Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Clinical Pharmacy Nephrotic Syndrome: Children
Caricato da
Kristine AbrahamTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Clinical Pharmacy Nephrotic Syndrome: Children
Caricato da
Kristine AbrahamCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CLINICAL PHARMACY
NEPHROTIC SYNDROME
F. Detection
A. Definition 1. A urine test can check for the amount
Nephrotic syndrome is the combination of of protein, blood and other things to
nephrotic-range proteinuria with a low indicate kidney damage.
serum albumin level and edema. 2. A blood test can indicate how well
Nephrotic-range proteinuria is the loss of 3 your kidneys are working.
grams or more per day of protein into the 3. The doctor will also check for other
urine or, on a single spot urine collection, diseases that may be causing the
the presence of 2 g of protein per gram of nephrotic syndrome.
urine creatinine. 4. Diagnosis may also require a kidney
biopsy.
B. Epidemiology
It primarily affects adults with an adult to G. Management
child ratio or 26:1. The condition is more MEDICATION
common in women than in men with a ratio Children
of 2:1. Higher rates of nephrotic syndrome Prednisone: For minimal-change
have been reported in children of Arabian nephropathy
and Asian racial origins, in contrast to Rituximab: an antibody against
Caucasian children.
B-cells, has proved an effective
steroid-sparing agent in children
C. Etiology with steroid-dependent
Common primary causes of nephrotic idiopathic nephrotic syndrome.
syndrome include kidney diseases such as
However, children dependent
minimal-change nephropathy, on both steroids and calcineurin
membranous nephropathy, and focal inhibitors are less likely to
glomerulosclerosis. Secondary causes
achieve drug-free remission with
include systemic diseases such as diabetes
rituximab. Rituximab may also
mellitus, lupus erythematosus, and be used in children with steroid-
amyloidosis. Congenital and hereditary resistant disease.
focal glomerulosclerosis may result from
Adults
mutations of genes that code for podocyte
proteins, including nephrin, podocin, or the Prednisone: For minimal change
cation channel 6 protein. Nephrotic nephropathy.
syndrome can result from drugs of abuse, Prednisone with
such as heroin. cyclophosphamide or
mycophenolate mofetil: Should
D. Pathophysiology induce remission in lupus
In a healthy individual, less than 0.1% of nephritis.
plasma albumin may traverse the Anti-inflammatory treatment: For
glomerular filtration barrier. Controversy secondary amyloidosis with
exists regarding the sieving of albumin nephrotic syndrome
across the glomerular permeability barrier. In membranous nephropathy,
On the basis of studies in experimental management with angiotensin
animals, it has been proposed that ongoing blockade but without
albumin passage into the urine occurs in immunosuppression can be
many grams per day, with equivalent used for the first 6 months in
substantial tubular uptake of albumin, the patients at low risk for
result being that the urine contains 80 mg progression (ie, those with serum
or less of albumin per day. However, studies creatinine level <1.5 mg/dL and
of humans with tubular transport defects less than 4 g of proteinuria per
suggest that the glomerular urinary space day). Patients with renal
albumin concentration is 3.5 mg/L. [4] At this insufficiency (serum creatinine
concentration, and a normal daily level >1.5 mg/dL) or those with
glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of 150 liters, higher amounts of urine protein
one would expect at most 525 mg per day are at risk for loss of kidney
of albumin in the final urine. In health, urine function and should receive
albumin is less than 50 mg/day, because immunosuppressive therapy. This
most of the filtered albumin is re-absorbed includes regimens that combine
by the tubules. Amounts above 500 prednisone with
mg/day point to glomerular disease. cyclophosphamide or
chlorambucil. *Mycophenolate
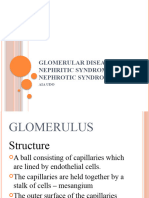
The glomerular capillaries are lined by a mofetil is not helpful in
fenestrated endothelium that sits on the membranous nephropathy.
glomerular basement membrane, which in
Rituximab: effective in
turn is covered by glomerular epithelium, or
membranous nephropathy in
podocytes, which envelops the capillaries
adults, but controlled trials are
with cellular extensions called foot
lacking.
processes. In between the foot processes
DIET AND ACTIVITY
are the filtration slits. These three
structures—the fenestrated endothelium, The diet in patients with
glomerular basement membrane, and nephrotic syndrome should
glomerular epithelium—are the glomerular provide adequate caloric
filtration barrier. intake and adequate protein (1
g/kg/d). Supplemental dietary
E. Risk Factors protein is of no proven value. A
1. Diabetes diet with no added salt will help
2. High blood pressure (hypertension) to limit fluid overload. Fluid
3. Being overweight restriction per se is not needed.
4. Age over 65 There are no activity restrictions
5. Family history of kidney disease for patients with nephrotic
6. Preeclampsia (high blood pressure syndrome. Ongoing activity,
and proteinuria during pregnancy) rather than bedrest, will reduce
7. Race and ethnicity: African- the risk of blood clots.
Americans, Native Americans,
Hispanics and Pacific Islanders are H. Reference
more likely to develop proteinuria Nephrotic Syndrome. (2017, November
than those of European ancestry. 03). Retrieved May 1, 2018, from
Abraham, Kristine D. 4B-Pharmacy
2 CLINICAL PHARMACY LECTRURE
https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/neph
rotic
Smith, Y. (2016, November 15). Nephrotic
Syndrome Epidemiology. Retrieved May 01,
2018, from https://www.news-
medical.net/health/Nephrotic-Syndrome-
Epidemiology.aspx
Nephrotic Syndrome. (2018, January 02).
Retrieved May 01, 2018, from
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/
244631-overview#a2
Living with Kidney Disease. (n.d.).
Retrieved May 01, 2018, from
https://nephcure.org/livingwithkidneydiseas
e/proteinuria-resource-center/what-are-
the-risk-factors/
Abraham, Kristine D. 4B-Pharmacy
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Nephrotic Syndrome Nursing Care Planning & Management - Study Guide PDFDocumento18 pagineNephrotic Syndrome Nursing Care Planning & Management - Study Guide PDFSanket Telang100% (1)
- Nephrotic Syndrome PirDocumento15 pagineNephrotic Syndrome PirNosirova ManijaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic Syndrome: Seminar 4Documento41 pagineNephrotic Syndrome: Seminar 4Kumutha MalarNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic Syndrome in Adults Role of RituximabDocumento50 pagineNephrotic Syndrome in Adults Role of RituximabJoel KennedyNessuna valutazione finora
- Treatment of Steroid Sensitive Nephrotic Syndrome: A.S. AbeyagunawardenaDocumento8 pagineTreatment of Steroid Sensitive Nephrotic Syndrome: A.S. AbeyagunawardenaZenithaMeidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic Syndrome ComplicationsDocumento16 pagineNephrotic Syndrome ComplicationsBeatri AyuzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento19 pagineOverview of Nephrotic Syndromefarmasi_hm100% (1)
- Nephrotic Syndrome FinalDocumento20 pagineNephrotic Syndrome FinalAndrew AdelNessuna valutazione finora
- SNDocumento7 pagineSNArdy Syahabuddin GofarNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic Syndrome: BackgroundDocumento25 pagineNephrotic Syndrome: BackgroundsDamnNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic Syndrome in Children: January 2013Documento7 pagineNephrotic Syndrome in Children: January 2013molenNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic SyndromeeDocumento28 pagineNephrotic SyndromeeRiteka SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 18 NephroticsyndromeDocumento7 pagine18 NephroticsyndromeKim's FamilyNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento29 pagineNephrotic SyndromeMusthafa Afif WardhanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Paediatric Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento44 paginePaediatric Nephrotic SyndromeAlvin OmondiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Nephrotic Nephritic SyndromesDocumento18 paginePediatric Nephrotic Nephritic SyndromesBryan AtasNessuna valutazione finora
- GlomerulonephritisDocumento46 pagineGlomerulonephritisvanessaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento57 pagineNephrotic SyndromePradnya WartheNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Presentation and Review of LiteratureDocumento65 pagineCase Presentation and Review of LiteratureShrey BhatlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Approach ConsiderationsDocumento12 pagineApproach ConsiderationsTyna Mew-mewNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic Syndrome PDFDocumento36 pagineNephrotic Syndrome PDFanwar jabariNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic Syndrome Treatment & Management - Approach Considerations, Acute NephroDocumento5 pagineNephrotic Syndrome Treatment & Management - Approach Considerations, Acute NephroErvirson Jair Cañon AbrilNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento32 pagineCase Nephrotic SyndromeTera SurbaktiNessuna valutazione finora
- SD Nefrotico en AdultosDocumento6 pagineSD Nefrotico en AdultosSebastian Ignacio Vega GonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 3Documento17 pagineTopic 3Jacqueline Tungcul DonatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Update For SNDocumento11 pagineEssential Update For SNshanksNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic Syndrome: Jaiganesh.M, M.D (General Medicine) Asst. Professor, S.M.C.HDocumento60 pagineNephrotic Syndrome: Jaiganesh.M, M.D (General Medicine) Asst. Professor, S.M.C.HJaiganesh MuruganandamNessuna valutazione finora
- Congenital Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento44 pagineCongenital Nephrotic Syndromeaad81kolrenmed50% (2)
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento14 pagineNephrotic SyndromeAnna Michael AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- SRS Kidney - 2016BDocumento3 pagineSRS Kidney - 2016ByayayanizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic Syndrome: Ron Christian Neil T. Rodriguez, MD 1 Year Pedia ResidentDocumento26 pagineNephrotic Syndrome: Ron Christian Neil T. Rodriguez, MD 1 Year Pedia ResidentRon Christian Neil RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Enfermedad GlomerularDocumento7 pagineEnfermedad GlomerularKatty ZanabriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento14 pagineNephrotic SyndromepoerbaantonNessuna valutazione finora
- Glomer Ds TadDocumento190 pagineGlomer Ds TadHaileprince MekonnenNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Naveen G Nadig Associate Professor Dept. of Paediatrics Ssims & RC DavanagereDocumento48 pagineDr. Naveen G Nadig Associate Professor Dept. of Paediatrics Ssims & RC DavanagereVeerabhadra RadhakrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Consensus and Audit Potential For Steroid Responsive Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento7 pagineConsensus and Audit Potential For Steroid Responsive Nephrotic Syndromedanielleon65Nessuna valutazione finora
- Glomerulopatías PrimariasDocumento8 pagineGlomerulopatías PrimariasGSENessuna valutazione finora
- By DR - Tosif Ahmad TMO-PediatricsDocumento27 pagineBy DR - Tosif Ahmad TMO-PediatricskamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Renal DisordersDocumento9 paginePediatric Renal DisordersNadia AmroNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento9 pagineNephrotic SyndromeSonny WijanarkoNessuna valutazione finora
- PIIS0272638696904928Documento11 paginePIIS0272638696904928Reshma rsrNessuna valutazione finora
- Isolated Glomerular Disease With Recurrent Gross HematuriaDocumento17 pagineIsolated Glomerular Disease With Recurrent Gross HematuriaArun GeorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Miscellaneous Renal DiseaseDocumento12 pagineMiscellaneous Renal DiseaseMusfian AgungNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic Syndrome Msn-3Documento12 pagineNephrotic Syndrome Msn-3Bibi Renu100% (3)
- 05 - GinjalDocumento119 pagine05 - GinjalAna ambiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephritic SyndromeDocumento24 pagineNephritic SyndromeMuhamed Al Rohani100% (1)
- Glomerular DiseasesDocumento92 pagineGlomerular Diseasesfrankozed1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento21 pagineNephrotic Syndromepreetie8750% (4)
- MCC QE1 Questions Answers 4Documento8 pagineMCC QE1 Questions Answers 4BasirQidwai100% (3)
- 3&4 Glomerular Diseases and Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento46 pagine3&4 Glomerular Diseases and Nephrotic SyndromeTor Koang ThorNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Glomerular DiseasesDocumento48 pagine2 Glomerular DiseasesDammaqsaa W BiyyanaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper English 3 - DONEDocumento21 paginePaper English 3 - DONESarita AmeliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar On Nephrotic Syndrome: Medical Surgical NursingDocumento15 pagineSeminar On Nephrotic Syndrome: Medical Surgical NursingGargi MP100% (1)
- Nephrotic Syndrome in ChildrenDocumento36 pagineNephrotic Syndrome in ChildrenMalueth AnguiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nefrotik SyndDocumento13 pagineNefrotik SyndJorianditha RamadhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Glomerulonephritis: Prof DR DR Haerani Rasyid, Mkes, SPPD, KGH, SPGK Tim Ginjal Hipertensi Unhas 2019Documento68 pagineGlomerulonephritis: Prof DR DR Haerani Rasyid, Mkes, SPPD, KGH, SPGK Tim Ginjal Hipertensi Unhas 2019uzan100% (1)
- Physiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)Da EverandPhysiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)S. Ali MirjaliliNessuna valutazione finora
- Factor Affecting Child Dental Behaviour PedoDocumento19 pagineFactor Affecting Child Dental Behaviour PedoFourthMolar.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Audit QuestionnaireDocumento7 pagineAudit QuestionnaireEmz Pleños ValerosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lingua Franca Core: The Outcome of The Current Times: Yue ShuDocumento4 pagineLingua Franca Core: The Outcome of The Current Times: Yue ShuThaiNessuna valutazione finora
- India: Labor Market: A Case Study of DelhiDocumento4 pagineIndia: Labor Market: A Case Study of DelhiHasnina SaputriNessuna valutazione finora
- Boiler-Water ChemistryDocumento94 pagineBoiler-Water ChemistryPRAG100% (2)
- Maths-Term End Examination-2020-2021 (2020-2021, MATHS)Documento6 pagineMaths-Term End Examination-2020-2021 (2020-2021, MATHS)Venkat Balaji0% (1)
- Main Book LR X PDFDocumento192 pagineMain Book LR X PDFjay danenjeyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fume Cup BrochureDocumento2 pagineFume Cup Brochuremfisol2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Towards (De-) Financialisation: The Role of The State: Ewa KarwowskiDocumento27 pagineTowards (De-) Financialisation: The Role of The State: Ewa KarwowskieconstudentNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding The School Curriculum Close Encounter With The School Curriculum SPARK Your InterestDocumento12 pagineUnderstanding The School Curriculum Close Encounter With The School Curriculum SPARK Your InterestJoshua Lander Soquita CadayonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Arendi v. GoogleDocumento16 pagineArendi v. GooglePriorSmartNessuna valutazione finora
- Drishti IasDocumento36 pagineDrishti Ias23010126269Nessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Image Processing Unit-8Documento4 pagineDigital Image Processing Unit-8Kpsteja TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF - 6 - 2852 COMMERCE-w-2022Documento13 paginePDF - 6 - 2852 COMMERCE-w-2022Anurag DwivediNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiche 2 ConnexionsDocumento2 pagineFiche 2 ConnexionsMaria Marinela Rusu50% (2)
- Trabajos de InglésDocumento6 pagineTrabajos de Inglésliztmmm35Nessuna valutazione finora
- CLASSIFICATION OF COSTS: Manufacturing: Subhash Sahu (Cs Executive Student of Jaipur Chapter)Documento85 pagineCLASSIFICATION OF COSTS: Manufacturing: Subhash Sahu (Cs Executive Student of Jaipur Chapter)shubhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Fontenot Opinion and OrderDocumento190 pagineFontenot Opinion and OrderInjustice WatchNessuna valutazione finora
- Missions ETC 2020 SchemesOfWarDocumento10 pagineMissions ETC 2020 SchemesOfWarDanieleBisignanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Andrea Falcon - Aristotle On How Animals MoveDocumento333 pagineAndrea Falcon - Aristotle On How Animals MoveLigia G. DinizNessuna valutazione finora
- Bhrighu Saral Paddhati - 1Documento212 pagineBhrighu Saral Paddhati - 1ErrovioNessuna valutazione finora
- Emilio Aguinaldo: The First Philippine Republic The Malolos CongressDocumento3 pagineEmilio Aguinaldo: The First Philippine Republic The Malolos CongressLIEZLE ANN EROYNessuna valutazione finora
- One Tequila, Two Tequila, Three Tequila, Floor!: The Science Behind A HangoverDocumento3 pagineOne Tequila, Two Tequila, Three Tequila, Floor!: The Science Behind A Hangoverkristal eliasNessuna valutazione finora
- ADVOCATE ACT - Smart Notes PDFDocumento30 pagineADVOCATE ACT - Smart Notes PDFAnonymous n7rLIWi7100% (2)
- RSC SCST Programme Briefing For Factories enDocumento4 pagineRSC SCST Programme Briefing For Factories enmanikNessuna valutazione finora
- HOPE 2A MODULE 1 Introduction To SportsDocumento11 pagineHOPE 2A MODULE 1 Introduction To SportsChristian Ray Lucnagan ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Main CharacterDocumento5 pagineMain CharacterFluffy RabbitNessuna valutazione finora
- Baccolini, Raffaela - CH 8 Finding Utopia in Dystopia Feminism, Memory, Nostalgia and HopeDocumento16 pagineBaccolini, Raffaela - CH 8 Finding Utopia in Dystopia Feminism, Memory, Nostalgia and HopeMelissa de SáNessuna valutazione finora
- 1416490317Documento2 pagine1416490317Anonymous sRkitXNessuna valutazione finora
- The Liberal Welfare Reforms 1906Documento5 pagineThe Liberal Welfare Reforms 1906Skye G-sNessuna valutazione finora