Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Triangle Inequality Theorem Lesson Plan
Caricato da
api-219434647Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Triangle Inequality Theorem Lesson Plan
Caricato da
api-219434647Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Triangle Inequality Theorem Lesson Plan
Description of Resource: This lesson plan allows students to explore and discover the Triangle Inequality
Theorem. This lesson has an interactive component using physical manipulatives to assist students in
understanding the definition of a triangle in relation to sides.
Technical & Cost considerations: The lesson is free to access. The lesson does require materials in order to
perform the interactive aspect of the lesson; however, most can be obtained at little cost.
Evaluation
1. Learning Activity Types
LA-Practice - practicing for fluency-
LA-Present - (read or attend to) presentation of new content/ideas
o LA-Present-Demo - demonstration- Teacher will use demonstration before students investigate in
groups.
o LA-Present-Explain - explanation- Opportunity for teacher to go over the introduction of
concepts and identifying triangles. Students are asked to explain their results at the end of the
lesson.
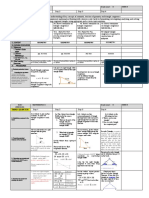
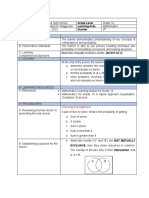
LA-Explore - exploring/investigating mathematical ideas- Exploring of triangles occur during the
interactive portion of the lesson. Students manipulate pipe cleaners representing sides of a triangle.
LA-Apply - applying mathematics to problems and situations- Students use their results during their
exploration to formulate a pattern. Using the pattern formed and their own reasoning, students determine if
measurements of provided sides will form a triangle.
2. What mathematics is being learned?
Standards
Common Core State Standards – Mathematics
CCSS.Math.Content.HSG.CO.C.10
Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 180
degrees; base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a
triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length; the medians of a triangle meet at a point.
CCSS.Math.Content.HSG.SRT.B.4
Prove theorems about triangles. Theorem include: a line parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other
two proportionally, and conversely; the Pythagorean Theorem proved using triangle similarity.
Proficiency Strands
conceptual understanding- Students use manipulative to explore the side lengths of triangles.
strategic competence- Students begin by hypothesizing sides that can make triangles and they explore
with manipulative to determine patterns.
adaptive reasoning- Students use logical thought to reflect and reason the definition of a triangle.
6. Additional Comments
I really liked that students got an opportunity to explore and determine patterns that are observed. This lesson does a
great job to incorporate individual work and allow collaboration during group work.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Triangle Congruence WorksheetDocumento17 pagineTriangle Congruence WorksheetDiana Wong Abio-MolinaNessuna valutazione finora
- DLP CO1 Solving Congruent TriangleDocumento4 pagineDLP CO1 Solving Congruent TriangleLourdes MoredoNessuna valutazione finora
- DLP CombinationDocumento10 pagineDLP CombinationAlexis Magana100% (1)
- Proving Properties of Parallel LinesDocumento3 pagineProving Properties of Parallel LinesisipMath Tutorial FilesNessuna valutazione finora
- DLP-Day 3 RectangleDocumento6 pagineDLP-Day 3 RectangleJonald ReyNessuna valutazione finora
- Instructional Planning Triangle InequalitiesDocumento2 pagineInstructional Planning Triangle InequalitiesPablo JimeneaNessuna valutazione finora
- III-Day 2Documento4 pagineIII-Day 2Rainman InsanityNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10 DLL 11 14Documento12 pagineGrade 10 DLL 11 14Jaymar SarvidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocumento8 pagineDetailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsResa MaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Q3 Grade 8 Week 6Documento15 pagineQ3 Grade 8 Week 6aniejeonNessuna valutazione finora
- I-Day 34Documento11 pagineI-Day 34Rainman InsanityNessuna valutazione finora
- DLP 8 - Week8 (Day5)Documento10 pagineDLP 8 - Week8 (Day5)Kriza Mae de TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL - Math 8 - Q3Documento15 pagineDLL - Math 8 - Q3TITO FERNANDEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Identify Angles Formed by Parallel Lines Cut by a TransversalDocumento10 pagineIdentify Angles Formed by Parallel Lines Cut by a TransversalFelix LlameraNessuna valutazione finora
- DLP 10Documento4 pagineDLP 10Pablo JimeneaNessuna valutazione finora
- G9 Activity Sheets Ncov 19Documento3 pagineG9 Activity Sheets Ncov 19Bea Bianca100% (1)
- Grade 8 Math Lessons on Triangle CongruenceDocumento5 pagineGrade 8 Math Lessons on Triangle CongruenceEric BernabeNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL Grade 7 Q3-Week 1-4Documento14 pagineDLL Grade 7 Q3-Week 1-4Angela Camille PaynanteNessuna valutazione finora
- K to 12 Math Curriculum GuideDocumento18 pagineK to 12 Math Curriculum Guideeiz catNessuna valutazione finora
- Measuring and Expressing Algebra: 7th Grade Math Curriculum MapDocumento4 pagineMeasuring and Expressing Algebra: 7th Grade Math Curriculum MapJeff LacasandileNessuna valutazione finora
- FuturesDocumento59 pagineFuturesMikhaela Pabinguit50% (2)
- Mathematical SystemDocumento3 pagineMathematical SystemHadzmie AgarNessuna valutazione finora
- LeaP Math G8 Week 7 Q3aDocumento4 pagineLeaP Math G8 Week 7 Q3aDave BillonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 8 DLL 4th Quarter Week 1 LC 48Documento6 pagineMath 8 DLL 4th Quarter Week 1 LC 48Cesar Abajo Lingolingo Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 9 Lesson PlanDocumento17 pagineGrade 9 Lesson PlanSamuel BaunNessuna valutazione finora
- LESSON PLAN 3RD Q (Asa)Documento2 pagineLESSON PLAN 3RD Q (Asa)JESSA CANOPINNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson-3 - AnglesDocumento23 pagineLesson-3 - AnglesAr Jay DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Math - Lesson4 - Proportion and The Fundamental Theorems of ProportionalityDocumento9 pagineMath - Lesson4 - Proportion and The Fundamental Theorems of ProportionalityFree TemplatesNessuna valutazione finora
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 8 Mathematics ON Basic Concepts of ProbabilityDocumento5 pagineA Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 8 Mathematics ON Basic Concepts of ProbabilityRachel Mae Roque EnarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 30 (Geometry) - Basic Concepts and Terms - LGDocumento10 pagineLesson 30 (Geometry) - Basic Concepts and Terms - LGSwag MooshroomNessuna valutazione finora
- Junior High School Department: Curriculum MapDocumento12 pagineJunior High School Department: Curriculum MapRowena BarcarseNessuna valutazione finora
- Reasoning in MathematicsDocumento5 pagineReasoning in MathematicsBingkay CaburalNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 1-12 Daily Lesson Log: Learning PlanDocumento8 pagineGrade 1-12 Daily Lesson Log: Learning PlanJesusa Salvador JardinelNessuna valutazione finora
- Sat Lesson Plan BiconditionalDocumento6 pagineSat Lesson Plan Biconditionalapi-526889056Nessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation For Subgroups PDFDocumento32 paginePresentation For Subgroups PDFMary John Pinuela100% (1)
- Using Geometric Figures to Solve Real-Life ProblemsDocumento3 pagineUsing Geometric Figures to Solve Real-Life ProblemsLavander BlushNessuna valutazione finora
- I-Day 35Documento3 pagineI-Day 35Rainman InsanityNessuna valutazione finora
- OBE SYLLABUS Mathematics in The Modern World 2020Documento7 pagineOBE SYLLABUS Mathematics in The Modern World 2020Reynold BaborNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Plan in Mathematics For Grade 8Documento6 pagineLearning Plan in Mathematics For Grade 8ZoeyNessuna valutazione finora
- (M8Ge-Ive-1) : Learning Activity 1: Can You See Me?Documento4 pagine(M8Ge-Ive-1) : Learning Activity 1: Can You See Me?juswa coralNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 10 - DLL - March 20 March 24 2023Documento9 pagineMath 10 - DLL - March 20 March 24 2023Ian Paul CauguiranNessuna valutazione finora
- Secondary Parts of A TriangleDocumento17 pagineSecondary Parts of A TriangleJeff CadimasNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Lesson Plan: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocumento4 pagineDaily Lesson Plan: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterIvy Borja SolisNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Lesson Plan of M8Al-Ih-2: Annex 18 Deped Order No. 42, S, 2016Documento3 pagineDaily Lesson Plan of M8Al-Ih-2: Annex 18 Deped Order No. 42, S, 2016Florita LagramaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics 10 1st Quarter Learning PlanDocumento3 pagineMathematics 10 1st Quarter Learning PlanManilyn BaltazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 8 Math Lesson Plan for Bayugan National CHSDocumento18 pagineGrade 8 Math Lesson Plan for Bayugan National CHSJo Mai HannNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 10 DLLDocumento5 pagineMath 10 DLLNoraisa MacabaasNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Circle Lesson PlanDocumento5 pagineUnit Circle Lesson Plankcarr13100% (1)
- The Following Are The Steps in Constructing Perpendicular Bisector of A Segment Using A Compass and A StraightedgeDocumento4 pagineThe Following Are The Steps in Constructing Perpendicular Bisector of A Segment Using A Compass and A StraightedgeAnjelo Amar BarcenasNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard Score Lesson PlanDocumento15 pagineStandard Score Lesson Plandulce mosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Lesson PlanDocumento9 pagineSample Lesson PlanMenchie AnieteNessuna valutazione finora
- g7 SolutionsDocumento10 pagineg7 SolutionsNobhe Grace PinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Right Triangle Lesson PlanDocumento6 pagineRight Triangle Lesson PlanErra PeñafloridaNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 2. FIDPDocumento11 paginePart 2. FIDPReyboy TagsipNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 7 - PROBABILITY OF UNION OF TWO EVENTS-Lesson PlanDocumento6 pagineWeek 7 - PROBABILITY OF UNION OF TWO EVENTS-Lesson PlanAubrey Elaine MagpusaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 8 DLL 4th Quarter Week 10 LC 56Documento5 pagineMath 8 DLL 4th Quarter Week 10 LC 56Cesar Abajo Lingolingo Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Lesson Log of M7Ge-Iif-1 (Week Six-Day 2)Documento3 pagineDaily Lesson Log of M7Ge-Iif-1 (Week Six-Day 2)Zile Smith100% (1)
- Mathematics9 q4 Week1 v4Documento9 pagineMathematics9 q4 Week1 v4jayson karl dumasNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Triangle Congruence Lesson PlanDocumento1 paginaBasic Triangle Congruence Lesson Planapi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tangram LessonDocumento17 pagineTangram Lessondbrizzolara191Nessuna valutazione finora
- Courtney Ruhno-Cep822 Research PaperDocumento7 pagineCourtney Ruhno-Cep822 Research Paperapi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Geogebra-Ssa Exploration EvaluationDocumento2 pagineGeogebra-Ssa Exploration Evaluationapi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- 21st Century Lesson PlanDocumento3 pagine21st Century Lesson Planapi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Measuring Angles EvaluationDocumento2 pagineMeasuring Angles Evaluationapi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Geogebra-Special Right Triangle EvaluationDocumento2 pagineGeogebra-Special Right Triangle Evaluationapi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Illuminations Congruence TheoremsDocumento2 pagineIlluminations Congruence Theoremsapi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Soccer Coordinates EvaluationDocumento2 pagineSoccer Coordinates Evaluationapi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Triangle Congruence Lesson PlanDocumento1 paginaBasic Triangle Congruence Lesson Planapi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Courtney L Ruhno Resume 4-10-15Documento4 pagineCourtney L Ruhno Resume 4-10-15api-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Flip NDocumento2 pagineFlip Napi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Exploring Transformations Through Modeling and Computer Games Lesson PlanDocumento2 pagineExploring Transformations Through Modeling and Computer Games Lesson Planapi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Running Records Monthly ChecklistDocumento2 pagineRunning Records Monthly Checklistapi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Portal Transformation EvaluationDocumento2 paginePortal Transformation Evaluationapi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sticker ChecklistDocumento2 pagineSticker Checklistapi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Balanced Literacy WritingDocumento1 paginaBalanced Literacy Writingapi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Balanced Literacy ReadingDocumento1 paginaBalanced Literacy Readingapi-219434647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1: Background, Rationale, and Development of Melcs: Module 2: Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs)Documento5 pagineLesson 1: Background, Rationale, and Development of Melcs: Module 2: Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs)LenielynBisoNessuna valutazione finora
- NJIT Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture on Angular Momentum and TorqueDocumento35 pagineNJIT Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture on Angular Momentum and TorqueArslanNessuna valutazione finora
- Academic Calendar 2018 LSUDocumento3 pagineAcademic Calendar 2018 LSUHelder OliveiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lynair Alston Resume FinalDocumento4 pagineLynair Alston Resume Finalapi-417373169Nessuna valutazione finora
- Program Evaluation: Provincial Training Center-OrionDocumento3 pagineProgram Evaluation: Provincial Training Center-OrionMariam SalongaNessuna valutazione finora
- How Young Teachers Experience Their Professional Work in ChileDocumento14 pagineHow Young Teachers Experience Their Professional Work in ChilefohollowNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Tle-IctDocumento2 pagineLesson Plan Tle-IctKramMark100% (5)
- Curriculum Guide For Grade 10 MathematicsDocumento5 pagineCurriculum Guide For Grade 10 MathematicsPaolo Xavier CoNessuna valutazione finora
- Traineeship Program in Maternal Health CareDocumento2 pagineTraineeship Program in Maternal Health CareLaila AcehNessuna valutazione finora
- Project ProposalDocumento25 pagineProject Proposalapi-400236820Nessuna valutazione finora
- Motivation in Learning PDFDocumento359 pagineMotivation in Learning PDFlaily100% (1)
- HRTM 134 Course Outline, 2nd 2017-18Documento4 pagineHRTM 134 Course Outline, 2nd 2017-18aireen cloresNessuna valutazione finora
- ICOMOS CCHWG - Final - Print PDFDocumento62 pagineICOMOS CCHWG - Final - Print PDFYussef Campos100% (1)
- Csit 101 Abdullahi Resume FinalDocumento2 pagineCsit 101 Abdullahi Resume Finalapi-329754693Nessuna valutazione finora
- Motion Along Two and Three Dimensions: Prerequisites: VectorsDocumento4 pagineMotion Along Two and Three Dimensions: Prerequisites: VectorsCharl CuaNessuna valutazione finora
- q3w5 DLLDocumento3 pagineq3w5 DLLCatherine AradaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effect of Using Authentic Materials in TeachingDocumento6 pagineThe Effect of Using Authentic Materials in TeachingvioletavaleryNessuna valutazione finora
- Social ConstructivismDocumento2 pagineSocial Constructivismleeza dizonNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of The Program 14 May 2016Documento28 pagineOverview of The Program 14 May 2016rkhanna1965Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 - Training EvaluationDocumento28 pagineChapter 6 - Training EvaluationChaudry AdeelNessuna valutazione finora
- Essentialism and ProgressivismDocumento9 pagineEssentialism and Progressivismapi-395812185Nessuna valutazione finora
- KONSTRUKTIVISME, PENGEMBANGAN MODEL, MEDIA, DAN BLENDED LEARNINGDocumento28 pagineKONSTRUKTIVISME, PENGEMBANGAN MODEL, MEDIA, DAN BLENDED LEARNINGordeNessuna valutazione finora
- Deped Order No.35 s.2016Documento15 pagineDeped Order No.35 s.2016Genesis Damaso100% (2)
- Jenipe R. Codium BSED ENGLISH3A Activity 4.1 Sequencing Curricular ProcessesDocumento4 pagineJenipe R. Codium BSED ENGLISH3A Activity 4.1 Sequencing Curricular ProcessesJenipe CodiumNessuna valutazione finora
- InnovationDocumento14 pagineInnovationJane Bunuan SaludaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Testimonials from Industry Leaders on Process Technology EducationDocumento2 pagineTestimonials from Industry Leaders on Process Technology EducationNaseer HydenNessuna valutazione finora
- Case StudyDocumento2 pagineCase StudyKiran AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 8 Physics WorksheetDocumento6 pagineGrade 8 Physics Worksheetsanathd67% (18)
- Chapter 3 Linear MotionDocumento18 pagineChapter 3 Linear MotionMuhd Faizal MdkNessuna valutazione finora
- The Analysis of Equity Vs EqualityDocumento5 pagineThe Analysis of Equity Vs Equalityapi-384543912Nessuna valutazione finora