Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chapter 4
Caricato da
Azmi Bin A MataliTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 4
Caricato da
Azmi Bin A MataliCopyright:
Formati disponibili
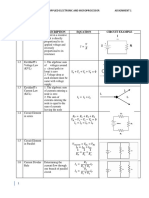
CHAPTER 4: ECONOMICS
Methodology of economics
- Economics is a social science that studies individuals and organizations
engaged in the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and
services.
- Macroeconomics looks at the total output of a nation and the way nation
allocates its limited resources of land, labor and capital in an attempt to
maximize production levels and promote trade and growth for future
generations. -
- When one or more of these variables change, there is a change in demand and
- Microeconomics studies the economic behavior of individual decision makers
therefore a shift of the demand curve.
such as consumers, resource owners, and business firms.
- Economics theories can only describe expected behavior. Monopoly
Law of Demand
- Pure monopoly is the form of market organization in which there is a single
seller of a commodity
- Monopoly may be the result of:
o Increasing returns to scale
Customer side o Control over the supply of raw materials
o Patents
o Government franchise
- These natural monopolies usually operate under a government franchise and
are subject to government regulation.
- - Under pure monopoly, the firm face negatively sloped industry demand curve.
- The relationship between price and quantity demanded is inverse: more units - Example: Astro
are purchased at lower prices because of a substitution effect and an income
effect. Oligopoly
- The demand schedule for an individual specifies the units of a good or service
that the individual is willing and able to purchase at alternative prices during a - Is a market from wherein a market or industry is dominated by a small number
given a period of time. of large sellers
- Only a few firms makes up an industry
Law of Supply - They control over the price
- Product often identical
- Example: Celcom, Digi and Maxis.
Perfect competition
- Many buyers and sellers
Supplier side - Many products similar in nature
- Less barriers to entry a new company
- Price determine by supply and demand
- Example: Giant, Tesco, Carrefour
-
- The supply curve normally has a positive upward slope, indicating that the Gross National Income (GNI) / Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
producer must receive a higher price for increase output due to the principle
of increasing costs. - Gross National Income(GNI)/Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a total value of
- A market supply curve is derived by summing the units each individual goods and services produces added to the value of income received from other
producer is willing to supply at alternative prices. nations.
- It is the total number of payments made to foreign nations id deducted from
Equilibrium price and quantity production and income.
Gross Domestic Output
- Gross domestic product (GDP) measures total output in the domestic
economy,
- Nominal GDP, real GDP, and potential GDP are three different measures of
aggregate output.
- Nominal GDP is the market value of all final goods and services produced in the
domestic economy in a one-year period at current prices.
- - Because nominal GDP values are inflated by prices that increase over time,
- Equilibrium – occurs at intersection point of the market supply and market aggregate output is also measured holding the prices of all goods and services
demand curves. (most efficient) constant over time.
- Surplus – Prices higher than the equilibrium price, quantity demand is less than - Real GDP is the evaluation of GDP at constant prices.
quantity supply. (Excess supply) - Potential GDP is the maximum production that can take place in the domestic
- Shortage – Price lower than equilibrium price, quantity demand exceeds economy without putting upward pressure on the general level of prices.
quantity supply. (supply demand)
Gross National Product (GNP)
Price movements
- Tool used to measure national income
- Caused by only change in price - Total value of goods and services a nation produces over a particular time
period
- Does not include income from foreign sources and does no deduct payments
to foreign sources.
- However, it does allow for depreciation and indirect business taxes such as
sales or property tax.
Tax
- - Contribution levied on persons, property, or business for the support of
- Reduce the price, demand will increase: Jusco sale
government.
Price shifts - Is an amount of money which is taken from your earnings to help towards
some of the cost of services we received in the country
- Ensuring stable growth in revenue to finance the annual budget
- Providing incentives within the tax system to promote growth, especially in the
private sector.
- Type of tax:
Direct tax – income tax, stamp duty and petroleum income tax
Indirect tax – Sale tax, Service Tax and GST
- GST – goods and services tax is a single tax right from the manufacturer to the
consumer.
- Advantages of GST
Help the diversification of income sources for the government
Transparent form of taxation and reduces the number of indirect taxes
incurred.
GST allows business to show the tax applied directly in the sales invoice itself
- Disadvantages of GST
Reduce demand among consumers since price will increases.
It becomes a burden to the public.
Market demand decreasing
Inflation and productivity
- Price inflation – increase of price or it cost
- Money inflation – increase in money supply. The currency is losing its purchase
power and increase in item and service priced.
Business cycles
- A business cycle is a cumulative fluctuation in aggregate output that last for
some time.
- A peak is point which marks the end of economic expansion and the beginning
of a recession.
Productivity
- The amount of acceptable work employees does for each dollar they earn
- The number of acceptable products manufactured with a given amount of
resources.
- Productivity = Output / Input
𝑠𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑖𝑐𝑒 𝑖𝑡𝑒𝑚 𝑥 𝑝𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒
- 𝑀𝑢𝑙𝑡𝑖𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑖𝑡𝑦 =
𝐿𝑎𝑏𝑜𝑟+𝑀𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑙+𝑜𝑣𝑒𝑟ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑
Constraint on productivity
- Management limitations
- Employee attitudes and skills
- Government regulation
- Union rule
Cost of Living
- How to much to pay for housing, gas, food, clothing and other everyday items.
- Cist of living index gives you the percentage difference in the cost of living at
difference location.
- Factors influence cost of living
Rising food prices
Slow wage growth
GST
Types of financing
- Sources of finance
Internal source (within organization)
Owner’s investment (start up or additional capital))
Retained profits
Sale of stock
Sale of fixed assets
Debt collection
External source (outside organization)
o Bank loan or overdraft
o Additional partners
o Share issue
o Leasing
o Hire purchase
o Mortgage
o Trade credit
o Government grants
- Factors affecting choice of source of finance
Purpose
Time period
Amount
Ownership and size of the business
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Assignment 1 CFDDocumento11 pagineAssignment 1 CFDAzmi Bin A MataliNessuna valutazione finora
- Mec532 Logbook v2Documento8 pagineMec532 Logbook v2Fikri RahimNessuna valutazione finora
- FEA and Optimization of Telescopic Boom of Mobiles Hydraulic CraneDocumento6 pagineFEA and Optimization of Telescopic Boom of Mobiles Hydraulic CraneAzmi Bin A MataliNessuna valutazione finora
- Beam and Frame AnalysisDocumento4 pagineBeam and Frame AnalysisAzmi Bin A MataliNessuna valutazione finora
- Sustainability DevelopmentDocumento26 pagineSustainability DevelopmentAzmi Bin A MataliNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1 DRSDocumento18 pagineAssignment 1 DRSAzmi Bin A MataliNessuna valutazione finora
- Spring - Axial Load Only: C AE/L and C EI/L Frame in Global Coordinate K (E/L) X (K) (K)Documento4 pagineSpring - Axial Load Only: C AE/L and C EI/L Frame in Global Coordinate K (E/L) X (K) (K)Azmi Bin A MataliNessuna valutazione finora
- Spring - Axial Load Only: C AE/L and C EI/L Frame in Global Coordinate K (E/L) X (K) (K)Documento4 pagineSpring - Axial Load Only: C AE/L and C EI/L Frame in Global Coordinate K (E/L) X (K) (K)Azmi Bin A MataliNessuna valutazione finora
- Free Download Autodesk AutoCAD Mechanical 2018.1 Full CrackDocumento16 pagineFree Download Autodesk AutoCAD Mechanical 2018.1 Full CrackAzmi Bin A Matali100% (1)
- Root LocusDocumento27 pagineRoot LocusAzmi Bin A MataliNessuna valutazione finora
- Wind Tunnel PDFDocumento7 pagineWind Tunnel PDFAzmi Bin A MataliNessuna valutazione finora
- Wooden Fishing Lure - 8 StepsDocumento8 pagineWooden Fishing Lure - 8 StepsAzmi Bin A MataliNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Compressible FlowDocumento7 pagineFluid Compressible FlowNathan MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Patient Medical RecordsDocumento9 paginePatient Medical RecordsAzmi Bin A MataliNessuna valutazione finora
- Patient Medical RecordsDocumento9 paginePatient Medical RecordsAzmi Bin A MataliNessuna valutazione finora
- Nota KimiaDocumento18 pagineNota KimiaAzmi Bin A Matali100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Limitations of Subscription Services - A Critical ExaminationDocumento2 pagineThe Limitations of Subscription Services - A Critical ExaminationRicardo GulapaNessuna valutazione finora
- BAO6504 Lecture 2, 2014Documento20 pagineBAO6504 Lecture 2, 2014LindaLindyNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Statement Analysis and Security Valuation Solutions Chapter 6Documento6 pagineFinancial Statement Analysis and Security Valuation Solutions Chapter 6Mia Greene100% (1)
- Chettinad Cement Corporation LTD 2008Documento10 pagineChettinad Cement Corporation LTD 2008joosuganya8542Nessuna valutazione finora
- Byzantium CoinsDocumento3 pagineByzantium CoinsbhambyNessuna valutazione finora
- Essay On Market EfficiencyDocumento2 pagineEssay On Market EfficiencyKimkhorn LongNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Are Some Services Better Than OthersDocumento4 pagineWhy Are Some Services Better Than Othersthapar1teenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Profitability Ratios: Return On Asset (ROA)Documento11 pagineProfitability Ratios: Return On Asset (ROA)Saddam Hossain EmonNessuna valutazione finora
- MBA Project On Fundamental and Technical Analysis of Kotak BankDocumento109 pagineMBA Project On Fundamental and Technical Analysis of Kotak BankSneha MaskaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Securities Analysis & Portfolio Management For BSEC Investor EducationDocumento37 pagineSecurities Analysis & Portfolio Management For BSEC Investor EducationHole StudioNessuna valutazione finora
- EBIT/EPS Analysis GraphDocumento4 pagineEBIT/EPS Analysis Graphpranajaya2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Apply Home Loan FormDocumento7 pagineApply Home Loan Formrahulgeo05Nessuna valutazione finora
- 09-EOT Crane Girders 5TDocumento18 pagine09-EOT Crane Girders 5TAdeeb ShahzadaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 Statistical YearbookDocumento125 pagine2016 Statistical YearbooklamillionnaireNessuna valutazione finora
- AbcDocumento11 pagineAbcAchal SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Depreciation Provisions and Reserves Class 11 NotesDocumento48 pagineDepreciation Provisions and Reserves Class 11 Notesjainayan8190Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vincent Mallardi: HOT MARKETS For Print Supply 2014-2020Documento18 pagineVincent Mallardi: HOT MARKETS For Print Supply 2014-2020Vincent MallardiNessuna valutazione finora
- BDO UITFs 2017 PDFDocumento4 pagineBDO UITFs 2017 PDFfheruNessuna valutazione finora
- Narda, Ashlee Kaith Jubasan, Jenyfer Bagsit, Crestina Maguiwe, Jhamaica Nicanor, Diereme Andy 1BSA-1 Om & TQM 1:30PM-4:30PMDocumento16 pagineNarda, Ashlee Kaith Jubasan, Jenyfer Bagsit, Crestina Maguiwe, Jhamaica Nicanor, Diereme Andy 1BSA-1 Om & TQM 1:30PM-4:30PMCrestina Chu BagsitNessuna valutazione finora
- Investing in Perak's Manufacturing SectorDocumento12 pagineInvesting in Perak's Manufacturing SectorPrasath RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Benneton Case StudyDocumento4 pagineBenneton Case StudyAlexandra GoguNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Module 7Documento7 pagineRevision Module 7avineshNessuna valutazione finora
- PBSA Portugal InformationDocumento4 paginePBSA Portugal InformationHua YunNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5Documento13 pagineUnit 5Sharine ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Commercial Vehicles Market Analysis and Segment Forecasts To 2025Documento58 pagineCommercial Vehicles Market Analysis and Segment Forecasts To 2025pinku13Nessuna valutazione finora
- SSB 1995 - Part 1 Overview of Forward Rate Analysis - Understanding The Yield Curve Part 1Documento24 pagineSSB 1995 - Part 1 Overview of Forward Rate Analysis - Understanding The Yield Curve Part 1Arjun PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Apple Case StudyDocumento17 pagineApple Case StudyLeopoldo PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 5 - 1Documento25 pagineCH 5 - 1api-251535767Nessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling Investments - in - TaxEquityPartnerships - Bloomberg Oct 2012Documento7 pagineModeling Investments - in - TaxEquityPartnerships - Bloomberg Oct 2012Gary McKayNessuna valutazione finora
- Achievement Test 4: Chapters 7-8 Managerial AccountingDocumento7 pagineAchievement Test 4: Chapters 7-8 Managerial AccountingLey EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora