Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
A Study of Academic Achievement of Different Streams of B. Ed. Students
Caricato da
Anonymous CwJeBCAXpTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
A Study of Academic Achievement of Different Streams of B. Ed. Students
Caricato da
Anonymous CwJeBCAXpCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Scholarly Research Journal for Interdisciplinary Studies,
Online ISSN 2278-8808, SJIF 2016 = 6.17, www.srjis.com
UGC Approved Sr. No.49366, NOV-DEC 2017, VOL- 4/37
https://doi.org/10.21922/srjis.v4i37.10523
A STUDY OF ACADEMIC ACHIEVEMENT OF DIFFERENT STREAMS OF B. ED.
STUDENTS
B. P. Singh, Ph. D.
Associate Professor, MLRS College of Education, Charkhi Dadri (Haryana)
This study compares the academic achievement of different streams of B.Ed. students of Bhiwani and
Palwal district of Haryana. Result of first year of 400 B.Ed. students from two government colleges
and two private colleges were taken randomly for analysis of data. The result of analyzed data
indicates that a significant difference exists i) Between male and female B.Ed. students of different
streams. ii) Between rural and urban B.Ed. students. iii) Between English medium and Hindi medium
B.Ed. students. iv) There is no significant difference between government and private B.Ed. students.
v) Academic achievement was not normally distributed. vi) B.Ed. students possess high academic
achievement. Based on the findings, the following recommendations were made i) That parents should
devote more time and attention to their children ii) Government should provide better facilities in the
colleges iii) Teachers should be motivated to use new techniques, instructional strategies and
professional values in government colleges iv) Urban students participate effectively in co-curricular
and extra-curricular activities so more hostel facilities should be provided to rural students so that
they have less impact of their family v) Bilingual medium should be used by the teacher to explain the
subject.
Keywords: Academic achievement, B.Ed., Streams
Scholarly Research Journal's is licensed Based on a work at www.srjis.com
Students are assets for the educational institution. Academic achievement of the student
plays a vital role in transforming economical and social structure of the nation. Academic
achievement of each student depends upon learning environment, social, economical,
personal and psychological factors. Most of researchers used the GPA (Grade point average)
to evaluate the performance of the students in exams (Stephan and Schaban, 2002). Others
used the percentage of their marks in previous exams. (Tahir and Naqvi,2006). Some used
achievement test in a particular subject to evaluate the performance of the students. Education
is growing as a profitable industry. Its needs is realized now-a-days as each corporate sector
wants well educated good mannered, skilled and dynamic young students who can cope with
the requirement of growing market. All the students have different abilities, these abilities
help them to complete in the modern world. This is the reason that some students opt for
Copyright © 2017, Scholarly Research Journal for Interdisciplinary Studies
Dr. B. P. Singh 8227
(Pg. 8226-8231)
science, some for commerce and other for arts because of the individual differences among
them.
Academic achievement or performance is the extent to which a student, teacher or
institution has achieved their short or long term educational goals. Academic achievement
represents performance outcomes that indicate the extent to which a person has accomplished
specific goals that were the focus of activities in instructional environment, specifically in
school, college and university.
Hansen, Joe B. (2000) has found that there are other factors like race, gender, sex
that can affect student performance. Students achievement is also related with economical
condition (Goldman, N. 1988). Those who are residing near the institution show better
results. Winston et al. (2002) focused on student impatience that influences his own
academic performance. Kola Soyibo (1988) elaborated that student performance is very
much dependent on SEB (socio-economic back ground). The results of Zimmerman (1999,
2001) proved that student performance is reduced in the company of weak peers.
NEED OF THE STUDY:
It is found that the teaching method of science and maths students was slightly better
than arts and commerce students. Results of science students were generally better than
commerce and arts students. In order to see the difference of academic performance of
different streams of B.Ed. students, this study was taken to compare the academic
achievement in gender, rural and urban, govt. and private B.Ed. students.
OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY:
1. To compare the academic achievement of male and female B.Ed. students of
different streams.
2. To compare the academic achievement of rural and urban B.Ed. students of
different streams.
3. To compare the academic achievement of government and private college B.Ed.
students of different streams.
4. To compare the academic achievement of English and Hindi medium B.Ed.
students of different streams.
HYPOTHESES:
i) B.Ed. students do not possess high academic achievement.
ii) There is no significant difference in academic achievement of male and female B.Ed.
students of different streams.
Copyright © 2017, Scholarly Research Journal for Interdisciplinary Studies
Dr. B. P. Singh 8228
(Pg. 8226-8231)
iii) There is no significant difference in academic achievement of rural and urban B.Ed.
students of different streams. iv) There is no significant difference in academic achievement
of government and private college B.Ed. students of different streams.
v) There is no significant difference in academic achievement of English and Hindi medium
B.Ed. students of different streams.
METHODOLOGY: The present study was carried out using the survey method of research. It
was conducted on one variable (academic achievement) and on demographic variable.
POPULATION: The population of the study consists of two private/ government colleges of
education of Bhiwani and Palwal district of Haryana.
SAMPLE: For the present study four colleges of education of Bhiwani & Palwal districts
were taken from the population as sample. Total 400 B.Ed. students were taken as sample
from the population by random sampling method; out of which 67 were male and 333 were
female. 321 were rural and 79 urban students; and 81 were government and 319 were private
college students; 145 were English medium and 255 were Hindi medium college students.
TOOL USED: B.Ed. first year marks were collected to assess the academic achievement of
B.Ed. College students of different streams. Marks were collected from the university results
of these students.
STATISTICAL TECHNIQUES USED:
The marks of the first year of B.Ed. students so obtained were analyzed. Mean, S.D.
and critical ratio and chi-square test were used to find results.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION:
Table-1: Academic achievement of B.Ed. college students.
Group N Mean S.D.
Whole 400 461.69 10.12
Table-1 reveals that mean score of B.Ed. students of all streams is 461.69 which shows that
all the students of different streams fall under the category of high academic achievement.
Standard deviation is 10.12 which indicate that academic achievement widely dispersed.
Table-2: Distribution of academic achievement of B.Ed. students.
N Low Average High Ch-square
value
400 Fo 35 Fo 284 Fo 81 18.17*
Fe 64 Fe 272 Fe 64
*Significant at .05 level (5.99) and at .01 level (9.2)
Table-2 reveals that academic achievement of B.Ed. students was not normally distributed.
Hence, the hypothesis, “the B.Ed. students do not possess high academic achievement” is
rejected as the academic achievement of these students was high.
Copyright © 2017, Scholarly Research Journal for Interdisciplinary Studies
Dr. B. P. Singh 8229
(Pg. 8226-8231)
Table-3: Comparison of academic achievement of male and female B.Ed. students.
Group N Mean S.D. CR value
Male 67 455.0 9.89
Female 333 463.05 8.78 6.192*
Significant at .05 level (1.96) and .01 level (2.60).
Table-3 reveals that mean score of female students (463.05) was slightly higher than
male students (455.0). CR value is 6.192 which was found to be significant at .05. It indicates
that there exists significant difference in academic achievement of male and female B.Ed.
students of different stream. Hence, the hypothesis, “there is no significant difference
between the academic achievement of male and female B.Ed. students of different streams” is
rejected.
Table-4: Distribution of academic achievement of male and female B.Ed. students.
Group N Low Average High Chi-square
value
Male 67 Fo 3 Fo 22 Fo 20
Fo 11 Fe 45 Fe 11 23.56*
Female 333 Fo 35 Fo 233 Fo 65
Fo 53 Fe 227 Fe 53 8.97**
**Significant at .05 level (5.99) but not significant at .01 level (9.2).
Table-4 reveals that chi-square values are higher than table value at .05 level hence, the
distribution of academic achievement of male and female B.Ed. college students were not
normal. Academic achievement is widely dispersed among both male and female students.
Table-5: Comparison of academic achievement of rural and urban B.Ed. college
students.
Group N Mean S.D. CR value
Rural 321 460.18 9.67
Urban 79 467.8 8.23 7.14*
Significant at .05 level (1.96) and .01 level (2.60)
Table-5 reveals that mean score of urban students (467.8) was slightly higher than rural
students (460.18). CR value is 7.14 which express significant difference in academic
achievement of rural and urban B.Ed. students of different stream. Hence, the hypothesis,
“there is no significant difference exists between the academic achievement of rural and
urban B.Ed. students of different streams” is rejected.
Table-6: Distribution of academic achievement of rural and urban B.Ed. students.
Group N Low Average High Chi-square
value
Rural 321 Fo 36 Fo 188 Fo 97
Fo 51 Fe 219 Fe 51 50.20*
Urban 79 Fo 2 Fo 50 Fo 27
Fo 12 Fe 55 Fe 12 27.53*
* Significant at both .05 level (5.99) and .01 level (9.210)
Copyright © 2017, Scholarly Research Journal for Interdisciplinary Studies
Dr. B. P. Singh 8230
(Pg. 8226-8231)
The obtained chi-square values with df 2 is greater than the table value even at .01 level of
significance. The null hypothesis is rejected. The difference is highly significant. It may be
stated that distribution of academic achievement is not normally distributed among rural and
urban B.Ed. students.
Table-7: Academic achievement of government and private B.Ed. students.
Group N Mean S.D. C.R. value
Govt. 81 465.24 9.78
Private 319 460.788 9.29 1.20*
* Not significant at .05 level (1.96).
Table-7 reveals that CR value is 1.20 which is smaller than table value even at .05 level
(1.96). It is non-significant. The null hypothesis is accepted at.05 level of significance. It may
be interpreted that there is no significance difference between B.Ed. students of government
and private college. Hence, the hypothesis, “there is no significant difference between the
academic achievement of government and private college B.Ed. students” is accepted.
Table-8: Distribution of academic achievement of government and private B.Ed.
College students.
Group N Low Average High Chi-square
value
Govt. college 81 Fo 2 Fo 50 Fo 29
students Fe 13 Fe 55 Fe 13 29.44*
Private 319 Fo 18 Fo 230 Fo 71
College Fe 51 Fe 217 Fe 51 34.20*
*Significant at both .05 level (5.99) and .01 level (9.21)
Table-8 reveals that obtained chi-square values are higher than the table value both at .05
and .01 level of significance. This shows that distribution of academic achievement of
government and private B.Ed. college students was not normally distributed.
Table-9: Distribution of academic achievement of English and Hindi medium B.Ed. students.
Group N Mean S.D. C.R. Value
English medium 145 469.38 8.35
Hindi medium 255 457.31 9.84 13.034*
*Significant at .05 level (1.96) and .01 level (2.60).
Table-9 reveals that CR value is 13.034 which is higher than the table value both at .05 and at
.01 level of significance. The null hypothesis, “there is no significant difference in academic
achievement of English and Hindi medium B.Ed. students” is rejected. It shows that
difference between English and Hindi medium students is highly significant. It indicates that
English medium students performance is significantly higher than Hindi medium students.
Copyright © 2017, Scholarly Research Journal for Interdisciplinary Studies
Dr. B. P. Singh 8231
(Pg. 8226-8231)
Table-10 :- Distribution of academic achievement of English and Hindi medium B.Ed.
students.
Group N Low Average High Chi-square
value
English 145 Fo 6 Fo 69 Fo 75
medium Fe-23 Fe 99 Fe 46 48.41*
Hindi 255 Fo 51 Fo 225 Fo 25
medium Fe 41 Fe 173 Fe 41 89.84*
*Significant at both .05 level (5.99) and .01 level (9.21).
Table-10 reveals that chi-square values are higher than the table value both at .05 and .01
level of significance. It shows that distribution of academic achievement of English and Hindi
medium students was not normally distributed.
EDUCATIONAL IMPLICATIONS: Following points should be considered to accelerate the
academic achievement in the students:
(i) Students who achieve better in the first year should be motivated to clear various
competitive exams for better future in teaching as well as non-teaching field.
ii) Enhance learning facilities and better communication skills can improve academic
achievement.
iii) Proper guidance from parents and teacher can improve academic achievement of the
students.
iv) Motivate female and rural students to participate actively in co-curricular and extra-
curricular activities.
v) Government should provide better facilities in the institution for effective teacher learning
process.
vi) Motivate the teachers to use new techniques, instructional strategies and adopt
professional values.
REFERENCES:
Ali, Shoukat, Haider Zubair: Factors contributing to the students academic performance. American
Journal of Educational research. 2013, 1(8), 283-289.
Best, J.W. & Kahn, J.V. (1995): Research in education, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi.
Hijazi, S.T. and Naqvi S.M.M. (2006): Factors affecting students performance Bangladesh e-journal
of sociology. Volume 3, Number 1, January, 2006.
Huitt, W.H. (2009) : A system-based synthesis of research ‘related to improving students’ academic
performance. http://www. edpsycinteractive. Org/papers/improving-school achievement.
Katsikas, Elias (2010): Student status and academic performance: an approach of the quality
determinants of university studies in Greece. The London school of economics and political
science.
Copyright © 2017, Scholarly Research Journal for Interdisciplinary Studies
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- 29.yuvraj SutarDocumento4 pagine29.yuvraj SutarAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- 25.suresh ChenuDocumento9 pagine25.suresh ChenuAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Customers' Consciousness About Financial Cyber Frauds in Electronic Banking: An Indian Perspective With Special Reference To Mumbai CityDocumento13 pagineCustomers' Consciousness About Financial Cyber Frauds in Electronic Banking: An Indian Perspective With Special Reference To Mumbai CityAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- Historical Development of Play Schools in IndiaDocumento11 pagineHistorical Development of Play Schools in IndiaAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- 13.nasir RasheedDocumento9 pagine13.nasir RasheedAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Aggression Among Senior Secondary School Students in Relation To Their Residential BackgroundDocumento8 pagineAggression Among Senior Secondary School Students in Relation To Their Residential BackgroundAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- 4.Dr Gagandeep KaurDocumento13 pagine4.Dr Gagandeep KaurAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Homesh RaniDocumento7 pagineHomesh RaniAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- 19.Dr Ibrahim Aliyu ShehuDocumento29 pagine19.Dr Ibrahim Aliyu ShehuAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- 1.prof. Ajay Kumar AttriDocumento8 pagine1.prof. Ajay Kumar AttriAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study of Effect of Age and Gender On Stress of AdolescentsDocumento5 pagineA Study of Effect of Age and Gender On Stress of AdolescentsAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- Technostress, Computer Self-Efficacy and Perceived Organizational Support Among Secondary School Teachers: Difference in Type of School, Gender and AgeDocumento13 pagineTechnostress, Computer Self-Efficacy and Perceived Organizational Support Among Secondary School Teachers: Difference in Type of School, Gender and AgeAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- A Lookout at Traditional Games Played by Tribes in IndiaDocumento4 pagineA Lookout at Traditional Games Played by Tribes in IndiaAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Effect of Life Skill Training On Mental Health Among B.ed. Interns in Relation To Their Impulsive BehaviourDocumento9 pagineEffect of Life Skill Training On Mental Health Among B.ed. Interns in Relation To Their Impulsive BehaviourAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Women Empowerment and Religion's Role in Gender Relations in KargilDocumento10 pagineWomen Empowerment and Religion's Role in Gender Relations in KargilAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Use of English Language During PandemicDocumento7 pagineThe Use of English Language During PandemicAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- 31 Dr. Suman Kumari, Prof. Sudarshana Rana & Ms. Anita VermaDocumento9 pagine31 Dr. Suman Kumari, Prof. Sudarshana Rana & Ms. Anita VermaAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- The Need of Remote Voting Machine in Indian Voting SystemDocumento7 pagineThe Need of Remote Voting Machine in Indian Voting SystemAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- 30 Trishala BhaskarDocumento7 pagine30 Trishala BhaskarAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- 29 Balwinder SinghDocumento8 pagine29 Balwinder SinghAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- 24 Adv Raj KumarDocumento5 pagine24 Adv Raj KumarAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- 28 Shailaja KanwarDocumento12 pagine28 Shailaja KanwarAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- 21 DR ReniDocumento6 pagine21 DR ReniAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- 26 Dr. Reni Francis Mr. Rajendra DeshmukhDocumento5 pagine26 Dr. Reni Francis Mr. Rajendra DeshmukhAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- 23 JayalakshmiDocumento9 pagine23 JayalakshmiAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- Suyambukani VDocumento6 pagineSuyambukani VAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- 25 AshaDocumento5 pagine25 AshaAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- 22 Pavithra.g ArticleDocumento8 pagine22 Pavithra.g ArticleAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Deepa AnwarDocumento17 pagineDeepa AnwarAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- Payal BhatiDocumento10 paginePayal BhatiAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- Pedagogy of Teaching Social ScienceDocumento18 paginePedagogy of Teaching Social ScienceDrMijanur RahamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Kajian Jurnal Pentingnya Media Matematika Manipulatif KonkretDocumento6 pagineKajian Jurnal Pentingnya Media Matematika Manipulatif Konkretamalia fitrianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Entropy and Syntropy PDFDocumento23 pagineEntropy and Syntropy PDFClaudio ChagasNessuna valutazione finora
- The Psychology of PrayerDocumento22 pagineThe Psychology of PrayerParminder Singh RaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 12 Thesis TemplateDocumento23 pagineGrade 12 Thesis TemplateJoshua Tundag100% (1)
- Spelling Bee Game Chapter1Documento12 pagineSpelling Bee Game Chapter1Mustofa AjaiNessuna valutazione finora
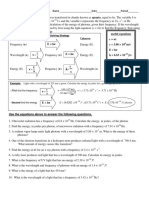
- Plancks Constant WorksheetDocumento1 paginaPlancks Constant WorksheetMichelle ArredondoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing leadership course approvalDocumento4 pagineNursing leadership course approvalSkye M. Peters33% (3)
- COLAPIETRO 1989 Peirce Intro SelfDocumento8 pagineCOLAPIETRO 1989 Peirce Intro SelfjunginesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Universe of Food QualityDocumento6 pagineThe Universe of Food QualityAlexRiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Math Worksheet 11Documento2 pagineMath Worksheet 11Mohan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- SSP Reflection Paper - MANLUCOB, Lyra Kaye B.Documento6 pagineSSP Reflection Paper - MANLUCOB, Lyra Kaye B.LYRA KAYE MANLUCOBNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2 Component of Curriculum and Curricular Approaches Purita P. Bilbao, Ed. DDocumento51 pagineLesson 2 Component of Curriculum and Curricular Approaches Purita P. Bilbao, Ed. DYen ZaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Roy 1988Documento9 pagineRoy 1988lmatchimNessuna valutazione finora
- Gold C1 Advanced NE PT04Documento7 pagineGold C1 Advanced NE PT04Noé Cambrón CortésNessuna valutazione finora
- Method Statement Pressure RecorderDocumento2 pagineMethod Statement Pressure RecorderMuhamed RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Prediction of Information Diffusion Probabilities For Independent Cascade ModelDocumento9 paginePrediction of Information Diffusion Probabilities For Independent Cascade ModelMichał StaniszewskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Art and Ideology: Althusser's PerspectiveDocumento7 pagineArt and Ideology: Althusser's PerspectivefabioramosbfNessuna valutazione finora
- Garbage Can ModelDocumento3 pagineGarbage Can ModelHozefadahodNessuna valutazione finora
- All Planet Research ProjectsDocumento9 pagineAll Planet Research Projectsapi-489862967Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge IGCSE Maths Skills Teachers SupportDocumento14 pagineCambridge IGCSE Maths Skills Teachers SupportJumana SmairatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pia - MP - Automation - Egr - 2015136Documento18 paginePia - MP - Automation - Egr - 2015136Eleazar GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- B Curtis - PCC Grad PlanDocumento3 pagineB Curtis - PCC Grad Planapi-508432665Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 1 - Spectrophotometry TechniquesDocumento13 paginePractical 1 - Spectrophotometry TechniquesDhanen DranNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Research Methods SyllabusDocumento8 pagineBusiness Research Methods SyllabusRohit JaiswaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiparadigm Accounting Research AgendaDocumento20 pagineMultiparadigm Accounting Research AgendaJasmine VianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Has Made Modern Life Better But Not Necessary EasierDocumento4 pagineScience Has Made Modern Life Better But Not Necessary EasierABCNessuna valutazione finora
- Carl RitterDocumento3 pagineCarl Ritterjbarasa03Nessuna valutazione finora
- Theory and Scope of Public AdministrationDocumento33 pagineTheory and Scope of Public AdministrationJovi Griego0% (1)
- Curriculum PlanDocumento79 pagineCurriculum PlanAris Nur AzharNessuna valutazione finora
- How to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipDa EverandHow to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (1135)
- Weapons of Mass Instruction: A Schoolteacher's Journey Through the Dark World of Compulsory SchoolingDa EverandWeapons of Mass Instruction: A Schoolteacher's Journey Through the Dark World of Compulsory SchoolingValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (149)
- Summary: I'm Glad My Mom Died: by Jennette McCurdy: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: I'm Glad My Mom Died: by Jennette McCurdy: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Summary: Trading in the Zone: Trading in the Zone: Master the Market with Confidence, Discipline, and a Winning Attitude by Mark Douglas: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Trading in the Zone: Trading in the Zone: Master the Market with Confidence, Discipline, and a Winning Attitude by Mark Douglas: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (15)
- Summary: The Laws of Human Nature: by Robert Greene: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: The Laws of Human Nature: by Robert Greene: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (30)
- The 16 Undeniable Laws of Communication: Apply Them and Make the Most of Your MessageDa EverandThe 16 Undeniable Laws of Communication: Apply Them and Make the Most of Your MessageValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (72)
- Summary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (22)