Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Development and Evaluation of A Novel Transungual Formulation (Nail Patch) For The Treatment of Onychomycosis
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Development and Evaluation of A Novel Transungual Formulation (Nail Patch) For The Treatment of Onychomycosis
Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Development and Evaluation of a Novel Transungual
Formulation (Nail Patch) for the Treatment of
Onychomycosis
Samyuktha Metta1, Dr. K.S .Murali Krishna2, Swapna. Kandukuri3,
Sravya Maddukuri4 , Swarna Latha Nagadhani5
1
Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, M L R Institute of Pharmacy,
Hyderabad,Telangana,India
2
Principal, Professor, Department of Pharmacognosy, M L R Institute of Pharmacy,
Hyderabad,Telangana,India
3, 4, 5
Assistant Professor ,Department of Pharmaceutics, M L R Institute of Pharmacy,
Hyderabad, Telangana, India
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 562
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
ABSTRACT
Nail may be defined as translucent plates of hard keratin lying fused with nail bed except at distal
end. Toe nails and finger nails protects the tissues of toes and fingers. Nail are made up of a harden
protein known as Keratin, which are also present in hair and skin. The health of nails can be a better clue
of overall health. Nail diseases are mainly associated with conditions like bacterial & fungal infections,
iron deficiency anemia, congenital defects. Toenail fungal diseases are much more common than finger
nail fungal diseases. Onychomycosis or tinea unguium is most common toenail fungal infection usually
caused by a special type of fungus known as a dermatophyte.this toenail fungal infection is responsible
for approxiamatelt 50% of all nail disorders characterized by discoloration and thickening of the nail
and which also effects nail plate,nail bed and nail flods (1).Since most of these infections are relatively
superficial,topical therapies are commonly used for treatment which are limited by keratinized cells in
human nail plate. This type of topical therapeutic application is not sufficient to provide a successful
therapy of such nail diseases as the nail unit is relatively impermeable. Hence current research work
focus on nail permeation by altering the nail plate barrier by means of permeation enhancers.A novel
transungual formulation(Nail patch ) is desirable in treartment of nail diseases like
Onychomycosis.Research work main aim is to formulate and evaluate matrix –type transungual delivery
system containing an antifungal drug,Itraconazole with different permeation enhancers (in 2 different
ratios) by the film casting technique and explores the effect of permeation enhancers on the invitro
permeability of Itraconazole across nail.Matrix transungual patches were prepared by using hydroxyl
propyl methyl cellulose (HPMC E 5) and ethyl cellulose (EC) as polymers,Eudragit RL 100 as pressure
sensitive adhesive by incorporating di ethyl phthalate as plasticizer and Propylene Glycol, Poly ethylene
glycol, and oleic acid as permeation enhancers in 2 different ratios of 4% and 6% v/v in whole
formula.Prepared patches were subjected to different evalution studies in which permeation studies were
performed by using Franz diffusion cell apparatus. All the formulated patches that evaluated shows
uniformity with respect to physiochemical evaluation. The in-vitro permeation study indicated that
formulation INP-4 propylene glycol (6%) showed maximum release of 74.719 % in 12 hrs emerging to
be ideal formulation. The developed transungual patches shows increase in the efficacy of Itraconazole
for the treatment of a fungal disease such as Onychomycosis.
Keywords:- Onychomycosis , Transungual, Permeation enhancers, Itraconazole, in-vitro permeation study .
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 563
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
I. INTRODUCTION
Over the years, the human nail has become a fashion accessory, and even with a slacking economy,
people are willing to spend money for inexpensive ways to make their nails look good. Continuous oral
medication may affect all organs, often causing kidney damage and anti-fungal class Itraconazole drug may
produce nausea/vomiting, diarrhoea, gas, headache, dizziness or stomach upset(2). Some infections,trauma,
diseases,improper growth and use of some medications may responsible for the cause of nail disorders.
Certain infections of the nail are caused by bacteria,fungi and virus. Common diseases of nail may include
Onychomycosis, Onychatrophia, Onychogryposis, Leuconychia, Koilonychia,
Onychauxis,psoriasis,onychocryptosis,onychorrhexis,psoriatic onychodystrophy etc., There are variety of
topical formulations like gels,creams and also ointiments which are commonly used for the treatment of nail
infections but affect in the treatment is limited because of their relatively low impermeability. Present work
involves the formulation of transungual drug delivery which is a new drug delivery system to treat nail
infection with effective permeation. Transungual topical administration of therapeutic agents offers many
advantages over conventional oral and invasive methods of drug delivery, and also provides controlled release
of the drug for extended period of the time (3). Topical delivery of antifungal agents through the human nail
offer several advantages over oral therapy including lower incidence of adverse events and lower potential for
drug-drug interaction with drugs used to treat diabetes, HIV/AIDS and psoriasis. Transungual drug delivery
system has been accepted as potential non-invasive route of drug administration, with advantages of prolonged
therapeutic effect, reduced side effects, improved bioavailability, decreased hepatic metabolism, predetermined
rate of drug permeation, better patient compliance and easy termination of drug therapy(4).
Transungual is a greek word that is derived from two words “Trans” means “Through” and “Unguis”
means “Nails”.Transungual drug delivery system is a system associated with drug delivery through the nail to
achieve a target drug delivery system of the nail to treat the nail diseases . Nail plate is main route for
penetration of drug across it and delivery of the drug through nail (nail plate) is known as transungual drug
delivery system(5).
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 564
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
II. ONYCHOMYCOSIS
Onchomycosis (Tinea unguium) is a fungal toe nail infection which is responsible for about 50% of other
nail disorders. Approximately 5% of worldwide population affected by Onychomycosis. (6,7).the word
Onchomycosis is derived from two greek words ,namely onyx-anail,mykes-a fungus.It may affects any part of
the nail unit such as nail plate,nail bed and nail matrix(8).
Fig 1:- Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is a common, chronic and hard to eradicate fungal disease of toe nails and finger nails
affecting 10-30% of the population globally. Clinically onychomycosis presents with discoloration, thickening
and irregular surface. It is responsible for approximately 50% of all nail disorders. Risk factors for nail infection
are diabetes, age, smoking, compromised immune system such as in HIV and peripheral vascular diseases
(9)
.Transungual drug delivery systems with antifugal agent are novel preparations used to treat diseases such as
onychomycosis. Use of this system avoids oral toxicity of anti fungal drugs (10).
A. Tissues affected by Onychomycosis.
Onychomycosis (Tinea unguium) is a fungal nail infection which mainly affects human toe nails.The nail
is a highly differentiated appendage of the skin serving protective functions.(11) Apart from their protective
functions, the nails also play a role in amplifying the sense of touch in the fingertips (12).The nail apparatus
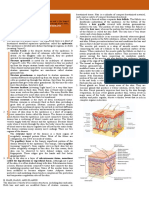
consists of the nail plate ,nail bed ,nail folds,nail matrix and the hyponychium,(13) as shown in figure 2 .The
human nail is composed on 8 0 - 9 0 l a ye r s o f d e a d , h i gh l y k e r a t i n i z e d f l a t t e n e d t i gh t l y b o u n d
c e l l s which lack cell organelles and nucleus . The nail plate is transculent, but appears pink is color due to
the rich vasculature in the nail bed underneath . The nail matrix is thick, specialized germinative epithelial
structure responsible for generation of bulk of the cornified cells of the nail plate (14). The process of
keratinization is different in the nail matrix relative to that in the epidermis because; the onychocytes in the nail
matrix undergo complete keratinization without formation of keratohyalin granules. The proximal nail fold
covers and protects the nail matrix.The newly formed nail emerges out of the proximal nail fold and is
supported by the nail bed. The nail bed extends from the lunula to the hyponychium .About 20% of the
thickness and the mass of the ventral layer of the nail plate is produced by the nail bed (14). The nail bed is
viable epidermis. The inter digitations on the ventral side of the nail plate hold the nail plate firmly in the
place with the nail bed .The lateral nail folds help to hold the nail plate in the place. The
hyponychium is epidermis between the distal nail groove and the nail bed.The nail bed,the nail matrix and the
nail folds are well perfused with blood and lymphatic vessels (15, 16).
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 565
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
B. Treatment available for Onychomycosis(17)
Identified methods of treatment fall into three categories:
Removal of all or division of the affected nails
Oral/systemic therapy
Topical/Ungual therapy
Fig 2:- Components of the Human Nail
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 566
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
III. MATERIALS AND METHODS
A. Materials
Itraconazole was obtained as gift sample from Hetero Pharma LTD., Hyderabad. Polymers such as
Hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose E5 (HPMC) ,Ethyl cellulose (EC) and Penetration enhancers such as
propylene glycol, Poly ethylene glycol 400, Oleic acid was provided by the institute and Pressure sensitive
Adhesive (Eudragit RL-100) was provided by Nacto Pharma Ltd. Analytiacal grade of chemicals such as
Diethyl phthalate, Sodium hydroxide, Potassium dihydrogen Orthophosphate, Di chloro methane and methanol
used and methanol were used for the study.
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 567
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
IV. METHODS OF PREPARATION
A. Preparation of standard solution
Accurately weigh 100mg of pure drug Itraconazole in 100ml volumetric flasks and dissolve in small
quantity of 7.4 pH phosphate buffer inorder to form a clear solution.Then the volume was made with buffer
solution upto 100ml mark so as to obtain a solution containing 1mg/ml(18).
B. Preparation of stock solution
From the standard solution,a stock solution was prepared by pipette out 1ml of above standard solution in
a 100ml volumetric flask and then the volume was with 7.4 pH phosphate buffer solution,to give a solution
containing 100 µg/ml.
C. Preparation of working standard solution
Series of aliquoters 2,4,6,8,and 10 ml of stock solution were pipette out into different volumetric flasks of
10ml volume.The volume was made upto the mark with 7.4 pH phosphate buffer.These dilutions indicates
different concentrations namely 2,4,6,8 and 10 µg/ml concentration of Itraconazole.The prepared solutions were
subjected for the measurement of absorbance at 262 nm by using UV spectrophotometer (Model---Shimadzu-
1800) against an appropriate blank (7.4 pH buffer).
D. Design and Formulation Development of the Transungual Patch
The initial design for the transungual patch was based on the simple DIA ( Drug-in-adhesive) design(19)
In order to meet the key properties for a successful topical patch a DIA type nail patch was designed as
shown in figure 3 .
The nail patches were prepared by film casting technique using liquid Paraffin as lubricant. Prepared
patches composed of four Layers.
Backing membrane
Pressure sensitive adhesive membrane
(Eudragit RL100 5 % w/v of aqueous solution)
Drug loaded HPMC film
( Itraconazole+PE+HPMC+EC+Plasticizer)
Release linear (Peeling paper)
Fig 3:- Drug-matrix-in-adhesive
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 568
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Formulation Code INP1 INP2 INP3 INP4 INP5 INP6
Itraconazole (mg) 200 200 200 200 200 200
HPMC(mg) 800 800 800 800 800 800
Ethyl cellulose(mg) 200 200 200 200 200 200
Eudragit RL 100
5 5 5 5 5 5
(%W/V)
OleicAcid (%) 4 6 --- --- --- ---
Propylene Glycol (%) --- --- 4 6 --- ---
PEG 400 (%) --- --- --- --- 4 6
Diethyl phthalate (ml) 5 5 5 5 5 5
DCM: Methanol(ml) 15 15 15 15 15 15
Table 1. Formulation table of transungual patches of Itraconazole
*Each patch contains 200 mg of drug in 15.896 sq.cm area.
*Each Sq.cm contains 12.5 mg of Itraconazole.
*INP=Itraconazole Nail patch.
The quantities of the components of the matrix were calculated as percentage (%) of dry weight polymer.
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 569
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
V. FABRICATION OF TRANSUNGUAL PATCHES
Fig 4:- Prepared and Fabricated Itraconazole Transungual Patches
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 570
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
VI. EVALUATION OF TRANSUNGUAL PATCHES
Formulation development of a transungual dosage form involves a complex extensive research
process.Transungual patches have been developed to improve the clinical efficacy of the therapeutic drug and
there by enhancing the patient compliance by delivering smaller amounts of drug at predetermined rate.This
ensures the importance of evaluation studies to define the patches performance and reproducibility .
A. Physical appearance:
All the formulated transungual patches were visually inspected for color,transparency,clarity,flexibility
and smoothness.
B. Patch Weight Uniformity:
Weight variation is studied by calculating the average weight of randomly selected individually weighed
patches.The individual weight that evaluated from weight variation test should not be deviated significantly
form average weight.
C. Patch Thickness uniformity:
Patch thickness uniformity test was performed by measuring the formulated patch at 3 different points by
using venier calipers and average of three readings was calculated.
D. Folding Endurance:
The folding endurance test of formulated patches was performed manually by folding the patch repeatedly
at the same place (single point) till it broken.The number of times that the patch subjected to repeated folding at
the same place without cracking/breaking indicates the folding endurance value . Folding endurance evauation
test involves the determination of folding capacity of the films that subjected to folding at the frequent extreme
conditions which also a indicative of brittleness.
E. Percentage moisture absorption:
Accurately weighed patches were placed in a desiccators containing 100ml of saturated solution of
potassium chloride ,which maintains at 80-90% RH.After 3 days,the desiccated patches were taken out and
subjected to weighing.
The percentage moisture absorption was calculated using the formula:
Final Weight – Initial Weight
Percentage moisture absorption = -------------------------------- x 100
Initial Weight
F. Percentage Moisture Loss:
Accurately weighed patches were placed in a desiccator containing anhydrous calcium chloride. After 3
days ,the desiccated patches were taken out and subjected to weighing.
The moisture loss was calculated using the formula:
Final Weight – Initial Weight
Percentage moisture absorption = -------------------------------- x 100
Initial Weight
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 571
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
G. Drug content uniformity
Weigh accurately portion of patch (equivalent to 100 mg of drug) and dissolve in 100ml of phosphate
buffer solution (7.4 pH ) in a 100ml volumetric flask .Place the flask on to the shaker for 24 hrs to achieve the
complete dissolution.Then the obtained solution was filtered and the content was estimated
spectrophotometrically at 262nm by appropriate dilution.
H. Invitro Transungual permeation studies
Franz diffusion cell or Keshary-chien diffusion cell was used to determine the invitro nail permeation of
Itraconazole from various formulated transungual patches.Difussion cell composed of two compartments
i.e.,donar and receptor.The receptor compartment comprises effective surface area of 3x3 cm2 and 5ml capacity
of volume.Permeation studies was carried by placing the fabricated patch with prehydrated nail in between
receptor and donar compartment of the diffusion cell in which the receptor compartment was filled with 7.4 pH
phosphate buffer .Transungual patch was placed in such a way that the nail facing towards the donor
compartment and the patch towards the receptor compartment containing buffer solution(20) in which the
receiver compartment was maintained at body temperature and was subjected to continuous stirring with the
help of magnetic stirrer.
Fig 5:- Franz diffusion cell
Ideally dissolution medium of pH ranging between 5 to 8 and temperature that typically set at 37 o C
should be used which will reflecting skin and nail physiological conditions.100 rpm is a typical agitation rate
for testing a patch section ( According to European Pharmacopoeia).A constant speed of agitation and
temperature should be considered.
At predetermined time intervals the samples to be analysed are withdrawn and equal volume of pre-
thremostated of fresh receptor fluid is replaced each time inorder to maintain skin conditions.Then the samples
were analysed spectrophotometrically after appropriate dilution.
Type of design used to formulate transungual system,size of patch,thickness of nail etc., are some
important variables that may affect the release of the drug from the system.
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 572
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
VII. RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Physicochemical evaluation
A. Physical appearance
The Nail patches of formulations that prepared by using penetration enhancers such as oleic acid and
propylene glycol are thin, transparent, flexible, smooth and uniform where as formulations prepared by PEG
400 yielded thick patches. The transparent nature of patches can be seen more prominently in formulations
prepared by oleic acid. The flexibility can be due to HPMC. (Table -2).
B. Patch weight uniformity
The weights of all transungual patches were found to be uniform. The weight of formulations was
determined by digital electronic balance and results are given in table-3. The weights of formulations were
found to be in the range of 0.295gm. to 0.299 gm. This indicates that there is no significant weight variation in
all formulations.
C. Thickness uniformity
Thicknesses of formulations were measured using venier calipers, and results are given in table-3.
Thickness of transungual patches were found to be in the range of 0.18mm to 0.25mm.The results showed
that thickness was uniform for all the prepared transungual patches.
D. Drug content uniformity
Drug content uniformity of transungual patch was one of the important criteria which will ensure the
uniform and reproducible sustained release of drug drug from the patch.The drug content uniformity of all the
formulations was determined and the results indicated that the drug is uniformly distributed throughout the
patches.the results of drug content uniformity in all the formulations were found to be in the range of 97.21% to
98.95%. (Table-3).
E. Moisture Gain
Among the formulations, INP5 showed maximum moisture uptake i.e. 2.93 % and INP4 showed minimum
moisture uptake i.e. 2.19 %. (Table.3).
F. Moisture Loss
Among all the formulations,INP5 showed maximum moisture loss i.e. 1.56 % and INP2 showed
minimum moisture loss i.e.1.10 %. (Table.3).
G. Folding Endurance
The ability of patch to withstand to rupture can be assessed by folding endurance measurement. All the
patches were evaluated for folding endurance by folding the patch at the same place till it breaks. The folding
endurance measurement shows that the patches were quite flexible and results was found to be satisfactory
(Table-3).The results indicates that the patches would maintain integrity without any breaking upon general
folding when used.The folding endurance values were found in the range of 250 to 316 times. The formulation
INP2 was found to have lowest folding endurance, whereas formulation INP5 was found to have highest folding
endurance. The folding endurance of patches increases with increase in the concentration of penetration
enhancers.
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 573
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
H. In-vitro drug permeation
The drug permeability depends on the penetration enhancer concentration and the cross link density of
patches.Chemical properties of the drug,type of design as well as physicochemical properties of the dialysis
membrane are the considerable characterstics which may influence the release of the drug from the transungual
patch.
In the present study patches were prepared with different permeation enhancers in different
concentrations.Penetration enhancers were used inorder to overcome the barrier properties of nail and skin. To
enhance the permeation efficiency of drug ,chemical enhancers were used.
The in-vitro diffusion study was performed and data obtained from different formulations of Itraconazole
transungual patches are shown in table 4.
The release of the drug from its transungual patch formulations can be ranked in the following descending
order.
INP4>INP2>INP3>INP6>INP1>INP5
Where the amounts of the drug release of formulations INP1, INP2, INP3, INP4, INP5 and INP6 after 12
hours were found to be 64.916%, 72.065%, 70.186%, 74.719%, 64.916%, 67.131% respectively. INP4 shows
highest cumulative amount of drug permeation at the end of 12 hours.
The highest % release from INP4 formulation may be due to the presence of high concentration of
permeation enhancer propylene glycol. The permeability of Itraconazole with propylene glycol (6%) was found
highest in our study.
Formulation
Physical Appearance
Code
Thin ,Transparent,
F1
flexible, Smooth
Thin, Transparent,
F2
Smooth, uniform, soft
Thin, Transparent
F3
Smooth, uniform
Thin, Transparent,
F4
Smooth, uniform, flexible
F5 Smooth, uniform, Thick
F6 Smooth , Sticky ,Thick
Table 2. Physical appearance of Transungual Patches
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 574
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Percent Percenta
Drug Folding
Formulat Weight Thickn age ge
content Endura
ion code uniform ess Moistur Moistur
uniform nce
(mm) e gain e Loss
ity(mg) ity(%)
(%) (%)
INP1 295 0.19 97.91 2.62 1.20 309
INP2 299 0.18 97.86 2.82 1.10 316
INP3 297 0.18 97.21 2.26 1.46 293
INP4 298 0.20 98.95 2.19 1.30 297
INP5 297 0.23 97.42 2.93 1.56 250
INP6 299 0.25 98.85 2.23 1.36 257
*INP=Itraconazole Nail Patch
Table 3. Evaluation parameter of transungual patches
FORMULATION CODE
Time in hours
INP1 INP2 INP3 INP4 INP5 INP6
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 12.633 13.778 13.612 15.789 11.088 13.451
2 19.577 23.558 20.817 26.802 15.817 17.644
4 24.706 34.673 33.368 39.159 21.341 22.794
6 36.727 44.856 40.557 46.239 28.398 34.987
8 42.976 56.567 53.782 58.404 36.938 45.425
10 56.053 63.893 63.322 66.292 53.004 56.127
12 64.916 72.065 70.186 74.719 62.863 67.131
Table 4. Cumulative % drug release data of Transungual patches INP-1 to INP 6
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 575
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
80
Cumulative % Drug Release
70
INP1
60
INP2
50
INP3
40
INP4
30
20 INP5
10 INP6
0
0 Time in 5Hours 10 15
Fig 6:- Cumulative % drug release plot of Trans ungual patches INP-1 to INP-6
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 576
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
VIII. CONCULSION
All the formulated patches that evaluated shows good physiochemical properties with respect to their
thickness,weight variation,folding endurance,moisture gain,moisture loss and optimum cumulative % drug
release from transungual patches of antifungal drug Itraconazole. All the evaluated parameter results shows
promising results.Permeability effect of permeation enhancers like oleic acid, propylene glycol, PEG400 has
been evaluated by in-vitro permeation studies of formulatd tranungual patches and the results was found to be
effective.From these studies it has been understood that as the concentration of penetration enhancer
increases,drug permeation was shown to be increased. This results proved that the problems of Itraconazole on
oral administration This result revealed that the problems of Itraconazole on oral administration like absorption
of drug is rate determined by dissolution rate,nausea/vomiting ,diarrhea,headache,dizziness,stomach upset and
other gastric side effects can be overcome by administration of antifungal drug in the form of transungual patch
with incorporation of suitable penetration enhancers instead of topical therapies. From the above observations it
can be concluded that the present research work has scope for further invivo evaluation (pharmacokinetic and
pharmacodynamicstudy).
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 577
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
IX. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors wish to thank: Itraconazole was kindly gifted from Hetero Pharma Ltd,Hyderabad,, India.
And also thankful to management of MLR Institute of Pharmacy,Dundigal, Hyderabad for providing all the
facilities for carried out research work.
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 578
Volume 3, Issue 6, June – 2018 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
REFERENCES
[1]. The human nail:structure,growth & pathological changes.Current problem in dermatology.9,1981,page
no.,102-110.
[2]. Manvi F.V and Dandagi,P.M,Gada,A.P.,Mastiholimath,V.S.and Jagadeesh,Indian J.Pharma.239-
243,2003.
[3]. Kavitha K and Mangesh Rajendra,Patel Dipen,Mangaibai,SAndeep DS, Ganesh N S,international
journal of pharma and biosciences,vol-2,2011.
[4]. Prabhakara, Sreekanth J, Jayaveera K N, International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science & Research,
1, (3), 259-266. 2 Runne, U.
[5]. VBRajendra:ABaro:AKumari:DLDhamacha:SRLahoti:SD shelke.J.APPL.Pharm.Sci,2012,2910,203-
209.
[6]. MA Ghannoum:RA Hajjeh:R Scher.J.Am.Acad.Dermatol.,2000,43,641-648.
[7]. R Kaur:B KASHYAP:P BHALLA. Ind.j.Med.Micobiol.,2008,26,108-116.
[8]. A Shemer . Dermatol.ther.,2012,25,582-593.
[9]. R Elkeeb:X Hui:N Murthy:HI Maibach:Expert opin.Emerg.drugs,2014,19(4),489-495.
[10]. DH Singh :S Roychowhdhury:D Sharma:V Bhandari:M Singh. Indo Amer
.J.Pharma.Res.,2013,3(6),4460-4470.
[11]. Cashman, M.W. and Sloan, S.B. 2010 and Stenn K. and Fleckman, P., (2000).
[12]. Murdan S. 2008 and Conejo-Mir, J. and Requena, L.( 2007).
[13]. Dykyj,J.D.Anotomy of the nail clipadia .med.surgery.
[14]. Cashman, M.W. and Sloan, S.B. ( 2010) and Picardo, M. et al 1994.
[15]. Forslind,B.On the structure of the normal nail.Ascanning electron microscopy study.
[16]. Rania Elkeeb, Ali Alikhan, Laila Elkeeb’s, Transungual drug delivery:Current status, IJP,
2010,pg no:1-8.
[17]. RK,Tavakol A,sigurgeirsson Br,HayRJ,Joseph WS,Tosti,Onychomycosis.
[18]. H. N. Shivakumar. Murthy Narashima. Transungual drug delivery department of pharmaceutics,
university of Mississippi, 2006; 4: 92-94.
[19]. S Firoz,MN Sirisha,R Rajalakshmi..Int.J.Innovative Drug Delivery ,2011,1(1),9-14.
[20]. MURDAN S (2002),Explained the “Enhancing the nail permeability of topically applied
drugs”,Expert Opinion Drug Delivery”.
IJISRT18JU354 www.ijisrt.com 579
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Detection and Counting of Fake Currency & Genuine Currency Using Image ProcessingDocumento6 pagineDetection and Counting of Fake Currency & Genuine Currency Using Image ProcessingInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (9)
- An Overview of Lung CancerDocumento6 pagineAn Overview of Lung CancerInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrepreneurial Creative Thinking and Venture Performance: Reviewing the Influence of Psychomotor Education on the Profitability of Small and Medium Scale Firms in Port Harcourt MetropolisDocumento10 pagineEntrepreneurial Creative Thinking and Venture Performance: Reviewing the Influence of Psychomotor Education on the Profitability of Small and Medium Scale Firms in Port Harcourt MetropolisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Finance-Fintech and it’s Impact on Financial Inclusion in IndiaDocumento10 pagineDigital Finance-Fintech and it’s Impact on Financial Inclusion in IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of Stress and Emotional Reactions due to the Covid-19 Pandemic in IndiaDocumento6 pagineImpact of Stress and Emotional Reactions due to the Covid-19 Pandemic in IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Auto Tix: Automated Bus Ticket SolutionDocumento5 pagineAuto Tix: Automated Bus Ticket SolutionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Designing Cost-Effective SMS based Irrigation System using GSM ModuleDocumento8 pagineDesigning Cost-Effective SMS based Irrigation System using GSM ModuleInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Vision Gestures Recognition System Using Centralized Cloud ServerDocumento9 pagineComputer Vision Gestures Recognition System Using Centralized Cloud ServerInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Solid Waste Management on Socio-Economic Development of Urban Area: A Case of Kicukiro DistrictDocumento13 pagineEffect of Solid Waste Management on Socio-Economic Development of Urban Area: A Case of Kicukiro DistrictInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Utilization of Waste Heat Emitted by the KilnDocumento2 pagineUtilization of Waste Heat Emitted by the KilnInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ambulance Booking SystemDocumento7 pagineAmbulance Booking SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Predictive Analytics for Motorcycle Theft Detection and RecoveryDocumento5 paginePredictive Analytics for Motorcycle Theft Detection and RecoveryInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Smart Cities: Boosting Economic Growth Through Innovation and EfficiencyDocumento19 pagineSmart Cities: Boosting Economic Growth Through Innovation and EfficiencyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Factors Influencing The Use of Improved Maize Seed and Participation in The Seed Demonstration Program by Smallholder Farmers in Kwali Area Council Abuja, NigeriaDocumento6 pagineFactors Influencing The Use of Improved Maize Seed and Participation in The Seed Demonstration Program by Smallholder Farmers in Kwali Area Council Abuja, NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Assessing Viability of Installing 20kw Solar Power For The Electrical & Electronic Engineering Department Rufus Giwa Polytechnic OwoDocumento6 pagineStudy Assessing Viability of Installing 20kw Solar Power For The Electrical & Electronic Engineering Department Rufus Giwa Polytechnic OwoInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Forensic Advantages and Disadvantages of Raman Spectroscopy Methods in Various Banknotes Analysis and The Observed Discordant ResultsDocumento12 pagineForensic Advantages and Disadvantages of Raman Spectroscopy Methods in Various Banknotes Analysis and The Observed Discordant ResultsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cyber Security Awareness and Educational Outcomes of Grade 4 LearnersDocumento33 pagineCyber Security Awareness and Educational Outcomes of Grade 4 LearnersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Unmasking Phishing Threats Through Cutting-Edge Machine LearningDocumento8 pagineUnmasking Phishing Threats Through Cutting-Edge Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- An Industry That Capitalizes Off of Women's Insecurities?Documento8 pagineAn Industry That Capitalizes Off of Women's Insecurities?International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain Based Decentralized ApplicationDocumento7 pagineBlockchain Based Decentralized ApplicationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Smart Health Care SystemDocumento8 pagineSmart Health Care SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Visual Water: An Integration of App and Web To Understand Chemical ElementsDocumento5 pagineVisual Water: An Integration of App and Web To Understand Chemical ElementsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Parastomal Hernia: A Case Report, Repaired by Modified Laparascopic Sugarbaker TechniqueDocumento2 pagineParastomal Hernia: A Case Report, Repaired by Modified Laparascopic Sugarbaker TechniqueInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Implications of Adnexal Invasions in Primary Extramammary Paget's Disease: A Systematic ReviewDocumento6 pagineImplications of Adnexal Invasions in Primary Extramammary Paget's Disease: A Systematic ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of Silver Nanoparticles Infused in Blood in A Stenosed Artery Under The Effect of Magnetic Field Imp. of Silver Nano. Inf. in Blood in A Sten. Art. Under The Eff. of Mag. FieldDocumento6 pagineImpact of Silver Nanoparticles Infused in Blood in A Stenosed Artery Under The Effect of Magnetic Field Imp. of Silver Nano. Inf. in Blood in A Sten. Art. Under The Eff. of Mag. FieldInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Insights Into Nipah Virus: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic AdvancesDocumento8 pagineInsights Into Nipah Virus: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic AdvancesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Compact and Wearable Ventilator System For Enhanced Patient CareDocumento4 pagineCompact and Wearable Ventilator System For Enhanced Patient CareInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Parkinson's Detection Using Voice Features and Spiral DrawingsDocumento5 pagineParkinson's Detection Using Voice Features and Spiral DrawingsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Quality Index Prediction Using Bi-LSTMDocumento8 pagineAir Quality Index Prediction Using Bi-LSTMInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Predict The Heart Attack Possibilities Using Machine LearningDocumento2 paginePredict The Heart Attack Possibilities Using Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Beauty Care-Day 1 NewDocumento4 pagineBeauty Care-Day 1 NewMichelle Cassandra CalanogNessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Lesson Plan Beauty Cair Nail Care - AnjDocumento5 pagineDetailed Lesson Plan Beauty Cair Nail Care - AnjRonelio Marabante100% (2)
- Tle Reviewer BDocumento6 pagineTle Reviewer BmaryjeandolinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nail Designing ToolsDocumento15 pagineNail Designing ToolsJudith VargasNessuna valutazione finora
- Pattern Diagnosis of OnycholysisDocumento12 paginePattern Diagnosis of OnycholysisVal Constantine Say CuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Feasibility Spna Beauty ParlourDocumento14 pagineFeasibility Spna Beauty Parlourapi-1966585240% (1)
- The Skin (Anaphy)Documento2 pagineThe Skin (Anaphy)ALEXANDRA COLLEEN ALEGRENessuna valutazione finora
- Introhc NotesDocumento15 pagineIntrohc NotesAalliyah YadaoNessuna valutazione finora
- African Child - Poem by Eku Mcgred2Documento10 pagineAfrican Child - Poem by Eku Mcgred2Jovert ManadongNessuna valutazione finora
- Nail Care Tools and Equipment ToolsDocumento5 pagineNail Care Tools and Equipment ToolsTeenish100% (1)
- Lp-Grade 10Documento13 pagineLp-Grade 10Jovelyn TakilidNessuna valutazione finora
- 4th Quarter Assessment Examination in TLEDocumento2 pagine4th Quarter Assessment Examination in TLEMichelle Copones LlanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nail Care Tools and EquipmentDocumento2 pagineNail Care Tools and EquipmentdawnNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 1 IntroductionDocumento15 pagineCHAPTER 1 IntroductionPuteri EizyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Steps in Trimming NailsDocumento21 pagineSteps in Trimming NailsMariel Liza HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- q3 Mod2 Activity SheetsDocumento2 pagineq3 Mod2 Activity SheetsainsleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Test in Tle 8: Ocampo National High SchoolDocumento2 paginePre-Test in Tle 8: Ocampo National High SchoolMariflor TibusNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutritional CuresDocumento40 pagineNutritional CuresTURGIS100% (2)
- Reading Discovery 2 - Transcripts PDFDocumento10 pagineReading Discovery 2 - Transcripts PDFFrancisco Antonio López Revelles100% (1)
- TLE Beauty Care (Nail Care) Services: Module 2: Apply Hand Treatment Quarter 1, Week 2Documento15 pagineTLE Beauty Care (Nail Care) Services: Module 2: Apply Hand Treatment Quarter 1, Week 2Maria Jane RubioNessuna valutazione finora
- Nail Care TOOLS and Equipment: By: Ms - PurplebloodDocumento47 pagineNail Care TOOLS and Equipment: By: Ms - PurplebloodrobertNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 - The Perionychium PDFDocumento21 pagine10 - The Perionychium PDFFlorin PanduruNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Assessment - MIDTERM-TRANSDocumento36 pagineHealth Assessment - MIDTERM-TRANSShene Claire VigillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Beauty-Care-G11-Bnc First Quarter TestDocumento3 pagineBeauty-Care-G11-Bnc First Quarter TestVivian VillacortesNessuna valutazione finora
- OPI Nail PolishDocumento3 pagineOPI Nail PolishChunne LinqueNessuna valutazione finora
- 4th Periodical TestDocumento3 pagine4th Periodical TestShellane Blanco SarduaNessuna valutazione finora
- Project in TLE 7Documento28 pagineProject in TLE 7Justin Rei AlcuizarNessuna valutazione finora
- CBLM CORE 2 Beauty CareDocumento55 pagineCBLM CORE 2 Beauty CareJocelyn Velez Candido100% (48)
- Fingernails Condition and Body HealthDocumento16 pagineFingernails Condition and Body HealthDevarajan RNessuna valutazione finora
- TLE Reviewer Part 1 PDFDocumento6 pagineTLE Reviewer Part 1 PDFAbelardo Banaay SumagangNessuna valutazione finora