Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Current Generator
Caricato da
faisalsmkpnCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Current Generator
Caricato da
faisalsmkpnCopyright:
Formati disponibili
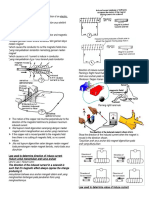
Direct Current Generator / Penjana arus terus
•Sisi AB bergerak ……………, sisi CD bergerak ke …...
……..
Bila gegelung berputar, sisinya memotong garisan daya
medan magnet dan arah arus aruhan melalui gegelung
adalah…………………….
Commutator: reverses the connections of the coil with the Jarum galvanometer akan terpesong ………………………….
external circuit after every half cycle, so that the current in
the outside circuit always flows in the same direction. iii)At 180°
Komutator menyongsangkan sambungan gegelung dengan
litar luar setiap separuh kitar, supaya arus di litar luar
mengalir dalam arah yang sama
• The sides AB and CD are moving ……………….to the
magnetic field and thus do not ………..the magnetic field
lines.
No …………. …………..is produced at the instant.
The galvanometer pointer shows ………… mark.
• Sisi AB dan CD bergerak ……………………dengan
i) At 0°
garisan medan magnet, maka tidak ……………………….
garisan medan magnet.
Galvanometer menunjukkan bacaan ……………………….
iv)At 270°
• The sides AB and CD are moving ……………….…….to the
magnetic field lines and thus do not ……...…..the magnetic
field lines.
No ……………………. …………..is produced at the instant.
• Coil AB moves …………., coil CD moves………..
When the coil rotates, its sides cut across the magnetic
The galvanometer pointer shows ………………………mark.
field lines and direction of induced current in the coil is
• Sisi AB dan CD bergerak ………………………….…dengan
……………….
The galvanometer pointer will deflect to ……………
garisan medan magnet, maka tidak ……………………….
The process continues.
garisan medan magnet.
Galvanometer menunjukkan bacaan ……………………….
•Sisi AB bergerak …………, sisi CD bergerak
ke…………...
ii)At 90°
Bila gegelung berputar, sisinya memotong garisan daya
medan magnet dan arah arus aruhan melalui gegelung
adalah…………………….
Jarum galvanometer akan terpesong
……………………….
Proses ini akan berterusan
• Coil AB moves …………., coil CD moves………..
When the coil rotates, its sides cut across the magnetic
field lines and direction of induced current in the coil is
……………….
Galvanometer pointer will deflect to ……………
When the coil rotates, its sides cut across the magnetic
field lines and direction of induced current in the coil is
…………….
Alternating Current Generator / Penjana arus ulang-alik Direction of current at the outer circuit is from …… to ……
•Sisi AB bergerak ……………, sisi CD bergerak ke …...
……..
Bila gegelung berputar, sisinya memotong garisan daya
medan magnet dan arah arus aruhan melalui gegelung
adalah…………………….
Arah arus dilitar luar adalah dari………. ke …………
• The galvanometer will deflect to ……………
iii)At 180°
i)At 0°
• The sides AB and CD are moving ……………….to the
magnetic field and thus do not ………..the magnetic field
lines.
No …………. …………..is produced at the instant.
The galvanometer shows …………mark.
• The sides AB and CD are moving ……………….to the
• Sisi AB dan CD bergerak ……………………dengan
magnetic field and thus do not ………..the magnetic field
lines. garisan medan magnet, maka tidak ……………………….
No …………. …………..is produced at the instant. garisan medan magnet.
Galvanometer menunjukkan bacaan ……………………….
The galvanometer shows …………mark.
iv)At 270°
• Sisi AB dan CD bergerak ……………………dengan
garisan medan magnet, maka tidak ……………………….
garisan medan magnet.
Galvanometer menunjukkan bacaan ……………………….
ii)At 90°
•Coil AB moves …………., coil CD moves………..
When the coil rotates, its sides cut across the magnetic field
lines and direction of induced current in the coil is…………
Direction of current at the outer circuit is from...… to …....
•Coil AB moves …………., coil CD moves………..
•Sisi AB bergerak ……………, sisi CD bergerak ke …...
……..
Bila gegelung berputar, sisinya memotong garisan daya
medan magnet dan arah arus aruhan melalui gegelung
adalah…………………….
Arah arus dilitar luar adalah dari………. ke …………
Compare direct current and alternating current.
1. A direct current is a 1. An alternating current is a
current that flows in one current which flows to and
direction only in a circuit. fro in two opposite directions
2. The magnitude of a direct in a circuit. It changes its
current may be: direction periodically. (a) Name the principle used in the generator.
(a) constant
(b) changes with time ……………………………………………………………….[1]
(b) Mark the directions of current flow in WX and YZ when
the side WX of the coil is displaced in downwards
direction. [1]
(c) Draw a graph to show the variation with time of the
current in conductor YZ.
[2]
(d) What happens to the current flows in conductor YZ when
A direct current can flow An alternating current can the speed of the coil’s rotations is increased?
through a resistor but cannot flow through both a resistor
flow through a capacitor. and a capacitor. ……………………………………………………………...[1]
2. Fig. 10 shows a simple current generator which consists
of a rectangular coil of wire that rotates at constant speed
between the poles of a permanent magnet.
Both the direct current and alternating current have a heating
effect on the filament of a bulb and can light up the bulb.
Example 1
Figure shows an alternating current with a magnitude that
changes with time.
(a) What is the peak current? Fig 10
(b) What is the period of the a.c. current? (a) Name the type of generator shown in Fig. 10.
(c) What is the frequency of the a.c current?
..………………………………………………………...[1]
(b) Underline the correct answer to complete the
sentence. Fleming (left,right) hand rule is used to
determine the direction of induce current in the coil.
[1]
(c) Figs. 10.1, 10.2 and 10.3 show views from one end
of the coil, when the coil is in different positions.
Questions
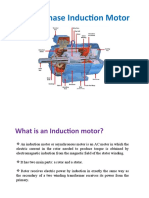
1. The diagram shows the structural design of a generator.
Fig. 10.1 Fig. 10.2 Fig. 10.3
Which diagram shows the coil in the position where
(i) the induced e.m.f. in the coil is at its maximum,
………………………………………………………………….
...........................................................................[1]
.......................................................................................[2]
(ii) the induced e.m.f. in the coil is zero?
(e)State the position of the coil where there is no induced
............................................................................[1] e.m.f. Explain why.
(c)On Fig. 10.4, sketch the graph of e.m.f. against time, for …………………………………………………………………..
one complete rotations of the coil.
........................................................................................[2]
(f)On Fig. 10.4, sketch the graph of e.m.f. against time, for
one complete rotations of the coil.
[2]
(d) Explain why the magnet used in Fig 10 is a curved
magnet.
[2]
……..............................................................................[1] 4.Diagram 10.1 and Diagram 10.2 show the deflection of a
galvanometer when a bar magnet are pushed into two
(e) The current generator shown in Fig. 10 produces a identical solenoids.
small induce current. Suggest to ways to increase the
induce current produce.
………………………………………………………………….
.......................................................................................[2]
3. Fig. 8.1 shows a simple current generator.
Diagram 10.1
Fig. 8.1
(a) Name the part labelled X
………………………………………………………..………[1] Diagram 10.2
(a) What is meant by electromagnetic induction?
(b) Explain why current is induce in the coil when the coil (b) Using Diagram 10.1 and Diagram 10.2,
rotates. (i) State the magnetic pole at end P when the bar
magnets are pushed into the solenoids.
……………………………………………………..……...…[1] (ii) Compare the number of the bar magnets and the
deflection of the galvanometer.
(c) Name the type of generator shown in Fig. 8.1 (c) State the relationship between
(i) The number of bar magnets and the strength of the
...……………………………………………………..………[1] magnetic field
(ii) The strength of the magnetic filed and the deflection of
(d) At the instant shown in Fig. 8.1, the induced e.m.f. is a galvanometer
maximum. Explain why the induced e.m.f. is a maximum. (d) Diagram 10.3 shows an ideal transformer.
(i) Name the type of transformer.
(ii) Explain how the current is induced in the secondary
coil.
(e) Diagram 10.4 shows a generator.
Diagram 10.4
Suggest modifications that can be made to increase the
output current to the generator in Diagram 10.4. State
and modifications based on the following aspects:
(i) Material used to make the slip ring
(ii) Shape of the magnet
(iii) Number of turns of the coil
(iv) Diameter of the wire of the coil
(v) The speed of rotation [10 marks]
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Resume Terkini FaisalDocumento3 pagineResume Terkini FaisalfaisalsmkpnNessuna valutazione finora
- Statement of Account: Penyata AkaunDocumento3 pagineStatement of Account: Penyata AkaunfaisalsmkpnNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM 2003Documento18 pagineSPM 2003faisalsmkpnNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuantiti Fizikal Yg Lain: Prefix/ ImbuhanDocumento10 pagineKuantiti Fizikal Yg Lain: Prefix/ ImbuhanfaisalsmkpnNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnet 1Documento4 pagineElectromagnet 1faisalsmkpnNessuna valutazione finora
- Vector and Scalar QuantitiesDocumento10 pagineVector and Scalar QuantitiesfaisalsmkpnNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnetic InductionDocumento5 pagineElectromagnetic InductionfaisalsmkpnNessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Instruction Manual FOR Brushless A.C. Generaior Tilodel TWYDocumento17 pagineInstruction Manual FOR Brushless A.C. Generaior Tilodel TWYTahan Lodewyk Butar ButarNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic Effects of CurrentsDocumento41 pagineMagnetic Effects of CurrentsV V Satyanarayana PasupuletiNessuna valutazione finora
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocumento13 pagineThree Phase Induction MotorElsa WatsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Vlsi Chap 1Documento3 pagineVlsi Chap 1unchalliNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture - 5 AC Machinary FundamentalsDocumento58 pagineLecture - 5 AC Machinary FundamentalsutsmanheruNessuna valutazione finora
- BAJOJODocumento3 pagineBAJOJOMark Benjie Molina PaosNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Conversion and Transport: George G. Karady & Keith HolbertDocumento45 pagineEnergy Conversion and Transport: George G. Karady & Keith Holbertaswardi8756Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of Discontinuities Influence of Manufacture and MaterialDocumento6 pagineAssessment of Discontinuities Influence of Manufacture and MaterialShahazad ShaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Parallel CircuitsDocumento9 pagineParallel CircuitsAngelo Contreras Isla TayoNessuna valutazione finora
- II Puc Physics Hand BookDocumento58 pagineII Puc Physics Hand BookBeeresha R SNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic Particle Testing MethodDocumento6 pagineMagnetic Particle Testing Methodgbsubbu100% (4)
- Laboratory Experiment 4Documento10 pagineLaboratory Experiment 4Nervic Salcedo CamachoNessuna valutazione finora
- INDIABIXDocumento314 pagineINDIABIXvon kervy onradeNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetism BansalDocumento31 pagineMagnetism BansalAryaveer Sharma100% (1)
- Motor Protection - Customer-FINAL PDFDocumento85 pagineMotor Protection - Customer-FINAL PDFJulio LoaizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Magne-Artistic!: Learning Activity SheetDocumento4 pagineMagne-Artistic!: Learning Activity SheetJ-heart Basabas MalpalNessuna valutazione finora
- Img 20240110 0001Documento10 pagineImg 20240110 00019E EYAD AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.3 Analysing Electromagnetic InductionDocumento27 pagine3.3 Analysing Electromagnetic InductionEmil HelmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Conglomerate / Sandstone Samples From Khairagarh and Chhattisgarh Basin, CRDocumento2 pagineConglomerate / Sandstone Samples From Khairagarh and Chhattisgarh Basin, CRKeertana GadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 1 Machines 1Documento9 pagineExp 1 Machines 1Ysa JasaNessuna valutazione finora
- CEIAPresentation GBDocumento48 pagineCEIAPresentation GBFranck Yvan Lantohery RaveloarisonNessuna valutazione finora
- ANSWER KEY CCT V - April 2020Documento4 pagineANSWER KEY CCT V - April 2020Great Ashur YTNessuna valutazione finora
- 1291 Guide For Partial Discharge Measurement Power SwtgearDocumento26 pagine1291 Guide For Partial Discharge Measurement Power SwtgearZhaqir HusseinNessuna valutazione finora
- Bump Grade Force On Wire TeacherDocumento1 paginaBump Grade Force On Wire TeacherBenjamin WatsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Use of Magnetic Levitation For An ElevatorDocumento11 pagineUse of Magnetic Levitation For An ElevatorVenkatesh PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Eddy Current Testing: - General ProcedureDocumento7 paginePractical Eddy Current Testing: - General Procedurekhizer mohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical Theory of Electromagnetism Jeans 1911 PDFDocumento606 pagineMathematical Theory of Electromagnetism Jeans 1911 PDFAlbertoKrawczykNessuna valutazione finora
- Mod3 PPT 14-29Documento16 pagineMod3 PPT 14-29Mukul RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sem Question BanksDocumento3 pagineSem Question BanksthangarajelectresNessuna valutazione finora