Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Synchronous or Phase-Sensitive Detector
Caricato da
Joao CelloCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Synchronous or Phase-Sensitive Detector
Caricato da
Joao CelloCopyright:
Formati disponibili
12.
4 Synchronous or Phase-Sensitive Detector
(SD) (PSD)
+1
LPF
Signal A low-pass
B filter
Φ
–1
Switch control
Reference
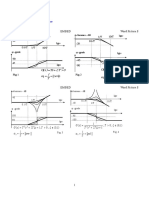
Figure 12.29 Phase-sensitive detector: principles of operation
Signal
2VS
Сигнал
0
t
V Reference
+ + +
Опорный
сигнал
- - t
Switch output
2VS Output from low-pass filter выход с ФНЧ
Выход с
ключа
0
t
Идеальная синхронизация 0 0
An ideal synchro Φ=00
Figure 12.30 Waveforms in a phase-sensitive detector operating with an in-phase sine
wave signal
Phase-sensitivity and Output-polarity of the SD
V V V
V
0 0 0
Signal
Сигнал
Сигнал
0
Сигнал
t t t
t
V V V
+ + + + + +
Reference
Опорный
0
сигнал
0
Опорный
0
сигнал
Опорный
0
сигнал
- - - t
- - - t
- - t
V V
V
0
Switch output
Выход с
ключа
0
Выход с
ключа
0
Выход с
ключа
t t
t среднее
значение
среднее
значение
среднее
значение
Average value, V0
(а) (b) (c)
Figure 12.31 Waveforms in a phase-sensitive detector for different phase conditions:
(а) θ=180˚; (b) θ=90˚; (с) arbitrary phase;
V0=k*Vi*cos θ
Φs-Φr=0 Φs-Φr=180
t
t
θ=0˚, cos θ=+1 θ=180˚, cos θ=-1 ˚
Φs - Φr = 90˚ Φs - Φr = 270˚
θ=90˚, cos θ=0 --- θ=270˚, cos θ=0
Characteristics of the SD (phase-sensitive detector)
time const. τс
Output
Signal input Low-
pass
filter
(υR at fR )
Inverting
Amplifier
Reference input
Signal input and reference input related and in step (in-phase)
Напр
Signal input
0
Reference input
Output of p.s.d.
No synchro 0
output of filter
cos90=0
time
P.s.d. characteristic
Output
bandwidth 1 / π·τс
cos θ
50Hz
180
0
90 270 θ fr
frequency
noise
power per unit bandwidth
cosine phase-sensitivity
Phase-sensitive detector’s output
versus phase difference between inputs θ
sinusoidal input square wave input
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Poster WSDocumento1 paginaPoster WSAnonymous GhQ1eIyxunNessuna valutazione finora
- Drive Unit 2 & 3 DC ChopperDocumento26 pagineDrive Unit 2 & 3 DC ChopperswamNessuna valutazione finora
- 0700-038-EU - FGFD - Leaflet - Rev13 - EN - 2023Documento8 pagine0700-038-EU - FGFD - Leaflet - Rev13 - EN - 2023senchromNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical-Engineering Engineering Power-Electronics Dc-Choppers Notes PDFDocumento26 pagineElectrical-Engineering Engineering Power-Electronics Dc-Choppers Notes PDFyemane gebremichalNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital To Analog Converters - TutorialspointDocumento5 pagineDigital To Analog Converters - Tutorialspointdiether.gozumNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 4 - Flip Flop & RegistersDocumento27 pagineMODULE 4 - Flip Flop & RegistersChaitanya J S ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Potassium Enz Cobas c-701 702Documento2 paginePotassium Enz Cobas c-701 702MaherNessuna valutazione finora
- Diode (Semicond) - PART BDocumento30 pagineDiode (Semicond) - PART Bnur ain natasyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Speelklaar 185-2002Documento24 pagineSpeelklaar 185-2002MsnLMT100% (2)
- OP Amp 1Documento14 pagineOP Amp 1Hesham EbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 VerteDocumento78 pagine3 VertePrasann KatiyarNessuna valutazione finora
- TRA LeegDocumento1 paginaTRA LeegMark van DorstenNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Documento1 pagina4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNessuna valutazione finora
- Shema 1Documento4 pagineShema 1Ali KENAANNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3Documento54 pagineModule 3Sidharth GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical-Engineering Engineering Power-Electronics Dc-Choppers NotesDocumento29 pagineElectrical-Engineering Engineering Power-Electronics Dc-Choppers NotesAsha PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Toggle Switches Mil-S-83731Documento1 paginaToggle Switches Mil-S-83731Russell GouldenNessuna valutazione finora
- L2: Combinational Logic Design (Construction and Boolean Algebra)Documento27 pagineL2: Combinational Logic Design (Construction and Boolean Algebra)Kaleb FikreNessuna valutazione finora
- SIPART DR20 Compact Controller Project Planning ManualDocumento2 pagineSIPART DR20 Compact Controller Project Planning ManualDavlos IngNessuna valutazione finora
- R L C V I R L C R L C I - T: G 2 S T D 2 SDocumento1 paginaR L C V I R L C R L C I - T: G 2 S T D 2 SBrijendra SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyristors: Power Electronics Circuits, Devices, and Applications Third Edition Muhammad H. RashidDocumento65 pagineThyristors: Power Electronics Circuits, Devices, and Applications Third Edition Muhammad H. RashidTuhin ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Capacitance of Forward Biased DiodeDocumento46 pagineCapacitance of Forward Biased DiodeMesi WijayaNessuna valutazione finora
- 83 Transistor3 PDFDocumento1 pagina83 Transistor3 PDFarturoNessuna valutazione finora
- Intelligent Digital Display Controller: FeaturesDocumento4 pagineIntelligent Digital Display Controller: FeaturesLisovencu GigiNessuna valutazione finora
- User and Safety GuideDocumento2 pagineUser and Safety GuidecarsolutionscaboNessuna valutazione finora
- The Inverter ReportDocumento47 pagineThe Inverter Reportronaldbolorbaral8809Nessuna valutazione finora
- EE109Unit18 NoiseMarginCMOS NotesDocumento7 pagineEE109Unit18 NoiseMarginCMOS NotesEmin KültürelNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar "Signals and Systems 1" Seminar Theme 2: "Signals in The Time-And Frequency Domain"Documento8 pagineSeminar "Signals and Systems 1" Seminar Theme 2: "Signals in The Time-And Frequency Domain"Ummu Abiha AssociatesNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalog ProbeDocumento76 pagineCatalog ProbeTamil SelvanNessuna valutazione finora
- AC Circuit & Diode BasicDocumento45 pagineAC Circuit & Diode BasicKamaruz DanialNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 PDFDocumento45 pagineUnit 3 PDFYashika choudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 PDFDocumento45 pagineUnit 3 PDFGlenn Paul PaceteNessuna valutazione finora
- DC ChoppersDocumento140 pagineDC ChopperspsoumyaNessuna valutazione finora
- NR V2X Communication: Ji Min LeeDocumento21 pagineNR V2X Communication: Ji Min LeeLastNightMixNessuna valutazione finora
- Cmos Logic 2: Key ConceptsDocumento36 pagineCmos Logic 2: Key ConceptsVivek100% (2)
- Clippers and Doublers PrintDocumento1 paginaClippers and Doublers PrintSuseel MenonNessuna valutazione finora
- Quick Guide Interface: Mounting Base Interfaces AlarmDocumento6 pagineQuick Guide Interface: Mounting Base Interfaces AlarmAlexandro HotnandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Clip, ClampDocumento9 pagineClip, ClampESNessuna valutazione finora
- Rflab 7Documento4 pagineRflab 7maimoonaziz2003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Power Electronic 1Documento48 paginePower Electronic 1Joo AdelNessuna valutazione finora
- EE3101 Communication Engineering: Chapter 3-2, SynchronizationDocumento15 pagineEE3101 Communication Engineering: Chapter 3-2, SynchronizationfishkantNessuna valutazione finora
- SodapdfDocumento18 pagineSodapdfby767ronNessuna valutazione finora
- Edcp - 2Documento34 pagineEdcp - 2Raja AdnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel I - Beam Calculation Note Steel I - Beam Calculation NoteDocumento2 pagineSteel I - Beam Calculation Note Steel I - Beam Calculation NoteMarvin ItolondoNessuna valutazione finora
- DC ChoppersDocumento38 pagineDC ChoppersBelayneh TadesseNessuna valutazione finora
- T66340 EN Catalog 2012 1207-NewDocumento6 pagineT66340 EN Catalog 2012 1207-Newmy_mal2002Nessuna valutazione finora
- LB1 2021-3Documento4.968 pagineLB1 2021-3amelia niitaNessuna valutazione finora
- V: +5V V: +5V: InstructionsDocumento1 paginaV: +5V V: +5V: Instructions056S7HRITIK GUPTANessuna valutazione finora
- Nx-Dspic30f eDocumento4 pagineNx-Dspic30f eCemil_Baki_K_y_3546Nessuna valutazione finora
- Active Filters: Conventional Passive Filters Consist of LCR Networks. Inductors Are Undesirable ComponentsDocumento18 pagineActive Filters: Conventional Passive Filters Consist of LCR Networks. Inductors Are Undesirable Componentsmaithuong85Nessuna valutazione finora
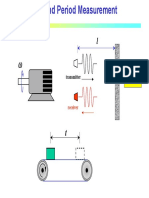
- Frequency and Period Measurement: TransmitterDocumento24 pagineFrequency and Period Measurement: TransmitterSavuDanielFNessuna valutazione finora
- For Capacitor of C 1uf 2. For Capacitor of C 10ufDocumento3 pagineFor Capacitor of C 1uf 2. For Capacitor of C 10ufSuseel MenonNessuna valutazione finora
- Ew412 - Ew512Documento2 pagineEw412 - Ew512Carlos PosadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Iii: DC To DC ConverterDocumento58 pagineUnit Iii: DC To DC ConverterGabriel SanthoshkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- HRN-55 55N DatasheetDocumento1 paginaHRN-55 55N DatasheetJeff CooperNessuna valutazione finora
- Input Filter Interactions With Switching by BassoDocumento166 pagineInput Filter Interactions With Switching by BassoshrikrisNessuna valutazione finora
- 5977SS2q3 PDFDocumento1 pagina5977SS2q3 PDFarturoNessuna valutazione finora
- Probleme Control OptimalDocumento2 pagineProbleme Control OptimalCostica PoienaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Log and Antilog AmplifiersDocumento8 pagineLog and Antilog AmplifiersDeepanshi RuhelaNessuna valutazione finora
- AMG Error CodesDocumento1 paginaAMG Error CodesSarra Chouchene100% (1)
- Rating Sheet FinalDocumento7 pagineRating Sheet FinalJazelle FacunNessuna valutazione finora
- Ze Gcs04a20-Eng 247-270Documento24 pagineZe Gcs04a20-Eng 247-270ikrima BenNessuna valutazione finora
- P MAN PUB Brivo ACS6000 Installation ManualDocumento40 pagineP MAN PUB Brivo ACS6000 Installation ManualGerson FelipeNessuna valutazione finora
- MPR 45SDocumento4 pagineMPR 45Sกรสกล มุทะสินNessuna valutazione finora
- Microwave: Microwaves Are A Form ofDocumento9 pagineMicrowave: Microwaves Are A Form ofDhanmeet KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- ERICSSON Business Objects KPIs Generation Process DocumentationDocumento13 pagineERICSSON Business Objects KPIs Generation Process DocumentationAbhishek Sharma100% (2)
- SoundHack Max MSP and PD Externals - SliDocumento15 pagineSoundHack Max MSP and PD Externals - SliJuli?n r?osNessuna valutazione finora
- Linkwitz Riley Crossovers Primer PDFDocumento14 pagineLinkwitz Riley Crossovers Primer PDFloach71Nessuna valutazione finora
- Panasonic+Th 46pz85u+Service+ManualDocumento128 paginePanasonic+Th 46pz85u+Service+Manuala1electronicsNessuna valutazione finora
- User Manual 4009600Documento3 pagineUser Manual 4009600Ahmed ProlicNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No 5 Single-Phase Current Transformer: ObjectiveDocumento3 pagineExperiment No 5 Single-Phase Current Transformer: ObjectiveMr Hassan RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2Documento3 pagineAssignment 2Shahid KhattakNessuna valutazione finora
- Kết hợp hệ thống lưu trữ năng lượng pin vào hệ thống PV kết nối lưới nhiều MWDocumento9 pagineKết hợp hệ thống lưu trữ năng lượng pin vào hệ thống PV kết nối lưới nhiều MWHung leNessuna valutazione finora
- Samsung 713bm 913bm Plus CH Ls17plm Ls19plmDocumento34 pagineSamsung 713bm 913bm Plus CH Ls17plm Ls19plmCristian Valentin0% (1)
- BBP Mockman PDFDocumento1 paginaBBP Mockman PDFFernando de LuccaNessuna valutazione finora
- LTC3305Documento28 pagineLTC3305Lu HoaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lorain BD 2000 DatasheetDocumento2 pagineLorain BD 2000 DatasheetalfredoculajayNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 ALCE Low Voltage Transformers 13R01Documento28 pagine4 ALCE Low Voltage Transformers 13R01Amílcar DuarteNessuna valutazione finora
- AOC E2043fs LCD MonitorDocumento50 pagineAOC E2043fs LCD MonitorFranko Ney FélixNessuna valutazione finora
- Panasonic Nv-gs50 ManualDocumento16 paginePanasonic Nv-gs50 Manualstotall100% (1)
- 2 SB 1370Documento2 pagine2 SB 1370wilsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Bosch Edna Mall Pricelist Jul 2016 Euro-1Documento30 pagineBosch Edna Mall Pricelist Jul 2016 Euro-1tesemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Operational AmplifiersDocumento49 pagineOperational Amplifiersangelo rodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lovepedal Purple Plexi 800Documento1 paginaLovepedal Purple Plexi 800Shibbit100% (1)
- Руководство По Протоколу ModBus RTU (Protocol Manual)Documento2 pagineРуководство По Протоколу ModBus RTU (Protocol Manual)imaginshield100% (1)
- Analog PyqDocumento172 pagineAnalog PyqNisha SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 01-04 Optical and Electrical ModulesDocumento22 pagine01-04 Optical and Electrical ModulesFranco RHNessuna valutazione finora
- Atestat EnglezaDocumento16 pagineAtestat EnglezaCosmin CrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Magellan Maestro 4700: User ManualDocumento49 pagineMagellan Maestro 4700: User Manualcriggs63Nessuna valutazione finora