Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Short Circuit Calculation - 33 KV, 1C X 500 SQ - MM XLPE
Caricato da
jamilTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Short Circuit Calculation - 33 KV, 1C X 500 SQ - MM XLPE
Caricato da
jamilCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Detail Calculations of Screen to Demonstrate Withstanding Earth Fault Current
33KV, 1-Core x 500 Sq.mm U/G XLPE Copper Cable
General formula
I=ε×IAD
Based on IEC 949, permissible short-circuit current is given by:
Where:
I: Permissible short-circuit current
IAD: Short-circuit current calculated on an adiabatic basis
ε: Factor to allow for heat loss into the adjacent component. For adiabatic calculations, ε=1.
Calculation of adiabatic short-circuit current:
I 2AD×t = K 2×S 2 ×ln((θf+β)/(θi+β))
Where:
IAD: Short-circuit current (r.m.s. over duration) calculated on an adiabatic basis (A)
t: Duration of short-circuit (s),t=1s
K: Constant depending on the material of the current carrying component, derived from Table 1 of
IEC949: K=226 (As1/2/mm2)
θf: Final temperature (℃),θf = 250℃
θi: Initial temperature (℃),θi = 90℃
β: Reciprocal of temperature coefficient of resistance of the current carrying component at 0℃
(K),β= 234.5 K (see Table 1 of IEC949)
Copper tape screen earth fault current calculation
S: Geometrical cross-sectional area of the current carrying component (mm 2)
S=SCW = PI()/4×d2×n
SCW: Geometrical cross-sectional area of total copper wires
d = Diameter of each copper wire
n = Number of copper wires
1. The number of copper wires for metallic screen, n = 46
2. Diameter of each copper wire for screen, d = 2.21 mm
3. The area of copper wires screen, SCW = PI()/4×(2.21)2×46=176.45 sq.mm
4. Combined screen area(S), S=SCW= 176.45 sq.mm
5. Screen short-circuit current duration 1 sec,
I 2AD×t = K 2×S 2 ×ln((θf+β)/(θi+β))
IAD =Sqrt.( K 2×S 2 ×ln((θf+β)/(θi+β)))/ Sqrt.(t)
IAD =Sqrt.(2262×176.452×ln((250+234.5)/(90+234.5)))/ Sqrt.(1)
=25210 A
≈25.2 kA
Note: This satisfies the required earth fault current of 25 kA/S.
11KV, 3-Core x 185 Sq.mm U/G XLPE Copper Cable
General formula
I=ε×IAD
Based on IEC 949, permissible short-circuit current is given by:
Where:
I: Permissible short-circuit current
IAD: Short-circuit current calculated on an adiabatic basis
ε: Factor to allow for heat loss into the adjacent component. For adiabatic calculations, ε=1.
Calculation of adiabatic short-circuit current:
I 2AD×t = K 2×S 2 ×ln((θf+β)/(θi+β))
Where:
IAD: Short-circuit current (r.m.s. over duration) calculated on an adiabatic basis (A)
t: Duration of short-circuit (s),t=1s
K: Constant depending on the material of the current carrying component, derived from Table 1 of
IEC949: K=226 (As1/2/mm2)
θf: Final temperature (℃),θf = 250℃
θi: Initial temperature (℃),θi = 90℃
β: Reciprocal of temperature coefficient of resistance of the current carrying component at 0℃
(K),β= 234.5 K (see Table 1 of IEC949)
Copper tape screen earth fault current calculation
S: Geometrical cross-sectional area of the current carrying component (mm 2)
S=SCW×3 =( (PI()/4×d2×n)+ (Thickness × Width)) ×3
SCW: Geometrical cross-sectional area of total copper wires
d = Diameter of each copper wire
n = Number of copper wires
1. The number of copper wires for metallic screen, n = 42
2. Diameter of each copper wire for screen, d = 0.85 mm
3. The single phase area of copper wires screen, SCW = PI()/4×(0.85)2×42=23.83sq.mm
4. Three phase combined screen area(S), S=SCW×3=23.83 ×3=71.50sq.mm
5. Screen short-circuit current duration 1 sec,
I 2AD×t = K 2×S 2 ×ln((θf+β)/(θi+β))
IAD =Sqrt.( K 2×S 2 ×ln((θf+β)/(θi+β)))/ Sqrt.(t)
IAD =Sqrt.(2262×71.502×ln((250+234.5)/(90+234.5)))/ Sqrt.(1)
=10215A
≈10.2 kA
Note: This satisfies the required earth fault current of 10 kA/S.
11KV, 1-Core x 500 Sq.mm U/G XLPE Copper Cable
General formula
I=ε×IAD
Based on IEC 949, permissible short-circuit current is given by:
Where:
I: Permissible short-circuit current
IAD: Short-circuit current calculated on an adiabatic basis
ε: Factor to allow for heat loss into the adjacent component. For adiabatic calculations, ε=1.
Calculation of adiabatic short-circuit current:
I 2AD×t = K 2×S 2 ×ln((θf+β)/(θi+β))
Where:
IAD: Short-circuit current (r.m.s. over duration) calculated on an adiabatic basis (A)
t: Duration of short-circuit (s),t=1s
K: Constant depending on the material of the current carrying component, derived from Table 1 of
IEC949: K=226 (As1/2/mm2)
θf: Final temperature (℃),θf = 250℃
θi: Initial temperature (℃),θi = 90℃
β: Reciprocal of temperature coefficient of resistance of the current carrying component at 0℃
(K),β= 234.5 K (see Table 1 of IEC949)
Copper tape screen earth fault current calculation
S: Geometrical cross-sectional area of the current carrying component (mm 2)
S=SCW+SCT = (PI()/4×d2×n)+ (Thickness × Width)
SCW: Geometrical cross-sectional area of total copper wires
SCT: Geometrical cross-sectional area of copper tape
d = Diameter of each copper wire
n = Number of copper wires
1. The number of copper wires for metallic screen, n = 46
2. Diameter of each copper wire for screen,d = 1.38 mm
3. The area of copper wires screen, SCW = PI()/4×(1.38)2×46=68.80 sq.mm
4. The copper tape screen area, SCT = (Thickness × Width)=0.12×35=4.20 sq.mm
5. Combined screen area(S), S=SCW+SCT = (68.80+4.20) =73.0 sq.mm
6. Screen short-circuit current duration 1 sec,
I 2AD×t = K 2×S 2 ×ln((θf+β)/(θi+β))
IAD =Sqrt.( K 2×S 2 ×ln((θf+β)/(θi+β)))/ Sqrt.(t)
IAD =Sqrt.(2262×73.02×ln((250+234.5)/(90+234.5)))/ Sqrt.(1)
=10445 A
≈10.4 kA
Note: This satisfies the required earth fault current of 10 kA/S.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Cable Fault Current CalculationDocumento5 pagineCable Fault Current Calculationskc1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Earthing Calculation - DC SideDocumento2 pagineEarthing Calculation - DC SideANAND100% (1)
- Cable Design Calculations (Direct Burial & Short Circuit Current) PDFDocumento12 pagineCable Design Calculations (Direct Burial & Short Circuit Current) PDFInayat Hathiari0% (1)
- Earthing CalculationDocumento1 paginaEarthing Calculationsreenath raoNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Non-Metallic Gland Plate Is Required For Single Core Cable Glanding?Documento5 pagineWhy Non-Metallic Gland Plate Is Required For Single Core Cable Glanding?krajeev28020% (1)
- Busbar CalculationDocumento8 pagineBusbar Calculationd_rosembergNessuna valutazione finora
- Conductor Design SubstationDocumento101 pagineConductor Design Substationt_syamprasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Determining Cross Section Area of The Protective ConductorDocumento4 pagineDetermining Cross Section Area of The Protective ConductorS Amila C RajapaksaNessuna valutazione finora
- SS Earthing Mat Design 22 8 12Documento7 pagineSS Earthing Mat Design 22 8 12Vishal ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthing Calculation For NGR PANEL: Sr. No. Description DataDocumento4 pagineEarthing Calculation For NGR PANEL: Sr. No. Description Datanaran19794735Nessuna valutazione finora
- GTP For TransformerDocumento5 pagineGTP For TransformerSatheesh Kumar NatarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- GTP - 33KV (E) 3C AL XLPE Armd CableDocumento1 paginaGTP - 33KV (E) 3C AL XLPE Armd Cableshivam dwivediNessuna valutazione finora
- Typical HT and LT Power Cable Sizing PDFDocumento26 pagineTypical HT and LT Power Cable Sizing PDF1382ace100% (2)
- Earthing CalculationDocumento21 pagineEarthing CalculationbhavikNessuna valutazione finora
- NGR Sizing Calculation As Per IEEE 32Documento3 pagineNGR Sizing Calculation As Per IEEE 32Soumya MukherjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculation of Short Circuit Capacity of Conductor For 1 Sec. and 3 SecDocumento3 pagineCalculation of Short Circuit Capacity of Conductor For 1 Sec. and 3 SecAbdullah Al AsikNessuna valutazione finora
- Type 2 Coordination Chart TeSys IE3-IE4 PDFDocumento28 pagineType 2 Coordination Chart TeSys IE3-IE4 PDFDevendra RawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthing Grid Calculations For Khondbond R3 For ApprovalDocumento27 pagineEarthing Grid Calculations For Khondbond R3 For ApprovalDipankar ChatterjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Determine Correct Number of Earthing Electroding FactorDocumento14 pagineHow To Determine Correct Number of Earthing Electroding FactorumerNessuna valutazione finora
- IEC 60287 Current Capacity of Cables - Rated CurrentDocumento1 paginaIEC 60287 Current Capacity of Cables - Rated CurrentxsystemNessuna valutazione finora
- 33 KV Cable Sizing CalculationDocumento3 pagine33 KV Cable Sizing CalculationmohanadsamaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth Mat Design Calculation For 33 KV S/STN For M/s Sukhbir Agro Energy LTD, Shahjahanpur, U.PDocumento7 pagineEarth Mat Design Calculation For 33 KV S/STN For M/s Sukhbir Agro Energy LTD, Shahjahanpur, U.PDipak BandyopadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Is 2309 1989Documento72 pagineIs 2309 1989Jagdish PalariyaNessuna valutazione finora
- EWT Earthing TransformersDocumento4 pagineEWT Earthing TransformersSibolis NaburjuNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Specification 2500kva Transformer ABB: EVN: Efficiency 99,42%@50% Loading and Power Factor 1Documento3 pagineTechnical Specification 2500kva Transformer ABB: EVN: Efficiency 99,42%@50% Loading and Power Factor 1Lê Đình LậpNessuna valutazione finora
- EP-MS-P4-S3-050 - XLPE Insulated Pilot Cables - (KM Material Spec)Documento8 pagineEP-MS-P4-S3-050 - XLPE Insulated Pilot Cables - (KM Material Spec)dimaomarNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth Mat Calculations PDFDocumento7 pagineEarth Mat Calculations PDFsouvikbesu89Nessuna valutazione finora
- 22 Standard Earthing Philosophy of GETCO R 2 25-0-711Documento4 pagine22 Standard Earthing Philosophy of GETCO R 2 25-0-711Ramesh AnanthanarayananNessuna valutazione finora
- 2240 162 Pve U 004 SHT 3 3 01Documento13 pagine2240 162 Pve U 004 SHT 3 3 01Anagha DebNessuna valutazione finora
- Tariff Metering PanelsDocumento2 pagineTariff Metering PanelsSaraswatapalitNessuna valutazione finora
- Bus Duct Calculations For 4000A Rated CurrentDocumento4 pagineBus Duct Calculations For 4000A Rated CurrentGnanavel GNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Specificationof IDT Solar ProjectDocumento12 pagineTechnical Specificationof IDT Solar ProjectJitendra Pathak100% (1)
- Earthing System PDFDocumento24 pagineEarthing System PDFasexyguyNessuna valutazione finora
- GT TRANSFORMER Soak Pit Sizing.Documento1 paginaGT TRANSFORMER Soak Pit Sizing.Thangarajan NagarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- ABB (Pro-E Type Test) - PanelDocumento16 pagineABB (Pro-E Type Test) - Panelari bowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth Electrode CalculationDocumento3 pagineEarth Electrode CalculationNanban VkyNessuna valutazione finora
- Substation Earthing by JGNDocumento49 pagineSubstation Earthing by JGNrupamNessuna valutazione finora
- Fault Level Calcn in 11KV & 415VDocumento4 pagineFault Level Calcn in 11KV & 415Vvaithy201180% (5)
- Voltage Dip CalculationDocumento69 pagineVoltage Dip CalculationCalvert WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Jamalpur Earthing Calculation Final PDFDocumento10 pagineJamalpur Earthing Calculation Final PDFarafinNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthing Calculation - V - 0.2Documento18 pagineEarthing Calculation - V - 0.2Ravishankar.AzadNessuna valutazione finora
- DSLP CalculationDocumento7 pagineDSLP Calculationravi shankar100% (1)
- IS 2026-5 (2011) - Power Transformers, Part 5 - Ability To Withstand Short CircuitDocumento23 pagineIS 2026-5 (2011) - Power Transformers, Part 5 - Ability To Withstand Short Circuitrajiv71Nessuna valutazione finora
- GTP - 02 BreakersDocumento6 pagineGTP - 02 Breakersraj_stuff0060% (1)
- Earthing CalculationDocumento4 pagineEarthing CalculationNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNessuna valutazione finora
- CBIP Publication 223 PDFDocumento32 pagineCBIP Publication 223 PDFEric Taylor100% (4)
- 2 - Earthing Calculation No.1Documento2 pagine2 - Earthing Calculation No.1Sharik KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 230kv Cable Sizing 1Documento6 pagine230kv Cable Sizing 1Thirunavukkarasu VaratharajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathcad - Ampacity CalculationDocumento76 pagineMathcad - Ampacity CalculationAlex Ribeiro100% (4)
- Short Circuit CalculationDocumento6 pagineShort Circuit CalculationMohamad HishamNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthing CalculationDocumento14 pagineEarthing CalculationNatarajan Ramakrishnan100% (18)
- Larsen & Toubro Limited: ECC Division - EDRC (Electrical)Documento10 pagineLarsen & Toubro Limited: ECC Division - EDRC (Electrical)jm.mankavil6230Nessuna valutazione finora
- Contoh Proteksi Katodik PerhitunganDocumento6 pagineContoh Proteksi Katodik PerhitunganDeo Harita100% (1)
- Short Circuit Calc 33kv (E) 26.12.07Documento2 pagineShort Circuit Calc 33kv (E) 26.12.07cherif yahyaouiNessuna valutazione finora
- Panel No: S08: Design of Two Way SlabDocumento48 paginePanel No: S08: Design of Two Way SlabAbdul AzeemNessuna valutazione finora
- EarthingDocumento8 pagineEarthingboopelectraNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 EarthingDocumento4 pagine5 EarthingPrabhash Verma0% (1)
- Short CT Calc Cu Tube 500 and 1000sqmmDocumento2 pagineShort CT Calc Cu Tube 500 and 1000sqmmrenjithas2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Earthing Design Calculation: Project: Document No. DateDocumento9 pagineEarthing Design Calculation: Project: Document No. Dateboopathy1705100% (1)
- Cable Impedances CalculationDocumento30 pagineCable Impedances Calculationjimmy_barredoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1x300 RM Nyy (FRTR)Documento1 pagina1x300 RM Nyy (FRTR)jamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Ki LSHF 3401 IsDocumento2 pagineKi LSHF 3401 IsjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- TDS For Paraffin WaxDocumento1 paginaTDS For Paraffin Waxjamil100% (1)
- Inv & PLDocumento2 pagineInv & PLjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- SQ EpDocumento1 paginaSQ EpjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- 1x300 RM Nyy (FRTR)Documento1 pagina1x300 RM Nyy (FRTR)jamilNessuna valutazione finora
- BS 6004-12Documento34 pagineBS 6004-12jamilNessuna valutazione finora
- TDS For Bisphenol ADocumento1 paginaTDS For Bisphenol AjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- TDS For Chlorinated Paraffin Wax (CPW)Documento1 paginaTDS For Chlorinated Paraffin Wax (CPW)jamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Prescription (30.10.2022)Documento1 paginaPrescription (30.10.2022)jamilNessuna valutazione finora
- TDS For PVC Resin PropertiesDocumento1 paginaTDS For PVC Resin PropertiesjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Capacitance FormulaDocumento4 pagineCapacitance FormulajamilNessuna valutazione finora
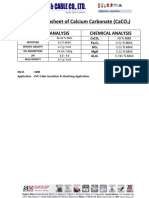
- TDS For Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3)Documento1 paginaTDS For Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3)jamilNessuna valutazione finora
- IT Information-Form (Md. Iqbal Hasan)Documento1 paginaIT Information-Form (Md. Iqbal Hasan)jamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Composition For Red Master BatchDocumento1 paginaComposition For Red Master BatchjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- TDS For PVC FRLS SheathDocumento1 paginaTDS For PVC FRLS SheathjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- IT Information-Form (Md. Iqbal Hasan) CommonDocumento1 paginaIT Information-Form (Md. Iqbal Hasan) CommonjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Composition For Grade-7 PVC (Grey)Documento1 paginaComposition For Grade-7 PVC (Grey)jamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Composition For Grade-7 PVC (Black)Documento1 paginaComposition For Grade-7 PVC (Black)jamilNessuna valutazione finora
- IT Information-Form (Jamil Sharif)Documento1 paginaIT Information-Form (Jamil Sharif)jamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Composition For Grade-1 PVCDocumento1 paginaComposition For Grade-1 PVCjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Composition For PVC Master Batch (Orange)Documento1 paginaComposition For PVC Master Batch (Orange)jamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Composition For Grade-1 PVC (Brown)Documento1 paginaComposition For Grade-1 PVC (Brown)jamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Composition For Grade-5 PVCDocumento1 paginaComposition For Grade-5 PVCjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Energypac ProfileDocumento59 pagineEnergypac ProfilejamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Acsr Merlin (TR)Documento3 pagineAcsr Merlin (TR)jamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Bill Application (Jamil Sharif)Documento1 paginaMobile Bill Application (Jamil Sharif)jamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Composition For PVC Master Batch (Brown)Documento1 paginaComposition For PVC Master Batch (Brown)jamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Income Tax Form LutforDocumento10 pagineIncome Tax Form LutforjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- REB Item, Quantity & WeightDocumento1 paginaREB Item, Quantity & WeightjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Wpe ExercisesDocumento11 pagineWpe ExercisesjoeNessuna valutazione finora
- 8JDocumento8 pagine8JVivianne YongNessuna valutazione finora
- High-Density Polyethylene Foams. I. Poly PDFDocumento9 pagineHigh-Density Polyethylene Foams. I. Poly PDFamirsuryahidayahNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetrad Formulation of The Einstein Field Equations: The Newman-Penrose EquationsDocumento16 pagineTetrad Formulation of The Einstein Field Equations: The Newman-Penrose EquationsRockBrentwoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical Cross Sections For Monte Carlo Simulation of Photon Transport PDFDocumento22 pagineAnalytical Cross Sections For Monte Carlo Simulation of Photon Transport PDFFernanda RibeiroNessuna valutazione finora
- SSC Je Civil Engineering: Set - 7 Daily 9:00PMDocumento43 pagineSSC Je Civil Engineering: Set - 7 Daily 9:00PMNishikanta Mondal100% (1)
- PhysicsDocumento18 paginePhysicsNelsonNessuna valutazione finora
- ChE 140 1.01 IntroductionDocumento30 pagineChE 140 1.01 IntroductionJelor GallegoNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework 02Documento6 pagineHomework 02Ben MacKenzieNessuna valutazione finora
- JKCET Medical 2015 Answer Key Phy CheDocumento12 pagineJKCET Medical 2015 Answer Key Phy CheRuchi SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of Polarization Index and IEEE Standard 43-2000Documento5 pagineA Review of Polarization Index and IEEE Standard 43-2000vasanth11kvNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Kinematics - Inception of Modern KinematicsDocumento137 pagineHistory of Kinematics - Inception of Modern KinematicsMartín FigueroaNessuna valutazione finora
- Normativ Panouri SandwichDocumento58 pagineNormativ Panouri SandwichAlex ChiraNessuna valutazione finora
- FEA Report - Ravi Patel 1101066Documento7 pagineFEA Report - Ravi Patel 1101066RAVNessuna valutazione finora
- Interpreting Motion Using Charts & Graphs (Module) PDFDocumento10 pagineInterpreting Motion Using Charts & Graphs (Module) PDFPretty SwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Third Quarter Examination 2017 in Science 6 (New) For DistrictDocumento6 pagineThird Quarter Examination 2017 in Science 6 (New) For DistrictMarlon Yap100% (2)
- Em 18 Equilibrium of A ParticleDocumento2 pagineEm 18 Equilibrium of A ParticleFattihi EkhmalNessuna valutazione finora
- Montalk - Dimensional Shift - The Physics of 2012 - Fringe ScienceDocumento4 pagineMontalk - Dimensional Shift - The Physics of 2012 - Fringe ScienceKamal HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- PARATIE EN - Advanced-Modelling-2014 PDFDocumento50 paginePARATIE EN - Advanced-Modelling-2014 PDFJPachasNessuna valutazione finora
- Einstein, String Theory and The FutureDocumento38 pagineEinstein, String Theory and The FutureAlexandra100% (1)
- Optimisation of Bench-BermDocumento25 pagineOptimisation of Bench-BermMacarena Ulloa MonsalveNessuna valutazione finora
- William Liller - Space AstrophysicsDocumento290 pagineWilliam Liller - Space Astrophysicsmuhamad dimas arifin a.k.a Ahmd El ArfNessuna valutazione finora
- P-Y Curves Methods - Laterally Loaded PilesDocumento3 pagineP-Y Curves Methods - Laterally Loaded PilesRamanathan GnanasambandamNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - MsiDocumento81 pagineChapter 1 - MsiYua CincoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9: Center of Gravity and CentroidDocumento19 pagineChapter 9: Center of Gravity and CentroidNezie Tacay GondalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Printing InkDocumento23 paginePrinting InkGema SukmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Efficiency Analysis of Canards-Based Course Correction Fuze For A 155-mm Spin-Stabilized ProjectileDocumento10 pagineEfficiency Analysis of Canards-Based Course Correction Fuze For A 155-mm Spin-Stabilized Projectileali_raza117Nessuna valutazione finora
- Richard Shoup and Thomas Etter - The RetroComm Experiment - Using Quantum Randomness To Send A Message Back in TimeDocumento7 pagineRichard Shoup and Thomas Etter - The RetroComm Experiment - Using Quantum Randomness To Send A Message Back in TimeCanola_OliveNessuna valutazione finora
- A Lifting Line Theory For A Three-Dimensional Hydrofoil: Hui Liang and Zhi ZongDocumento7 pagineA Lifting Line Theory For A Three-Dimensional Hydrofoil: Hui Liang and Zhi ZongKoShweBaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12 Notes Gas Laws NotesDocumento2 pagineChapter 12 Notes Gas Laws NotesNancy Richardson RollinsNessuna valutazione finora