Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
How To Classify Walls in A Building
Caricato da
suryakantame0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
18 visualizzazioni2 pagineHow to classify walls in a building
Titolo originale
How to Classify Walls in a Building
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoHow to classify walls in a building
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
18 visualizzazioni2 pagineHow To Classify Walls in A Building
Caricato da
suryakantameHow to classify walls in a building
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
HOW TO CLASSIFY WALLS IN A
BUILDING? [BASED ON FUNCTION]
Walls are built to partition living area into different parts. They impart privacy and protection against
temperature, rain and theft. Depending upon their functions, Walls may be classified into the
following two primary classes
1. Load bearing walls
2. Partition walls.
1. LOAD BEARING WALLS
If beams and columns are not used, load from roof and floors are transferred to foundation by walls.
Such walls are called load bearing walls. They are to be designed to transfer the load safely. The
critical portion of the walls are near the openings of doors and windows and the positions where
concrete beams rest.
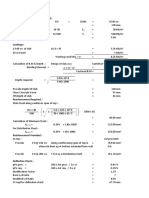
Minimum wall thickness used is 200 mm. It is also recommended that the slenderness ratio of wall
defined as ratio of effective length or effective height to thickness should not be more than 27. The
effective height and effective length of a wall may be taken as shown in tables-1 and 2 respectively.
Table-1 [Effective height of walls in terms of actual height H]
End Condition Effective Height
Lateral as well as rotational restraint 0.75 H
Lateral as well as rotational restraint at one
0.85 H
end and only lateral restraint at other
Lateral restraint but no rotational restraint at
1.0 H
both ends
Lateral and rotational restraint at one end and
no restraint at other ends (compound walls, 1.5 H
parapet walls etc.).
Table-2 [Effective length of walls of length L]
End Condition Effective Length
Continuous and supported by cross walls 0.8 L
Continuous at one end and supported by cross
0.9 L
walls at the other end
Wall supported by cross walls at each end 1.0 L
Free at one end and continuous at other end 1.5 L
Free at one end and supported by cross wall at
2.0 L
other end
2. PARTITION WALLS
In framed structures partition walls are built to divide floor area for different utilities. They rest on
floors. They do not carry loads from floor and roof. They have to carry only self-weight. Hence
normally partition walls are thin. Table 8.4 shows the differences between load bearing walls and
partition walls. Depending upon the requirement these walls may be brick partition, clay block
partition, glass partition, wood partition, and aluminium and glass partition.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN LOAD BEARING AND
PARTITION WALLS
Differences between a load bearing wall and a partition wall is given in the following table
LOAD BEARING WALLS PARTITION WALLS
They carry loads from roof, floor, self-
They carry self-weight only.
weight etc.
They are thick and hence occupy more These walls are thin and hence occupy less
floor area. floor area.
As the material required is more the As the material required is less,
construction cost is more. construction cost is less.
Stones or bricks are used for the Stones are generally not used for the
construction construction
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Brick Maso.2Documento9 pagineBrick Maso.22K20CO016 ABHAY THAKURNessuna valutazione finora
- Wall and Floor System (Building Construction)Documento22 pagineWall and Floor System (Building Construction)shobitadhi1820Nessuna valutazione finora
- Scaffoldings, Bonds in Bricks and Masonry WallsDocumento30 pagineScaffoldings, Bonds in Bricks and Masonry WallsDeepak Singh100% (1)
- Plinth BeamDocumento9 paginePlinth BeamUjwal UjwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Wall & Wall FootingDocumento33 pagineWall & Wall FootingVictor Eric NacionNessuna valutazione finora
- BUILDING MATERIAL (Types of Walls) and Swimming Pool DetailDocumento63 pagineBUILDING MATERIAL (Types of Walls) and Swimming Pool DetailTejas Joshi100% (1)
- Chapter-2 Literature ReviewDocumento13 pagineChapter-2 Literature ReviewKyaw Ye Htut HeinNessuna valutazione finora
- ScaffoldingDocumento6 pagineScaffoldingUmar Bello NuhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction Technology Terminology (Session 2)Documento26 pagineConstruction Technology Terminology (Session 2)aye chan monNessuna valutazione finora
- WallsDocumento21 pagineWallsesubalew yayenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-Iii Building Components and ServicesDocumento22 pagineUnit-Iii Building Components and ServicesCh VenkateshNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 Part 1Documento39 pagineUnit 2 Part 1AamirNessuna valutazione finora
- Masonry TutorialDocumento45 pagineMasonry TutorialGajendra Joshi100% (2)
- Civil Engineering Drawing & Graphics: Engr. Ahmad Jan Lecturer Civil Engg DepartmentDocumento10 pagineCivil Engineering Drawing & Graphics: Engr. Ahmad Jan Lecturer Civil Engg DepartmentAsadullah Khan GhalibNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Load BDocumento4 pagineTypes of Load BStephane WadieneNessuna valutazione finora
- CTM3Documento6 pagineCTM3Sajil KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Part 2 SuperstructuresDocumento39 pagineChapter 3 Part 2 Superstructuresrashidaweisabdullahi01Nessuna valutazione finora
- ConsTech2 ProjectDocumento27 pagineConsTech2 Projectjames RunplestilskinNessuna valutazione finora
- Tall BuildingsDocumento9 pagineTall BuildingshishamNessuna valutazione finora
- Load Bearing and Rigid FrameDocumento11 pagineLoad Bearing and Rigid FrameParisthi ShresthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Design ProcessDocumento5 pagineStructural Design ProcessPandal RajNessuna valutazione finora
- مكتبة نور مشروع خرسانة 2 3 PDFDocumento220 pagineمكتبة نور مشروع خرسانة 2 3 PDFAsra AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of WallsDocumento9 pagineTypes of WallsjarihNessuna valutazione finora
- New Microsoft Word Document PDFDocumento7 pagineNew Microsoft Word Document PDFhishamNessuna valutazione finora
- Building ElementsDocumento57 pagineBuilding ElementsjahnvighoghariNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewed - IJCE-Format-The Wall As Architecture SpaceDocumento12 pagineReviewed - IJCE-Format-The Wall As Architecture Spaceiaset123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Prefabricated Structures: Unit Ii Prefabricated ComponentsDocumento71 paginePrefabricated Structures: Unit Ii Prefabricated ComponentsraviciviltNessuna valutazione finora
- Load Bearing and Non-Load Bearing WallDocumento9 pagineLoad Bearing and Non-Load Bearing WallTsegaye TsegayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Walls in BuildingDocumento6 pagineWalls in BuildingHasbullah HamzahNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance of Simple StructureDocumento6 paginePerformance of Simple StructurePradeepLokhandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Shear WallDocumento23 pagineShear WallSamit RajakNessuna valutazione finora
- Acoustic Technique-Cavity WallDocumento33 pagineAcoustic Technique-Cavity WallPriyadharshini MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- BDG NotesDocumento18 pagineBDG NotesTaiwo AyomideNessuna valutazione finora
- BLD 212 Lecture 2Documento9 pagineBLD 212 Lecture 2Umar Bello NuhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 4Documento4 pagineGroup 4Fahim Sarker StudentNessuna valutazione finora
- Waffle SlabDocumento9 pagineWaffle SlabRick SarazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Type of WallDocumento48 pagineType of Wallkamardeen mustafa100% (3)
- Wall SystemDocumento38 pagineWall SystemMarion ValeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Walls: ' T Io TDT .1F!. .'1oiiiu ' (LL - Scmon PJ Bi2S1 ".Documento21 pagineWalls: ' T Io TDT .1F!. .'1oiiiu ' (LL - Scmon PJ Bi2S1 ".esubalew yayenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Retaining Walls and Road PavementDocumento14 pagineRetaining Walls and Road PavementPraise SamuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Walls: ' T Io TDT .1F!. .'1oiiiu ' (LL - Scmon PJ Bi2S1 ".Documento27 pagineWalls: ' T Io TDT .1F!. .'1oiiiu ' (LL - Scmon PJ Bi2S1 ".esubalew yayenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 7 Wall SystemDocumento39 pagineLecture 7 Wall Systemリ0315Nessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Masonry WallsDocumento30 pagineTypes of Masonry Wallsbereket100% (1)
- WallsDocumento23 pagineWallsKhalid aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Walls Structure Walls StructureDocumento32 pagineWalls Structure Walls StructureNor Alia Shafia100% (1)
- Building & Furniture S.B.A.: WallsDocumento8 pagineBuilding & Furniture S.B.A.: WallsJordan BrownNessuna valutazione finora
- StructureDocumento19 pagineStructureisra hamadNessuna valutazione finora
- Types and Materials Used For FormworkDocumento17 pagineTypes and Materials Used For FormworkAshrutha Harshini100% (1)
- Shear Wall MainDocumento37 pagineShear Wall MainMr420• NeffexNessuna valutazione finora
- Installation of LintelsDocumento3 pagineInstallation of LintelsJustine Noel De CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- New Google 1Documento14 pagineNew Google 1Deepesh NakumNessuna valutazione finora
- Building TechnologyDocumento14 pagineBuilding TechnologyBob ButantanNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation and FootingDocumento16 pagineFoundation and FootingNorma Alvares RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Design of StructuresDocumento4 pagineFunctional Design of StructuresJaved ZakhilNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Construction Lecture Note.Documento31 pagineBuilding Construction Lecture Note.Umar Bello NuhuNessuna valutazione finora
- 009-wms For Wood Partition WorkDocumento6 pagine009-wms For Wood Partition WorkRaman BhadouriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 DMDocumento17 pagineUnit 4 DMSanthu DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- GRP 1 Building Tech.Documento59 pagineGRP 1 Building Tech.Kevin EdwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Civil NotesDocumento43 pagineBasic Civil Notessyedaleem1167100% (2)
- The Performance of Concrete AdmixturesDocumento1 paginaThe Performance of Concrete AdmixturessuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Field Determination of Surface Moisture of Aggregate PDFDocumento5 pagineField Determination of Surface Moisture of Aggregate PDFsuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Type of Incident in ConstructionDocumento10 pagineType of Incident in ConstructionsuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Geodetic Surveying and Theory of ErrorsDocumento79 pagineGeodetic Surveying and Theory of ErrorsJay Tomolin CabuñasNessuna valutazione finora
- Defects in Plaster WorkDocumento2 pagineDefects in Plaster WorksuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Is 2720 2 1973 PDFDocumento24 pagineIs 2720 2 1973 PDFTanvir HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Triangulation and Trilateration: 1.1 GeneralDocumento38 pagineTriangulation and Trilateration: 1.1 GeneralSantosh Yadav80% (5)
- Water-to-Cement Ratio and Aggregate Moisture CorrectionsDocumento11 pagineWater-to-Cement Ratio and Aggregate Moisture CorrectionssuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effect of Aggregate Properties On ConcreteDocumento3 pagineThe Effect of Aggregate Properties On ConcretesuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Water-to-Cement Ratio and Aggregate Moisture CorrectionsDocumento11 pagineWater-to-Cement Ratio and Aggregate Moisture CorrectionssuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Survey Topographical PDFDocumento420 pagineSurvey Topographical PDFsuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Influence of Aggregate Properties On ConcreteDocumento4 pagineInfluence of Aggregate Properties On ConcretesuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Contraction Joint in ConcreteDocumento3 pagineContraction Joint in ConcretesuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Types of Errors in Chaining and Ways To Mitigate ItDocumento7 pagine5 Types of Errors in Chaining and Ways To Mitigate ItsuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of Hardened ConcreteDocumento2 pagineProperties of Hardened ConcretesuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Principle For Supervision of Stone MasonryDocumento1 paginaPrinciple For Supervision of Stone MasonrysuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of Hardened ConcreteDocumento2 pagineProperties of Hardened ConcretesuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- How Aggregate Properties Affects Concrete PropertiesDocumento10 pagineHow Aggregate Properties Affects Concrete PropertiessuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Shot CreteDocumento4 pagineShot CretesuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Repair of Cracks in Reinforced Concrete BeamsDocumento2 pagineRepair of Cracks in Reinforced Concrete BeamssuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Resisting Properties of Common Building MterialsDocumento2 pagineFire Resisting Properties of Common Building MterialssuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are The Requirements of BentoniteDocumento1 paginaWhat Are The Requirements of BentonitesuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Determine Splitting Tensile Strength of Cylindrical Concrete SpecimensDocumento5 pagineDetermine Splitting Tensile Strength of Cylindrical Concrete SpecimenssuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Relation Between Void Ratio and Porosity PDFDocumento2 pagineRelation Between Void Ratio and Porosity PDFsuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is The Effect of Tree Roots On BuildingDocumento2 pagineWhat Is The Effect of Tree Roots On Buildingsuryakantame100% (1)
- Fire Resisting Properties of Common Building MterialsDocumento2 pagineFire Resisting Properties of Common Building MterialssuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Weathering of Rock MassDocumento2 pagineWeathering of Rock MasssuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Sources of Defects in Brick MasonryDocumento3 pagineSources of Defects in Brick MasonrysuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- Defects in BrickworkDocumento3 pagineDefects in BrickworksuryakantameNessuna valutazione finora
- G 010715 RDocumento1 paginaG 010715 RLiva DesnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bollhoff HeliCoil Plus ImperialDocumento48 pagineBollhoff HeliCoil Plus ImperialAce Industrial SuppliesNessuna valutazione finora
- Manolea H Modern Approaches in Choosing Materials For Implant Supported ProsthesisDocumento7 pagineManolea H Modern Approaches in Choosing Materials For Implant Supported ProsthesisHoriaManNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Sprinkler Testing 2015Documento104 pagineFire Sprinkler Testing 2015Jose R Birmighan S100% (1)
- Project Report Group 4Documento28 pagineProject Report Group 4Akame TakashitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atienza, Arjay M. ST - Anne College Lucena Inc. Roof Plan: Hip RollDocumento1 paginaAtienza, Arjay M. ST - Anne College Lucena Inc. Roof Plan: Hip RollAtienza ArjayNessuna valutazione finora
- Minor Electrical Installation Works CertificateDocumento2 pagineMinor Electrical Installation Works Certificate1e7tejp027041100% (1)
- Technical Specifications: Proposed Two Storey Residential BuildingDocumento10 pagineTechnical Specifications: Proposed Two Storey Residential BuildingAeron AcioNessuna valutazione finora
- Gajjar Industries ADocumento15 pagineGajjar Industries AMPNessuna valutazione finora
- DNV RP F106Documento32 pagineDNV RP F106sharif339Nessuna valutazione finora
- ASTM E309 Eddy-Current Examination of Steel Tubular Products UsingDocumento5 pagineASTM E309 Eddy-Current Examination of Steel Tubular Products UsingmidmereNessuna valutazione finora
- Furnace Replace Carrier 302075 304 Board Ig LIAF044 1Documento2 pagineFurnace Replace Carrier 302075 304 Board Ig LIAF044 1topogigio240Nessuna valutazione finora
- Busducts: Low and Medium VoltageDocumento14 pagineBusducts: Low and Medium VoltagesaturasatuNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Instalac. Victaulic I-6000 - Estilo 44Documento3 pagineManual Instalac. Victaulic I-6000 - Estilo 44Nilton Inca TitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nozzle Thrust and Efficiency MeasurementDocumento12 pagineNozzle Thrust and Efficiency MeasurementDhruvNagpalNessuna valutazione finora
- XSXSX - NotepadDocumento8 pagineXSXSX - NotepadAshutosh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Cantilever Walkway Design WS1Documento2 pagineCantilever Walkway Design WS1Raju SainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial: Concrete TechnologyDocumento6 pagineTutorial: Concrete TechnologyMuhammad Wazim AkramNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Motion Bearings & Linear ShaftDocumento177 pagineLinear Motion Bearings & Linear ShaftFerry KurniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lps Estimte & RCC RoomDocumento39 pagineLps Estimte & RCC RoomanbugobiNessuna valutazione finora
- Marcegaglia Heavy-Plates en Gen11Documento12 pagineMarcegaglia Heavy-Plates en Gen11lucidbaseNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 11 - TMS402 602 22 ArcCastStoneDocumento2 pagine2022 11 - TMS402 602 22 ArcCastStonejomargatemarceloNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On Composite Honeycomb Sandwich Panel StructureDocumento5 pagineA Study On Composite Honeycomb Sandwich Panel StructureÖmer ŞenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Facilities PDFDocumento16 paginePhysical Facilities PDFYudhi AdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Aerospace Applications of Shape Memory Alloys PDFDocumento16 pagineAerospace Applications of Shape Memory Alloys PDFjtpqNessuna valutazione finora
- Cable Tray Systems. Cable Trays & Accessories Cable Ladder & Accessories U - Channels & Accessories Cable CleatsDocumento30 pagineCable Tray Systems. Cable Trays & Accessories Cable Ladder & Accessories U - Channels & Accessories Cable CleatsSyed Rahmath AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Arc Catalog of Products: Protec Tion Against Corrosion, Abrasion, Impac T, and Chemical at TackDocumento40 pagineArc Catalog of Products: Protec Tion Against Corrosion, Abrasion, Impac T, and Chemical at TackcesarNessuna valutazione finora
- Hot Tap ProcedureDocumento6 pagineHot Tap ProcedureNatarajan MurugesanNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.1 Catalogue Hang SangjinDocumento77 pagine4.1 Catalogue Hang SangjinKiến Huy LưuNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnesium Matrix Composite Reinforced by NanopartiDocumento21 pagineMagnesium Matrix Composite Reinforced by Nanopartivenkatesh198910Nessuna valutazione finora