Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
StepByStep CMDB Build
Caricato da
Walter León CórdovaCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
StepByStep CMDB Build
Caricato da
Walter León CórdovaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
BMC industry insights
Step-by-Step Approach for Building and Managing
Your CMDB
Widespread adoption of the IT Infrastructure
Library® (ITIL ® ) and other best-practice and
control frameworks is motivating a growing
number of enterprises to implement a con-
figuration management database (CMDB).
A CMDB is the core database that “powers”
the configuration management system (CMS),
introduced in ITIL Version 3 (V3). The CMS
is the foundation that supports a complete
service lifecycle across IT. (ITIL definitions
for the CMS, CMDB, and configuration items
(CIs) are included at the end of this article.)
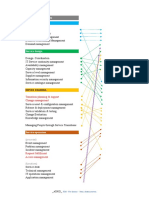
Stage I Stage II Stage III Stage IV Stage V
Some IT organizations have already made Assemble the team Define requirements Select solution Construct and Drive ongoing
Define the project Create a blueprint and tools maintain the CMDB value
great progress and are starting to see
substantial returns. Still, some companies
Figure 1. Five stages for building and managing a CMDB
hesitate to get a CMDB project underway
because of the level of effort involved. How
ever, our five-stage approach, summarized benefits, and the tasks required to build it. In Step 3, your team creates and agrees on
in Figure 1, can help you organize your efforts This upfront investment eliminates confusion the goals and mission. At this time, the
so you can build a comprehensive CMDB and increases your ability to clearly describe team should start to identify the measure-
with minimum risk and maximum reward. the reasons for pursuing the project. ments used to judge how the goals will be
Each stage is broken down into smaller achieved. To do this, the team needs to
steps that are simple to understand and
straightforward to complete.
Stage I Stage III
Assemble the Team and Define the Project Select Your Solution and Tools
Figure 2 provides a high-level checklist to
1. Assemble the project team 1. Select CMDB solution
guide you through the stages and steps.
2. Obtain CMDB knowledge 2. Plan CMDB population
3. Establish goals and mission 3. Select tools to automate population
Stage I 4. Review and define benefits 4. Calculate project ROI
Assemble the Team and Define the Project 5. Build a business case
Stage I involves forming a team, scoping the
Stage II Stage IV
project, gathering input, and getting funding
Define Requirements and Create a Blueprint Construct and Maintain the CMDB
and approval. Your first step in this stage is
1. Identify and review governance requirements 1. Construct the CMDB
to assemble the team. As you do this, keep
2. Review and select supporting best practices 2. Create CI lifecycle management processes
in mind that success comes from engaging 3. Identify requirements to address potential problems 3. Build supporting processes
all key constituents and affected IT functions 4. Identify inventory and asset requirements 4. Populate the CMDB
in the project. The right team members will 5. Define service catalog requirements 5. Train CMDB team and users
increase your probability of success. 6. Define CMDB requirements to support other processes
7. Define CI level and IT service model
Stage V
8. Define CI relationships Drive Ongoing Value
Step 2 is about education, that is, bringing
9. Define CI attributes 1. Implement measures and metrics
team members up to speed on all aspects
10. Design IT service model blueprint 2. Create a service improvement program
of a CMDB — its structure, terminology,
scope, relationships with other IT processes, Figure 2. Checklist for building a CMDB
review the current environment and 2. Review and select supporting 8. Define CI relationships. Identify
problems to be solved, and develop best practices. Start with the IT the specific CI relationship data that
a statement of the goals and mission processes that you have targeted you will maintain in the CMDB.
for the project. This effort is critical for improvement through access 9. Define CI attributes. Define which
to getting the project approved. to a CMDB, and then identify best CI attributes will reside in the
practices that these IT processes CMDB, and which will reside in
The goal of Step 4 is to define project can use. federated data stores.
benefits and communicate them in 3. Identify requirements to address 10. Design the IT service model
terms of key business metrics and potential problems. If there have blueprint. Construct the blueprint
measures. An important part of this been previous CMDB projects, using the requirements you have
step is gathering detailed information identify problems encountered and identified for the service catalog,
that will help you build a business case turn lessons learned into project the IT business processes, and the
and estimate ROI for the project. requirements. This effort can help IT service model design.
you avoid many potential imple-
Finally, in Step 5, you use the output mentation and support issues.
of the first four steps to build a solid Stage III
4. Identify inventory and asset Select Your Solution and Tools
business case that gains the buy-in
requirements. Pinpoint how Stage III completes the planning pro-
and approval of key constituents, the
inventory and asset management cess and technology selection so that
project executive board, and the over-
requirements will affect the project. you can move ahead with building,
all project sponsor. A logical, simple
Keep in mind that while asset, populating, and deploying your CMDB.
business case works best for winning
inventory, and configuration Step 1 for this stage is evaluating
approval over other projects request-
management are similar, they are available solutions with respect to
ing scarce resources.
different enough to warrant your requirements, selecting a CMDB
specific requirements. solution and supporting technologies
Stage II
Define Requirements and Create 5. Define service catalog require- that align with those requirements,
a Blueprint ments. Identify requirements that and procuring the solution and tools.
During Stage II, you document the specify how the service catalog will
requirements that will drive the selec- leverage the relationships between During Step 2, you plan how to popu-
tion of a CMDB solution and guide you services and the underlying CIs. late the CMDB, including federation
in the implementation. In this stage, Understanding which CIs relate strategy and mapping CIs to data
you work with key stakeholders to to a particular service enables sources. You’ll also need to document
document and obtain approval on their you to better meet service level business rules that enable automated
subset of requirements. These stake- agreements and allows you to handling of precedence, reconciliation,
holders are the process owners of conduct service-based costing. and normalization. This is essential
IT functions that will leverage the 6. Define CMDB requirements to to populating the CMDB initially and
CMDB, as well as those responsible support other processes. Turn IT maintaining ongoing data accuracy.
for compliance and IT asset manage- process touchpoints with other IT
ment. You also capture CI-level functions into specific require- In Step 3, you identify and purchase
requirements that specify what CI ments. Make sure the require- additional discovery and automation
relationships the CMDB will maintain. ments reflect how other groups will tools to facilitate CMDB population.
interact with the CMDB, and A broad range of tools is available
There are ten steps in this stage: incorporate any special needs to help automate CMDB data
these groups have. management.
1. Identify and review governance
requirements. Focus on identifying 7. Define CI level and IT service
Finally, in Step 4, you use data collected
governance and regulatory compli- model. Define the optimum level
from the previous steps to create a
ance efforts that you want to improve for CIs to help determine the overall
financial analysis of the expected costs,
with the CMDB project, and breadth and depth of the structure
benefits, and ROI. This information
document the CMDB requirements. of your CMDB data model.
will guide the project implementation Stage V
team as you move into Stage IV. Drive Ongoing Value ITIL V3 Definitions
The final stage of your CMDB project
Stage IV Configuration Management System (CMS):
is about continual service improvement.
Construct and Maintain the CMDB In the first step, you implement metrics
“A set of tools and databases that are
With the first three stages behind you, used to manage an IT service provider’s
that enable effective ongoing manage-
you’re ready to construct your CMDB configuration data. The CMS also includes
ment of CMDB-related processes. You
and build CI lifecycle management information about incidents, problems,
identify metrics that support the overall
processes and CMDB supporting known errors, changes, and releases, and
goals of the project, as well as metrics
processes. Step 1 involves installing may contain data about employees, suppliers,
that help the CMDB manager and CI
CMDB hardware, software, and locations, business units, customers, and
owners with the ongoing management
supporting technologies to make users. The CMS includes tools for collecting,
and update of the CMDB.
your plans a reality. You will also storing, managing, updating, and presenting
need to determine your federation data about all configuration items and their
Step 2 calls for following a service
strategy so that you can identify relationships. The CMS is maintained by
improvement program that focuses
and establish integration points to configuration management and is used
on a narrow set of key metrics and
federated data stores. by all IT service management processes.”1
related targets. If met, these key
metrics will ensure that the CMDB
With installation complete, you pro- Configuration Management Database
continues to have quality data and that
ceed to Step 2, creating CI lifecycle (CMDB): “A database used to store configu-
it will deliver the key benefits that were
management processes. This step ration records throughout their lifecycle.
expected when the overall project
establishes processes for adding new The Configuration Management System
business case was approved.
CIs and updating CI data throughout maintains one or more CMDBs, and each
the CI lifecycle. You define a lifecycle A Final Thought CMDB stores attributes of CIs and relation-
plan for each CI type and then docu- ships with other CIs.”2
CMDB technologies have matured
ment how you will perform and control in recent years, and companies are
each part of the plan. Configuration Item (CI): “Any component
beginning to realize numerous benefits
that needs to be managed in order to deliver
from a fully functional CMDB. These
In Step 3, you document the processes an IT service. Information about each CI
benefits, along with the wider adoption
required to support and manage the is recorded in a configuration record within
of ITIL V3, will motivate many more
CMDB. Any flaws in current processes the configuration management system and
companies to implement CMDBs.
must be eliminated, and any new pro- is maintained throughout its lifecycle by
The CMDB is the key component
cesses must be built and documented. configuration management.
of the ITIL V3 CMS — a central logical
system that covers the data, integration,
Now you’re ready for Step 4, capturing “CIs are under the control of change man-
knowledge, and presentation layers.
the CIs along with their associated agement. CIs typically include IT services,
Many IT organizations have the CMS
attributes and relationships. Populating hardware, software, buildings, people, and
elements already, but they have it
the CMDB includes federating data formal documentation such as process
without the combination of an inte
stores, gathering data, and reconciling documentation and SLAs.”3
grated system.
data. At the end of this step, your
CMDB is ready to use. The experiences of companies that
have already put a CMDB in place
Last, but not least, Step 5 is about shows that a staged approach works
training the CMDB team and users. best. By breaking down the overall
Training is critical for ongoing manage- CMDB construction process into
ment and maintenance of the CMDB. achievable component parts, you can
Training also encourages wide adop- make rapid progress while ensuring
tion, which will result in faster ROI. that you end up with a solution that
provides visibility into how the IT infra-
structure relates to business services.
BMC industry insights
By following the lifecycle approach outlined About BMC Software
in ITIL V3, you ensure that IT integrates with BMC Software delivers the solutions IT
the business to derive business benefits. The needs to increase business value through
resulting CMDB solution will empower your better management of technology and IT
IT staff to make business-savvy decisions processes. Our industry-leading Business
that move the enterprise forward. Service Management solutions help you
reduce cost, lower risk of business disrup-
For a copy of BMC Software’s in-depth tion, and benefit from an IT infrastructure
Step-by-Step Guide to Building a CMDB, built to support business growth and flexibil-
visit www.bmc.com/stepbystep. ity. Only BMC provides best-practice IT
processes, automated technology manage-
End Notes ment, and award-winning BMC Atrium
1 ITIL® V3 Glossary V3.1.24, 11 May 2007,
technologies that offer a shared view into
www.best-management-practice.com/gempdf/
ITIL_Glossary_V3_1_24.pdf. See Configuration how IT services support business priorities.
Management System. Known for enterprise solutions that span
2 Ibid. See Configuration Management Database. mainframe, distributed systems, and end-
3 Ibid. See Configuration Item. user devices, BMC also delivers solutions
that address the unique challenges of the
midsized business. Founded in 1980, BMC
has offices worldwide and fiscal 2008 reve-
nues of $1.73 billion. Activate your business
with the power of IT. www.bmc.com.
Ken Turbitt, President and CEO, Service
Management Consultancy (SMCG) Ltd.,
and Atwell Williams, Solutions Architect,
CTO Office, BMC Software, contributed
to this article.
To learn more about how BMC can help activate your business, visit www.bmc.com or call (800) 841-2031.
BMC, BMC Software, and the BMC Software logo are the exclusive properties of BMC Software, Inc., are registered with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, and may be registered or pending
registration in other countries. IT Infrastructure Library® is a registered trademark of the Office of Government Commerce and is used here by BMC Software, Inc., under license from and with the
permission of OGC. ITIL® is a registered trademark, and a registered community trademark of the Office of Government Commerce, and is registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, and
is used here by BMC Software, Inc., under license from and with the permission of OGC. All other BMC trademarks, service marks, and logos may be registered or pending registration in the U.S.
or in other countries. All other trademarks or registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. © 2008 Copyright BMC Software, Inc. All rights reserved.
*94055*
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Step-By-Step Approach For Building and Managing Your CMDBDocumento4 pagineStep-By-Step Approach For Building and Managing Your CMDBHai Nguyen KhuongNessuna valutazione finora
- ITOM IT Operations Management Software Complete Self-Assessment GuideDa EverandITOM IT Operations Management Software Complete Self-Assessment GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Service Desk Transformation A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandService Desk Transformation A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Trend AnalysisDocumento5 pagineTrend AnalysisvijayskbNessuna valutazione finora
- Support and Troubleshooting - Credentials Troubleshooting On Discovery, Service Mapping, OrchestrationDocumento5 pagineSupport and Troubleshooting - Credentials Troubleshooting On Discovery, Service Mapping, OrchestrationkkuppachiNessuna valutazione finora
- Service Desk Automation Software A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandService Desk Automation Software A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Improving Configuration Item Data QualityDocumento14 pagineImproving Configuration Item Data QualityRocco BurocoNessuna valutazione finora
- IT Asset Management A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionDa EverandIT Asset Management A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- The CMDB As The Brain of ITDocumento4 pagineThe CMDB As The Brain of ITmojo_92Nessuna valutazione finora
- BMC Remedy IT Service Management SuiteDocumento4 pagineBMC Remedy IT Service Management SuiteAlexandru SteleaNessuna valutazione finora
- Incident and Problem Management The Ultimate Step-By-Step GuideDa EverandIncident and Problem Management The Ultimate Step-By-Step GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- CSDM 2.0 White Paper FinalDocumento23 pagineCSDM 2.0 White Paper FinalhwyNessuna valutazione finora
- IT Disaster Recovery Management A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandIT Disaster Recovery Management A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Hub Architecture The Ultimate Step-By-Step GuideDa EverandData Hub Architecture The Ultimate Step-By-Step GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Azure Active Directory A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionDa EverandAzure Active Directory A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Integration A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandCloud Integration A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- ITSM Knowledge Management Implementation Workshop - New YorkDocumento124 pagineITSM Knowledge Management Implementation Workshop - New YorkvenvenchanNessuna valutazione finora
- IT Service Catalog A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandIT Service Catalog A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- UI Policy DocumentationDocumento10 pagineUI Policy DocumentationYKNessuna valutazione finora
- NICF - Advanced - Network - Project - Presentation - Muhammad SalihinDocumento11 pagineNICF - Advanced - Network - Project - Presentation - Muhammad Salihinمحمد صالحين بن سنينNessuna valutazione finora
- Deep Dive: Incident & Problem ManagementDocumento6 pagineDeep Dive: Incident & Problem Managementbala2610Nessuna valutazione finora
- Active Directory Migrations A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandActive Directory Migrations A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- ITIL Service Operation Ver-1.2Documento43 pagineITIL Service Operation Ver-1.2InvensislearningNessuna valutazione finora
- Service Transition Complete Self-Assessment GuideDa EverandService Transition Complete Self-Assessment GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Servicenow Csa Guide ExamDocumento7 pagineServicenow Csa Guide ExamRajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Specification For Integration of GroupID With ServiceNowDocumento10 pagineFunctional Specification For Integration of GroupID With ServiceNowMuhammad RizwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Iso Iec 20000Documento16 pagineIso Iec 20000Aswini Srinath100% (1)
- Step-by-Step Buide To Building A CMDB PDFDocumento253 pagineStep-by-Step Buide To Building A CMDB PDFrkamundimuNessuna valutazione finora
- BMC Remedy ITSM Suite Complete Self-Assessment GuideDa EverandBMC Remedy ITSM Suite Complete Self-Assessment GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Active Directory Migration Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandActive Directory Migration Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- ITIL 4 Foundation Notes - Sample SummaryDocumento9 pagineITIL 4 Foundation Notes - Sample SummaryMark Angat100% (1)
- Designing The Service Delivery ProcessDocumento15 pagineDesigning The Service Delivery ProcessJosante TaylorNessuna valutazione finora
- Incident Management Support Standard RequirementsDa EverandIncident Management Support Standard RequirementsNessuna valutazione finora
- Exploring ITIL4 Practices Monitor Support FulfilDocumento43 pagineExploring ITIL4 Practices Monitor Support FulfilSakuragiNessuna valutazione finora
- ServiceNow - CIS-ITSM - by .Koenzy.53qDocumento15 pagineServiceNow - CIS-ITSM - by .Koenzy.53qshailesh bachhavNessuna valutazione finora
- Change And Release Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandChange And Release Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Servicenow-ITOM-ITOM ITOM ITOM2Documento2 pagineServicenow-ITOM-ITOM ITOM ITOM2Giriprasad Gunalan0% (1)
- A Self-Assessment Tool For Estimation of IT MaturityDocumento1 paginaA Self-Assessment Tool For Estimation of IT MaturityVanessa García PinedaNessuna valutazione finora
- IT Operations Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandIT Operations Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Anonymization A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandData Anonymization A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Paris It Service Management 2-3-2021Documento121 pagineParis It Service Management 2-3-2021sucharitha100% (1)
- SN Kickoff v2 PDFDocumento78 pagineSN Kickoff v2 PDFkimandusaNessuna valutazione finora
- ITIL V3 Foundation Handbook ContentsDocumento2 pagineITIL V3 Foundation Handbook ContentsmadinewalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Release Management Process Documentation Standard RequirementsDa EverandRelease Management Process Documentation Standard RequirementsNessuna valutazione finora
- ITIL Foundation WorkshopDocumento12 pagineITIL Foundation WorkshopCeltem LearningNessuna valutazione finora
- Process To PraticesDocumento3 pagineProcess To PraticesAndrea GiulianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Best Practice Standard For Service Desk V8.2.2019.07Documento95 pagineGlobal Best Practice Standard For Service Desk V8.2.2019.07Enrique Freyre100% (1)
- M700 M70 Maintenance ManualDocumento543 pagineM700 M70 Maintenance ManualDavid ŘezáčNessuna valutazione finora
- Gmail - TATA Steel AET Program - 2019 - Test Login CredentialsDocumento2 pagineGmail - TATA Steel AET Program - 2019 - Test Login CredentialsPrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Disable Visual Studio Debugger - Stack OverflowDocumento4 pagineHow To Disable Visual Studio Debugger - Stack Overflowguruh anindraNessuna valutazione finora
- KMS, Artificial Intelligence, & The Economist 20150509Documento47 pagineKMS, Artificial Intelligence, & The Economist 20150509the1uploaderNessuna valutazione finora
- CoP027 Power Point StandardsDocumento2 pagineCoP027 Power Point StandardsORBeducationNessuna valutazione finora
- Apis PHP en PDFDocumento714 pagineApis PHP en PDFAdediran IfeoluwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Herbhub3 2Documento81 pagineHerbhub3 2Karl LoixNessuna valutazione finora
- JAVA Networking Classes and InterfacesDocumento5 pagineJAVA Networking Classes and InterfacesArchana R gopinathNessuna valutazione finora
- NPD With The Metaverse NFTs and CryptoDocumento4 pagineNPD With The Metaverse NFTs and CryptoManu Tamayo GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Philips Wac700 Wacs700Documento66 paginePhilips Wac700 Wacs700darekk34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Prisma Certified Cloud Security Engineer (PCCSE) BlueprintDocumento4 paginePrisma Certified Cloud Security Engineer (PCCSE) BlueprintJohn LinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Grade 11 & 12 (Day 2)Documento5 pagineLesson Plan Grade 11 & 12 (Day 2)HanessyNessuna valutazione finora
- Predictive Analysis Overview 2013Documento180 paginePredictive Analysis Overview 2013Sivaramakrishna Alpuri100% (1)
- Sarah Noblin Resume 2017aDocumento1 paginaSarah Noblin Resume 2017aapi-275489267Nessuna valutazione finora
- Carlson Software Retail Price List 03-24-15Documento29 pagineCarlson Software Retail Price List 03-24-15bechki5Nessuna valutazione finora
- World Tourism Day by SlidesgoDocumento56 pagineWorld Tourism Day by SlidesgoLe Anh Quan B2105684Nessuna valutazione finora
- Abusive Content Detection Using Sentimental Analysis FinalDocumento18 pagineAbusive Content Detection Using Sentimental Analysis FinalRuthwickNessuna valutazione finora
- Earlier.. We Are Having The sp-73 Issue.: Note 1629558 - Linux 3.x KernelDocumento4 pagineEarlier.. We Are Having The sp-73 Issue.: Note 1629558 - Linux 3.x KernelmenuselectNessuna valutazione finora
- Lexmark Device Quotas Administrator's GuideDocumento22 pagineLexmark Device Quotas Administrator's Guidegeko1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Procurement Cloud Integration Options R13Documento20 pagineStrategic Procurement Cloud Integration Options R13Sanjeev ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Kelly Hadoop Hyd May 2018Documento14 pagineKelly Hadoop Hyd May 2018dilip kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- BBU Hardware Description (V100R009C00 - 01) (PDF) - enDocumento196 pagineBBU Hardware Description (V100R009C00 - 01) (PDF) - enMyce Elu100% (3)
- Himax: Digital Output Module ManualDocumento52 pagineHimax: Digital Output Module ManualRoberto FinaNessuna valutazione finora
- AutoCad 2000 Command List - 300 ComandosDocumento6 pagineAutoCad 2000 Command List - 300 Comandosdossantos1975100% (2)
- Resonant Interface: Steven HeimDocumento11 pagineResonant Interface: Steven HeimDeepak DahiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wi-Fi IP Camera Quick Start Guide AliDocumento14 pagineWi-Fi IP Camera Quick Start Guide AliElisa Cano FerrerNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide To Computer Forensics and Investigations Fifth EditionDocumento76 pagineGuide To Computer Forensics and Investigations Fifth EditionBe RelaxedNessuna valutazione finora
- 701P49624 Freeflow Accxes Service Manual Yke Yke-N FRX LVX UxcDocumento172 pagine701P49624 Freeflow Accxes Service Manual Yke Yke-N FRX LVX Uxcvladimir2426100% (1)
- TWS Troubleshooting GuideDocumento203 pagineTWS Troubleshooting GuideJosé E. FélixNessuna valutazione finora
- CC Lab Manual - PART IDocumento92 pagineCC Lab Manual - PART Ijagadeesh210802Nessuna valutazione finora