Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Impaired Verbal Communication
Caricato da
Chenee MabulayTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Impaired Verbal Communication
Caricato da
Chenee MabulayCopyright:
Formati disponibili
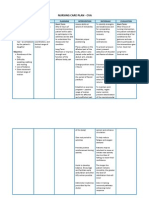
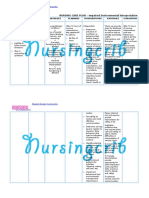
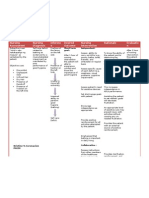
ASSESSMENT NURSING SCIENTIFIC OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS RATIONALE
Subjective: N/A Impaired verbal Stroke is when a Short term: 1. Establish means of 1. Eye contact assures client Short term:
communication clogged or burst After 1 hour of communication, for of interest in After 1 hour of
Objective: related to impaired artery interrupts nursing example, maintain eye communicating; if client is nursing intervention,
Known case of Acute cerebral circulation blood flow deprives intervention, the contact; ask yes/no able to move head, blink the patient was able to
cerebral infarction as evidenced by the brain needed patient will be able questions; provide eyes, or is comfortable establish method of
Left MCA prob. incomprehensible oxygen and causes to establish method magic slate, paper and with simple gestures, a communication in
Embolic in nature sounds the affected brain of communication pencil, or picture or great deal can be done which needs can be
cells to die. It in which needs can alphabet board; use with yes/no questions. understood.
LOC: alert usually affects one be understood. sign language as Pointing to letter boards or
side of the brain. appropriate; and writing is often tiring to Long term:
GCS: 12 (E4V2M6) When brain cells Long term: validate meaning of client, who can then After 5 days of
die, the functioning After 5 days of attempted become frustrated with the nursing interventions,
Able to make of the body parts nursing communications. effort needed to attempt the patient will be
incomprehensible that they control is interventions, the conversations. Use of able to communicate
sounds impaired or lost. A patient will be able picture boards that express needs and desired
stroke can cause to communicate a concept or routine needs effectively.
paralysis or muscle needs and desired may simplify
weakness, loss of effectively. communication. Family
feelings, speech members and other
and language caregivers may be able to
problems, memory assist and interpret needs
and reasoning 2. Alerts all staff members to
problems, respond to client at the
swallowing bedside instead of over the
difficulties, 2. Place call light or bell intercom
problems of vision within reach and place
and visual note at central call
perception, coma, station informing staff 3. Helpful in reducing
and even death. that client is unable to frustration when
speak dependent on others and
3. Anticipate and meet cannot communicate
the needs of patients meaning.
4. Cues are often difficult to
recognize (glancing out of
the corner of the eye)
4. Recognize subtle cues 5. Naming objects and
indicating the client is describing actions,
paying attention or thoughts, and feelings
attempting to helps the client to use
communicate. symbolic language.
5. Describe for the client 6. To maximize patient’s
what is happening, and sense of independence
put into words what the 7. To keep patient focused,
client might be decrease stimuli going to
experiencing the brain for interpretation,
6. Pace important objects and enhance the nurse’s
within reach ability to listen
7. Keep distractions such 8. It may be difficult for
as television and radio patients to respond under
at a minimum when pressure; they may need
talking to patient extra time to organize
8. Give the patient ample responses, find the correct
time to respond word, or make necessary
language translations
9. This approach provides the
patient with more channels
through which information
can be communication
10. The inability to
communicate enhances a
patient’s sense of isolation
9. Speak slowly and may promote a sense
of helplessness
11. Improves general
communication skills
10. Praise patient’s
accomplishments.
Acknowledge his or
her frustrations
11. Use and assist patient 12. SO may feel self-
or significant others to conscious in one-sided
learn therapeutic conversation, but
communication skills knowledge that he or she
of acknowledgement, is assisting the client to
active-listening, and regain or maintain contact
messages with reality and enabling
12. Encourage family and client to feel part of family
SO to talk with client, unit can reduce feelings of
providing information awkwardness
about family and daily 13. Enhances participation and
happenings commitment to plan
Collaboration
1. Specialized services
may be required to
meet the patient’s
needs.
13. Involve family and
significant others in
plan of care as much as
possible
Collaboration
1. Refer to appropriate
resources (e.g.
speech therapist,
group therapy,
individual/ family
and/ or psychiatric
counselling)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- FAR EASTERN UNIVERSITY NURSING CARE PLANDocumento3 pagineFAR EASTERN UNIVERSITY NURSING CARE PLANDesiree Deleon Guerrero0% (2)
- NCP Impaired Verbal CommunicationDocumento2 pagineNCP Impaired Verbal CommunicationLovelie Grace GalarpeNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Self Care Deficit Neuromuscular Impairment Secondary To CVADocumento1 paginaNCP - Self Care Deficit Neuromuscular Impairment Secondary To CVAHannah BatallonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan CVADocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan CVAhermesdave175% (4)
- NCP CvaDocumento3 pagineNCP CvaJey PangilinanNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDocumento4 pagineImpaired Verbal CommunicationKM95% (19)
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDocumento1 paginaImpaired Verbal Communicationdana100% (3)
- Impaired Communication AssessmentDocumento1 paginaImpaired Communication AssessmentCzarina_May_Tr_429888% (8)
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDocumento3 pagineImpaired Verbal CommunicationCalimlim KimNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Impaired Verbal Communication Related To Neuromascular Impairment As Manifested by AphaisaDocumento2 pagineNCP - Impaired Verbal Communication Related To Neuromascular Impairment As Manifested by AphaisaKristina Angela CarbonNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDocumento2 pagineImpaired Verbal CommunicationEjay Barayuga100% (2)
- Self Care DeficitDocumento3 pagineSelf Care DeficitAddie Labitad100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan (CVA)Documento2 pagineNursing Care Plan (CVA)Mel Rodolfo50% (2)
- Acute Confusion Nursing DiagnosisDocumento4 pagineAcute Confusion Nursing Diagnosisasmika danaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP CvaDocumento4 pagineNCP CvamannyV1990100% (1)
- NCP STROKE - Impaired Verbal CommDocumento2 pagineNCP STROKE - Impaired Verbal CommCath BrilNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBDocumento3 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (1)
- Anatomy Physiology Nervous System Brain Stroke Risk FactorsDocumento4 pagineAnatomy Physiology Nervous System Brain Stroke Risk FactorsKimsha ConcepcionNessuna valutazione finora
- Disturbed Thought ProcessDocumento3 pagineDisturbed Thought ProcessAira AlaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDocumento6 pagineImpaired Verbal CommunicationLaura Sansonetti100% (1)
- Self Care DeficitDocumento2 pagineSelf Care DeficitRen Aezzle Garcia Aceveda100% (1)
- CVA Activity IntoleranceDocumento1 paginaCVA Activity IntoleranceNursesLabs.com75% (4)
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocumento3 pagineDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJashtine JingcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk For Aspiration Related To Impaired Swallowing Secondary To Cerebrovascular AccidentDocumento3 pagineRisk For Aspiration Related To Impaired Swallowing Secondary To Cerebrovascular AccidentChenee MabulayNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - CvaDocumento3 pagineNCP - CvaBrenda Lee0% (1)
- NCPDocumento17 pagineNCPbalongetzNessuna valutazione finora
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocumento2 pagineDisturbed Sensory Perceptionsuper ahga-once0% (1)
- Possible NCP For CVDDocumento6 paginePossible NCP For CVDVincent Bulla50% (2)
- Risk For InjuryDocumento2 pagineRisk For InjuryRo-anne AkuNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPderic100% (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning ImplementationDocumento4 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning ImplementationMG PolvorosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocumento3 pagineDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJoenna GaloloNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento4 pagineAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationTedd CamilingNessuna valutazione finora
- Ncp-Impaired Verbal CommunicationDocumento4 pagineNcp-Impaired Verbal CommunicationEzra TuanNessuna valutazione finora
- NURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocumento2 pagineNURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeNader AbdurasadNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocumento5 pagineNCP Activity IntoleranceRea HashimNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Risk Impaired Skin RT Altered Circulation (Spinal Injury)Documento2 pagineNCP - Risk Impaired Skin RT Altered Circulation (Spinal Injury)yanny0350% (2)
- Impaired Verbal CommDocumento3 pagineImpaired Verbal CommKM100% (2)
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7Documento2 pagineIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7dana100% (4)
- Self Care Deficit BahtingDocumento1 paginaSelf Care Deficit BahtingNaj SoliveresNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan SeizureDocumento8 pagineNursing Care Plan SeizureSuzette Rae Tate75% (4)
- NCP PottsDocumento3 pagineNCP PottsFenie Jane Quinlat LapastoraNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP IcuDocumento12 pagineNCP IcuHazel Palomares50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With SchizophreniaDocumento14 pagineNursing Care Plan For A Patient With SchizophreniaMary Luz De GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Close Complete Fracture Knowledge DeficitDocumento2 pagineNCP Close Complete Fracture Knowledge DeficitArt Christian Ramos0% (1)
- Nursing Interventions for Unilateral Neglect PatientDocumento6 pagineNursing Interventions for Unilateral Neglect PatientNicole Palarca92% (12)
- NCP Cushing's SyndromeDocumento2 pagineNCP Cushing's SyndromeChristine LebicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Non Compliance NCPDocumento3 pagineNon Compliance NCPlibdub75% (4)
- Nursing Care Guide for Cushing's SyndromeDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Guide for Cushing's Syndromerngeneral50% (6)
- CVA NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento2 pagineCVA NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceJoanne Kaye Taylor100% (1)
- Self Care NCPDocumento2 pagineSelf Care NCPMick De Leon100% (3)
- Activity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDocumento3 pagineActivity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDarkCeades100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan Autism Spectrum DisorderDocumento1 paginaNursing Care Plan Autism Spectrum DisorderHarold Peranduz100% (5)
- NCP CvaDocumento3 pagineNCP CvaJey PangilinanNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTONessuna valutazione finora
- NCP MentalDocumento3 pagineNCP MentalColleen De la RosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento1 paginaAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTONessuna valutazione finora
- AGOTILLA - Neuro Case ActivityDocumento5 pagineAGOTILLA - Neuro Case Activitypaulineamado19Nessuna valutazione finora
- NCP-Alzheimer's Disease (Caguimbay)Documento9 pagineNCP-Alzheimer's Disease (Caguimbay)Christine Claire CaguimbayNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For Cerebrovascular AccidentDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan For Cerebrovascular AccidentJobelle AcenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Checklist For Writing Audit Proof IepsDocumento2 pagineChecklist For Writing Audit Proof Iepsapi-2307242610% (1)
- Forceps DeliveryDocumento22 pagineForceps DeliveryN. Siva100% (1)
- Please Quote This Reference Number in All Future CorrespondenceDocumento2 paginePlease Quote This Reference Number in All Future CorrespondenceSaipraveen PerumallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Hepatitis: Causes, Types, and TreatmentsDocumento2 pagineUnderstanding Hepatitis: Causes, Types, and TreatmentsChandra SaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Notrox Research - We Are ExpandingDocumento1 paginaNotrox Research - We Are ExpandingDr. Shiva Murthy NNessuna valutazione finora
- Mammograms and Other Breast Imaging Procedures: What Is A Mammogram?Documento25 pagineMammograms and Other Breast Imaging Procedures: What Is A Mammogram?Marina StosicNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Coercion in Mental Healthcare The Principle of Least Coercive CareDocumento8 pagine4 Coercion in Mental Healthcare The Principle of Least Coercive CarePedro Y. LuyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Gender Studies Lecture 6Documento30 pagineGender Studies Lecture 6Shahzaib KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Educational Strategies For Children With Emotional and Behavioral ProblemsDocumento74 pagineEducational Strategies For Children With Emotional and Behavioral Problemsmaeydel50% (2)
- Teacher's Guide: To The Magnificent Mei and Friends Comic SeriesDocumento44 pagineTeacher's Guide: To The Magnificent Mei and Friends Comic SeriesVarizka SalsabilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Enhancing Your Skills in Stroke Quality Improvement and Data AnalysisDocumento50 pagineEnhancing Your Skills in Stroke Quality Improvement and Data AnalysisRaisha Klinik Vaksinasi YogyakartaNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Care Disparities - Stereotyping and Unconscious BiasDocumento39 pagineHealth Care Disparities - Stereotyping and Unconscious BiasCherica Oñate100% (1)
- The State of Mental Health in The Philippines PDFDocumento4 pagineThe State of Mental Health in The Philippines PDFKatrina Francesca SooNessuna valutazione finora
- SAFETY DATA SHEET TITLEDocumento10 pagineSAFETY DATA SHEET TITLELokesh HNessuna valutazione finora
- Disorders of The Vulva - Common Causes of Vulvar Pain, Burning, and Itching - ACOGDocumento7 pagineDisorders of The Vulva - Common Causes of Vulvar Pain, Burning, and Itching - ACOGAYI NURHIDAYAHNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Ethics and Legal Medicine For Public Health StudentsDocumento99 pagineHealth Ethics and Legal Medicine For Public Health StudentsChimdesa JabesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Health and Safety Policy Manual Issue 14Documento34 pagineHealth and Safety Policy Manual Issue 14caskevNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental Health ResourcesDocumento5 pagineMental Health ResourcesAnna R ZahorNessuna valutazione finora
- Level 1 Q& A Og - KoncptDocumento14 pagineLevel 1 Q& A Og - KoncptadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Method of Statement and Risk Assessment FormDocumento4 pagineMethod of Statement and Risk Assessment FormBala KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- MAPEH 1 (2nd Quarter Complete)Documento60 pagineMAPEH 1 (2nd Quarter Complete)Roselyn GutasNessuna valutazione finora
- Ensuring-Competence Changing Scope of Practice and Re-Entering PracticeDocumento8 pagineEnsuring-Competence Changing Scope of Practice and Re-Entering Practicesatheeshkrishna.jeyarajNessuna valutazione finora
- Attention, Verbal Learning and Memory Deficits in Somatization DisorderDocumento21 pagineAttention, Verbal Learning and Memory Deficits in Somatization Disordertaneja_rahul82Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bronchial Asthma & Cardiac AsthmaDocumento7 pagineBronchial Asthma & Cardiac AsthmaAbraham Chiu100% (1)
- Maternity and Newborn MedicationDocumento34 pagineMaternity and Newborn MedicationNicholas ClaytonNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Practice in Sports and ExerciseDocumento32 pagineSafety Practice in Sports and ExercisePrincess Reiann LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2. Nutritional Requirements and Food Based Dietary Guidelines Study Questions 2 (SQ 2)Documento2 pagineChapter 2. Nutritional Requirements and Food Based Dietary Guidelines Study Questions 2 (SQ 2)Julie Amor ZantuaNessuna valutazione finora
- METHODS AND STRATEGIES IN TEACHING MAPEH MODULE 1 - BajadoDocumento40 pagineMETHODS AND STRATEGIES IN TEACHING MAPEH MODULE 1 - Bajadoacademic coordinatorNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Care Surgery: Aryono D.Pusponegoro Warko KarnadihardjaDocumento9 pagineAcute Care Surgery: Aryono D.Pusponegoro Warko KarnadihardjaDimas ErlanggaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Tools in NutritionDocumento23 pagineBasic Tools in NutritionSeanmarie Cabrales0% (1)