Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
The Endocrine System: Hormone Solubility
Caricato da
Juelle0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
15 visualizzazioni2 pagineThe endocrine system is made up of glands that secrete hormones to regulate bodily processes like metabolism, growth, reproduction, and stress responses. These hormones enter cells through cell membranes and alter gene expression by producing proteins that change cellular activity. Lipid soluble hormones enter cell nuclei while water soluble hormones bind to cell membranes and trigger chemical reactions that alter protein production. The major glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, thymus, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries, and testes, each controlling important bodily functions.
Descrizione originale:
An overview of the Human Endocrine System
Titolo originale
Endocrine
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThe endocrine system is made up of glands that secrete hormones to regulate bodily processes like metabolism, growth, reproduction, and stress responses. These hormones enter cells through cell membranes and alter gene expression by producing proteins that change cellular activity. Lipid soluble hormones enter cell nuclei while water soluble hormones bind to cell membranes and trigger chemical reactions that alter protein production. The major glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, thymus, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries, and testes, each controlling important bodily functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
15 visualizzazioni2 pagineThe Endocrine System: Hormone Solubility
Caricato da
JuelleThe endocrine system is made up of glands that secrete hormones to regulate bodily processes like metabolism, growth, reproduction, and stress responses. These hormones enter cells through cell membranes and alter gene expression by producing proteins that change cellular activity. Lipid soluble hormones enter cell nuclei while water soluble hormones bind to cell membranes and trigger chemical reactions that alter protein production. The major glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, thymus, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries, and testes, each controlling important bodily functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
S
The Endocrine System
T
The endocrine system works as a system of glands
in the body to regulate internal bodily processes.
These glands secrete hormones that maintain
R
homeostasis, growth and development, metabolism,
reproduction, and responses to stress and/ or
injuries.
A
Hormone Solubility
H
Lipid soluble hormones
enter the target cell
through the membrane
and enter the nucleus
C
where it alters the gene
expression by producing
proteins that alter the
cell’s activity.
D
Water soluble hormones
work by binding to the
cell membrane which
R
causes a number of
What are Glands? chemical reactions
inside the cell which
Glands are what make the endocrine system
O
work and they are strategically placed result in certain proteins
around the body to regulate and control being produced that alter
body processes. the cell’s activity.
F
S
Glands and their Functions
Hypothalamus: The portion of the brain
that maintains the body’s internal
T
balance and is the link between the
endocrine and nervous systems.
Pineal: The pineal gland secretes a
single hormone, melatonin, which
R
controls the body’s circadian rhythm.
Pituitary: AKA the “master gland,” which
controls the functions of other
endocrine glands.
A
Thyroid: The thyroid’s role in the
endocrine system is to regulate your
metabolism, which is the body’s ability
to break down food and convert it to
H
energy.
Parathyroid: The parathyroid hormone
regulates the body’s calcium levels.
Thymus: The thymus gland will help the
C
body protect itself against
autoimmunity, which occurs when the
immune system turns against itself.
Adrenal: This gland produces hormones
D
that are vital to life, such as cortisol and
aldosterone.
Pancreas: The pancreas maintains the
body’s blood glucose balance.
R
Ovaries: The ovaries maintain the health
of the female reproductive system
Testes: The testes are a pair of sperm-
producing organs that maintain the
O
health of the male reproductive system.
F
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Bio 225 Concordia NotesDocumento5 pagineBio 225 Concordia NotesretterateNessuna valutazione finora
- The Endocrine SystemDocumento41 pagineThe Endocrine SystemОксана КрасильниковаNessuna valutazione finora
- HomeostasisDocumento26 pagineHomeostasisTauqeer AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam #1 Physiology Study GuideDocumento27 pagineExam #1 Physiology Study GuideKamille TucaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System Lectu RaDocumento8 pagineEndocrine System Lectu RaChrista BalderasNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System - Multiple Choice TestDocumento2 pagineEndocrine System - Multiple Choice TestshasagailNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 Endocrine SystemDocumento53 pagineLecture 2 Endocrine SystemLouella ArtatesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Endocrine System Anaphy ReviewDocumento4 pagineThe Endocrine System Anaphy ReviewAdiel CalsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System HandoutsDocumento5 pagineEndocrine System HandoutsBeatriz IcayNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System PDFDocumento38 pagineEndocrine System PDFUlfat NiazyNessuna valutazione finora
- 11J Caybot Jashjovian Task12Documento18 pagine11J Caybot Jashjovian Task12JASH JOVIAN CAYBOTNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System Endocrine System: "The Body Regulator"Documento31 pagineEndocrine System Endocrine System: "The Body Regulator"angelus008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9Documento8 pagineChapter 9Bea SeloterioNessuna valutazione finora
- O Level Biology Notes - CellsDocumento3 pagineO Level Biology Notes - CellsRakib Ahsan86% (7)
- Endocrine Answer KeyDocumento10 pagineEndocrine Answer KeyJoyce LimNessuna valutazione finora
- GROUP 9 Edocrine System ReportDocumento52 pagineGROUP 9 Edocrine System Reportroyeth montezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic3.1 Physiology Introduction To EndocrinologyDocumento7 pagineTopic3.1 Physiology Introduction To EndocrinologyRen AlvNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IV Lecture NotesDocumento9 pagineUnit IV Lecture NotesSteve SullivanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 9 Human AnatomyDocumento4 pagineLecture 9 Human AnatomyAngelica CruzNessuna valutazione finora
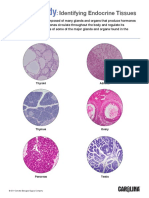
- Human Body: Identifying Endocrine TissuesDocumento3 pagineHuman Body: Identifying Endocrine TissuesDiana VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Science 10Documento4 pagineLesson Plan Science 10Glorylyn LacreNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System: Organs and Their FunctionDocumento61 pagineEndocrine System: Organs and Their FunctionSherifaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System: 3.6 Functions, Definitions & VocabularyDocumento20 pagineEndocrine System: 3.6 Functions, Definitions & VocabularyD AngelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System Practice TestDocumento10 pagineEndocrine System Practice TestFarrah Turner Matthews0% (1)
- Endocrine System: Adesanya O.A Department of Anatomy Kampala International University, TanzaniaDocumento29 pagineEndocrine System: Adesanya O.A Department of Anatomy Kampala International University, TanzaniaAnnette MhenggaNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning JournalDocumento82 pagineLearning JournalAnnapurna RavelNessuna valutazione finora
- Muslimah D. Diangca - Activity 4Documento4 pagineMuslimah D. Diangca - Activity 4Baby Corner MarawiNessuna valutazione finora
- EndocrineDocumento2 pagineEndocrineHoney Mie MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- 337 Pdfsam NMS PhysiologyDocumento166 pagine337 Pdfsam NMS PhysiologydrpnnreddyNessuna valutazione finora
- EndocrineDocumento18 pagineEndocrineAzmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrinology Course OutllokDocumento59 pagineEndocrinology Course OutllokJeff ParkNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemDocumento7 pagineEndocrine SystemIvy Jana BelenNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System NotesDocumento14 pagineEndocrine System NotesSteven100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocumento95 pagineEndocrine SystemUmar Ilyasu JibrilNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 45Documento9 pagineCH 45homamunfatNessuna valutazione finora
- AP2 Unit 6 Exam Review CASDocumento12 pagineAP2 Unit 6 Exam Review CASMarera DomnicNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolic Endocrinology (Week-1)Documento11 pagineMetabolic Endocrinology (Week-1)wasimsafdarNessuna valutazione finora
- Blok 4 Skenario 1Documento14 pagineBlok 4 Skenario 1Dots FfastNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemDocumento4 pagineEndocrine SystemCELLINA CLARISSE DE LEONNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System Web QuestDocumento8 pagineEndocrine System Web QuestBraedyn JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Ms Word Notes - Template (May 2022)Documento4 pagineMs Word Notes - Template (May 2022)Jaycee Anne AregloNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Group Phsiology.....Documento14 pagine6 Group Phsiology.....Ayat ChaudaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Quarter 3 Week 1 Module 1Documento34 pagineQuarter 3 Week 1 Module 1Juliana Sophia BungalsoNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry HormonesDocumento13 pagineBiochemistry HormonesKeziah GillNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry Hormone Lecture PDFDocumento13 pagineBiochemistry Hormone Lecture PDFKeziah GillNessuna valutazione finora
- Portfolio IN Histology Laboratory: Submitted To: Tom Anthony Tonguia, RMT Submitted By: Charlene Caro 2A-BsmlsDocumento9 paginePortfolio IN Histology Laboratory: Submitted To: Tom Anthony Tonguia, RMT Submitted By: Charlene Caro 2A-BsmlsFearless AngelNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System-1Documento90 pagineEndocrine System-1markmuiruri581Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry Assignment Submitted To: Dr. Noureen Submitted byDocumento15 pagineBiochemistry Assignment Submitted To: Dr. Noureen Submitted bySalman KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 8-Endocrine SystemDocumento30 pagineLec 8-Endocrine SystemHarahap DarwisNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System Study GuideDocumento6 pagineEndocrine System Study GuideCarla Andrea AbayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endrocrinology - PPTX Version 1Documento40 pagineEndrocrinology - PPTX Version 1Abishek BhadraNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Body Chemistry: Processes That Characterise LifeDocumento4 pagineIntroduction To Body Chemistry: Processes That Characterise LifeLeo OrtegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System BendoyDocumento6 pagineEndocrine System BendoyNiel GomezNessuna valutazione finora
- EndocrinologyDocumento4 pagineEndocrinologyRekesh SaeedNessuna valutazione finora
- HORMONESDocumento3 pagineHORMONESkevbrgsNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 The Endocrine SystemDocumento7 pagineChapter 9 The Endocrine SystemAshy LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Hormones Endocrine System WorksheetDocumento4 pagineHormones Endocrine System WorksheetRia LouNessuna valutazione finora
- Signaling Molecules and Their ReceptorsDocumento13 pagineSignaling Molecules and Their ReceptorsShweta SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous Vs HormoneDocumento106 pagineNervous Vs HormoneakupunadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Epidemiology of Skin DiseasesDocumento33 pagineEpidemiology of Skin DiseasesMahmoud AbuAwadNessuna valutazione finora
- Rle Requirements Wardspcl Area NCP DSDocumento3 pagineRle Requirements Wardspcl Area NCP DSAzhly AntenorNessuna valutazione finora
- Panic DisorderDocumento50 paginePanic Disorderheshm300020001790100% (3)
- Spinal InjuryDocumento24 pagineSpinal InjuryFuad Ahmad ArdiansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Prumychild EngDocumento12 paginePrumychild EngAmirol Ariff NazarudinNessuna valutazione finora
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia CaseDocumento6 pagineCommunity-Acquired Pneumonia Caseapi-648891519Nessuna valutazione finora
- B-Blood Banking History 2-4-21: RequiredDocumento5 pagineB-Blood Banking History 2-4-21: RequiredFlorenz AninoNessuna valutazione finora
- Phase II CurriculumDocumento136 paginePhase II CurriculumNil NilNessuna valutazione finora
- Radioembolization of Hepatic Malignancies - Background, Quality Improvement Guidelines, and Future DirectionsDocumento15 pagineRadioembolization of Hepatic Malignancies - Background, Quality Improvement Guidelines, and Future DirectionsVeronica AlexanderNessuna valutazione finora
- Tatalaksana ACS HUT Harkit 2015 - 1 PDFDocumento35 pagineTatalaksana ACS HUT Harkit 2015 - 1 PDFKevin EdroNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study 10Documento4 pagineCase Study 10Rachael OyebadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Concepts in Aesthetic Dentistry ADocumento247 pagineModern Concepts in Aesthetic Dentistry AHamad KayaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Quisted en P Menopausicas Guias GTG - 34 PDFDocumento32 pagineQuisted en P Menopausicas Guias GTG - 34 PDFAdela Marìa P LNessuna valutazione finora
- The Influence of Probiotics and Antibiotic Growth PromoterDocumento7 pagineThe Influence of Probiotics and Antibiotic Growth PromoterOliver TalipNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Assessment - Ukrainian World Congress. July 28th - August 8th, 2014Documento53 pagineMedical Assessment - Ukrainian World Congress. July 28th - August 8th, 2014Patrick ChellewNessuna valutazione finora
- Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Atan Baas Sinuhaji, Spa (K)Documento35 pagineSupervisor: Prof. Dr. Atan Baas Sinuhaji, Spa (K)Ranap HadiyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pe Lesson 1 LifestyleDocumento17 paginePe Lesson 1 LifestyleKeil San PedroNessuna valutazione finora
- Incentive SpirometerDocumento25 pagineIncentive SpirometerAnalyn Salvacion100% (2)
- Septimo MCP Plan 2013Documento8 pagineSeptimo MCP Plan 2013daniel tafoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Traumatic Liver Injuries: DR Junaid Ahmad SofiDocumento80 pagineManagement of Traumatic Liver Injuries: DR Junaid Ahmad SofiNatalindah Jokiem Woecandra T. D.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dumitrita Rodica Bagireanu U4 Assessment Feedback2 (PASS)Documento4 pagineDumitrita Rodica Bagireanu U4 Assessment Feedback2 (PASS)Rodica Dumitrita0% (1)
- Midterms Psyc LecDocumento14 pagineMidterms Psyc LecMiden AlbanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dsfasdfsadf PDFDocumento246 pagineDsfasdfsadf PDFrpascua123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeDocumento2 pagineGi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeEvangeline Villa de Gracia100% (1)
- Fluid Balance Case StudyDocumento9 pagineFluid Balance Case StudyAna BienneNessuna valutazione finora
- Casilan, Ynalie Drug Study (Morphine)Documento5 pagineCasilan, Ynalie Drug Study (Morphine)Ynalie CasilanNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S0169409X20301034 Main PDFDocumento30 pagine1 s2.0 S0169409X20301034 Main PDFChrispinus LinggaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassRheegell Ellar-Fuertes100% (3)
- Cytochemistry PrimerDocumento2 pagineCytochemistry PrimerMunish Dogra100% (1)
- Arero Primary Hospital Pain MGT ProtocolDocumento9 pagineArero Primary Hospital Pain MGT Protocolsami ketemaNessuna valutazione finora