Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Calcium Caronate: Indication: Classification: Indications For Use: Preparation Administration Monitoring
Caricato da
Kyla Barrera TabungarTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Calcium Caronate: Indication: Classification: Indications For Use: Preparation Administration Monitoring
Caricato da
Kyla Barrera TabungarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Patient’s Name: Age/Sex: Ward/Bed No:
Medical Diagnosis: Date of Assignment:
W
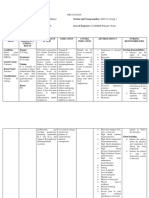
CALCIUM CARONATE
INDICATION: CLASSIFICATION: ANTACID, CALCIUM SUPPLEMENT
INDICATIONS FOR USE: PREPARATION ADMINISTRATION MONITORING
□ PO, IV: Treatment and prevention of hypocalcemia. Available forms: PO route • Monitor for adverse side effects such as:
□ PO: Adjunct in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Chewable tabs: 350, 420, 450, 500, • Administer as antacid 1 hr after meals and at bedtime GI: Constipation, anorexia, nausea,
750, 1000, 1250 mg
□ IV: Emergency treatment of hyperkalemia and hypermagnesemia and • Administer as supplement 1½ hr after meals and at bedtime vomiting, flatulence, diarrhea, rebound
adjunct in cardiac arrest or calcium channel blocking agent toxicity Tabs: 500, 600, 650, 667, 1000, 1250,
1500 mg • Administer only with regular tablets or capsules; do not give Hyperacidity, eructation
with enteric-coated tablets
Gum: 300, 450 500 mg GU: Calculi, hypercalciuria
• Administer laxatives or stool softeners if constipation occurs
Susp: 1250 mg/5 ml • Monitor Ca1 (serum, urine); Ca1 should be
8.5-10.5 mg/dl, urine Ca1 should be 150 mg day,
Caps: 1250 mg monitor weekly Assess for milk-alkali syndrome:
nausea, vomiting, disorientation, headache
Powder: 6.5 g/packet
• Assess for constipation; increase bulk in the diet
if needed
• Assess for hypercalcemia: headache, nausea,
vomiting, confusion; hypocalcemia: paresthesia,
CONTRAINDICATIONS: twitching, colic, dysrhythmias,
Chvostek’s/Trousseau’s sign
□ Hypersensitivity
• Assess those taking digoxin for toxicity
□ hypercalcemia,
• Assess those taking for abdominal pain,
□ Hyperparathyroidism
heartburn, indigestion before, after administration
□ bone tumors
□ Precautions: Precautions: Pregnancy C, breastfeeding, geriatric, fluid
restriction, decreased GI motility, GI obstruction, dehydration, renal
disease Watch out for: drug-drug interactions
• Atenolol, etidronate, phenytoin, risedronate,
ketoconazole: decreased levels of each drug
• Digoxin: increased toxicity from hypercalcemia
• QuiNIDine: increased quiNIDine levels
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Allopurinol Drug StudyDocumento3 pagineAllopurinol Drug StudyFrancis Corpuz0% (2)
- The Perfect Insulin Resistance Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Losing Weight, Reversing Insulin Resistant And And Preventing Pre-Diabetes With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesDa EverandThe Perfect Insulin Resistance Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Losing Weight, Reversing Insulin Resistant And And Preventing Pre-Diabetes With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNessuna valutazione finora
- LACTULOSEDocumento2 pagineLACTULOSEkhelxoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrochlorothiazide, Allopurinol, KetosterilDocumento9 pagineHydrochlorothiazide, Allopurinol, KetosterilcotyboyNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDocumento2 pagineDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic NameSHEILA MAE SACLOTNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDocumento3 pagineDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic NameSHEILA MAE SACLOTNessuna valutazione finora
- Calcium CarbonateDocumento1 paginaCalcium CarbonateMikko EnocNessuna valutazione finora
- Print MeDocumento4 paginePrint MeDoneva Lyn MedinaNessuna valutazione finora
- SEVC - DrugStudy - Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocumento10 pagineSEVC - DrugStudy - Type 2 Diabetes Mellituskarl eiron delos santosNessuna valutazione finora
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Documento6 pagineDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNessuna valutazione finora
- GLYBURIDEDocumento2 pagineGLYBURIDEanne marieNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study Vitamin DDocumento1 paginaDrug Study Vitamin DErica VelascoNessuna valutazione finora
- SpironolactoneDocumento3 pagineSpironolactoneapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- PantoprazoleDocumento1 paginaPantoprazolehahahahaaaaaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study: West Visayas State UniversityDocumento2 pagineDrug Study: West Visayas State UniversityDivine Mercy De JulianNessuna valutazione finora
- Furosemid Citicoline Clexane, LevofloxacinDocumento9 pagineFurosemid Citicoline Clexane, Levofloxacincotyboy50% (2)
- DRUG STUDY Pedia WardDocumento3 pagineDRUG STUDY Pedia WardCARLOZ MIGUEL MARAVILLANessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Studies and Health Teaching PlanDocumento28 pagineDrug Studies and Health Teaching PlansfkjalkhsafgNessuna valutazione finora
- Laranang, Mica Joy R. Drug Study: BSN 123 Group 90Documento5 pagineLaranang, Mica Joy R. Drug Study: BSN 123 Group 90Gerard Louise Esmao RNNessuna valutazione finora
- Bumetanide Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocumento2 pagineBumetanide Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kayexalate Drug StudyDocumento3 pagineKayexalate Drug StudyAngelou Joefred Congreso100% (1)
- KCL 2Documento2 pagineKCL 2Hoseña, Kathea Khyll BSN3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Valproic AcidDocumento4 pagineValproic Acidapi-3797941100% (2)
- Drug Study: Name of Patient: Mr. DG U Date: January 12, 201Documento2 pagineDrug Study: Name of Patient: Mr. DG U Date: January 12, 201ceian230% (1)
- FUROSEMIDEDocumento6 pagineFUROSEMIDEPark JeongyeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Neutralizers - v2Documento1 paginaAcid Neutralizers - v2Sibel ErtuğrulNessuna valutazione finora
- Canine Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Diagnostic Tree /ENDOCRINOLOGYDocumento3 pagineCanine Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Diagnostic Tree /ENDOCRINOLOGYPetrisor GheorghiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study MMMCDocumento14 pagineDrug Study MMMCKathleen Pagulayan Intalan-GloriosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro K (Potassium Chloride)Documento2 pagineMicro K (Potassium Chloride)ENessuna valutazione finora
- Brand/ Generic Name LACTULOSEDocumento3 pagineBrand/ Generic Name LACTULOSEjgc18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Acetaminophen - ParacetamolDocumento3 pagineAcetaminophen - Paracetamolammar amerNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFDocumento4 pagineDrug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Abas Drug Study Nicu PDFDocumento4 pagineAbas Drug Study Nicu PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFDocumento4 pagineDrug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasNessuna valutazione finora
- SimvastatinDocumento1 paginaSimvastatinGracia Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- DS PantoprazoleDocumento2 pagineDS PantoprazoleMatt Reyes Del CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugstudy BangkalDocumento16 pagineDrugstudy BangkalClaire MachicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocumento4 pagineFurosemide Drug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rani Ti DineDocumento2 pagineRani Ti DineJeffNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Used in Pediatrics: Criteria For Dose CalculationDocumento21 pagineDrugs Used in Pediatrics: Criteria For Dose CalculationSanthosh.S.U100% (4)
- RandomDocumento2 pagineRandomAllen YnionNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Study Drugs Classification Adverse Effect Mechanism of Action Contrandication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento6 pagineDrugs Study Drugs Classification Adverse Effect Mechanism of Action Contrandication Nursing ResponsibilitiesRachel BotonNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento8 pagineDrug StudyjovanneyNessuna valutazione finora
- Name of DrugDocumento4 pagineName of DrugMicahEuranneCastillo-GoliNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For ConcussionDocumento3 pagineNCP For Concussiontamtam_antonio100% (1)
- Cimetidine (Drug Study)Documento2 pagineCimetidine (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Drugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcDocumento12 pagineDrugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcMargaret Cortinas75% (4)
- MS Drug Study 1Documento6 pagineMS Drug Study 1Elijah MarfilNessuna valutazione finora
- Nausea and Vomiting PDFDocumento8 pagineNausea and Vomiting PDFRoosita Arbaane SafitriNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento8 pagineDrug StudyKaty PerchieNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineDrug StudyMaxine RicafortNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti EpilepticsDocumento9 pagineAnti Epilepticsnur qistina humaira zulkarshamsiNessuna valutazione finora
- NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsDocumento1 paginaNURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsAdhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Antipyretics, Nonopioid AnalgesicsDocumento6 pagineAntipyretics, Nonopioid AnalgesicsLeevi Paul LaviñaNessuna valutazione finora
- CALCITRIOLDocumento2 pagineCALCITRIOLdesshe09Nessuna valutazione finora
- Prevalite DSDocumento1 paginaPrevalite DSMarc Johnuel HumangitNessuna valutazione finora
- CaCO3 Drug StudDocumento2 pagineCaCO3 Drug StudAubrey SungaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cirrhosis of LiverDocumento1 paginaCirrhosis of LiverShaini ChristianNessuna valutazione finora
- Paralytic Shallfish PoisoningDocumento33 pagineParalytic Shallfish PoisoningKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Airways Resistance - Lab ReportDocumento10 pagineAirways Resistance - Lab ReportKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- DOCOS - SA BiblioDocumento5 pagineDOCOS - SA BiblioKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Sector MainDocumento18 pagineHealth Sector MainKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Urinary Tract Infection Case StudyDocumento17 paginePediatric Urinary Tract Infection Case StudyKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Genital TractDocumento7 pagineFemale Genital TractKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mon IdbDocumento8 pagineMon IdbKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Title of Lecture: Name of Lecturer/Presenters 01 Jan 2020 - S01.T01Documento3 pagineTitle of Lecture: Name of Lecturer/Presenters 01 Jan 2020 - S01.T01Kyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Guidelines For Informed Consent Dec 2011Documento8 paginePractice Guidelines For Informed Consent Dec 2011Kyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of Hereditary Fructose Intolerance: Tiberius Mogoș, Andra Evelin IacobiniDocumento5 pagineA Review of Hereditary Fructose Intolerance: Tiberius Mogoș, Andra Evelin IacobiniKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- (14796805 - Journal of Endocrinology) Hyperprolactinemia Induced by HCG Leads To Metabolic Disturbances in Female MiceDocumento13 pagine(14796805 - Journal of Endocrinology) Hyperprolactinemia Induced by HCG Leads To Metabolic Disturbances in Female MiceasfsdfsdfNessuna valutazione finora
- Malignant Hyperthermia PDFDocumento5 pagineMalignant Hyperthermia PDFKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bond University Research RepositoryDocumento36 pagineBond University Research RepositoryKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethics Assignment - Karen-2Documento1 paginaEthics Assignment - Karen-2Kyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 6 Electromyography (EMG)Documento11 pagineExperiment 6 Electromyography (EMG)Kyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Subtitle: EducatorDocumento3 pagineSubtitle: EducatorKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal ExptDocumento1 paginaRenal ExptKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Relationships Patch AdamsDocumento1 paginaRelationships Patch AdamsKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Marine Drugs: Neurotoxins From Marine Dinoflagellates: A Brief ReviewDocumento23 pagineMarine Drugs: Neurotoxins From Marine Dinoflagellates: A Brief ReviewKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 6 Electromyography (EMG)Documento11 pagineExperiment 6 Electromyography (EMG)Kyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Regulation of Enzyme Activity A. Pathway ControlDocumento4 pagineRegulation of Enzyme Activity A. Pathway ControlKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- C. Tight Junctions: References Batch 2022-B TranscriptionDocumento2 pagineC. Tight Junctions: References Batch 2022-B TranscriptionKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 6 Electromyography (EMG)Documento11 pagineExperiment 6 Electromyography (EMG)Kyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho PneumoniaDocumento2 paginePatho Pneumoniaailyne_galicia100% (2)
- BiochemDocumento1 paginaBiochemKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lisondra DrugsDocumento6 pagineLisondra DrugsKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study TemplateDocumento5 pagineDrug Study TemplateKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study TemplateDocumento5 pagineDrug Study TemplateKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Paracetamol : Indication: ClassificationDocumento1 paginaParacetamol : Indication: ClassificationKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study TemplateDocumento5 pagineDrug Study TemplateKyla Barrera TabungarNessuna valutazione finora
- Antineoplastic Agents ReportDocumento3 pagineAntineoplastic Agents ReportMegan Rose MontillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rapid Analysis of Genotoxic Nitrosamines by HPLC MS MSDocumento3 pagineRapid Analysis of Genotoxic Nitrosamines by HPLC MS MSMarcio SchiavelliNessuna valutazione finora
- รายการยา PDFDocumento57 pagineรายการยา PDFPangpond CharoensukNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar ObatDocumento26 pagineDaftar ObatAnonymous x3d71bWbP7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Obat Alkes Trolley EmergencyDocumento15 pagineDaftar Obat Alkes Trolley EmergencydevitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Organ Bath ReportDocumento13 pagineOrgan Bath ReportYusri Yusoff100% (1)
- Over The Counter DrugsDocumento28 pagineOver The Counter DrugsManjusha KondepudiNessuna valutazione finora
- Inactive Ingredient Search For Approved Drug ProductsDocumento52 pagineInactive Ingredient Search For Approved Drug Productsfall princeNessuna valutazione finora
- Medicatia În Afecțiunile Digestive I. Medicatia AntiulceroasaDocumento13 pagineMedicatia În Afecțiunile Digestive I. Medicatia AntiulceroasaMariana FragăNessuna valutazione finora
- Mother Tincture in HomeopathyDocumento10 pagineMother Tincture in Homeopathydineshgomber100% (1)
- Diluent RateDocumento3 pagineDiluent RateMohamed Abdel-AzizNessuna valutazione finora
- Ferrous Sulfate Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaFerrous Sulfate Drug Studyjanice paralejas100% (1)
- Brief Medication Questionnaire-1 BMQ-1Documento5 pagineBrief Medication Questionnaire-1 BMQ-1Kumar PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- GENERAL ANAESTHESIA - Presentation Editted RecordedDocumento31 pagineGENERAL ANAESTHESIA - Presentation Editted RecordedTatenda SibandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacokinetic Drug InteractionsDocumento40 paginePharmacokinetic Drug Interactionsabdullah2020Nessuna valutazione finora
- VenoferinfDocumento10 pagineVenoferinfzerin_atinNessuna valutazione finora
- SP Awal Pareto A SP Senin 17 Feb 2020 KF CLMDocumento172 pagineSP Awal Pareto A SP Senin 17 Feb 2020 KF CLMIis IstikomahNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Abbreviations Used in Medical PrescriptionsDocumento4 pagineList of Abbreviations Used in Medical PrescriptionsKarla FralalaNessuna valutazione finora
- 26805550dft SV and Pharmacy Bulk Packages For PN Aluminum Content LabelingDocumento26 pagine26805550dft SV and Pharmacy Bulk Packages For PN Aluminum Content LabelingTumma RamaraoNessuna valutazione finora
- Fall 2017FINALSyllabus Cottrell ALH 130Documento8 pagineFall 2017FINALSyllabus Cottrell ALH 130vinhson65-1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diuretics IIDocumento14 pagineDiuretics IIأمجد محمدNessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Selective Cox 1&2 Inhibitors: AspirinDocumento13 pagineNon-Selective Cox 1&2 Inhibitors: AspirinKristijan GoldašićNessuna valutazione finora
- Code Blue Form: Part of The Medical RecordDocumento1 paginaCode Blue Form: Part of The Medical RecordassepNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Harga Ogb Januari 2021Documento2 pagineDaftar Harga Ogb Januari 2021rsubk sumedangNessuna valutazione finora
- Case AnalysisDocumento3 pagineCase AnalysisSi Pi TiNessuna valutazione finora
- Jan 2018Documento8 pagineJan 2018Anonymous VGkG2AUBNessuna valutazione finora
- Actinic Keratosis - Topical AgentsDocumento4 pagineActinic Keratosis - Topical AgentsBirhane GebreegziabiherNessuna valutazione finora
- Phenyl Eph RineDocumento1 paginaPhenyl Eph RineSam SonNessuna valutazione finora
- Alumni PDF HubDocumento14 pagineAlumni PDF HubasanyogNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm E3219 20Documento11 pagineAstm E3219 20ehsan050628100% (1)