Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Practical 26 - Resistance of A Thermistor With Temperature PDF
Caricato da
Nasrin SultanaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Practical 26 - Resistance of A Thermistor With Temperature PDF
Caricato da
Nasrin SultanaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1 of 1 Student
Practical 26 The resistance of a thermistor
Purpose Safety
The aim of the experiment is to investigate how Eye protection is advised.
the resistance of an NTC thermistor changes with Take care not to spill the beaker, the water
temperature. will be hot.
mA
� �
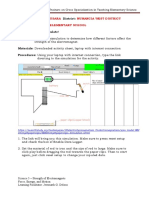
Figure 1: Diagrams of the experimental arrangement
You will need:
• NTC thermistor connected to leads that • Thermometer (0 – 100 ºC) or
have been insulated with silicone jelly temperature sensor
• Variable voltage dc power supply (0 – 6 V) • Bunsen burner, tripod, gauze and mat
• Milliammeter (0 – 100 mA) • Set of connecting leads
• dc voltmeter (0 – 6 v) • An ohmmeter can be used in place of the
• Beaker of water power supply, voltmeter and milliammeter
Experimental instructions
Set up the circuit shown in the diagram and place the thermistor in the beaker of water
at room temperature. Measure the temperature of the water, the current shown by the
milliammeter and the voltage shown by the voltmeter (or the resistance shown by the
ohmmeter).
Heat the water and record readings of temperature, current and voltage roughly every 5 ºC.
Analysis and conclusions
Work out the resistance of the thermistor for each temperature value (V) and record
I
them in a table.
The calculation will be unnecessary if the ohmmeter is used since the resistance values
can be entered directly.
Plot a graph of resistance (y-axis) against temperature (x-axis).
Calculate the rate of change of resistance of resistance at four points on your graph.
Suggest the more sensitive range of the thermistor for use as a temperature-sensing device.
30
M01_ASPhys_TB_6399.indd 30 27/5/08 17:40:36
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- API NTC Engineering NotesDocumento4 pagineAPI NTC Engineering NotesPanagiotis PlatisNessuna valutazione finora
- GRADE 12 SAHODAYA PREBOARD -2 PHYSICS (042) MSDocumento7 pagineGRADE 12 SAHODAYA PREBOARD -2 PHYSICS (042) MSMohd AdilNessuna valutazione finora
- STD Xii Physics Ms Set IIDocumento8 pagineSTD Xii Physics Ms Set IIRagavNessuna valutazione finora
- (Template) Physics Cls 12Documento9 pagine(Template) Physics Cls 12sreelakshmiNessuna valutazione finora
- MTC2 Seminar Questions 2022-1Documento6 pagineMTC2 Seminar Questions 2022-1Majanga JohnnyNessuna valutazione finora
- (Class Xii Physics Practicals) : Physics Practical Term-1 Experiment - 1Documento17 pagine(Class Xii Physics Practicals) : Physics Practical Term-1 Experiment - 1Aksar AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Resistance IA PDFDocumento10 pagineInternal Resistance IA PDFtuvvacNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current QuestionsDocumento2 pagineMagnetic Effects of Electric Current QuestionsVinod KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYSICS EXPERIMENT RESISTANCE AND OHM'S LAWDocumento24 paginePHYSICS EXPERIMENT RESISTANCE AND OHM'S LAWGKJ kalaiyagamNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry SET A QPDocumento8 pagineChemistry SET A QPdahaka7609Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocumento7 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: Sciencehweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- 12th Physics Sahodaya Set2 QPDocumento12 pagine12th Physics Sahodaya Set2 QPAdiboiiiNessuna valutazione finora
- General Instructions:: Retest SESSION (2018-19) Class: Xi Subject: Physics M.M.: 50 Time: 2 HrsDocumento2 pagineGeneral Instructions:: Retest SESSION (2018-19) Class: Xi Subject: Physics M.M.: 50 Time: 2 HrsAshish GambhirNessuna valutazione finora
- Finding Refractive Index Using Travelling Microscope For Glass SlabDocumento2 pagineFinding Refractive Index Using Travelling Microscope For Glass Slabanamika7005865200Nessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment - 01 Aim Apparatus/ Material RequiredDocumento23 pagineExperiment - 01 Aim Apparatus/ Material RequiredAdi PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- ICSE Class 10 Physics ExperimentsDocumento2 pagineICSE Class 10 Physics ExperimentsRakesh Yadav0% (1)
- JEE Chemistry Exercises on Solid State Structures and PropertiesDocumento16 pagineJEE Chemistry Exercises on Solid State Structures and PropertiesKrishna BajpaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mid-Term Chemistry QuestionsDocumento4 pagineMid-Term Chemistry QuestionsRavindar PurohitNessuna valutazione finora
- Ans. (A) Applying: Electric Charges and Fields - 1 (I) Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento12 pagineAns. (A) Applying: Electric Charges and Fields - 1 (I) Multiple Choice Questionspaige100% (1)
- Experiment B6 Aim: Apparatus:: Characteristics of DiodeDocumento9 pagineExperiment B6 Aim: Apparatus:: Characteristics of DiodeAnurag BajpaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Exam Questions Cover Key ConceptsDocumento8 pagineScience Exam Questions Cover Key ConceptsGurukul PatnaNessuna valutazione finora
- PB II Xii Maths QP Jan 2023Documento6 paginePB II Xii Maths QP Jan 2023VardhiniNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEMISTRYDocumento20 pagineCHEMISTRYdishugirdhar08Nessuna valutazione finora
- Phy - II Pu Previous Year Questions (Electric Charges & Fields and Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance)Documento2 paginePhy - II Pu Previous Year Questions (Electric Charges & Fields and Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance)Madhu ammuNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 2 Let's SimulateDocumento3 pagineActivity 2 Let's SimulateResa Consigna MagusaraNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022-23 Phy Lab Manual Class 12Documento32 pagine2022-23 Phy Lab Manual Class 12Rasu 789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Csec E&ET TestDocumento5 pagineCsec E&ET TestkesnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Meter Bridge Lab ManualDocumento25 pagineMeter Bridge Lab ManualKiller GamingNessuna valutazione finora
- GRADE 12 PHYSICS ACTIVITIES LISTDocumento15 pagineGRADE 12 PHYSICS ACTIVITIES LISTHARSHA VARDAN KARTHIK SELVAN 6466100% (1)
- Verification of Kirchhoff's Voltage Law Lab ReportDocumento3 pagineVerification of Kirchhoff's Voltage Law Lab Report2290Md Nurnabi Rana0% (1)
- X ScienceDocumento5 pagineX ScienceMickey xzNessuna valutazione finora
- Comp Sci Cluster PaperDocumento8 pagineComp Sci Cluster Paperhelloo hehjeklNessuna valutazione finora
- CUET Physics ChapterwiseDocumento273 pagineCUET Physics ChapterwiseNafeesNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 12 Inv Daniel PDF 1Documento19 paginePhysics 12 Inv Daniel PDF 1Karan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- XII Physics Practical 2020 21Documento39 pagineXII Physics Practical 2020 21HITEN SOLANKINessuna valutazione finora
- Cape Unit 1 Phys Ia #1 Sept 2019Documento6 pagineCape Unit 1 Phys Ia #1 Sept 2019Ariel BroderickNessuna valutazione finora
- Convert Galvanometer into AmmeterDocumento4 pagineConvert Galvanometer into AmmeterSulman Abbasi0% (2)
- Measuring Carbon Resistors Using Color CodesDocumento6 pagineMeasuring Carbon Resistors Using Color CodesAliNessuna valutazione finora
- LIQUID SOLUTIONS CONCENTRATIONDocumento33 pagineLIQUID SOLUTIONS CONCENTRATIONSandipan SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Precaution and Sources of ErrorDocumento3 paginePrecaution and Sources of ErrorSuresh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- PD Labe Refractive Index and FrequencyDocumento3 paginePD Labe Refractive Index and FrequencyBilly Moses0% (1)
- Ph203 CH23 WorksheetDocumento5 paginePh203 CH23 WorksheetEko Bambang SaputroNessuna valutazione finora
- Dielectrics: Differences Between Dielectrics and ConductorsDocumento9 pagineDielectrics: Differences Between Dielectrics and ConductorsPrudhvi Raghu TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- XII CS PB-I Sample Paper-IV by KVS RO KolkattaDocumento11 pagineXII CS PB-I Sample Paper-IV by KVS RO Kolkattafaisal ShamimNessuna valutazione finora
- AIPMT 2009 Solved PaperDocumento27 pagineAIPMT 2009 Solved PaperFirdosh Khan100% (3)
- 2014 CXC Elec Paper 2Documento15 pagine2014 CXC Elec Paper 2api-255989257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bangalore Sahodaya School Complex Association Preboard Examination - (Set-2) Subject: PhysicsDocumento8 pagineBangalore Sahodaya School Complex Association Preboard Examination - (Set-2) Subject: PhysicsMohd AdilNessuna valutazione finora
- Set 1 PDFDocumento15 pagineSet 1 PDFMohamed AnasNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Logic GatesDocumento16 paginePhysics Logic GatesAniket LavandNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Emitter Transistor CharacteristicsDocumento6 pagineCommon Emitter Transistor CharacteristicsShiv Mangal Singh Rajawat67% (3)
- Class X CBSE Science Question PaperDocumento10 pagineClass X CBSE Science Question PaperVinayak Singh OberoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Science Sample PaperDocumento16 pagineComputer Science Sample PapercosidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuits Physic LabDocumento5 pagineCircuits Physic LabAaliyah SeniorNessuna valutazione finora
- XII 1st PRE BOARD QP Withsolution 2023Documento13 pagineXII 1st PRE BOARD QP Withsolution 2023kalashNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Education-1 231231 200610Documento79 paginePhysical Education-1 231231 200610mehaktyagi422Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class Xii Physics Set A PDFDocumento10 pagineClass Xii Physics Set A PDFJ NNessuna valutazione finora
- Class XII Physics Previous QuestionsDocumento12 pagineClass XII Physics Previous QuestionsAnonymous dW6e9PusZNessuna valutazione finora
- Measure Temperature with Wheatstone Bridge & ThermistorDocumento3 pagineMeasure Temperature with Wheatstone Bridge & ThermistorAnonymous AK2M4TE4Nessuna valutazione finora
- DM 10 Practical 6Documento2 pagineDM 10 Practical 6Roshan WijewardanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No 6 IAS-GTU-6th Sem CivilDocumento5 pagineExperiment No 6 IAS-GTU-6th Sem CivilJATINKUMAR CHAUDHARINessuna valutazione finora
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Physics (6734/01)Documento10 pagineMark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Physics (6734/01)Nasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2-As Biology Core Practical SummaryDocumento2 pagine2-As Biology Core Practical SummaryJoel Oh SukJuNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 13 - Melde's Experiment (Vibrator Generator)Documento1 paginaPractical 13 - Melde's Experiment (Vibrator Generator)Nasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 27 - Flow of Electrical Charge PDFDocumento1 paginaPractical 27 - Flow of Electrical Charge PDFNasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Edexcel A2 Biology Practicals Complete PDFDocumento45 pagineEdexcel A2 Biology Practicals Complete PDFnathaaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 26 - Resistance of A Thermistor With Temperature PDFDocumento1 paginaPractical 26 - Resistance of A Thermistor With Temperature PDFNasrin Sultana0% (1)
- 2-As Biology Core Practical SummaryDocumento2 pagine2-As Biology Core Practical SummaryJoel Oh SukJuNessuna valutazione finora
- UniassistDocumento37 pagineUniassistNasrin Sultana0% (1)
- IELTS TASK 1 BAND 9 MODEL ANSWER AND ANALYSISDocumento3 pagineIELTS TASK 1 BAND 9 MODEL ANSWER AND ANALYSISNasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- REV1Documento123 pagineREV1MarzanSayeedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 27 - Flow of Electrical Charge PDFDocumento1 paginaPractical 27 - Flow of Electrical Charge PDFNasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 13 - Melde's Experiment (Vibrator Generator)Documento1 paginaPractical 13 - Melde's Experiment (Vibrator Generator)Nasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 25 - Temperature Coefficient of Resistance PDFDocumento1 paginaPractical 25 - Temperature Coefficient of Resistance PDFNasrin Sultana50% (2)
- Practical 25 - Temperature Coefficient of Resistance PDFDocumento1 paginaPractical 25 - Temperature Coefficient of Resistance PDFNasrin Sultana50% (2)
- Practical 15 - Refractive Index Measurement - 1 of 3 PDFDocumento1 paginaPractical 15 - Refractive Index Measurement - 1 of 3 PDFNasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 16 - Stress Concentration Polarised LightDocumento1 paginaPractical 16 - Stress Concentration Polarised LightNasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 15 - Refractive Index Measurement - 1 of 3 PDFDocumento1 paginaPractical 15 - Refractive Index Measurement - 1 of 3 PDFNasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 16 - Stress Concentration Polarised LightDocumento1 paginaPractical 16 - Stress Concentration Polarised LightNasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 14 - The Sonometer PDFDocumento1 paginaPractical 14 - The Sonometer PDFNasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 4 - Effect of Force On Acceleration PDFDocumento1 paginaPractical 4 - Effect of Force On Acceleration PDFNasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 1 - Speed & AccelerationDocumento1 paginaPractical 1 - Speed & AccelerationHinameismyjeffNessuna valutazione finora
- Edexcel A Level Bk2 Physics Answers FINAL PDFDocumento39 pagineEdexcel A Level Bk2 Physics Answers FINAL PDFNasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 9 - Power of An Electric MotorDocumento1 paginaPractical 9 - Power of An Electric MotorNasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Edexcel A Level Bk2 Physics Answers FINAL PDFDocumento39 pagineEdexcel A Level Bk2 Physics Answers FINAL PDFNasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Edexcel As A Level Physics Answers (2015)Documento34 pagineEdexcel As A Level Physics Answers (2015)AbdulRahman Mustafa50% (4)
- Phy Shahid PDFDocumento5 paginePhy Shahid PDFNasrin SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy U1Documento9 paginePhy U1Abdull ShdcareNessuna valutazione finora
- Bioclimatic ChartDocumento15 pagineBioclimatic ChartCarolina MacielNessuna valutazione finora
- User Manual HortiMaX-Go! enDocumento51 pagineUser Manual HortiMaX-Go! enDeguchi ChizuruNessuna valutazione finora
- Compressors, Chillers & Condensers: Part Numbering Guide HermeticDocumento2 pagineCompressors, Chillers & Condensers: Part Numbering Guide HermeticMichael MartinNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 1 Temperature and Thermal Expansion SDocumento2 pagineTutorial 1 Temperature and Thermal Expansion STeh wenjie0% (1)
- General Chemistry 2: Learning Activity Sheet Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsDocumento10 pagineGeneral Chemistry 2: Learning Activity Sheet Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsJenny Rose Butac OcdenNessuna valutazione finora
- Ieee 99-1980Documento11 pagineIeee 99-1980juaninjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Series 500 ValumassDocumento4 pagineSeries 500 ValumassFrancoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mil DTL 12560KDocumento52 pagineMil DTL 12560KGökhan ÇiçekNessuna valutazione finora
- NTC Thermistors: Resistive ProductsDocumento11 pagineNTC Thermistors: Resistive ProductsIlham Adi PanuntunNessuna valutazione finora
- 9-Kinetic Model of MatterDocumento22 pagine9-Kinetic Model of MatterMr. DoctorNessuna valutazione finora
- Loss On Heating of Oil and Asphaltic Compounds: Standard Test Method ForDocumento3 pagineLoss On Heating of Oil and Asphaltic Compounds: Standard Test Method ForRed FolderNessuna valutazione finora
- CBC Monitor For DYMIND-DF50&51&52&53&55&56Documento4 pagineCBC Monitor For DYMIND-DF50&51&52&53&55&56郑伟健Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ducting SystemDocumento56 pagineDucting SystemJohn OstreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Set A: National Entrance Screening Test (Nest - 2013)Documento24 pagineSet A: National Entrance Screening Test (Nest - 2013)Rishi Dey ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- LG Multi V 5 Key Facts for Ultimate Efficiency, Performance and ComfortDocumento81 pagineLG Multi V 5 Key Facts for Ultimate Efficiency, Performance and ComfortFernando CabreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ace Cma Analysis Nesc Rev 2Documento55 pagineAce Cma Analysis Nesc Rev 2gasriosNessuna valutazione finora
- Pd10016 Tetra Therm Lacta 1Documento4 paginePd10016 Tetra Therm Lacta 1Omar ArguelloNessuna valutazione finora
- Kilnloq Gas Analysis System DatasheetDocumento40 pagineKilnloq Gas Analysis System DatasheetFranz Alegria50% (2)
- Physlca ®: Scaling Law For Vortex Dynamics in SuperconductorDocumento5 paginePhyslca ®: Scaling Law For Vortex Dynamics in SuperconductorpietrasekNessuna valutazione finora
- BS en 01062-7-2004 PDFDocumento34 pagineBS en 01062-7-2004 PDFjohn100% (4)
- Piping System DesignDocumento15 paginePiping System DesignsirtaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Laws Test Review GuideDocumento2 pagineGas Laws Test Review GuideERICA BURNSNessuna valutazione finora
- Transmisores de Presion DyniscoDocumento37 pagineTransmisores de Presion DyniscoFrancisco Mones RuizNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat 200 McqsDocumento41 pagineHeat 200 McqsParshantKumarBajaj100% (2)
- Dynafluid (Ficha SXS)Documento4 pagineDynafluid (Ficha SXS)Nz CaNessuna valutazione finora
- Decompression TheoryDocumento182 pagineDecompression TheoryyodamnNessuna valutazione finora
- Determination of Changes in Internal Energy and Enthalpy:: Thermodynamics Session - 7Documento5 pagineDetermination of Changes in Internal Energy and Enthalpy:: Thermodynamics Session - 7mukesh3021Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Comparison Study On Non-Isothermal Decomposition Kinetics of Chitosan With Different Analysis MethodsDocumento15 pagineA Comparison Study On Non-Isothermal Decomposition Kinetics of Chitosan With Different Analysis MethodsElisabeta StamateNessuna valutazione finora
- Phase Changes Independent Practice Spring 2016Documento3 paginePhase Changes Independent Practice Spring 2016Jarrod CollinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Concentration and Temperature on Viscosity of Oat MilkDocumento9 pagineEffect of Concentration and Temperature on Viscosity of Oat MilkZobyNessuna valutazione finora