectiveness for Language Learning Project Criteria support and define the Teacher Effectiveness
Measure (TEM) Evaluation Criteria used in SCS in a content specific manner. The curricula are developed to
provide teachers the necessary tools to develop student proficiency via a series of performances throughout the
year. These performances become the basis of your Alternative Growth Measures Portfolio and directly affect
your evaluation. An example of the correlation between TEM and TELL follows with a rationale for how the
curricula support the identified criteria.
TEM Criteria TELL Criteria Curricula Support
Curricula are developed to
Teach 1: Objective-Driven
promote proficiency growth
Lesson P1: I plan learning experiences
through carefully structured and
& based on local curriculum and
sequenced units of learning
Teach 3: Appropriately state and national standards.
designed to promote success on
Challenging Work
your annual portfolio submission.
A complete crosswalk can be found at http://scsworldlanugages.weebly.com/professionalgrowth.
© Level One 2016 Introduction
Level One Curriculum Framework
INTRODUCTION (CONTINUED)
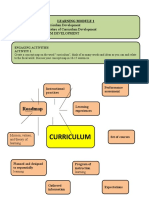
The 2015 Curricula design was developed using the
backward design process beginning with the Advanced
Placement (AP) themes. Through unpacking the AP
themes and analyzing how each theme manifests at
designated proficiency levels, we were able to design the
curricula to provide ample performance opportunities for
students. These performances empower students to build
their language skill in addition to content knowledge in a
manner that prepares the students for future AP
coursework and to be life-long language learners.
Each year, the AP themes replicate in the same pattern to
provide concrete scaffolding of content as linguistic skill
develops, improves and refines. The replicating pattern is
demonstrated in the image on the left. Two remaining AP
themes: Beauty and Aesthetics and Science and
Technology, are integrated throughout the units as they
impact all of the topics studied. Our goal is through
intentional planning and supportive implementation of the
designed curricula, AP enrollment will continue to increase
district wide as well as scores continue to increase
providing successful language learning opportunities to as
many students as possible.
TARGETS
ANNUAL PERFORMANCE TARGET: INTERMEDIATE LOW OR HIGHER
Intermediates can:
• participate in simple direct conversations
• ask and answer questions
• handle basic uncomplicated communication needed in daily life (survival language)
• “create” with the language by combining language to express their own thoughts
• use discrete sentences and strings of sentences; can use sentence connectors
For more information visit:
• American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Languages (ACTFL) Performance Descriptors:
https://www.actfl.org/sites/default/files/pdfs/PerformanceDescriptorsLanguageLearners.pdf
• American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Languages (ACTFL)Proficiency Guidelines:
http://www.actfl.org/publications/guidelines-and-manuals/actfl-proficiency-guidelines-2012
• ACTFL Assessment of Performance Toward Proficiency in Languages (AAPPL) Rubrics:
http://aappl.actfl.org/scores
© Level One 2016 Introduction
Level One Curriculum Framework
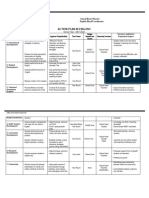
Performance Descriptor by Skill
Speaking Writing Listening Reading
Novice level speakers can Writers at the novice level are At the novice level, listeners At the novice level, readers
communicate short messages characterized by the ability to can understand key words, can understand key words and
on highly predictable every produce lists and notes, true aural cognates, and cognates., as well as formulaic
day topics that affect them primarily by writing words and formulaic expressions that are phrases that are highly
directly. They do so primarily phrases. They can provide highly contextualized and contextualized. Novice level
through the use of isolated limited formulaic information highly predictable, such as, readers are able to get a
words and phrases that have on simple forms and those found in introductions limited amount of information
been encountered, documents. These writers can and basic courtesies. Novice from highly predictable texts
memorized, and recalled. produce practiced material to level listeners understand in which the topic or context is
Novice level speakers may be convey the most simple words and phrases from very familiar such as a hotel
difficult to understand even by messages. In addition, they simple questions, statements, bill, a credit card receipt, or a
the most sympathetic can transcribe familiar words and high frequency weather map. Readers at the
interlocutors accustomed to and phrase, copy letters of the commands. They typically novice level may rely heavily
non-native speech. alphabetic to reproduce basic require repetition, rephrasing, on their own background
characters with some accuracy. and or a slowed rate of speech knowledge and extra-linguistic
for comprehension. They rely support (such as imagery on
heavily on extra-linguistic the weather map or the format
support (i.e. pictures) to derive of a credit card bill) to derive
meaning. meaning.
© Level One 2016 Introduction
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- DNSC Doctoral Curr DevDocumento11 pagineDNSC Doctoral Curr DevDenan Cavan Solo CariňoNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus in EEng 1 (2nd sem 2020-2021)Documento14 pagineSyllabus in EEng 1 (2nd sem 2020-2021)mlbejarin21Nessuna valutazione finora
- AS A Level Global Perspectives and Research WYNTKDocumento4 pagineAS A Level Global Perspectives and Research WYNTKstephNessuna valutazione finora
- Action Plan (English)Documento3 pagineAction Plan (English)Eipol de la VegaNessuna valutazione finora
- ESL Grade 8 Curriculum Guide - Quarter 2 FocusDocumento65 pagineESL Grade 8 Curriculum Guide - Quarter 2 FocusEra Darren NacenoNessuna valutazione finora
- English For Specific PurposeDocumento27 pagineEnglish For Specific PurposekillpreyNessuna valutazione finora
- ESL Curriculum Planning Guide Grades 9-10 Quarter 1Documento65 pagineESL Curriculum Planning Guide Grades 9-10 Quarter 1Maribel DeleonNessuna valutazione finora
- LAREAC Course Outline ESL 1 Final 120915Documento42 pagineLAREAC Course Outline ESL 1 Final 120915EllenNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutor TesmcDocumento2 pagineTutor TesmcTOMMY-GUNNNessuna valutazione finora
- The Global Scale of English TeacherDocumento5 pagineThe Global Scale of English TeacherMonika MeszarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro Teaching Skills for Future English TeachersDocumento9 pagineMicro Teaching Skills for Future English TeachersMushawwir AkbarNessuna valutazione finora
- ESP Syllabus AnalysisDocumento8 pagineESP Syllabus AnalysisVanessa Mae SingcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Newby Ilp Form 2Documento5 pagineNewby Ilp Form 2api-679055080Nessuna valutazione finora
- Comparing Instructional Planning ModelsDocumento8 pagineComparing Instructional Planning ModelsAllyssa Jean MausaNessuna valutazione finora
- (Penalba) Lac Team 11 LDM2 Module 4 L2 A1 2Documento4 pagine(Penalba) Lac Team 11 LDM2 Module 4 L2 A1 2Nica PenalbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Newby Ilp FormDocumento4 pagineNewby Ilp Formapi-679055080Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reflecting on Teaching Skills and Planning Continuing Professional DevelopmentDocumento3 pagineReflecting on Teaching Skills and Planning Continuing Professional DevelopmentRosa Villaluz Banaira67% (3)
- TTL 2 - Activity 1Documento6 pagineTTL 2 - Activity 1John Lawrence A. BellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Glossary IBCPDocumento8 pagineGlossary IBCPAmit RastogiNessuna valutazione finora
- Action PlanDocumento7 pagineAction PlanAmalia AbadNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning Continuing Professional DevelopmentDocumento5 paginePlanning Continuing Professional DevelopmentOishin MariscalNessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum Development4Documento12 pagineCurriculum Development4Teacher SallyNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.0 Approaches To Course DesignDocumento4 pagine4.0 Approaches To Course DesignShainah Marie D. BorbonNessuna valutazione finora
- Englishevaluationtool 2013Documento12 pagineEnglishevaluationtool 2013ChrisNessuna valutazione finora
- EAQUALS Framework For Language Teacher TrainingDocumento50 pagineEAQUALS Framework For Language Teacher TrainingLukasz KnapNessuna valutazione finora
- CCRS WL FINAL Web - QualityDocumento90 pagineCCRS WL FINAL Web - Qualityasja skokNessuna valutazione finora
- Action Plan (English)Documento2 pagineAction Plan (English)ELNIDA DEQUINANessuna valutazione finora
- Wooten - MRK 1Documento16 pagineWooten - MRK 1api-291347908Nessuna valutazione finora
- SYL EL118 Language Learning Materials DevelopmentDocumento9 pagineSYL EL118 Language Learning Materials DevelopmentREAS FAITHNessuna valutazione finora
- CEFR For ESOL Classroom in Malaysia ContextDocumento22 pagineCEFR For ESOL Classroom in Malaysia ContextWan Hasniza OthmanNessuna valutazione finora
- ENGLISH-I Secondary Education Curriculum 2010Documento38 pagineENGLISH-I Secondary Education Curriculum 2010Hari Ng Sablay100% (10)
- Instructional Design: The Systematic ApproachDocumento19 pagineInstructional Design: The Systematic ApproachYoga TamaNessuna valutazione finora
- ELL Student Reading Success PlanDocumento12 pagineELL Student Reading Success PlanJeff RichNessuna valutazione finora
- English Action Plan 2021 2022Documento2 pagineEnglish Action Plan 2021 2022Jonefer Nazareno Paran100% (1)
- Guide Part 1 - FundamentalsDocumento14 pagineGuide Part 1 - FundamentalsLorenzo MagsipocNessuna valutazione finora
- Curtain Dahlberg 5th Edition 2016Documento73 pagineCurtain Dahlberg 5th Edition 2016Mónica Morales Garcia100% (1)
- Instructural Routines Teacher Guide For English Language LearnersDocumento170 pagineInstructural Routines Teacher Guide For English Language LearnersMartha BarraganNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Is A Constant Mechanism. in Our Jobs As Teachers, There Are Still A Lot of Things We Can Improve On, Even As We Go Through This PandemicDocumento4 pagineLearning Is A Constant Mechanism. in Our Jobs As Teachers, There Are Still A Lot of Things We Can Improve On, Even As We Go Through This Pandemicjmym0902Nessuna valutazione finora
- TEEG Wk6Documento5 pagineTEEG Wk6James SarabiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rise and Shine L6 GSE Teacher Mapping BookletDocumento39 pagineRise and Shine L6 GSE Teacher Mapping BookletJigoji GTNessuna valutazione finora
- Tot For The New Osh City Kgtesol Leaders: Introduction To Tot ProcessDocumento6 pagineTot For The New Osh City Kgtesol Leaders: Introduction To Tot ProcessGulnara AbdievaNessuna valutazione finora
- Amelia Louise Yoon Monroe - Te 892 Fa20 Amplified Lesson-CompressedDocumento30 pagineAmelia Louise Yoon Monroe - Te 892 Fa20 Amplified Lesson-Compressedapi-299462355Nessuna valutazione finora
- August 17th - New Hires PresentationDocumento16 pagineAugust 17th - New Hires Presentationapi-589645770Nessuna valutazione finora
- Arteaga - TED 407 Syllabus - Spring 2021 - TuesdayDocumento16 pagineArteaga - TED 407 Syllabus - Spring 2021 - TuesdayHenry PapadinNessuna valutazione finora
- Session GuideDocumento19 pagineSession GuideMa.Catherine Siton100% (2)
- Ldm2 Module 4 - Dennis MichelleDocumento4 pagineLdm2 Module 4 - Dennis MichelleMalabon-Kaingin Elementary SchoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Notes in English Based on Table of SpecificationsDocumento9 pagineReview Notes in English Based on Table of SpecificationsAlila-in John Ismael V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sample - T L Good To OutstandingDocumento11 pagineSample - T L Good To Outstandingapi-344945420Nessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 1: I Think I Need To Focus More On The Domain 1 Containing Knowledge andDocumento4 pagineActivity 1: I Think I Need To Focus More On The Domain 1 Containing Knowledge andMELANY A. MANRIZANessuna valutazione finora
- Eng211CO2021 22 DALUMAYDocumento5 pagineEng211CO2021 22 DALUMAYCiarrah PosterNessuna valutazione finora
- Development Reading 1Documento9 pagineDevelopment Reading 1Karen MolinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dever - Literacy PlanDocumento13 pagineDever - Literacy Planapi-331810252Nessuna valutazione finora
- Indigenous Languages Junior - Infant To JuniorDocumento31 pagineIndigenous Languages Junior - Infant To JuniorRutendo Christashel GwekwerereNessuna valutazione finora
- AAFI INSTRUCTIONAL DELIVERY PLAN For S.Y. 2020 - 20121Documento7 pagineAAFI INSTRUCTIONAL DELIVERY PLAN For S.Y. 2020 - 20121Tine Watts Azucena GalvezNessuna valutazione finora
- RPMS SY 2021-2022: Teacher Reflection Form (TRF)Documento4 pagineRPMS SY 2021-2022: Teacher Reflection Form (TRF)Mikael Tuazon100% (1)
- Planning For Learning and AssessmentDocumento3 paginePlanning For Learning and AssessmentTami WeissNessuna valutazione finora
- DepEd Cebu Mid-Year Teacher TrainingDocumento8 pagineDepEd Cebu Mid-Year Teacher TrainingAaron De DiosNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding by Design curriculum framework for the 2010 SECDocumento25 pagineUnderstanding by Design curriculum framework for the 2010 SECKlarisi VidalNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 LenieDocumento3 pagineModule 4 LenieJeramie Sarita SumaotNessuna valutazione finora
- The Study Skills Curriculum: Developing Organized Successful Students Elementary-High SchoolDa EverandThe Study Skills Curriculum: Developing Organized Successful Students Elementary-High SchoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Around The School DirectionsnotesheetDocumento1 paginaAround The School DirectionsnotesheetVivanie YanireeNessuna valutazione finora
- Spanish Book ReportDocumento1 paginaSpanish Book ReportVivanie YanireeNessuna valutazione finora
- El Verbo Ser NotesDocumento1 paginaEl Verbo Ser NotesVivanie YanireeNessuna valutazione finora
- Dice Cards PDFDocumento1 paginaDice Cards PDFVivanie YanireeNessuna valutazione finora
- Path To ProficiencyDocumento1 paginaPath To ProficiencyVivanie YanireeNessuna valutazione finora
- Rubric SDocumento2 pagineRubric SVivanie YanireeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 5. Challenges in TeachingDocumento21 pagineLesson 5. Challenges in TeachingMarjori Anne Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Academic Sessions 2010-2011Documento2 pagineAcademic Sessions 2010-2011indda_ar5615Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Three Branches of GovernmentDocumento2 pagineThe Three Branches of Governmentapi-619065553Nessuna valutazione finora
- Objectives: School: Grade Level: Teacher: Learning Area: Teaching Dates and Time: QuarterDocumento3 pagineObjectives: School: Grade Level: Teacher: Learning Area: Teaching Dates and Time: QuarterGracia MaeNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL - Science 6 - Q3 - W1Documento3 pagineDLL - Science 6 - Q3 - W1Mariejoy MonterubioNessuna valutazione finora
- Resume 2021Documento3 pagineResume 2021api-310182964Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Curriculum?: A Variety of DefinitionsDocumento42 pagineWhat Is Curriculum?: A Variety of DefinitionsKarti JasminNessuna valutazione finora
- Utilization of Contextualized Teaching and Learning (CTL) : Southern Luzon State UniversityDocumento116 pagineUtilization of Contextualized Teaching and Learning (CTL) : Southern Luzon State UniversityMarkChristianRobleAlmazanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chandu RESUMEDocumento2 pagineChandu RESUMEvijay_srivatsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Invisible Man CH 1Documento4 pagineInvisible Man CH 1api-295134416Nessuna valutazione finora
- Positive Self-Talk Part 2Documento2 paginePositive Self-Talk Part 2api-396767767Nessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation of "Talk a LotDocumento10 pagineEvaluation of "Talk a LotHenry OsborneNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 11 English Lesson on Academic Reading StrategiesDocumento3 pagineGrade 11 English Lesson on Academic Reading StrategiesMenjie AntiportaNessuna valutazione finora
- CertificatesDocumento13 pagineCertificatesMelvin SarteNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Management Rules and ImportanceDocumento3 pagineClassroom Management Rules and ImportanceLovely Rose MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Feedback Log 1Documento3 pagineFeedback Log 1api-660565967Nessuna valutazione finora
- Edu 201 Portfolio Project 12Documento2 pagineEdu 201 Portfolio Project 12api-609317321Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3Documento3 pagineLesson 3Analo Miranda AntigaNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Literature ContextDocumento3 pagineLearning Literature ContextHeart SophieNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebook Ed4 Unit 5Documento24 pagineEbook Ed4 Unit 5Zarry ZackNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Lesson 2 Unit 2 Cambridge English Book 3Documento3 pagineLesson Plan Lesson 2 Unit 2 Cambridge English Book 3Fatma EssamNessuna valutazione finora
- Tat1 Task 2 Day 2 Lesson 8Documento1 paginaTat1 Task 2 Day 2 Lesson 8api-404465268Nessuna valutazione finora
- Self Efficacy and Language Learning Strategies Inputs To Enhance English Students Performance in New NormalDocumento12 pagineSelf Efficacy and Language Learning Strategies Inputs To Enhance English Students Performance in New NormalLea Agan SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Early Childhood EducationDocumento7 pagineComparative Early Childhood Educationghulam nabi shakirNessuna valutazione finora
- Improvisation Crucial for Meaningful Music EducationDocumento2 pagineImprovisation Crucial for Meaningful Music EducationRui LeiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Education Is Important?Documento3 pagineWhy Education Is Important?kreizner calvinNessuna valutazione finora
- EOPS Application Checklist: Within 1 Week Within 2-3 Weeks Within The Month Over A Month AgoDocumento1 paginaEOPS Application Checklist: Within 1 Week Within 2-3 Weeks Within The Month Over A Month AgoCris Carry-onNessuna valutazione finora
- Katelyn Turner ResumeDocumento2 pagineKatelyn Turner Resumeapi-401943774Nessuna valutazione finora
- Non Digital Leanring MaterialsDocumento12 pagineNon Digital Leanring Materialsella florez0% (1)
- Research Into Identifying Effective Learning Environments: Oecd/Peb Evaluating Quality in Educational Facilities 2005Documento9 pagineResearch Into Identifying Effective Learning Environments: Oecd/Peb Evaluating Quality in Educational Facilities 2005SravyaSreeNessuna valutazione finora