Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Data Structures Concepts
Caricato da
Puspala ManojkumarDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Data Structures Concepts
Caricato da
Puspala ManojkumarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
DATA STRUCTURES
1.What is data structure?
A data structure is a way of organizing data that considers not only the items stored, but
also their relationship to each other. Advance knowledge about the relationship between
data items allows designing of efficient algorithms for the manipulation of data..
2. List out the areas in which data structures are applied extensively?
Compiler Design, Operating System, Database Management System, Statistical analysis
package, Numerical Analysis, Graphics, Artificial Intelligence, Simulation
3. What are the major data structures used in the following areas : RDBMS,
Network data model & Hierarchical data model.
1. RDBMS– Array (i.e. Array of structures)
2. Network data model– Graph
3. Hierarchical data model– Trees.
4. If you are using C language to implement the heterogeneous linked list, what
pointer type will you use?
The heterogeneous linked list contains different data types in its nodes and we need a
link, pointer to connect them. It is not possible to use ordinary pointers for this. So we go
for void pointer. Void pointer is capable of storing pointer to any type as it is a generic
pointer type..
5. Minimum number of queues needed to implement the priority queue?
Two. One queue is used for actual storing of data and another for storing priorities
6. What are the notations used in Evaluation of Arithmetic Expressions using prefix
and postfix forms?
Polish and Reverse Polish notations.
7. Convert the expression ((A + B) * C – (D – E) ^ (F + G)) to equivalent Prefix and
Postfix notations.
Prefix Notation: ^ - * +ABC - DE + FG
Postfix Notation: AB + C * DE - - FG + ^.
8. What are the methods available in storing sequential files?
1. Straight merging
2. Natural merging
3. Polyphase sort
4. Distribution of Initial runs.
9. How many different trees are possible with 10 nodes?
1014 If there are n nodes, there exist 2n-n different trees.
10. List out few of the Application of tree data-structure?
1. The manipulation of Arithmetic expression,
2. Symbol Table construction,
3. Syntax analysis.
11. List out few of the applications that make use of Multilinked Structures?
Sparse matrix,
Index generation.
12. In tree construction, which is the suitable efficient data structure?
Linked list.
13. What is the type of the algorithm used in solving the 8 Queens problem?
Backtracking.
14. In an AVL tree, at what condition the balancing is to be done?
If the ‘pivotal value’ (or the ‘Height factor’) is greater than 1 or less than –1.
15. What is the bucket size, when the overlapping and collision occur at same time?
One. If there is only one entry possible in the bucket, when the collision occurs, there is
no way to accommodate the colliding value. This results in the overlapping of values.
16. What is a spanning Tree?
A spanning tree is a tree associated with a network. All the nodes of the graph appear on
the tree once. A minimum spanning tree is a spanning tree organized so that the total
edge weight between nodes is minimized
17. Does the minimum spanning tree of a graph give the shortest distance between
any 2 specified nodes?
No. Minimal spanning tree assures that the total weight of the tree is kept at its minimum.
But it doesn’t mean that the distance between any two nodes involved in the minimum-
spanning tree is minimum.
18.which is the simplest file structure?
Sequential
19. Whether Linked List is linear or Non-linear data structure?
According to Access strategies Linked list is a linear one. According to Storage Linked
List is a Non-linear one..
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Data Structures Viva Question AnswersDocumento3 pagineData Structures Viva Question AnswersGrejoJobyNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structures Viva QuestionsDocumento3 pagineData Structures Viva QuestionsSumathi KannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structures IndiaBixDocumento3 pagineData Structures IndiaBixRanjith M KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Data StructureDocumento10 pagineData Structurebalashivashree9593Nessuna valutazione finora
- DS Viva QuestionsDocumento6 pagineDS Viva QuestionsDaniel MariadassNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure Interview QuestionDocumento8 pagineData Structure Interview QuestionrkerangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structures - Reference BookDocumento11 pagineData Structures - Reference BookranjitvenkatakrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure1Documento8 pagineData Structure1SelvaKrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Question BankDocumento15 pagineQuestion BankAmitabh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure: Ta Structures AptitudeDocumento10 pagineData Structure: Ta Structures Aptitudesachininsomaniac43Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Data StructureDocumento20 pagineWhat Is Data StructuregauravujjawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure Interview Questions and Answers PDFDocumento7 pagineData Structure Interview Questions and Answers PDFramashankar1hNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structures AptitudeDocumento3 pagineData Structures AptitudeNeema JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structures AptitudeDocumento80 pagineData Structures Aptituderavi_03dc13Nessuna valutazione finora
- Viva 1Documento21 pagineViva 1arefkNessuna valutazione finora
- Data StructuresDocumento6 pagineData StructuresArkadeep RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Data StructureDocumento2 pagineWhat Is Data StructureTila D-ShaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure AucseDocumento10 pagineData Structure AucseyogeshdxtNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure AucseDocumento10 pagineData Structure AucseJagannath SathwikNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structures: CRT Technical by Naresh I TechnologiesDocumento7 pagineData Structures: CRT Technical by Naresh I Technologieskark437Nessuna valutazione finora
- Data StructuresDocumento17 pagineData Structuresnaveen rajNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structures Interview Questions Set - 1Documento3 pagineData Structures Interview Questions Set - 1Swastik AcharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2MARKS (Data Structures Using Python)Documento22 pagine2MARKS (Data Structures Using Python)Lavanya JNessuna valutazione finora
- TCS QuestionsDocumento5 pagineTCS QuestionsFann KannNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE DS Notes 2010 NewDocumento92 pagineECE DS Notes 2010 NewNaveen RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Imp - Data-Structures QuestionsDocumento16 pagineImp - Data-Structures QuestionsBLACK xDEMONNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure Interview Questions (2021) - JavatpointDocumento16 pagineData Structure Interview Questions (2021) - JavatpointChandan GowdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Webyog PrepDocumento11 pagineWebyog PrepPriyatanu Bazinga DeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure Interview C Program: Questions To Create A Copy of A Linked ListDocumento11 pagineData Structure Interview C Program: Questions To Create A Copy of A Linked ListschintapNessuna valutazione finora
- Bca C201 QB01Documento21 pagineBca C201 QB01Anjali PawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ds Viva QDocumento13 pagineDs Viva Qhackers earthNessuna valutazione finora
- Mubeena Rajini C++Documento120 pagineMubeena Rajini C++RajiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Cs8391-Data StructureDocumento21 pagineCs8391-Data StructureAmudariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure Questions BankDocumento30 pagineData Structure Questions BankRj SahooNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure Interview Questions Updated On Jul 2018Documento7 pagineData Structure Interview Questions Updated On Jul 2018Ajay MundaniyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure Interview QuestionsDocumento15 pagineData Structure Interview QuestionsAmitAsthanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Question Bank: Computer ScienceDocumento14 pagineTechnical Question Bank: Computer ScienceUttam SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- DSA Interview Questions QuestionDocumento16 pagineDSA Interview Questions QuestionChiragNessuna valutazione finora
- Ec8393 - Fundamentals of Data Structures in C: Linear DatastructuresDocumento11 pagineEc8393 - Fundamentals of Data Structures in C: Linear DatastructuresRathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure MaterialDocumento22 pagineData Structure Materialgani525Nessuna valutazione finora
- Viva Questions and AnswersDocumento9 pagineViva Questions and AnswersENG21CS0205 Lingareddygari KavyanjaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structures Viva QuestionsDocumento5 pagineData Structures Viva Questionstanvideore91Nessuna valutazione finora
- TCS Technical Interview QuestionsDocumento22 pagineTCS Technical Interview Questionsmanchiraju raj kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Top 50 Data Structures Interview Questions & Answers: 1) What Is Data Structure?Documento8 pagineTop 50 Data Structures Interview Questions & Answers: 1) What Is Data Structure?Sudhanshu RanjanNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structures-1Documento26 pagineData Structures-1Raja KushwahNessuna valutazione finora
- 320 - CS8391 Data Structures - Important QuestionsDocumento22 pagine320 - CS8391 Data Structures - Important Questionscurrent job100% (4)
- Data Structure Ch1Documento22 pagineData Structure Ch1MD Sadique AnsariNessuna valutazione finora
- Ds Viva Questions and Answers: AIT ChikkamagaluruDocumento5 pagineDs Viva Questions and Answers: AIT Chikkamagalurusharadpati90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dsa Viva QuestionsDocumento13 pagineDsa Viva QuestionsAashu ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Iq Data StructuresDocumento3 pagineIq Data StructuresrosctNessuna valutazione finora
- KKP-BDS Lecture NotesDocumento78 pagineKKP-BDS Lecture NotesChennamadhavuni SahithiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 DsaDocumento7 pagineUnit 1 Dsa119th.cineNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To DATA STRUCTURES: Basic PrinciplesDocumento4 pagineIntroduction To DATA STRUCTURES: Basic PrinciplesAbhi MahajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure VIVA QuestionsDocumento11 pagineData Structure VIVA Questionshackers earthNessuna valutazione finora
- Mastering Data Structures and Algorithms in C and C++Da EverandMastering Data Structures and Algorithms in C and C++Nessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structures Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesDa EverandData Structures Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Magic Data: Part 1 - Harnessing the Power of Algorithms and StructuresDa EverandMagic Data: Part 1 - Harnessing the Power of Algorithms and StructuresNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Algorithms: A Practical Approach to Computer AlgorithmsDa EverandEssential Algorithms: A Practical Approach to Computer AlgorithmsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- WPF SolidColorBrushDocumento4 pagineWPF SolidColorBrushAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- WPF PasswordBoxDocumento5 pagineWPF PasswordBoxAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- WPF TutorialDocumento84 pagineWPF TutorialAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- SampleDocumento1 paginaSampleAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Installation of SPDocumento38 pagineInstallation of SPAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- WPF RadialGradientBrushDocumento6 pagineWPF RadialGradientBrushAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- WPF LinearGradientBrushDocumento6 pagineWPF LinearGradientBrushAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Developing and Deploying Custom Web2007Documento14 pagineDeveloping and Deploying Custom Web2007AbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- FBADocumento14 pagineFBAAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- WPF Date Picker ControlDocumento14 pagineWPF Date Picker ControlAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Using IComparer IComparable For Sorting in WPFDocumento6 pagineUsing IComparer IComparable For Sorting in WPFAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Show Delete Edit Data WPF DataGrid LINQ SQL ClassesDocumento7 pagineShow Delete Edit Data WPF DataGrid LINQ SQL ClassesAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Working With Pen in WPFDocumento8 pagineWorking With Pen in WPFAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- The DataGrid Contro - WPFDocumento9 pagineThe DataGrid Contro - WPFAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Timer in WPFDocumento3 pagineTimer in WPFAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
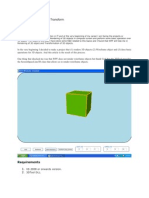
- WPF 3D Solid Wireframe TransformDocumento16 pagineWPF 3D Solid Wireframe TransformAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Treeview Control in WPFDocumento2 pagineTreeview Control in WPFAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Show Multiple Windows at Startup in WPFDocumento3 pagineShow Multiple Windows at Startup in WPFAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Skew Transform in WPFDocumento3 pagineSkew Transform in WPFAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotate Transform in WPFDocumento4 pagineRotate Transform in WPFAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Scale Transform in WPFDocumento3 pagineScale Transform in WPFAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Shaped Windows in WPFDocumento7 pagineShaped Windows in WPFAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Polyline in WPFDocumento3 paginePolyline in WPFAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pie Chart in WPFDocumento11 paginePie Chart in WPFAbhiNessuna valutazione finora