Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Tutorial - Chapter 5 - Perfect Competition - Questions
Caricato da
NandiieTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Tutorial - Chapter 5 - Perfect Competition - Questions
Caricato da
NandiieCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Managerial Economics – Tutorial – Perfect Competition
Hint: Tutorial questions are comprehensive. However, the respective lecturers should utilize
the questions based on the depth of the knowledge acquisition by students.
Essay Questions
1. If a firm operates at a loss, the loss is equal to TC - TR. If the firm shuts down instead, its loss
is equal to FC. Given this, show that price must exceed AVC for the firm to operate at a loss and
not shut down.
2. Firms in the sandbox industry have the long-run cost curve
C(q) = F + 6q + 5q2
Where F is a positive constant. The sandbox industry has a market demand of p = 90 - 2q
a. Suppose F=20. What is the competitive equilibrium price, quantity and number of firms?
b. Suppose F is actually an accreditation fee established by the sandbox sellers association. A
firm that avoids this fee will not be able to operate in the industry, and is therefore mandatory.
How does the equilibrium price and number of firms vary with F? You do not have to use calculus,
but explain whether each increases or decreases with F. How does the profit of each firm vary with
F?
3. Suppose market demand is Q = 1000 - 4p. If all firms have LRAC = 50 - 5q + q2, how many
identical firms will there be when this industry is in long-run equilibrium?
4. Explain why individual firms in competitive markets face more elastic demand curves than the
market as a whole.
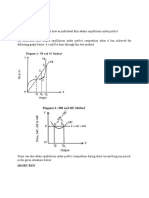
5. The above figure shows the cost curves for a typical firm in a competitive market. From the
graph, estimate the firm's profits when price equals $10 per unit.
6. The above figure shows the cost curves for a typical firm in a competitive market. If there are
200 identical firms, estimate the market quantity supplied when p = 4, 8, and 10.
7. Consider a competitive firm with the short-run cost function
C(q) = 20 + 6q + 5q2
The firm faces a market price of p for its output.
a. Derive the firm's profit maximizing condition. Is the sufficient second order condition
satisfied?
b. Suppose a specific tax of t (t < p) is levied on only this firm in the industry. What is the profit
maximizing level of output as a function of p and t? (Assume the price is high enough that the
firm does not shut down)
c. How does the output change as the tax increases? Use calculus to determine the relevant
comparative static.
d. How does the firm's profit chance as the tax increases? Again, use calculus to determine the
relevant comparative static. Show that profit decreases as t increases.
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Suppose TC = 10 + (0.1 ∗ q2). If there are 100 identical firms in the market, the market
supply
curve is
A) Q = 1000 ∗ p.
B) Q = 500 ∗ p.
C) Q = 100 ∗ p.
D) Q = 10.
2. The above figure shows the cost curves for a typical firm in a market and three possible
market supply curves. If there are 100 identical firms, the market supply curve is best
represented by
A) curve A.
B) curve B.
C) curve C.
D) either curve A or B, but definitely not C
3. A horizontal demand curve for a firm implies that
A) the firm is a monopoly.
B) the market the firm is operating in is not competitive.
C) the firm is selling in a competitive market.
D) the products of that firm are very different from other firms' products.
4. A small business owner earns $50,000 in revenue annually. The explicit annual costs equal
$30,000. The owner could work for someone else and earn $25,000 annually. The owner's
business profit is ________ and the economic profit is ________.
A) $20,000, $5,000
B) $20,000, -$5,000
C) $25,000, -$5,000
D) $45,000, -$5,000
5. The above figure shows the cost curves for a competitive firm. If the firm is to earn economic
profit, price must exceed
A) $0.
B) $5.
C) $10.
D) $11.
6. The above figure shows the cost curves for a competitive firm. The firm will incur economic
losses if the price is less than
A) $0.
B) $5.
C) $10.
D) $11.
7. The above figure shows the cost curves for a competitive firm. If the market price is $15 per
unit, the firm will earn profits of
A) $0.
B) $4.
C) $40.
D) $160.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Model Answer of Assignment 2 DR ShantalDocumento5 pagineModel Answer of Assignment 2 DR ShantalBishoy EmileNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions That Do Not Need A CalculatorDocumento14 pagineQuestions That Do Not Need A Calculatorkidest mesfinNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2 DR ShantalDocumento4 pagineAssignment 2 DR ShantalBishoy EmileNessuna valutazione finora
- ME Problems PC MonopolyDocumento7 pagineME Problems PC MonopolyDevan BhallaNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Dar Es Salaam Business School perfectly competitive market revision questionsDocumento6 pagineUniversity of Dar Es Salaam Business School perfectly competitive market revision questionsPETRONessuna valutazione finora
- Perfect Competition Practice Questions and AnswersDocumento4 paginePerfect Competition Practice Questions and Answersalex-bookNessuna valutazione finora
- Eco101a Tutorial Problem Set 06 Summer Term 2018 (16079)Documento4 pagineEco101a Tutorial Problem Set 06 Summer Term 2018 (16079)Mukul Chandra0% (1)
- Review QuestionsDocumento5 pagineReview QuestionsNahid IbrahimzadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics Chapter 7Documento10 pagineMicroeconomics Chapter 7Pearl LawrenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework Accounting 2-Chapter-6Documento9 pagineHomework Accounting 2-Chapter-6Nguyen HuongNessuna valutazione finora
- ECO101A Intro Economics Assignment 6 Key QuestionsDocumento2 pagineECO101A Intro Economics Assignment 6 Key QuestionsPratik RajNessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento9 pagine1MANISH ANAND1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice MCQ (CH 6 To CH 9)Documento7 paginePractice MCQ (CH 6 To CH 9)rhlvajpayeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 1 BDocumento8 pagineQuiz 1 BTahseenNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers To Summer 2010 Perfect Competition QuestionsDocumento7 pagineAnswers To Summer 2010 Perfect Competition QuestionsNikhil Darak100% (1)
- ECON 315 Practice For FinalDocumento9 pagineECON 315 Practice For Finaldimitra triantos0% (1)
- CH 9Documento9 pagineCH 9ceoji100% (1)
- MCQ Questions Related 2 Perfect Competitive MarketDocumento12 pagineMCQ Questions Related 2 Perfect Competitive Marketchittran313Nessuna valutazione finora
- MICRO Economics Group AssignmentDocumento4 pagineMICRO Economics Group Assignmentbeth elNessuna valutazione finora
- EC3099 - Industrial Economics - 2007 Exam - Zone-ADocumento4 pagineEC3099 - Industrial Economics - 2007 Exam - Zone-AAishwarya PotdarNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam 3 Study Guide: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocumento31 pagineExam 3 Study Guide: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Questionluka0309Nessuna valutazione finora
- Perfect Competition MC Practice With AnswersDocumento8 paginePerfect Competition MC Practice With AnswersMaría José AmezquitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ghadsway's Eco301 Question BNKDocumento18 pagineGhadsway's Eco301 Question BNKwww.desmondopoku615Nessuna valutazione finora
- MicroEconomics Practice TestDocumento7 pagineMicroEconomics Practice TestDavid BurfordNessuna valutazione finora
- 621904314547 (2)Documento6 pagine621904314547 (2)Furkan NazırNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of Chapter 11Documento8 pagineReview of Chapter 11visha183240Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 1 ADocumento7 pagineQuiz 1 ATahseenNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice: + 10Q and FC ($) 200, Where Q Is inDocumento2 paginePractice: + 10Q and FC ($) 200, Where Q Is insơn trầnNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 2Documento5 pagineQuiz 2Yazmine Aliyah A. CaoileNessuna valutazione finora
- ME - Problem Set 5Documento4 pagineME - Problem Set 5AbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Assgnmt 5Documento4 pagineAssgnmt 5Heap Ke XinNessuna valutazione finora
- EconomicsDocumento37 pagineEconomicsegy1971Nessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics Test 2Documento26 pagineMicroeconomics Test 2a24dk100% (4)
- Final Exam 4Documento4 pagineFinal Exam 4HealthyYOU100% (1)
- Monopolistically Competitive Markets ExplainedDocumento14 pagineMonopolistically Competitive Markets ExplainedApple' Mai LingNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Exam 3Documento8 pagineSample Exam 3Luu Nguyen Quyet ThangNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Test BankDocumento13 pagineChapter 8 Test BankMervat SabryNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8Documento11 pagineChapter 8Kalyani GogoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Answerstosummer2010perfectcompetitionquestions PDFDocumento7 pagineAnswerstosummer2010perfectcompetitionquestions PDFMohammad Javed QuraishiNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Exam Questions Chapter12Documento8 pagineSample Exam Questions Chapter12elserry.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Economics 2015 Quiz 3 AnswersDocumento3 pagineBusiness Economics 2015 Quiz 3 Answersanusha50067% (3)
- Economics Assessment 1Documento7 pagineEconomics Assessment 1John-Michael KuczynskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple choice questions on perfectly competitive marketsDocumento10 pagineMultiple choice questions on perfectly competitive marketsCristiSantínNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Q CH12Documento9 pagineStudy Q CH12Gaurav KenueNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 9.pure CompttvDocumento9 pagineChap 9.pure Compttvdeva ayuNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathecs, Assignment7.2Documento3 pagineMathecs, Assignment7.2della salsabilaNessuna valutazione finora
- DocumentDocumento4 pagineDocumentRyan CapistranoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 - Part 3Documento16 pagineChapter 8 - Part 3dylanNessuna valutazione finora
- HW 7 Solutions 2 PDFDocumento5 pagineHW 7 Solutions 2 PDFUmerSaeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Market Structure: Perfect Competition: Economics For Managers, 3e (Farnham)Documento25 pagineChapter 7 Market Structure: Perfect Competition: Economics For Managers, 3e (Farnham)ForappForapp100% (1)
- Micro Chapter 21 Practice Problems #2 Key: $ MC AVC ATCDocumento6 pagineMicro Chapter 21 Practice Problems #2 Key: $ MC AVC ATCSoweirdNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro Chapter 21 Practice Problems #2 Key: $ MC AVC ATCDocumento6 pagineMicro Chapter 21 Practice Problems #2 Key: $ MC AVC ATCAhmadnur JulNessuna valutazione finora
- ECN100 Chapter 8 Quiz A2Documento3 pagineECN100 Chapter 8 Quiz A2mikedjahnNessuna valutazione finora
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageDa EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Beyond Earnings: Applying the HOLT CFROI and Economic Profit FrameworkDa EverandBeyond Earnings: Applying the HOLT CFROI and Economic Profit FrameworkNessuna valutazione finora
- A to Z Cost Accounting Dictionary: A Practical Approach - Theory to CalculationDa EverandA to Z Cost Accounting Dictionary: A Practical Approach - Theory to CalculationNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Prep for:: Egypt Clothing and Textile Industry HandbookDa EverandExam Prep for:: Egypt Clothing and Textile Industry HandbookNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsDa EverandCost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Cost of Capital: Applications and ExamplesDa EverandCost of Capital: Applications and ExamplesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Tutorial - Introduction, Market Equilibrium, Demand and Supply-QDocumento2 pagineTutorial - Introduction, Market Equilibrium, Demand and Supply-QNandiieNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial - Chapter 1 - Introduction - Questions 1Documento4 pagineTutorial - Chapter 1 - Introduction - Questions 1NandiieNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial - Chapter 12 - BOP and Exchange Rate - QuestionDocumento3 pagineTutorial - Chapter 12 - BOP and Exchange Rate - QuestionNandiieNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial - Chapter 11 - Monetary Policy - QuestionsDocumento4 pagineTutorial - Chapter 11 - Monetary Policy - QuestionsNandiieNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial - Chapter 8 9 GNP and Domestic Economy - QuestionsDocumento2 pagineTutorial - Chapter 8 9 GNP and Domestic Economy - QuestionsNandiieNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial - Chapter 7 - Oligopoly and Monopolistic Competition - QuestionsDocumento5 pagineTutorial - Chapter 7 - Oligopoly and Monopolistic Competition - QuestionsNandiie100% (1)
- Tutorial - Cost Function-QDocumento2 pagineTutorial - Cost Function-QNandiie50% (2)
- Tutorial - Demand Elasticity-QDocumento1 paginaTutorial - Demand Elasticity-QNandiie100% (1)
- Tutorial - Chapter 4 - Cost of Production - QuestionsDocumento4 pagineTutorial - Chapter 4 - Cost of Production - QuestionsNandiie100% (1)
- Tutorial - Chapter 1 - Introduction - Questions 1Documento4 pagineTutorial - Chapter 1 - Introduction - Questions 1NandiieNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial - Chapter 10 - Fiscal Policy - QuestionDocumento4 pagineTutorial - Chapter 10 - Fiscal Policy - QuestionNandiieNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial - Chapter 6 - Monopoly QuestionsDocumento5 pagineTutorial - Chapter 6 - Monopoly QuestionsNandiieNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial - Chapter 3 - Consumer Behaviour - QuestionsDocumento5 pagineTutorial - Chapter 3 - Consumer Behaviour - QuestionsNandiie100% (1)
- Tutorial - Chapter 2-Market Equlibrium, Demand Supply - Questions 2Documento4 pagineTutorial - Chapter 2-Market Equlibrium, Demand Supply - Questions 2NandiieNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Thinking GuideDocumento6 pagineDesign Thinking Guideapi-269176213Nessuna valutazione finora
- Creative Idea Generation Techniques PDFDocumento21 pagineCreative Idea Generation Techniques PDFNandiieNessuna valutazione finora
- XLRI Casebook 2022Documento318 pagineXLRI Casebook 2022SathanandhNessuna valutazione finora
- Booth Casebook 2004 PDFDocumento168 pagineBooth Casebook 2004 PDFAnqi ZhouNessuna valutazione finora
- Product life cycle and new product development quizDocumento7 pagineProduct life cycle and new product development quizJolly Sushma0% (2)
- Business Ethics ANSWERSDocumento3 pagineBusiness Ethics ANSWERSMỹ HàNessuna valutazione finora
- AQA Specimen Paper 1 AS MCQsDocumento28 pagineAQA Specimen Paper 1 AS MCQsTahmid SiraziNessuna valutazione finora
- International Financial Management PgapteDocumento29 pagineInternational Financial Management PgapterameshmbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Average and Marginal Revenue - Relation Between AR and MR Curves - Importance of Revenue Costs - Equilibrium Determination - Assignment Help - Homework Help - Online TutoringDocumento3 pagineTotal Average and Marginal Revenue - Relation Between AR and MR Curves - Importance of Revenue Costs - Equilibrium Determination - Assignment Help - Homework Help - Online TutoringRajdeep SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1: Fundamentals of Economics, Management and Managerial EconomicsDocumento10 pagineModule 1: Fundamentals of Economics, Management and Managerial EconomicsmichelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Full AssignmentDocumento46 pagineFull AssignmentCassandra LimNessuna valutazione finora
- The Concept of Exchange Leads To The Concept of A MarketDocumento163 pagineThe Concept of Exchange Leads To The Concept of A MarketHarsh RajNessuna valutazione finora
- This Study Resource Was: Teaching NoteDocumento8 pagineThis Study Resource Was: Teaching NoteSuci NurlaeliNessuna valutazione finora
- The Financial - Supply Chain Management ConnectionDocumento3 pagineThe Financial - Supply Chain Management ConnectionbeccasundalNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Management Objectives and FunctionsDocumento3 pagineFinancial Management Objectives and FunctionsAmanDeep SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- BUS - MATH 11 Q1 Module 5Documento30 pagineBUS - MATH 11 Q1 Module 5Princess Salvador90% (29)
- Calculus2 1920 Extra Exer Ch4 SolDocumento5 pagineCalculus2 1920 Extra Exer Ch4 SolLucia BasabeNessuna valutazione finora
- Managerial Economics IntroductionDocumento17 pagineManagerial Economics IntroductionKentaro Panergo NumasawaNessuna valutazione finora
- Work Sheet-Ii: Dollar ($) Project A Project B Project CDocumento5 pagineWork Sheet-Ii: Dollar ($) Project A Project B Project Crobel popNessuna valutazione finora
- Managers Incentives and Accounting Theory DevelopmentDocumento4 pagineManagers Incentives and Accounting Theory DevelopmentAyusamNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture6 FinalDocumento43 pagineLecture6 FinalcmlimNessuna valutazione finora
- Name Netid Group Number: Website Link: Tutorial Details Time Spent On AssignmentDocumento10 pagineName Netid Group Number: Website Link: Tutorial Details Time Spent On AssignmentNawaporn TaechameekietichaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment - Market StructureDocumento5 pagineAssignment - Market Structurerhizelle19Nessuna valutazione finora
- Management AccountingDocumento10 pagineManagement Accountingnikhilgangwani100% (3)
- Mowen MA-7e-CH08-SM-FinalDocumento39 pagineMowen MA-7e-CH08-SM-FinalbereniceNessuna valutazione finora
- Measuring The Moat - 3Documento7 pagineMeasuring The Moat - 3piyushNessuna valutazione finora
- Iiaam Project-1Documento31 pagineIiaam Project-1SuryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Business ActivityDocumento53 pagineUnderstanding Business ActivityWill Barnard100% (1)
- Evaluate Marketing Opportunities Submission DetailsDocumento16 pagineEvaluate Marketing Opportunities Submission DetailsanushaNessuna valutazione finora
- PRODUCT MIX AND DEVELOPMENTDocumento7 paginePRODUCT MIX AND DEVELOPMENTkunjapNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview Your Client and Propose A Value-Based Price: Kai DavisDocumento20 pagineInterview Your Client and Propose A Value-Based Price: Kai DavisBryan BlanchotNessuna valutazione finora
- Productbrandmanagement 120120042411 Phpapp02Documento31 pagineProductbrandmanagement 120120042411 Phpapp02Amitash DeganNessuna valutazione finora