Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Unit 3 1 2 A BiologicalEngineeringSolutionsforFoodInsecurity
Caricato da
Paul Dequeña0%(1)Il 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
865 visualizzazioni6 paginea
Titolo originale
Unit 3 1 2 a BiologicalEngineeringSolutionsforFoodInsecurity
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoa
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0%(1)Il 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
865 visualizzazioni6 pagineUnit 3 1 2 A BiologicalEngineeringSolutionsforFoodInsecurity
Caricato da
Paul Dequeñaa
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 6
Activity 3.1.
2 Biological Engineering Solutions
for Food Insecurity
Introduction
In the previous activity, you learned about the contributing factors of food insecurity
and the impact it has in a particular region. You even thought about at least one
possible solution, which may not have involved biological engineering. There are
many solution that may involve other areas of engineering or even other areas of
study, such as civil engineering, politics, and sociology. In this activity you will
investigate some of the current capabilities that biological engineers have to alleviate
food insecurity.
Equipment
Computer with Internet access
Engineering notebook
“Facilitating Conservation Farming Practices and Enhancing Environmental
Sustainability with Agricultural Biotechnology” handout
Procedure
1. Read pages 1–7 and 18–22 of the article “Facilitating Conservation Farming
Practices and Enhancing Environmental Sustainability with Agricultural
Biotechnology.”
o In your engineering notebook, record two insights from this reading that
you found interesting or impactful.
2. Watch the short video under the “Motivation” tab at
http://challengesinverticalfarming.org/ to learn more challenges and
possibilities within the realm of biological engineering. (you may have to use
Internet Explorer or Firefox browser to view)
o In your engineering notebook, record two insights from this video that you
found interesting or impactful.
3. The following graph summarizes the problem that the world faces in terms of
food production for a growing population.
© 2015 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Environmental Sustainability Activity 3.1.2 Biological Engineering Solutions for Food Insecurity– Page 1
a. Explain what happens to the amount of farmland that is available as the
world’s population continues to grow.
b. How can biological engineers help with increasing yields of crops planted
on the land that is already available?
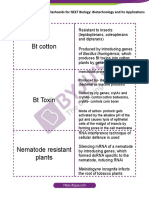
4. Investigate the following biological engineering solutions, each of which involves
genetically modifying organisms. Genetically modified organisms contain foreign
genes that were intentionally inserted to impart certain characteristics. This
should give you a clearer picture of what is possible through the use of genetic
modification as a method for solving various food-related problems. Take notes
on important information from these sources in your engineering notebook. Fill in
the benefits column of the table that follows as you learn what is possible through
genetic modification of organisms.
© 2015 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Environmental Sustainability Activity 3.1.2 Biological Engineering Solutions for Food Insecurity– Page 2
Inserted Gene(s) Protein/Product Positive Effects Negative Information
Organism
Consequences
- Cry1Ab gene Bt Endotoxin http://learner.org/co
Corn,
- Cry1Ac gene urses/biology/textb
cotton
- Cry9A gene ook/gmo/index.html
- Psy (Phytoene Produces phytoene (28 min video)
Rice
synthase) gene which is used to
- Crtl (carotene produce lycopene, Corn 2:00
desaturase) gene which plants then Rice 9:40
synthesize to beta- Goat 21:05
carotene
- Human Antithrombin III Note: The viewer will
Goat find other important
antithrombin gene
information on genetic
inserted in the goat engineering throughout
- Beta casein gene the video.
Anthocyanin gene Anthocyanin http://www.bbc.com
Tomato
from Snap Dragons /news/science-
environment-
25889792
(3 min video)
EPSPS 2 gene from 5- Reading:
Soybeans
bacteria enolpuruvylshikimate- “Facilitating
3-phosphate synthase Conservation…”
enzyme (EPSPS) Pgs 1–7, 18–22
essential for plant
growth
© 2015 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Environmental Sustainability Activity 3.1.2 Biological Engineering Solutions for Food Insecurity– Page 3
Genes to express E-1 endoglucanase Spartan Corn
Corn
cellulase and
hemicellulase
5. For each of the following challenges in growing enough food for our global community, describe two additional innovations
in agriculture that are being used or currently being researched to help solve the food shortage issue.
Innovation(s)
Challenge
Vertical farming (http://youtu.be/2nFQOkzEjxQ)
Space
Vertical farming, GMO—drought resistance
Water: conservation
and pollution
© 2015 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Environmental Sustainability Activity 3.1.2 Biological Engineering Solutions for Food Insecurity– Page 4
Erosion Vertical farming
GMO—pest resistance
Yield
GMO—more protein in carb-rich crops
Nutritional Value
GMO—longer shelf life
Distribution
© 2015 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Environmental Sustainability Activity 3.1.2 Biological Engineering Solutions for Food Insecurity– Page 5
6. After learning from the written and video resources and participating in the class
discussion on biological engineering solutions, you should have a better idea of
how biological engineering can be influential in solving food insecurity problems
around the world. Return to your groups from the last activity and come up with
one plausible solution to the food insecurity problem in your case study from
Activity 3.1.1.
a. Revisit the case study and identify one contributing factor to the problem
of food insecurity that could be solved using biological engineering.
b. Complete the first two steps of the engineering design process—Define
the Problem and Generate Concepts—to propose one solution that could
be further developed. At this time you may or may not know how you
could develop this into a workable solution, and that is alright. There is so
much more to learn in the area of biological and genetic engineering.
c. Document your work and ideas in your engineering notebook throughout
the process.
Conclusion
1. How might biological engineering also involve the integration of other fields of
engineering? Elaborate on at least two examples.
2. Explain at least one challenge you foresee associated with using biological
organisms to solve food insecurity problems.
3. What knowledge and skills might a bioengineer need in order to develop a
genetically modified organism?
© 2015 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Environmental Sustainability Activity 3.1.2 Biological Engineering Solutions for Food Insecurity– Page 6
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Genetically Modified Organisms in Food: Production, Safety, Regulation and Public HealthDa EverandGenetically Modified Organisms in Food: Production, Safety, Regulation and Public HealthValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Biomanufacturing History and PerspectiveDocumento12 pagineBiomanufacturing History and PerspectiveYedhaGuerrero100% (1)
- BIOTECHNOLOGY and Its Applications Class 12Documento4 pagineBIOTECHNOLOGY and Its Applications Class 12Albina Zainab P.TNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocumento8 pagineBiotechnology and Its ApplicationsS SURAJNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2 Genetic Engineering and Recombinant DNADocumento20 pagineLesson 2 Genetic Engineering and Recombinant DNAWynnie TorrecampoNessuna valutazione finora
- 7a - Plants For Food II GM 202122 - SVDocumento35 pagine7a - Plants For Food II GM 202122 - SVlam lamNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Genetic EngineeringDocumento72 pagineDNA Genetic EngineeringEmman Matthew GregorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen - Bio W2-Recombinant DnaDocumento6 pagineGen - Bio W2-Recombinant DnaLielanie NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- Biopharming: Program Studifarmasi UniversitasmataramDocumento23 pagineBiopharming: Program Studifarmasi UniversitasmataramRusmin AdhityaNessuna valutazione finora
- General Bio HandoutDocumento4 pagineGeneral Bio HandoutJamilah BaruangNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 12 Biology - Biotechnology and Its Applications AssignmentDocumento8 pagineCBSE Class 12 Biology - Biotechnology and Its Applications AssignmentSuresh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- GE 5 Module Week 8 9Documento33 pagineGE 5 Module Week 8 9Aldiano C. AldrenNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Recombinant-DNA TechnologyDocumento3 pagineApplication of Recombinant-DNA TechnologyCương Nông VănNessuna valutazione finora
- Pedoman Visite Untuk ApotekerDocumento30 paginePedoman Visite Untuk ApotekerMeliana LiuNessuna valutazione finora
- TM-08 Genetically Modified Organisms (2016)Documento33 pagineTM-08 Genetically Modified Organisms (2016)ZANUBA ULYA’ HAURA CELLIN 1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Biology ImpQ CH12 Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocumento8 pagine12 Biology ImpQ CH12 Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsSaiAbhijith100% (1)
- Genetic EngineeringDocumento30 pagineGenetic EngineeringDustin RojasNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Biotechnology in Different Field: By-Vinod KumarDocumento33 pagineApplication of Biotechnology in Different Field: By-Vinod KumarElvira Sta. MariaNessuna valutazione finora
- 160 PresentationDocumento46 pagine160 PresentationRuben MarquezNessuna valutazione finora
- 24 Updated BiotechnologyModuleDocumento15 pagine24 Updated BiotechnologyModulespeedrunner12256Nessuna valutazione finora
- NSSBIO3E SB4 Ch27 eDocumento40 pagineNSSBIO3E SB4 Ch27 eBernardNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications of Biotechnology (L1)Documento67 pagineApplications of Biotechnology (L1)Saksham MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- Exploitation of Ant TechniquesDocumento12 pagineExploitation of Ant TechniquessudinNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotechnology: and Its ApplicationDocumento19 pagineBiotechnology: and Its ApplicationRanjeet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture No: 26 Biotechnological Approaches in Pest ManagementDocumento6 pagineLecture No: 26 Biotechnological Approaches in Pest ManagementPratibha ChNessuna valutazione finora
- MicrobesDocumento8 pagineMicrobesKipkorir David LangatNessuna valutazione finora
- Producing Natural Smart Biopharmaceuticals From The Microalgae Living in The Dead Sea Utilizingphototube BioreactorDocumento9 pagineProducing Natural Smart Biopharmaceuticals From The Microalgae Living in The Dead Sea Utilizingphototube BioreactorEyad Al-KhraisatNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant As BioreactorDocumento46 paginePlant As BioreactorKelvin Khoa100% (1)
- Content Standard: Module 1: BiotechnologyDocumento8 pagineContent Standard: Module 1: BiotechnologyKRISHA CALAMBONessuna valutazione finora
- BIO-Chapter 20. BiotechDocumento27 pagineBIO-Chapter 20. Biotechkathleen hoNessuna valutazione finora
- XII-12-Biotechnology and Its ApplicationDocumento33 pagineXII-12-Biotechnology and Its Applicationmy yoNessuna valutazione finora
- Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology: Bacillus Pseudomycoides Strain MA02 Isolated From Poultry SlaughterDocumento7 pagineBiocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology: Bacillus Pseudomycoides Strain MA02 Isolated From Poultry SlaughterSathyabama University BiotechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotechnology and Its Applications PDFDocumento4 pagineBiotechnology and Its Applications PDFDeepikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Golden Yeast Student Instructions 1Documento14 pagineEngineering Golden Yeast Student Instructions 1api-272992171Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biotechnology ApplicationDocumento5 pagineBiotechnology ApplicationSabith tvNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity GMODocumento6 pagineActivity GMOJireh Mae JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of DNA Recombinant TechnologyDocumento27 pagineApplication of DNA Recombinant TechnologyisnahNessuna valutazione finora
- MICROBES IN GENETIC ENGINEERING SeminarDocumento19 pagineMICROBES IN GENETIC ENGINEERING SeminarPooja P. RajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sitanggang 2021Documento10 pagineSitanggang 2021Edwin HadrianNessuna valutazione finora
- Improved Erythromycin Production in A GeneticallyDocumento7 pagineImproved Erythromycin Production in A GeneticallyluisNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering Summary PPT Igcse CaieDocumento16 pagineBiotechnology and Genetic Engineering Summary PPT Igcse Caiearyan patelNessuna valutazione finora
- Module I - GeneticsDocumento20 pagineModule I - GeneticsJhay Luiz Cajigal ArquinesNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Biotech Tutorial-Oct30-Nov06 AlsoDocumento2 paginePlant Biotech Tutorial-Oct30-Nov06 Alsorgcgzjj2sdNessuna valutazione finora
- BiotechnologyDocumento81 pagineBiotechnologyYvonne Dulay BarrozoNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 Lesson 11Documento6 pagineModule 5 Lesson 11John eric CatayongNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotechnology Applications PyqsDocumento5 pagineBiotechnology Applications PyqsChethu ChethuNessuna valutazione finora
- 12th Chap 12 BoardDocumento3 pagine12th Chap 12 BoardVraj PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Transgenic Animals: Walking BioreactorsDocumento8 pagineTransgenic Animals: Walking BioreactorsEvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 1o, Unit 1 &2Documento30 pagineBio 1o, Unit 1 &2Ggvsrt FgjkjbNessuna valutazione finora
- Expression of Gene From A Novel Strain SY49-1 Active On Pest InsectsDocumento6 pagineExpression of Gene From A Novel Strain SY49-1 Active On Pest InsectsYounglife UGNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Engineering Part 3 and 4Documento42 pagineGenetic Engineering Part 3 and 4KSHITIJ K GAUTAMNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Recombinant DNA Technology Agricultural BiotechnologyDocumento27 pagineApplication of Recombinant DNA Technology Agricultural BiotechnologyAnastacio Elston EusoresNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotech ResearchDocumento7 pagineBiotech Researchthekingraja2602Nessuna valutazione finora
- 9-10 Genetically Modified Organisms and NanotechnologyDocumento5 pagine9-10 Genetically Modified Organisms and NanotechnologyBryan Andrei CanlasNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Human Gut Models Reveal The Distinct Fermentation Patterns of Arabinoxylan Versus Inulin Pieter Van Den Abbeele 2013Documento9 pagineDifferent Human Gut Models Reveal The Distinct Fermentation Patterns of Arabinoxylan Versus Inulin Pieter Van Den Abbeele 2013Mamen Casado MuñozNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotechnology and Its Applications NotesDocumento45 pagineBiotechnology and Its Applications NotesNarasimha Pavan BNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Engineering and Recombinant Dna: Lesson 1Documento5 pagineGenetic Engineering and Recombinant Dna: Lesson 1Dexie MusaNessuna valutazione finora
- © Ncert Not To Be Published: Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocumento10 pagine© Ncert Not To Be Published: Biotechnology and Its Applicationsaayushi24681438Nessuna valutazione finora
- QB Update E3 ch02 eDocumento4 pagineQB Update E3 ch02 eK CNessuna valutazione finora
- Disorders of The Nervous System2Documento20 pagineDisorders of The Nervous System2Ian Rizavi Villamor AntopinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Edwards Lifescience Vigileo CatalogoDocumento40 pagineEdwards Lifescience Vigileo CatalogoDeni Leonardo TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.8 Annex 4 - BOPIS DCF FORM 2-DDocumento2 pagine1.8 Annex 4 - BOPIS DCF FORM 2-DAida TagaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Ges New Jhs Syllabus Career Technology CCP Curriculum For b7 b10 Draft ZeroDocumento367 pagineGes New Jhs Syllabus Career Technology CCP Curriculum For b7 b10 Draft ZeroElvis Adjei Yamoah100% (1)
- Neil HillDocumento32 pagineNeil HillAndrés Felipe100% (1)
- Hawaii DOH: Embry Health Cease & Desist LetterDocumento5 pagineHawaii DOH: Embry Health Cease & Desist LetterHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Ader 1985Documento48 pagineAder 1985Renata MNessuna valutazione finora
- Ardyss Product CatalogDocumento32 pagineArdyss Product CatalogrolandakjonesNessuna valutazione finora
- COVID-19 Crisis Times and Graduate Students Attitude Towards Online Education The Case of A Cameroon UniversityDocumento6 pagineCOVID-19 Crisis Times and Graduate Students Attitude Towards Online Education The Case of A Cameroon UniversityInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- OptraSculpt Pad PDFDocumento2 pagineOptraSculpt Pad PDFSharmaine JucoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental Illness - DDTDocumento39 pagineMental Illness - DDTThato MathogojaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Stok 16 Juni 2023Documento62 pagineStok 16 Juni 2023Icha FransiscaNessuna valutazione finora
- DST Final Exam NotesDocumento56 pagineDST Final Exam NoteslmaoheartsNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychology Class 12 Chapter 2 Notes PDFDocumento12 paginePsychology Class 12 Chapter 2 Notes PDFhbaki0296Nessuna valutazione finora
- COWELL Implant Solution v28Documento146 pagineCOWELL Implant Solution v28Julian MachoNessuna valutazione finora
- A Testing Battery For The Assessment ofDocumento11 pagineA Testing Battery For The Assessment ofbrownsj1983Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anti Abortion EssayDocumento2 pagineAnti Abortion EssayMalika SadridinovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 3 Assignment: Lab: Due Sunday by 11:59pmDocumento7 pagineWeek 3 Assignment: Lab: Due Sunday by 11:59pmEssay NationNessuna valutazione finora
- Herbal Drugs For Thyroid - PDF: International Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences May 2016Documento10 pagineHerbal Drugs For Thyroid - PDF: International Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences May 2016Sanju TkNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Article: ISSN: 0975-833XDocumento5 pagineResearch Article: ISSN: 0975-833XSoumya prakash HotaNessuna valutazione finora
- BS320 - Assignment1-Malcolm TumanaDocumento3 pagineBS320 - Assignment1-Malcolm TumanaMal-Vii Dtmv TiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Committee 2020, Reporter, May Edition 2020, April 24, 2020Documento32 pagineCommittee 2020, Reporter, May Edition 2020, April 24, 2020ucopresident_2130533Nessuna valutazione finora
- Self-Affirmation Theory and The Science of Well-Being PDFDocumento19 pagineSelf-Affirmation Theory and The Science of Well-Being PDFAlex RichieNessuna valutazione finora
- Jadwal AntigenDocumento8 pagineJadwal AntigenBODACA HARI MURTINessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Ethical Choices in BusinessDocumento34 pagine4 Ethical Choices in BusinessE-ሽገር Online bussinessNessuna valutazione finora
- Update CV Hse Engineer SlimaniDocumento3 pagineUpdate CV Hse Engineer SlimanialiouecheNessuna valutazione finora
- Counseling - Its Principles, MethodsDocumento36 pagineCounseling - Its Principles, MethodsCarmz PeraltaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre - Registration Log BookDocumento14 paginePre - Registration Log BooksimbaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Woman's BodyDocumento4 pagineWoman's BodycnNessuna valutazione finora
- The Mediating Role of Emotional Intelligence in The Employees PerformanceDocumento11 pagineThe Mediating Role of Emotional Intelligence in The Employees PerformanceMårkö ÅlexövåNessuna valutazione finora