Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Bonding and Structure
Caricato da
rwongvipasDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bonding and Structure
Caricato da
rwongvipasCopyright:
Formati disponibili
4.
Bonding and Structure
Monday, February 6, 2017 9:48 AM
Overview of bonding
1. Elements , compound and Mixtures
a. Elements : contains only one type of atoms เช่น element of carbon contains only carbon atom.
b. Compound : contains more than one type of atoms, hold together with chemical bond , the same ratio, and cannot
separate them by physical means. (หยิบออก) เช่น CO2
c. Mixture : can contain any number of different substance (atom ก็ได ้ compound ก็ได ้, any ratio, Can sepate
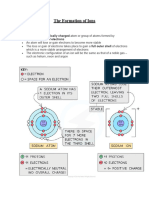
Atom and Ion ต่างกันอย่างไร
a. Atom : number of proton = number of electron , no charge เช่น Sodium atom (Na) มี proton = 11, electron = 11 , no
charge
b. Ion : atom or group of atom , can positive or negative charge because gian/loss electron เช่น Sodium ion (Na) มี
proton = 11, electron = 11, loss electron = 1 ดังนัน proton = 11, eletron = 10 --> Positive ion (cation) --> Na+ ส่วน
ใหญ่เกิดกับ Metal ยกเว ้น H เป็ น non-metal แต่ เป็ น Positive ion
เช่น cholide ion (Cl) มี proton = 17, electron = 17 (2,8,7) ดังนัน gain electron มา 1 เพือเติมให ้ stable ->
Negative ion(anion) -> Cl-
ส่วนใหญ่เกิดกับ Non-Metal
*** ถ ้าเปลียน proton -> new element , ถ ้าเปลียน eletron -> gain/loss
3. metal : properties -> conduct electricity and heat, maileable(, high melting point (solid at room temperature, positive ion ,
react with oxygen -> basic oxide (ละลายนํ าแล ้วได ้ PH>7)
non-metal :
exceptions: Mercury is metal but liquid at room temperature
sodium กับ potassium, have low density and low boiling point
diamond and graphite -> graphite is non-metal but good conductor of electricity, diamond is non-metal high
melting point , hardest เพราะ มี special structure
Metal and Alloy
1. Metals are elements , so they contain only one type of atom.
2. Alloy are mixture , at least one substance (can be metal or non-metal) is added to metal เช่น gold ทีขาย 97.5 % ถือเป็ น
alloy เพราะเติม silver ลงไป
Overview of bonding
1. Bonding is about how atoms are join together เพือ stable (atom <-> atom)
2. Structure is about how the boned atom are arrangement.
3. Bonding มี 3 Types
a. Covalent : electrons are share between atom. สําหรับพวก non-metal atom of same element or difference element
(give compound) , bond created by share electron.
b. Ionic : electron transfer from one atom to another for form ions. Metal bond with non-metal to give conpound. Metal
loss electron, non-metal gain electron then no charge. Bond created by opposite ions charge. + กับ -
c. Metallic : lattice of positive ion in a sea of electron , only metal atom -> same atom หรือ different element (Alloy)
b.กับ c. เป็ น electrostatic force
Why do atom bond ?
Atom bond to other atoms in order to gain the same arrangement of outer-shell electron as a noble gas atom.
Because this is a stable arrangement. เช่น He , Neon, Argon ทีมี outer-shell electrons = 8 ยกเว ้น He มี 2
1. When element in solid state , structure that regular arrangement, called lattice
2. Structure (molecule) แบ่งเป็ น simple molecular และ Giant
a. Simple molecular เจอใน covalent compound เท่านัน
- The lattice is built up of million of separate small molecules
- ตัวอย่าง iodine (I2), the lattice is made up of 2 molecule , each contain 2 atom
- Structure hold together with strong covalent bond but weak inter molecular force
- Result: solid has a low melting point, does not take much heat energy to break up lattice to form liquid.
b. Giant
- The lattice is built up from positive and negative joined by ionic bond หรือ metal ion joined by metalic bond หรือ
non-metalic atom joined by covalent bond (diamonกับgraphite)
- structure hold together with strong network bond
- solid high melting point , take great energy to break down lattice to form liquid.
Ionic bonding
4. Bonding and Structure Page 1
Ionic bonding
Cations and Anions. Ionic bonds involve a cation and an anion. The bond is formed when an atom, typically a metal, loses an
electron or electrons, and becomes a positive ion, or cation. Another atom, typically a non-metal, is able to acquire the
electron(s) to become a negative ion, or anion.
Ionic property : นึกถึง salt
Ionic bonding
- Metal atom bond with non-metal atom
- Electron transfer from Metal atom to non-metal atom
- The ions are stable because they have electron arrangement same as noble gas atom
- Join with electrostatic force หรือ Opposite charge attract together
Example -> Sodium (2,8,1) chloride (2,8,7)
- structure ของ sodium chloride จะอIonic compound จะอยูเ่ ป็ น latice structure , High melting and high boiling point
Ionic property : นึกถึง salt ถ ้าเอาไป heat ต ้องเกิน 100 ถึงจะ melt , high melting and boiling , bond are strong, conduct electrivity ได ้
เมือ ion มัน move ได ้ ดังนันต ้องเอาไป disolve in water เพือให ้ ion move
4. Bonding and Structure Page 2
Covelent bonding
- formed between same non-metal atom (element) หรือ different non-metal atom (compound)
- electrons are share between atom
- The ions are stable because they have electron arrangement same as noble gas atom
- boned atom formed a unit called "molecule" (group of boned atom)
Molecular element
- element คือ one type of atom เป็ น atom ของ non-metal เพือ form เป็ น Molecule
เช่น Hydrogen
Covalent bond is the attraction between the positive nuclei and negative share of electrons.
Molecular compound
4. Bonding and Structure Page 3
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- An Introduction to Physics (Material Science Metallurgy)Da EverandAn Introduction to Physics (Material Science Metallurgy)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bonding and StructureDocumento9 pagineBonding and StructureRija MughalNessuna valutazione finora
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDa EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Ions and Ionic BondDocumento21 pagineIons and Ionic Bondchickuwa pawawawaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionic and Covalent BondingDocumento39 pagineIonic and Covalent Bondingchickuwa pawawawaNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Chemistry - UNIT 4 - COMPOUNDSDocumento7 pagineIGCSE Chemistry - UNIT 4 - COMPOUNDSRaffaella LaxaldeNessuna valutazione finora
- F.3 Chemistry Ch.7 and Ch.8 NotesDocumento2 pagineF.3 Chemistry Ch.7 and Ch.8 Notesdislikeedison2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESODocumento6 pagineChemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESOurgazuNessuna valutazione finora
- Elements, Compounds and AtomsDocumento12 pagineElements, Compounds and Atomsananya.arumugarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bonding and Naming CompoundsDocumento10 pagineBonding and Naming CompoundsDaniel BerryNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Revision Notes-LibreDocumento17 pagineChemistry Revision Notes-LibreShridhar MathadNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry-Ch 3 - Chemical BondingDocumento8 pagineChemistry-Ch 3 - Chemical BondingHassan RiazNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsDocumento7 pagineIGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsdanielmahsaNessuna valutazione finora
- C2 Knowledge PowerpointsDocumento33 pagineC2 Knowledge PowerpointsMrs S BakerNessuna valutazione finora
- ScienceDocumento10 pagineScienceMazze Ashley SenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atoms CombiningDocumento12 pagineAtoms Combiningshehryar khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 1Documento11 paginePresentation 1Deadpool 426Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ch3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Documento11 pagineCh3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Amal HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- O Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical BondingDocumento16 pagineO Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical Bondingjave_yeongNessuna valutazione finora
- SCIENCEDocumento10 pagineSCIENCEMazze Ashley SenaNessuna valutazione finora
- BondsDocumento24 pagineBondsPavithran Kamaleswari Year 10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Definitions - Topic 3 Atoms Elements and Compounds - CAIE Chemistry IGCSEDocumento2 pagineDefinitions - Topic 3 Atoms Elements and Compounds - CAIE Chemistry IGCSEAtif BakhshNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1,2, and 3 - Atoms, Elements and CompoundsDocumento19 pagineUnit 1,2, and 3 - Atoms, Elements and CompoundsAbdelrahman GhanimNessuna valutazione finora
- Csec Chemistry Chapter 5 - Structures and BondingDocumento18 pagineCsec Chemistry Chapter 5 - Structures and Bondingchelsea AlexandriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ib CHEM Topic 4 Chemical BondingDocumento45 pagineIb CHEM Topic 4 Chemical Bondingyasser khairyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionic BondingDocumento23 pagineIonic BondingMark DichosonNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 3, ChemDocumento6 pagineCH 3, ChemAbdullah SalmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fbise Chapter 4 (I)Documento7 pagineFbise Chapter 4 (I)Zarish ZubairNessuna valutazione finora
- Science ReviewerDocumento4 pagineScience ReviewerLara RebaterNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Lewis Dot Structure and Types of BondDocumento71 pagine4 Lewis Dot Structure and Types of BondEren Micaella100% (1)
- BondingDocumento1 paginaBondingJhanelle S. Dixon-LairdNessuna valutazione finora
- BondingDocumento5 pagineBondinggkawsar22Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To BondingDocumento9 pagineIntroduction To BondingTheonie DavisNessuna valutazione finora
- BondingDocumento33 pagineBondingNathaniel WhyteNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionic BondingDocumento12 pagineIonic Bondingerum khanNessuna valutazione finora
- CH No 3Documento22 pagineCH No 3Ultimate chemistryNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 4 Chemistry Chapter 5Documento37 pagineForm 4 Chemistry Chapter 5SF CHENGNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionic Bonding 3A1 NotesDocumento9 pagineIonic Bonding 3A1 NotesmunasheNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5: Chemical Bond Stability of Noble GasesDocumento20 pagineChapter 5: Chemical Bond Stability of Noble GasesLuna LatisyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.1 7.2Documento2 pagine7.1 7.2noora.rami48Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry - Chapter 7 Study GuideDocumento2 pagineChemistry - Chapter 7 Study GuideJohnHana100% (1)
- Chemical BondingDocumento6 pagineChemical Bondingchong56100% (1)
- Form 2 8 Ionic BondingDocumento64 pagineForm 2 8 Ionic BondingOsmany Madrigal100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - Chemical BondingDocumento6 pagineChapter 5 - Chemical BondingSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionic Bonding Sem II G.E. and D.S.C.Documento34 pagineIonic Bonding Sem II G.E. and D.S.C.allenbrien077Nessuna valutazione finora
- Structure and Bonding: Bonding: The Structure of MatterDocumento8 pagineStructure and Bonding: Bonding: The Structure of MatterAngeline NgouNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Revision BondingDocumento7 pagineChem Revision BondingDaniel AntonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bonding Chemistry 1C Engr. Albert S. Revilla InstructorDocumento3 pagineChemical Bonding Chemistry 1C Engr. Albert S. Revilla Instructorgeng gengNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Chemical BondingDocumento16 pagineNotes Chemical BondingRammohan Balaji PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Privacy Statement Site Map Contact Us: GcseDocumento8 paginePrivacy Statement Site Map Contact Us: GcsetashaNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes W4Documento5 pagineNotes W4sy.valNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure & Bonding PosterDocumento1 paginaStructure & Bonding Posterchemyst3167Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bonding Notes 2Documento32 pagineChemical Bonding Notes 2arun iyer BitcoinminerandmathematicianNessuna valutazione finora
- Atoms, Elements and CompoundsDocumento3 pagineAtoms, Elements and CompoundsA wierd person on the internetNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Chemical BondingDocumento5 pagineIntroduction To Chemical BondingMini PGNessuna valutazione finora
- CH No 3Documento22 pagineCH No 3Ultimate chemistryNessuna valutazione finora
- Electron Dot Diagrams / Lewis Structures: Atom and Covalent Compound DiagrammingDocumento50 pagineElectron Dot Diagrams / Lewis Structures: Atom and Covalent Compound DiagrammingJoan Clarice CorlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure and BondingDocumento12 pagineStructure and BondingNisha JodhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionic Bonding - Compounds and PropertiesDocumento21 pagineIonic Bonding - Compounds and PropertiesJawaid IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Food Safety Plan of Catalonia: GuidelinesDocumento38 pagineFood Safety Plan of Catalonia: GuidelinesralapubsNessuna valutazione finora
- A Clinico-Microbiological Study of Diabetic Foot Ulcers in An Indian Tertiary Care HospitalDocumento6 pagineA Clinico-Microbiological Study of Diabetic Foot Ulcers in An Indian Tertiary Care HospitalJoko Cahyo BaskoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Sand Casting Lit ReDocumento77 pagineSand Casting Lit ReIxora MyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cinderella: From The Blue Fairy Book of Andrew LangDocumento7 pagineCinderella: From The Blue Fairy Book of Andrew LangnizamianNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 Lesson 1 Activity and Analysis: Special Needs EducationDocumento2 pagineModule 1 Lesson 1 Activity and Analysis: Special Needs EducationShalyn ArimaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Noli Me Tangere CharactersDocumento4 pagineNoli Me Tangere CharactersDiemNessuna valutazione finora
- Muslimah's Handbook of PurityDocumento60 pagineMuslimah's Handbook of PurityMuadh KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- POWEV2434234Documento461 paginePOWEV2434234John M. HemsworthNessuna valutazione finora
- The First Converts in Chin Hills - Ni Kong HongDocumento7 pagineThe First Converts in Chin Hills - Ni Kong HongLTTuangNessuna valutazione finora
- Amnesty - Protest SongsDocumento14 pagineAmnesty - Protest Songsimusician2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Filters SlideDocumento17 pagineFilters SlideEmmanuel OkoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Level - 1: Expansion of DeterminantsDocumento13 pagineLevel - 1: Expansion of DeterminantsAtomitronNessuna valutazione finora
- Leadership PaperDocumento6 pagineLeadership PaperSTANCIU VALENTINNessuna valutazione finora
- 9300 Servo Inverter TRDocumento10 pagine9300 Servo Inverter TRIhsan CanakogluNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Financial Management: Topic 1Documento85 pagineIntroduction To Financial Management: Topic 1靳雪娇Nessuna valutazione finora
- Credit Transactions Case Digestpdf PDFDocumento241 pagineCredit Transactions Case Digestpdf PDFLexa L. DotyalNessuna valutazione finora
- The Scopes TrialDocumento10 pagineThe Scopes Trialapi-607238202Nessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical Analysis: Prof. Dr. Süheyla ÇEHRELİDocumento15 pagineNumerical Analysis: Prof. Dr. Süheyla ÇEHRELİEzgi GeyikNessuna valutazione finora
- Cranial Deformity in The Pueblo AreaDocumento3 pagineCranial Deformity in The Pueblo AreaSlavica JovanovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Technique in The Audiologic Evaluation of Infants: Todd B. Sauter, M.A., CCC-ADocumento35 pagineCurrent Technique in The Audiologic Evaluation of Infants: Todd B. Sauter, M.A., CCC-AGoesti YudistiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Education: Learning Activity SheetDocumento13 paginePhysical Education: Learning Activity SheetRhea Jane B. CatalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hosea - A New Translation With Introduction and Commentary (Anchor Bible 24)Documento727 pagineHosea - A New Translation With Introduction and Commentary (Anchor Bible 24)Azoth ImóveisNessuna valutazione finora
- Thompson VarelaDocumento18 pagineThompson VarelaGiannis NinosNessuna valutazione finora
- Mcqmate Com Topic 333 Fundamentals of Ethics Set 1Documento34 pagineMcqmate Com Topic 333 Fundamentals of Ethics Set 1Veena DeviNessuna valutazione finora
- Past Simple (Regular/Irregular Verbs)Documento8 paginePast Simple (Regular/Irregular Verbs)Pavle PopovicNessuna valutazione finora
- (2016) The Role of Requirements in The Success or Failure of Software Projects-DikonversiDocumento11 pagine(2016) The Role of Requirements in The Success or Failure of Software Projects-DikonversiFajar HatmalNessuna valutazione finora
- 2007 - Q1 NewsletterDocumento20 pagine2007 - Q1 NewsletterKisara YatiyawelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kalki ProjectDocumento3 pagineKalki ProjectMandar SohoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Astro ExamDocumento7 pagineAstro ExamRitu DuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Notification On Deemed Examination Result NoticeDocumento2 pagineNotification On Deemed Examination Result Noticesteelage11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityDa EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideDa EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDa EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDa EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (137)
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideDa EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdaleNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDa EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeDa EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNessuna valutazione finora
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingDa EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDa EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (14)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeDa EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideDa EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 2: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDa EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 2: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactNessuna valutazione finora
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsDa EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsDa EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodDa EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (20)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (90)