Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Pharma M04L09 Antihelminthics
Caricato da
Athena BorjaCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Pharma M04L09 Antihelminthics
Caricato da
Athena BorjaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
PHARMACOLOGY
PHARMACOTHERAPY OF HELMINTHOSES M04L09
Dr. Calderon
NOV 03 2017
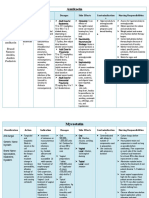
Pharmacotherapy of Helminthoses ALBENDAZOLE
I. Drugs that act against nematodes Benzimidazole carbamate
II. Drugs that act against trematodes Administered on an empty stomach when used against
III. Drugs that act against cestodes intraluminal parasites
IV. Cases Administered with a fatty meal when used against
tissue parasites
Italics – Transers Note, Box – Book, Broken Box – Key points
and Guides
NOTE: SABI NI DOC, MUST KNOW ANG SIGNS AND 3. PYRANTEL PAMOATE
SYMPTOMS OF THE DISEASE, DRUG OF CHOICE FOR Drug Class: Antihelminthic
THE DISEASE AND SIDE EFFECTS OF THE DRUGS MOA: Stimulates nicotinic receptors at NMJ of
HAPPY ARAL! nematodes. causes depolarization-induced
paralysis;
DRUGS THAT ACT AGAINST NEMATODES
Note: It doesn’t kill the worm BUT ONLY
1. MEBENDAZOLE PARALYZES it. NOT Ovicidal.
Drug Class: Antihelminthic
Clinical Use: Hookworm and roundworm
MOA: Selectively inhibits microtubule synthesis infections (drug of choice), Pinworms (backup)
(mitosis) and glucose uptake in nematodes;
Toxicities: GI distress, Headache, Weakness
Ovicidal
Wide activity against nematodes killing adult
Clinical Use: Ascariasis, Pinworm, Whipworm worms in the colon but not the eggs
infections (drug of choice), Visceral larval migrans Contraindicated in patients with hepatic
(backup) dysfunction
Toxicities: Gastrointestinal irritation,
Combantrin
Agranulocytosis, Alopecia
Contraindicated in pregnancy
Antiox 4. THIABENDAZOLE
Most antihelminthics act like anticancer drugs
because they inhibit the proliferation of cells. Drug Class: Antihelminthic
Worms have similar metabolism to humans. MOA: Selectively inhibits microtubule synthesis
Therefore, systemic toxicity might not be unusual and glucose uptake in nematodes. Inhibits
in treatment of protozoan and worm diseases. fumarate reductase. Ovicidal
Clinical Use: Trichinosis (drug of choice),
2. ALBENDAZOLE Strongyloidiasis (backup)
Toxicities: Gastrointestinal irritation, Headache,
Drug Class: Antihelminthic
Dizziness, Drowsiness, Leukopenia, Hematuria,
MOA: Inhibits microtubule assembly; Larvicidal Hypersensitivity reactions (SJS), Hepatotoxicity
and ovicidal (intrahepatic cholestasis, liver failure), Reactions
Clinical Use: Ascariasis, Hookworm, Pinworm, caused by dying parasites
Whipworm infections, Hydatid disease (drug of Contraindicated in pregnancy
choice), Threadworms, Filariasis, Larva migrans
(backup), Cysticercosis (larval stages of T. solium) Note: DOC for T. spiralis or trichinosis disease (from
Toxicities: Reversible leukopenia, Alopecia, meat; can infect man and lead to myocitis)
Elevation of liver function tests, Bone marrow
suppression
Not listed in the Philippine National Drug 5. DIETHYLCARBAMAZINE (DEC)
Formulary. It is only procured by the government Drug Class: Antihelminthic
Ideal drug of choice of deworming of children. MOA: Unknown. Immobilizes microfilariae
Clinical Use: Filariasis (drug of choice), Eye
worm disease (drug of choice), Onchocerciasis
(backup)
Toxicities: Headache, Malaise, Weakness,
Anorexia, Filarial fever (fever, rashes, ocular
damage, joint and muscle pain, lymphangitis)
Transcribed by: de Jesus, Murillo Checked by: mm Page 1 of 4
PHARMACOLOGY DRUGS USED IN HEART FAILURE M03L04
May cause Mazzotti reaction when used for
onchocerciasis 2. BITHIONOL
Alternative to triclabendazole for the treatment of
Note: DOC for W. bancrofti or filariasis disease fascioliasis (sheepliver fluke)
Also an alternative drug in the treatment of
6. IVERMECTIN pulmonary paragonimiasis
Drug Class: Antihelminthic
MOA: Intensifies GABA-mediated 3. METRIFONATE
neurotransmission in nematodes. Immobilizes Alternative drug for the treatment of Schistosoma
parasites. hematobium infections.
Clinical Use: Onchocerciasis, Cutaneous larva MOA: cholinesterase inhibition; this inhibition
migrans, Strongyloidiasis (drug of choice) temporarily paralyzes the adult worms
Toxicities: Mazzotti reaction (fever, headache, Combined with oxamniquine for mixed infections of
dizziness, rashes, pruritus, tachycardia, S haematobium and S mansoni
hypotension, pain in joints, muscles and lymph
Toxicities: Nausea and vomiting, diarrhea,
glands)
abdominal pain, bronchospasm, headache, sweating,
Contraindicated in pregnancy fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and vertigo
Note: Mazzoti reaction- flu-like symptoms that 4. OXAMNIQUINE
results after treatment on Diethylcarbamazine or
Ivermectin Alternative to praziquantel for the treatment of S
mansoni infections
Onchocerca volvulus Active against both mature and immature stage of S
- causes onchocerciasis, mansoni but does not appear to be cercaricidal
- transmitted by female blackfly (Simulium). MOA: Unknown. Contraction and paralysis of the
- clinical findings: dermal nodules worms
hanging groin, lizard skin, river blindness Effective in instances of praziquantel resistance
Toxicities: CNS symptoms (dizziness, headache,
DRUGS THAT ACT AGAINST TREMATODES drowsiness), nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, colic,
pruritus, and urticaria. Infrequent adverse effects are
1. PRAZIQUANTEL low-grade fever, orange to red discoloration of the
urine, proteinuria, microscopic hematuria, and a
Drug Class: Antihelminthic transient decrease in leukocytes
MOA: Increases membrane permeability to
calcium. Causes muscle paralysis, vacuolization DRUGS THAT ACT AGAINST CESTODES
and death.
Clinical Use: Drug of choice for trematodes 1. NICLOSAMIDE
(Schistosoma, Paragonimus, Clonorchis, Drug Class: Antihelminthic
Opistorchis) and cestodes (Taenia,
Diphyllobothrium) MOA: Uncouples oxidative phosphorylation or
by activating ATPases
Toxicities: Headache, Dizziness, Nausea, Malaise
Contraindicated in ocular cysticercosis (may Clinical Use: Alternative drug for cestode
cause irreparable eye damage), Used with infections (Taenia, Diphyllobothrium)
corticosteroids in treating neurocysticercosis. Toxicities: Gastrointestinal distress, headache,
rash, fever
Note: S. japonicum-acquired by swimming or drinking Kills scolices and cestode segments but has no
infected water; effect on ova.Avoid ethanol consumption for 48h
upon drug administration.
Paragonimiasis- acquired by ingestion of raw
crabmeat
Transcribed by: DE JESUS, TIBURCIO, MURILLO Checked by: TABUZO Page 2 of 4
PHARMACOLOGY DRUGS USED IN HEART FAILURE M03L04
CASES 3. A 50 year-old seaport carrier complains of cough for more
than one month, with hemoptysis. TB work-up was negative.
1. A 10-year-old girl from Forbes Park, Makati has had Further history reveals he is fond of eating pickled crabs
abdominal pain and cramps for the past few days. Her (burong talangka) when binge-drinking in his town. A repeat
examination produced normal findings except for nonspecific CXR showed a ring-shadowed opacity, and a sputum
abdominal discomfort with a complete blood count showing examination was positive for eggs. Which is the most
anemia and 22% eosinophilia. A stool specimen revealed the appropriate treatment?
characteristic eggs of A. lumbricoides. Which is the most
appropriate treatment? A. Praziquantel
B. Thiabendazole
A. Albendazole C. Ivermectin
B. Praziquantel D. Albendazole
C. Piperazine
D. Bithionol
2. A 30 year-old Filipino male working in Sudan is being
treated for Onchocerca volvulus infection. He then develops
fever, headache, dizziness, rashes, pruritus, pain in joints,
muscles and lymph glands. The physician suspects that he had
a Mazzotti reaction, which is due to which of the following?
A. Increased GABA-mediated neurotransmission
B. Inflammatory reaction to lysis of the worms
C. Nicotinics stimulation at the myoneural junctions of
nematodes
D. Stress-induced hemolysis
APPENDIX
Transcribed by: DE JESUS, TIBURCIO, MURILLO Checked by: TABUZO Page 3 of 4
PHARMACOLOGY DRUGS USED IN HEART FAILURE M03 L04
Transcribed by: DE JESUS, TIBURCIO, MURILLO Checked by:TABUZO Page 4 of 4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Group-8 Antihelminthic DrugsDocumento76 pagineGroup-8 Antihelminthic Drugsjenet soleilNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 53: Antihelminthic Drugs: Drugs That Act Against NematodesDocumento4 pagineChapter 53: Antihelminthic Drugs: Drugs That Act Against NematodesChristian DeeNessuna valutazione finora
- AntelmintikDocumento17 pagineAntelmintikRama ArdianaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1000+ Drug CardsDocumento33 pagine1000+ Drug CardsArsalan khan100% (1)
- Pharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarDocumento33 paginePharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarfaizaNessuna valutazione finora
- PharmacologyDocumento6 paginePharmacologyZubair KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology AssignmentDocumento6 paginePharmacology AssignmentZubair KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti Helminthic DrugsDocumento3 pagineAnti Helminthic Drugsdhainey100% (2)
- Pharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarDocumento33 paginePharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarnamitaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Metronidazole Drug StudyDocumento4 pagine6 Metronidazole Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- Anthelmintic Drugs: Pharmacology IvDocumento27 pagineAnthelmintic Drugs: Pharmacology IvShashidharan MenonNessuna valutazione finora
- PEDIA - Drug Study & NCPDocumento24 paginePEDIA - Drug Study & NCPCzarina Mae Lomboy100% (1)
- Clinical Pharmacology of The Antihelminthic DrugsDocumento20 pagineClinical Pharmacology of The Antihelminthic DrugsGemson RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Metronidazole Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineMetronidazole Drug StudyA.Nessuna valutazione finora
- AntihelminthesDocumento50 pagineAntihelminthesColin MorganNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugsstudy Different ObDocumento8 pagineDrugsstudy Different ObElvis DuotNessuna valutazione finora
- Metronidazole Drug StudyDocumento3 pagineMetronidazole Drug StudySiafei RabeNessuna valutazione finora
- Before: Drug Therapeutic Record Indications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento9 pagineBefore: Drug Therapeutic Record Indications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesIcel Jean QuimboNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology MidtermsDocumento6 paginePharmacology MidtermsConcepcion NazaredoNessuna valutazione finora
- FTX Infeksi JamurDocumento64 pagineFTX Infeksi JamurNafisah SofiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Antihelminthic Therapy: Dr. Dumlao - April 25, 2020 Trans By: Del RosarioDocumento3 pagineAntihelminthic Therapy: Dr. Dumlao - April 25, 2020 Trans By: Del RosarioLloyd LinNessuna valutazione finora
- GentamicinDocumento2 pagineGentamicinMiguel Sanico0% (2)
- Obduty Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaObduty Drug StudyKhazelle Diene TanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Macrolide Drug StudyDocumento3 pagineMacrolide Drug StudyEmagra AzilNessuna valutazione finora
- Anthelmintic DrugsDocumento8 pagineAnthelmintic Drugs4088 kapil RathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Ward Drug StudyDocumento9 pagineMedical Ward Drug StudygorgeazNessuna valutazione finora
- MetronidazoleDocumento2 pagineMetronidazolehauteanicoleNessuna valutazione finora
- Dentistry Anti TB, Viral, Fungal, Parasitic 2020Documento38 pagineDentistry Anti TB, Viral, Fungal, Parasitic 2020Visayan Alliah GailNessuna valutazione finora
- AMIKACINDocumento2 pagineAMIKACINemanmohamed3444Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amoebiasis - Viral N DrashtiDocumento24 pagineAmoebiasis - Viral N DrashtiviralNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingDocumento3 pagineDrugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingHazel Palomares100% (1)
- Format For Case PresentationDocumento4 pagineFormat For Case Presentationmhimie_05Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemotherapy of Helminth Infections: DR - Rathnakar U.PDocumento39 pagineChemotherapy of Helminth Infections: DR - Rathnakar U.PDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNessuna valutazione finora
- A Drug Study On: Monaliza J. Lee, RN, MNDocumento6 pagineA Drug Study On: Monaliza J. Lee, RN, MNJeah Bearl AbellarNessuna valutazione finora
- Anthelmentics Version 2Documento21 pagineAnthelmentics Version 2N Gv FcNessuna valutazione finora
- Isah Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineIsah Drug StudyJames AbendanNessuna valutazione finora
- AntprotozoalsDocumento18 pagineAntprotozoalsAmany El-fakhranyNessuna valutazione finora
- Antiviral and Anti-Fungal DrugsDocumento8 pagineAntiviral and Anti-Fungal DrugsAhmed HadeerNessuna valutazione finora
- Silver Sulfadiazine Drug StudyDocumento3 pagineSilver Sulfadiazine Drug StudyKenn Siasar100% (1)
- Hand Out AntibioticsDocumento13 pagineHand Out AntibioticsMinhwa KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Farklin, AntivirusDocumento47 pagineFarklin, AntivirusFilhaqqiNessuna valutazione finora
- VancomycinDocumento3 pagineVancomycinAnika Pleños100% (1)
- Anti TB DrugsDocumento46 pagineAnti TB Drugs88AKKNessuna valutazione finora
- Santiago, Gwyneth Julia B. - Drug MonographDocumento1 paginaSantiago, Gwyneth Julia B. - Drug MonographGwyneth SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- CefuroximeDocumento1 paginaCefuroximeAbijah Leris SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- Antifungal AgentsDocumento23 pagineAntifungal AgentsDiriba feyisaNessuna valutazione finora
- DrugStudy FluconazoleCasilaoDocumento4 pagineDrugStudy FluconazoleCasilaoArone SebastianNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugstudy 20Documento9 pagineDrugstudy 20MahledJoy EnriquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Anthelmintic - Antiviral & Antiprotozoal Drugs Anthelmintic - Antiviral & Antiprotozoal DrugsDocumento39 pagineAnthelmintic - Antiviral & Antiprotozoal Drugs Anthelmintic - Antiviral & Antiprotozoal DrugsAhmed AmgedNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti-Helminthic Drugs GP 4Documento24 pagineAnti-Helminthic Drugs GP 4NABAKOOZA ELIZABETHNessuna valutazione finora
- 14-Antiameobic Antifungal 2021Documento22 pagine14-Antiameobic Antifungal 2021Amr SalemNessuna valutazione finora
- AntifungalDocumento5 pagineAntifungalbrendadsouza235Nessuna valutazione finora
- AmikacinDocumento4 pagineAmikacinkristineK100% (1)
- Drugstudy EamcDocumento5 pagineDrugstudy EamckillthealarmistNessuna valutazione finora
- Bumetanide MIMSDocumento2 pagineBumetanide MIMSIndri WahyuniNessuna valutazione finora
- Santiago, Gwyneth Julia B.-Bsn2-D-Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineSantiago, Gwyneth Julia B.-Bsn2-D-Drug StudyGwyneth SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Chemotherapy of Parasitic DiseaseDocumento86 pagine5 Chemotherapy of Parasitic DiseaseWovelyNessuna valutazione finora
- Liver Cirhosis Related To Hepatitis C Infection and Age With Sever DehydrationDocumento9 pagineLiver Cirhosis Related To Hepatitis C Infection and Age With Sever DehydrationSunny Mae T. PuigNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary Germicides PharmaDocumento11 pagineUrinary Germicides PharmaMaria Pina Barbado PonceNessuna valutazione finora
- Healing Lyme Disease Coinfections: Complementary and Holistic Treatments for Bartonella and MycoplasmaDa EverandHealing Lyme Disease Coinfections: Complementary and Holistic Treatments for Bartonella and MycoplasmaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Chapter 8 HandoutsDocumento2 pagineChapter 8 HandoutsAthena BorjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Coins Pathology PDFDocumento7 pagineCoins Pathology PDFAthena BorjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Labor Bar 2015 Final PDocumento15 pagineLabor Bar 2015 Final PAthena BorjaNessuna valutazione finora
- ADR 1 RevisedDocumento2 pagineADR 1 RevisedAthena BorjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 HandoutsDocumento2 pagineChapter 8 HandoutsAthena BorjaNessuna valutazione finora
- ADR 1 RevisedDocumento2 pagineADR 1 RevisedAthena BorjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharma M04L07b Vasoactive PeptidesDocumento5 paginePharma M04L07b Vasoactive PeptidesAthena BorjaNessuna valutazione finora
- CompilationDocumento110 pagineCompilationAthena BorjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Constitutional Law 1 (Syllabus)Documento11 pagineConstitutional Law 1 (Syllabus)Athena BorjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Histo and Anatomy (Lungs) : Capillary PressureDocumento1 paginaHisto and Anatomy (Lungs) : Capillary PressureAthena BorjaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Physiology Supplement Handout Based On Ganong For TOPNOTCH 21 by Jaffar PinedaDocumento46 pagine4 Physiology Supplement Handout Based On Ganong For TOPNOTCH 21 by Jaffar PinedaAthena Borja100% (3)
- Sensory ExaminationDocumento4 pagineSensory ExaminationAthena BorjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuroscience: Parts of The BrainDocumento5 pagineNeuroscience: Parts of The BrainAthena BorjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Schedule of Classes Second Semester A.Y. 2017-18: 30-Jan Preceptorials: Motor System, CerebellarsDocumento4 pagineSchedule of Classes Second Semester A.Y. 2017-18: 30-Jan Preceptorials: Motor System, CerebellarsAthena BorjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medication AdministrationDocumento8 pagineMedication AdministrationMarku LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- CBDRP Reporting Form 1Documento1 paginaCBDRP Reporting Form 1Romer EnajeNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiotherapy in Prostate Cancer Innovative Techniques and Current ControversiesDocumento288 pagineRadiotherapy in Prostate Cancer Innovative Techniques and Current ControversiesStirNessuna valutazione finora
- Anxiety: What Are Some Symptoms of Anxiety?Documento3 pagineAnxiety: What Are Some Symptoms of Anxiety?Khairil AshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Lista Preturi Teste Genetice GendiaDocumento227 pagineLista Preturi Teste Genetice GendiaMatei FloriNessuna valutazione finora
- Elevated Levels of Bcl-3 Inhibits Treg Development and Function Resulting in Spontaneous ColitisDocumento14 pagineElevated Levels of Bcl-3 Inhibits Treg Development and Function Resulting in Spontaneous ColitisPaviliuc RalucaNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiologi Gastrointestinal (Noted)Documento52 pagineRadiologi Gastrointestinal (Noted)desak 102018084Nessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Efficacy and Acceptability META-ANALYSIS 2015Documento11 pagineComparative Efficacy and Acceptability META-ANALYSIS 2015Alexandra CastellanosNessuna valutazione finora
- Icru 89 (229-260)Documento32 pagineIcru 89 (229-260)Christian Ordoñez100% (1)
- APA Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Substance Use DisordersDocumento276 pagineAPA Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Substance Use DisordersRaja Ahmad Rusdan MusyawirNessuna valutazione finora
- New Health Care Clinical: Laboratory SrinagarDocumento1 paginaNew Health Care Clinical: Laboratory SrinagarRajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vertical Root Fracture !Documento42 pagineVertical Root Fracture !Dr Dithy kkNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP JourrnallldsdDocumento17 pagineNCP JourrnallldsdCHRISTINE JOY. MOLINANessuna valutazione finora
- Treating Canine Distemper VirusDocumento23 pagineTreating Canine Distemper VirusJack HollandNessuna valutazione finora
- Disorders of Immunity Hypersensitivity Reactions: Dr. Mehzabin AhmedDocumento25 pagineDisorders of Immunity Hypersensitivity Reactions: Dr. Mehzabin AhmedFrances FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- HSBDocumento4 pagineHSBCarlos WebsterNessuna valutazione finora
- Cholera (5 5)Documento1 paginaCholera (5 5)Celestial, Maybelle MarieNessuna valutazione finora
- Acadia PharmaceuticalsDocumento3 pagineAcadia PharmaceuticalsAman DecoraterNessuna valutazione finora
- MR 190820 Dr. Haudhiya OkeDocumento53 pagineMR 190820 Dr. Haudhiya OkeRudy Arindra WijayaNessuna valutazione finora
- E341 FullDocumento7 pagineE341 FullwaribisalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medicina Chinesa JeremyDocumento2 pagineMedicina Chinesa JeremyJuan Gabriel CunhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Features and Diagnosis of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm - UpToDateDocumento53 pagineClinical Features and Diagnosis of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm - UpToDateALVARO ARIASNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study of Most Common Communicable DiseasesDocumento13 pagineCase Study of Most Common Communicable DiseasesnesjynNessuna valutazione finora
- Annotated BibliographyDocumento4 pagineAnnotated BibliographyJuanNessuna valutazione finora
- TicksDocumento1 paginaTicksTheChronicleHeraldNessuna valutazione finora
- Comorbidity: Apakah Merupakan Faktor Risiko: Infeksi Luka Operasi Pasca Seksio Sesarea?Documento10 pagineComorbidity: Apakah Merupakan Faktor Risiko: Infeksi Luka Operasi Pasca Seksio Sesarea?Dini AgustiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Medicine: Dr. Nindyasari Diajeng Larasati Tim UKMPPD FKU MalahayatiDocumento209 pagineInternal Medicine: Dr. Nindyasari Diajeng Larasati Tim UKMPPD FKU MalahayatiSilvi Qiro'atul AiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Infusion PumpDocumento14 pagineInfusion PumpSREEDEVI T SURESHNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain AbscessDocumento13 pagineBrain AbscessRian AprizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tercera SemanaDocumento9 pagineTercera SemanaJesús Torres MayaNessuna valutazione finora